Introduction
In the journey of nurturing children's growth and learning, understanding effective teaching methods is paramount. Discrete Trial Training (DTT) emerges as a pivotal strategy within Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, providing a clear, structured approach that breaks down complex skills into manageable parts. This method not only enhances the learning experience for children, particularly those with autism and ADHD, but also fosters a supportive environment where immediate feedback and reinforcement play crucial roles.
By exploring the principles of DTT and its practical applications, advocates can empower themselves and their children to navigate educational challenges with confidence, ensuring that every learning opportunity is maximized.
Understanding Discrete Trial Training: A Foundation for Learning
Discrete Trial Training (DTT) stands as a cornerstone in the realm of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, offering a structured and systematic approach to teaching. This method breaks down abilities into smaller, more manageable components, allowing for focused instruction on one element at a time. Each trial is comprised of three essential parts:
- The prompt or instruction delivered to the learner
- The learner's response
- The consequential feedback provided
This clear framework is especially advantageous for individuals with autism and ADHD, as it establishes defined expectations and provides prompt reinforcement, fostering a nurturing and effective educational environment. Recent research indicates that DTT has a success rate exceeding 80% in assisting individuals with autism in gaining new abilities. Ralph Moller notes,
While DTT is a widely recognized teaching method within ABA, it is important to note that ABA programs have evolved beyond solely implementing DTT.
This evolution highlights the necessity for parents and professionals to understand the fundamental aspects of DTT, as it plays a crucial role in improving learning and development for youngsters. Additionally, the case study titled 'Generalization and Real-World Application in ABA' highlights how ABA programs emphasize the importance of generalizing skills learned in one setting to other environments, addressing challenges faced by individuals with autism. By understanding DTT and its components, advocates can better support their offspring in navigating the educational landscape.
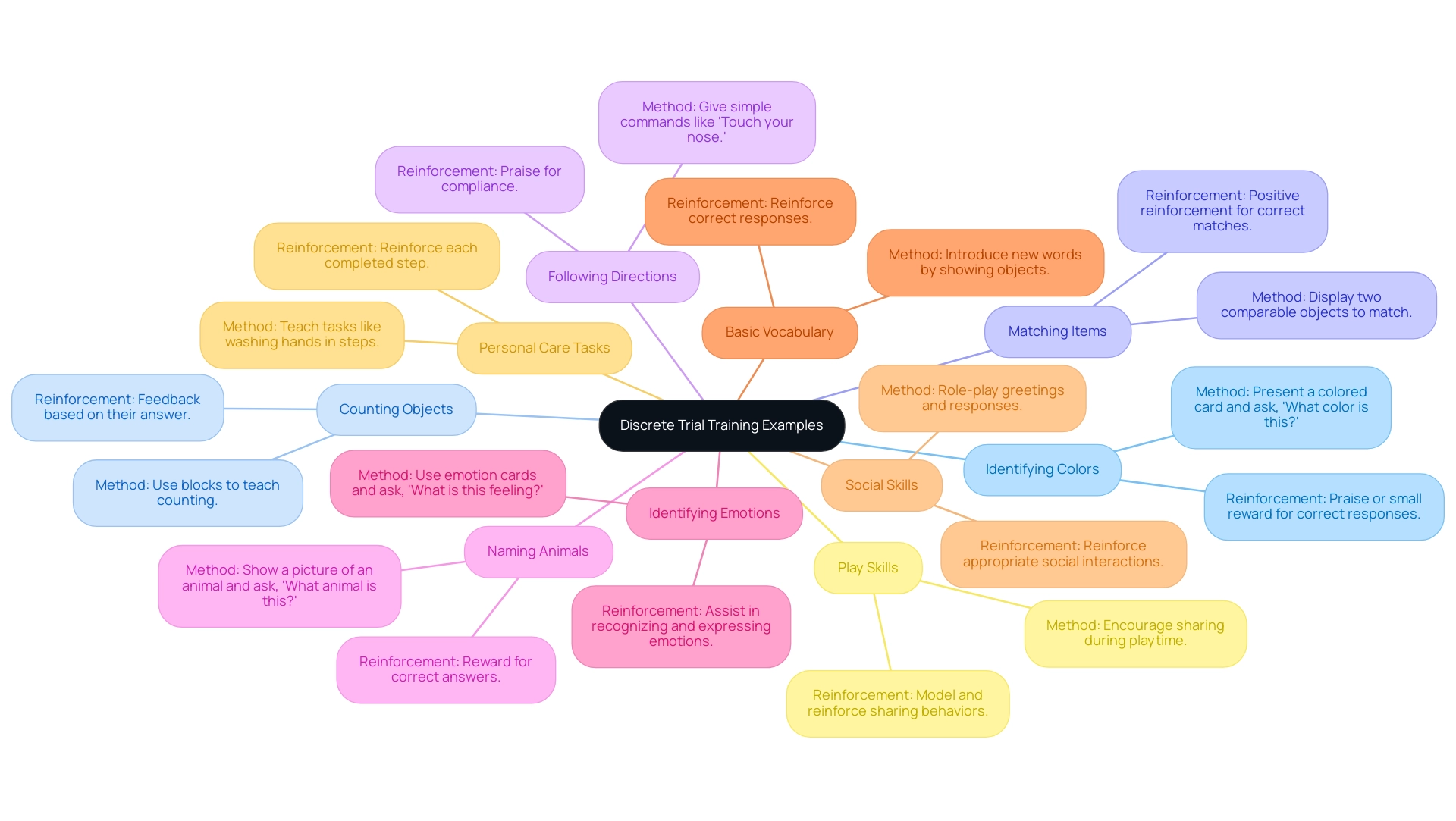
Practical Applications: 10 Effective Discrete Trial Training Examples
- Identifying Colors: Present a colored card and ask, 'What color is this?' Reinforce correct responses with praise or a small reward.
- Counting Objects: Use blocks to teach counting. Ask, 'How many blocks do you see?' and provide feedback based on their answer.
- Matching Items: Display two comparable objects and ask the young one to match them. Positive reinforcement should follow a correct match.
- Following Directions: Give simple commands such as 'Touch your nose' and reinforce compliance with praise.
- Naming Animals: Show a picture of an animal and ask, 'What animal is this?' Reinforce correct answers with a reward.
- Identifying Emotions: Use emotion cards and ask, 'What is this feeling?' to assist youngsters in recognizing and expressing emotions.
- Basic Vocabulary: Introduce new words by showing objects and asking the young learner to name them, reinforcing correct responses.
- Social Skills: Role-play greetings and responses, reinforcing appropriate social interactions.
- Personal Care Tasks: Teach tasks like washing hands by breaking it down into steps and reinforcing each completed step.
- Play Skills: Encourage sharing during playtime by modeling and reinforcing sharing behaviors.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of DTT in teaching various skills, making it an invaluable tool for improving education.
The Benefits of Discrete Trial Training: Enhancing Learning Outcomes
Discrete Trial Training provides various advantages that greatly improve educational results for individuals with autism and ADHD.
- Firstly, DTT offers a structured and predictable educational setting, which is essential for individuals who thrive on routine.
- Secondly, the immediate feedback and reinforcement help to solidify understanding and encourage positive behavior.
- Thirdly, DTT enables the customization of instruction, addressing each student's specific needs and pace of acquisition.
- Additionally, this method promotes skill generalization, as young learners learn to apply skills in various contexts.
Overall, the benefits of DTT contribute to more effective learning experiences and improved developmental outcomes for children, making it a valuable approach in ABA therapy.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing Discrete Trial Training (DTT) can transform the educational journey for children with autism and ADHD. This structured method breaks down complex skills into manageable components, fostering an environment where each learning opportunity is maximized through clear prompts, immediate feedback, and reinforcement.
The practical applications of DTT illustrate its versatility and effectiveness in teaching a variety of skills, from identifying colors to enhancing social interactions. By employing real-world examples, parents and advocates can utilize DTT to create tailored learning experiences that meet the unique needs of each child. The numerous benefits of this approach, including a predictable learning environment, individualized instruction, and skill generalization, underscore its significance in enhancing developmental outcomes.
Incorporating DTT into educational strategies empowers parents and advocates to support their children in navigating challenges with confidence. By embracing this method, they can foster a nurturing and effective learning atmosphere that encourages growth and success. As understanding of DTT expands, so too does the potential for children to thrive, making it an essential tool in the quest for effective education and skill acquisition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Discrete Trial Training (DTT)?
Discrete Trial Training (DTT) is a structured and systematic approach within Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy that breaks down abilities into smaller, manageable components for focused instruction.
What are the three essential parts of a DTT trial?
Each trial in DTT consists of three parts: the prompt or instruction delivered to the learner, the learner's response, and the consequential feedback provided.
Who benefits most from DTT?
DTT is particularly advantageous for individuals with autism and ADHD, as it establishes clear expectations and provides prompt reinforcement, creating an effective educational environment.
What is the success rate of DTT for individuals with autism?
Recent research indicates that DTT has a success rate exceeding 80% in helping individuals with autism acquire new abilities.
How has the implementation of ABA programs evolved beyond DTT?
While DTT is a widely recognized method, ABA programs have evolved to include various other approaches, emphasizing the importance of understanding DTT's fundamental aspects for improving learning and development.
What is the significance of generalizing skills in ABA programs?
ABA programs focus on the importance of generalizing skills learned in one setting to other environments, which helps individuals with autism navigate challenges effectively.
Can you provide examples of skills taught using DTT?
Examples of skills taught using DTT include identifying colors, counting objects, matching items, following directions, naming animals, identifying emotions, basic vocabulary, social skills, personal care tasks, and play skills.
What are the advantages of using DTT in education?
The advantages of DTT include providing a structured and predictable educational setting, immediate feedback and reinforcement, customization of instruction, and promoting skill generalization across various contexts.
How does DTT contribute to improved developmental outcomes?
The structured approach and personalized instruction of DTT contribute to more effective learning experiences, leading to improved developmental outcomes for children.




