Introduction
In the journey of nurturing children with developmental challenges, understanding effective teaching strategies is paramount. Discrete Trial Training (DTT) emerges as a powerful tool within Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), offering a structured method to break down complex skills into manageable steps. This approach not only enhances learning outcomes but also empowers children to engage more confidently with their environment.
With research backing its effectiveness, DTT stands out as a preferred technique among educators and therapists, making it essential for parent advocates seeking impactful strategies to support their children's growth. By delving into the core components and benefits of DTT, parents can better navigate the intricacies of their children's developmental journeys and champion their learning experiences.
Understanding Discrete Trial Training: An Overview
To understand what is discrete trial training, one must recognize that it serves as a fundamental method within Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), designed to teach complex abilities by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable components. This structured method includes a series of discrete trials, where each trial consists of three critical elements:
- An antecedent (the instruction)
- A behavior (the response)
- A consequence (the reinforcement)
This clear framework facilitates concentrated ability development in a controlled, supportive environment, making it especially advantageous for youngsters with autism and other developmental disorders.
Recent research, including a meta-analysis published in the Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, has demonstrated that DTT can result in significant advancements in learning outcomes, with effectiveness rates reported as high as 80% in acquisition for individuals with autism. Such findings underscore what is discrete trial training (DTT) in ABA therapy, highlighting it as a preferred method among educators and therapists. The advantages of DTT go beyond simple skill acquisition; it encourages vital learning behaviors, enhances confidence, and enables young individuals to interact with their environment more effectively.
This makes DTT an essential tool for parent advocates who are navigating the complexities of their offspring's development and seeking effective strategies to support their learning journey. For further assistance and resources on ABA techniques, parent advocates can reach out to Rising Above ABA at 888.572.7473, located at 135 Beaver St, 4th Floor, Waltham, MA 02452.
The Core Components and Steps of Discrete Trial Training
To understand what is discrete trial training, it's essential to know that the core components include the following steps:
- Instruction: The therapist or educator presents a clear instruction or question to the learner.
- Prompting: If needed, cues may be given to assist the young one towards the appropriate answer.
- Response: The child responds to the instruction.
- Reinforcement: Following the response, appropriate reinforcement is provided if the response is correct, or corrective feedback is given if the response is incorrect.
What is discrete trial training is an organized method that enables continuous practice and reinforcement, which is essential for mastery. By maintaining consistency in these steps, practitioners can effectively teach a wide range of abilities, from basic tasks to more complex behaviors.
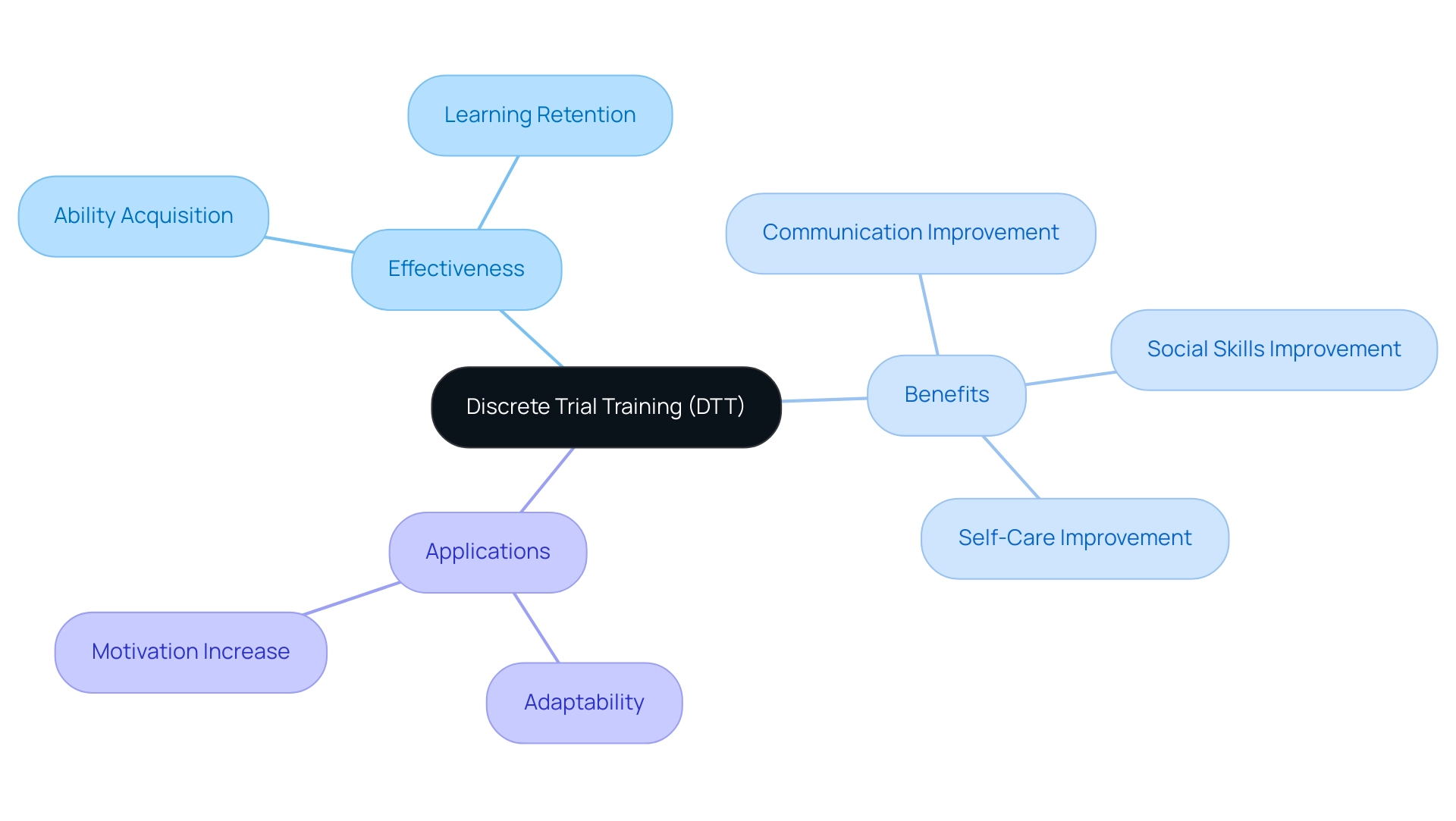
The Effectiveness and Benefits of Discrete Trial Training in Skill Development
What is discrete trial training? It has been demonstrated to be highly effective in promoting ability acquisition in youth with autism and related developmental disorders. Research indicates that DTT can lead to significant improvements in areas such as communication, social skills, and self-care. What is discrete trial training? It is a structured approach that allows for repeated practice and immediate reinforcement, which enhances learning retention.
Additionally, what is discrete trial training (DTT) is a method that can be tailored to meet the individual needs of each student, making it a versatile approach in various educational and therapeutic contexts. Many parents and educators report that children who engage in DTT show increased motivation and willingness to participate in learning activities, further underscoring the method's effectiveness.
Conclusion
The exploration of Discrete Trial Training (DTT) reveals its significance as a structured and effective approach within Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) for children with developmental challenges. By breaking down complex skills into smaller, manageable steps, DTT not only facilitates skill acquisition but also fosters essential learning behaviors. The core components—clear instruction, prompting, response, and reinforcement—create a consistent framework that enhances the learning experience, ensuring that children receive the support they need to thrive.
Research underscores the effectiveness of DTT, highlighting its ability to drive improvements in communication, social skills, and self-care among children with autism and related disorders. The high success rates reported in studies affirm that DTT is not just a method but a powerful tool that empowers children, boosts their confidence, and encourages active engagement with their environment.
For parent advocates, understanding and implementing DTT can significantly impact their children's developmental journeys. By embracing this evidence-based approach, parents can champion their children's learning experiences and navigate the complexities of their growth with greater confidence. As DTT continues to demonstrate its value in educational and therapeutic settings, it stands as a beacon of hope and a pathway to success for countless children and families.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is discrete trial training (DTT)?
Discrete trial training (DTT) is a fundamental method within Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) designed to teach complex abilities by breaking them down into smaller, manageable components through a structured series of discrete trials.
What are the key components of a discrete trial?
Each discrete trial consists of three critical elements: an antecedent (the instruction), a behavior (the response), and a consequence (the reinforcement).
How does DTT benefit children with autism and developmental disorders?
DTT facilitates concentrated ability development in a controlled environment, leading to significant advancements in learning outcomes, with effectiveness rates reported as high as 80% in skill acquisition for individuals with autism.
What are the steps involved in the DTT process?
The DTT process includes the following steps: 1. Instruction: The educator presents a clear instruction or question. 2. Prompting: Cues may be given to assist the learner. 3. Response: The learner responds to the instruction. 4. Reinforcement: Appropriate reinforcement is provided for correct responses, or corrective feedback is given for incorrect responses.
How does DTT enhance learning and motivation?
DTT allows for repeated practice and immediate reinforcement, which enhances learning retention. Many parents and educators report increased motivation and willingness to participate in learning activities among children who engage in DTT.
Can DTT be tailored to individual needs?
Yes, DTT is a versatile approach that can be customized to meet the individual needs of each student, making it effective in various educational and therapeutic contexts.
Where can parents find more resources on DTT and ABA techniques?
Parents can reach out to Rising Above ABA at 888.572.7473 for assistance and resources related to ABA techniques, located at 135 Beaver St, 4th Floor, Waltham, MA 02452.




