Overview
The symptoms of Asperger syndrome in adults primarily include difficulties with social interactions, such as interpreting non-verbal cues, maintaining conversations, and adapting to changes in routines. The article supports this by highlighting specific challenges faced by adults, including heightened anxiety and feelings of isolation, and emphasizes the need for tailored support strategies to improve their daily functioning and emotional well-being.
Introduction
Asperger Syndrome, a distinct developmental disorder within the autism spectrum, presents a unique set of challenges that affect individuals, particularly in social interactions and everyday functioning. Unlike other forms of autism, those with Asperger Syndrome typically do not experience significant delays in language or cognitive development, yet they often struggle with interpreting social cues and maintaining relationships.
As awareness of this condition grows, particularly among adults, understanding its implications becomes increasingly vital. From the nuances of communication to the emotional hurdles faced in personal and professional settings, exploring Asperger Syndrome reveals a complex landscape marked by both struggles and strengths.
This article delves into the defining characteristics, symptoms, and support strategies essential for enhancing the lives of those affected by Asperger Syndrome, shedding light on the importance of tailored interventions and community understanding.
Understanding Asperger Syndrome: Definition and Overview
Asperger's condition, a developmental disorder within the autism spectrum, presents unique challenges characterized by profound difficulties in social interaction alongside restricted and repetitive behaviors and interests. Unlike other types of autism, individuals with Asperger's condition typically show no considerable delays in language or cognitive growth. The condition is named after Hans, a pioneering pediatrician who first described these traits in the 1940s.
Recent research highlights the prevalence of the condition among adults, with 2024 statistics showing an increasing awareness of its effects. Experts emphasize that understanding the definition is crucial to recognize the unique challenges associated with Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms, especially in workplace communication and interpersonal interactions. Moreover, as the Cleveland Clinic notes, having a sibling with autism increases the risk for autism spectrum disorders (ASD), further complicating family dynamics and support systems.
Statistics show that monozygotic twins exhibit a 98% concordance for autism, while dizygotic twins show a concordance of 53% to 67%, underscoring the genetic factors involved. Thorough evaluations, including psychiatric assessments and genetic testing, as demonstrated in the case study titled "Comprehensive Medical Assessment for Autism Spectrum Disorder," play a vital role in establishing effective intervention strategies, thereby improving the quality of life for individuals with autism.
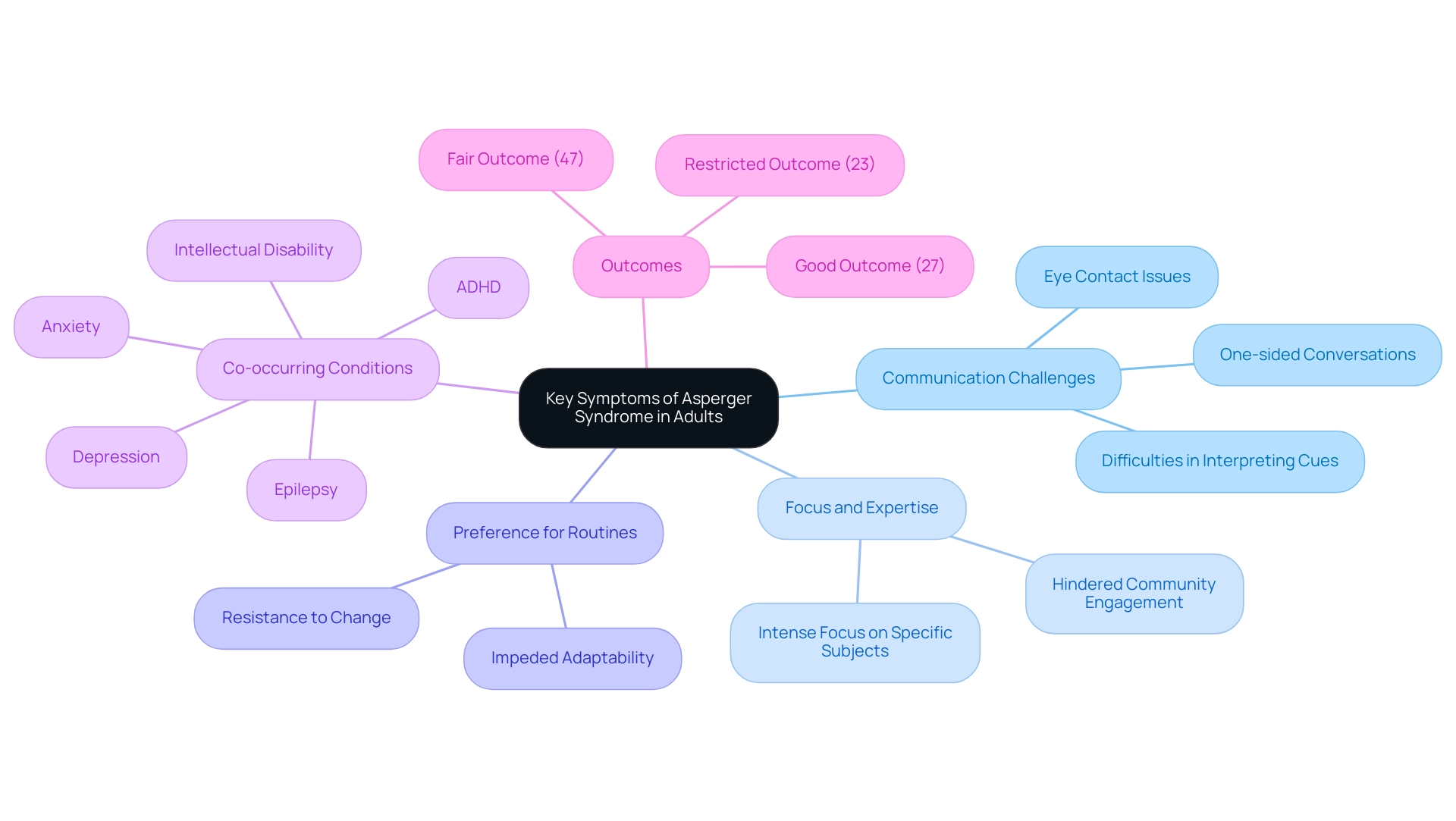
Key Symptoms of Asperger Syndrome in Adults
Adults with Asperger Syndrome often encounter various Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms that significantly impact their interpersonal interactions. Key challenges include:
-
Difficulties in interpreting cues, which often leads to one-sided conversations and misunderstandings in communication.
As Dr. Dannell Roberts, a leading expert in behavior analysis, notes,
Some autistic people find it hard to make eye contact with others,
highlighting a significant barrier in non-verbal communication.
-
An intense focus on specific subjects, allowing them to develop expertise in niche areas, yet this can hinder wider community engagement.
-
A preference for routines and resistance to change are additional characteristics that can impede adaptability in both interpersonal and work settings.
According to recent findings, approximately:
-
23% of adults with autism experience a restricted outcome,
-
47% have a fair outcome, and
-
27% achieve a good outcome,
emphasizing the variability in experiences among this population.
Additionally, common co-occurring conditions such as intellectual disability, ADHD, anxiety, depression, and epilepsy further complicate the challenges these adults face. The typical age of identification for the condition is approximately 5 years, but it can be postponed until adulthood due to compensatory techniques used by individuals, which can greatly affect their interactions with others. In real-life scenarios, adults may struggle to navigate social gatherings, leading to feelings of isolation or frustration.
The case study titled Life with a Partner or Spouse with Autism Spectrum Condition: Going Over the Edge? exemplifies these challenges, offering practical steps to enhance relationship dynamics impacted by autism. Identifying Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms is essential for creating supportive settings and formulating effective strategies that address the specific needs of adults with autism.
Social Interaction and Communication Challenges
Adults with Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms often face significant challenges in interpersonal interactions, especially in interpreting body language and tone of voice. These difficulties can hinder their ability to initiate or maintain conversations, which are often seen as asperger syndrome in adults symptoms, leading to misunderstandings and heightened feelings of isolation. In professional environments, where effective teamwork and collaboration are essential, the interpersonal impairments associated with asperger syndrome in adults symptoms can further complicate interactions.
A significant case study illustrates how people exhibiting asperger syndrome in adults symptoms may communicate in a formal manner, neglecting the social context, which can create awkward situations during job interviews and limit their ability to express their skills in socially acceptable ways. Recent studies indicate that over 70% of people with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) face additional psychiatric and physical disorders that affect their overall functioning and clinical management. Furthermore, a longitudinal study found that:
- Approximately 23% of patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder had a restricted outcome
- 47% had a fair outcome
- 27% had a good outcome
This underscores the variability in experiences among people.
As isolation rates among young adults with ASD are alarmingly high, it becomes increasingly vital for persons to develop coping strategies and seek supportive environments that promote skill enhancement. Understanding these dynamics is crucial, especially considering the broader context of environmental factors influencing ASD, such as parental age and perinatal events, which underscore the complexity of these disorders. It is also important to note that, based on systematic reviews of multiple extensive epidemiologic studies, there is no evidence to support an association between ASD and immunization as an environmental risk factor, clarifying misconceptions that may affect perceptions of ASD.
Emotional and Behavioral Symptoms in Adults with Asperger Syndrome
Adults with Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms often grapple with significant emotional challenges, particularly heightened anxiety and depression, which can arise from persistent interpersonal difficulties and feelings of isolation. The financial burden associated with therapeutic behavioral services, averaging $175.44, underscores the investment required for effective coping strategies in managing these emotional difficulties. Many people report experiencing meltdowns or shutdowns as behavioral responses to overwhelming situations, which illustrate important Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms.
One participant poignantly remarked,
After a lifetime of observing people, trying to work out why I am different and so isolated, it seems to me that my lack of comprehension of non-verbal communication limits my interaction with NTs looking for expected responses and results in them looking past me.
This sentiment highlights the profound impact of social interactions on emotional well-being, particularly concerning Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms and the resulting isolation. Recent studies highlight the significance of autism acceptance in mental health, advocating for supportive settings that nurture those facing these challenges.
Furthermore, the limitations noted in recent studies, including reliance on self-reported data and a predominantly female sample, suggest a critical need for further research with a more diverse population to explore these emotional symptoms comprehensively. Establishing robust support systems, including therapy and peer support groups, is essential for helping individuals navigate the emotional complexities associated with Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms.
Diagnosis of Asperger Syndrome: Criteria and Challenges
The identification of the symptoms of Asperger syndrome in adults requires a comprehensive assessment by a qualified expert, adhering to the guidelines outlined in the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders). This process can be particularly challenging due to the symptom overlap with other conditions such as ADHD, anxiety disorders, and the symptoms of Asperger syndrome in adults. Many adults may have developed coping strategies that effectively mask Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms, further complicating the assessment.
Clinicians often encounter difficulties in distinguishing the symptoms of Asperger Syndrome in adults from other neurodevelopmental disorders, which can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed identification. Notably, symptoms of ASD can be identified as early as 1 to 3 years, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis. Additionally, over 70% of people with ASD experience extra psychiatric and physical disorders, significantly affecting their functioning and clinical management.
Recent developments in diagnostic criteria emphasize the need for a nuanced approach that incorporates personal histories and reflects Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms. As highlighted in various studies, early and precise diagnosis is essential for obtaining suitable support and interventions, ultimately allowing people to better manage their personal and professional lives. Furthermore, understanding the prognosis for those with autism spectrum disorder reveals that factors such as IQ, language skills, and family support play significant roles in determining outcomes.
For instance, the case study on professional challenges for people with ASD-AS illustrates how impaired pragmatic language skills can create difficulties in workplace settings, highlighting the need for tailored interventions.
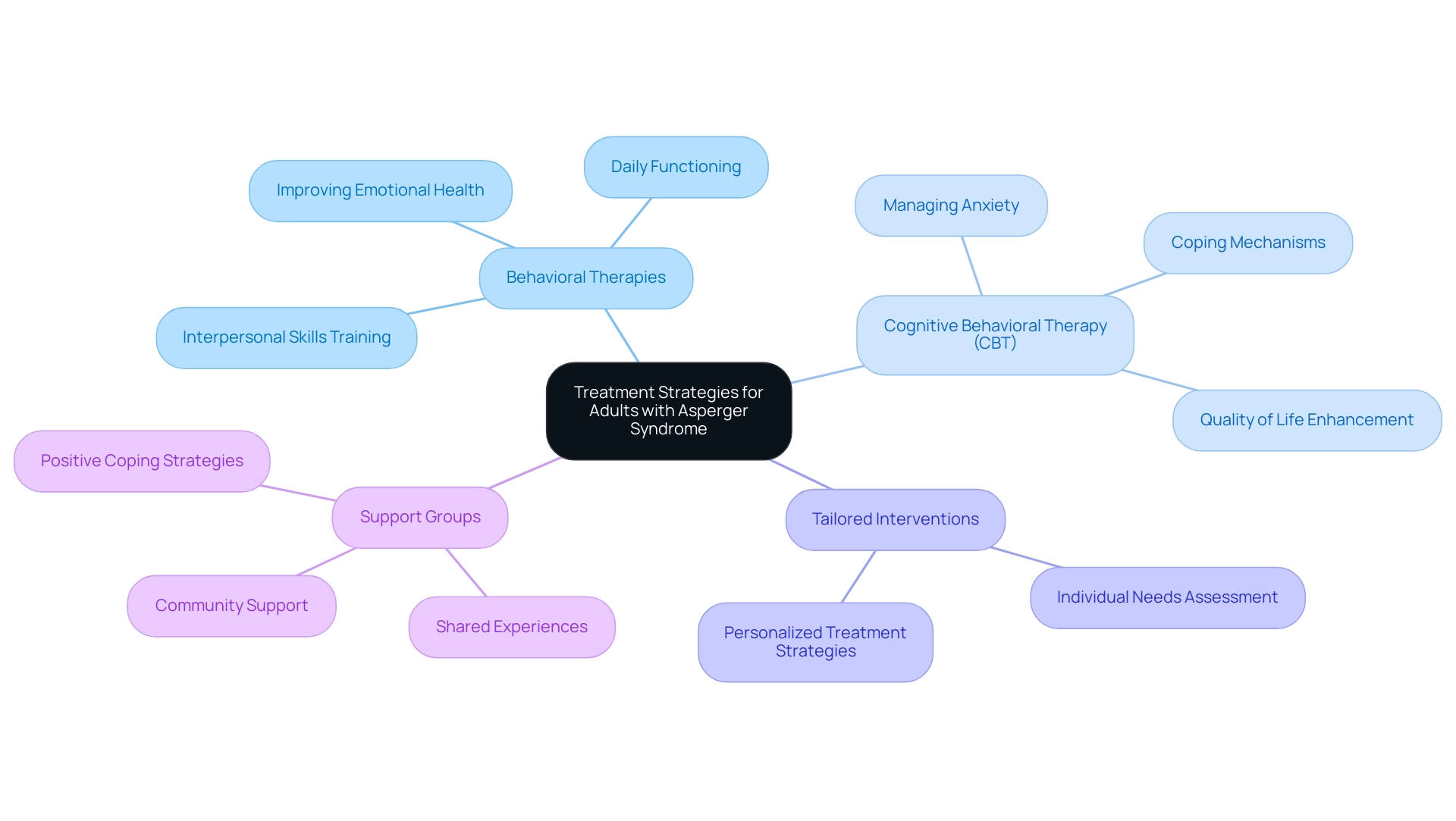
Treatment and Support Strategies for Adults with Asperger Syndrome
Care for adults with autism includes various methods focused on improving emotional health and daily functioning. Behavioral therapies, including interpersonal skills training and counseling, play a vital role in addressing the unique emotional challenges encountered by these people. Notably, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as one of the most effective modalities for managing anxiety and fostering improved coping mechanisms.
Experts emphasize that CBT can significantly enhance the quality of life for those experiencing Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms by equipping them with practical strategies to navigate social situations and emotional hurdles. As Seyed Alireza Hosseini Mohammed Molla notes, "It is widely acknowledged that the core features of Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms share similarities with other subpopulations within the ASD umbrella," underscoring the importance of tailored interventions. Support groups also serve as an invaluable resource, providing a sense of community and shared experiences that reinforce positive coping strategies.
It is essential to recognize that tailored interventions are critical, as the specific needs of each person may vary widely. Research indicates that ongoing support not only leads to substantial improvements in daily functioning but also enhances the overall quality of life. Furthermore, given the statistic that over 70% of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) face additional psychiatric and physical disorders, a comprehensive approach to treatment can significantly impact clinical management and functioning.
Additionally, children with ASD often exhibit strong interests in specific subjects, such as mechanics or music, which can inform and enhance personalized treatment strategies for adults with autism.
Living with Asperger Syndrome: Daily Life and Relationships
Navigating daily life with autism presents distinct challenges, particularly in maintaining relationships and effectively engaging in the workplace. Many adults experience symptoms of Asperger syndrome in adults, such as:
- Difficulties in initiating conversations
- Understanding figurative language
- Taking turns
These challenges can hinder their ability to connect with peers and lead to feelings of isolation. However, it is essential to recognize that people often cultivate meaningful relationships with those who appreciate and accommodate their unique communication styles.
Statistics reveal that a significant portion of adults face considerable obstacles; for instance, studies indicate that:
- 18% of people with autism have no daytime occupation
- Only 4% live [[[independently
Such statistics](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3769945](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3769945)/PMC3769945)) can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and disconnection. In professional settings, supportive measures such as flexible work environments and clear communication strategies can greatly enhance the ability of autistic people to thrive.
Moreover, community support plays a vital role in creating settings that empower adults with autism to build fulfilling lives. As highlighted in various case studies, including the 'Selected Outcome Studies of Adults with Autism,' many individuals face significant challenges in achieving independence and employment, with the studies revealing a range of outcomes. When communities prioritize understanding and acceptance, they can help facilitate successful relationship-building and improve the overall quality of life for those affected by Asperger syndrome in adults symptoms.
As D.M. noted in the report, addressing these challenges with a supportive community framework is essential for positive outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding Asperger Syndrome is crucial for fostering an inclusive environment that empowers individuals affected by this condition. Throughout the article, the unique characteristics and challenges faced by adults with Asperger Syndrome have been thoroughly explored, highlighting difficulties in social interactions, emotional regulation, and communication. The importance of early diagnosis and tailored support strategies has been emphasized, illustrating how effective interventions can significantly enhance the quality of life for those living with Asperger Syndrome.
Support systems, including behavioral therapies and community understanding, play a pivotal role in helping individuals navigate everyday challenges. By recognizing and accommodating the diverse needs of those with Asperger Syndrome, society can create environments that promote acceptance and understanding. This not only aids in personal development but also fosters meaningful relationships and professional success.
In conclusion, as awareness of Asperger Syndrome continues to grow, it is essential to advocate for comprehensive support and understanding. By addressing the specific needs of individuals with this condition, communities can help dismantle barriers and cultivate a more inclusive world where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Asperger's condition?
Asperger's condition is a developmental disorder within the autism spectrum characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and restricted, repetitive behaviors and interests. Unlike other autism types, individuals with Asperger's typically do not experience major delays in language or cognitive development.
Who is Asperger's condition named after?
The condition is named after Hans Asperger, a pioneering pediatrician who first described its traits in the 1940s.
What are the unique challenges faced by adults with Asperger's syndrome?
Adults with Asperger's syndrome often struggle with interpreting social cues, leading to one-sided conversations and misunderstandings. They may also have intense focus on specific subjects, which can limit broader community engagement, and a preference for routines, making them resistant to change.
How prevalent is Asperger's syndrome among adults?
Recent research indicates increasing awareness of Asperger's syndrome among adults, with statistics from 2024 showing a significant prevalence of the condition.
What are the outcomes for adults with autism?
Approximately 23% of adults with autism experience a restricted outcome, 47% have a fair outcome, and 27% achieve a good outcome, highlighting variability in experiences among this population.
What co-occurring conditions are common in adults with Asperger's syndrome?
Common co-occurring conditions include intellectual disability, ADHD, anxiety, depression, and epilepsy, which can further complicate the challenges faced by adults with Asperger's syndrome.
At what age is Asperger's syndrome typically identified?
The typical age for identification of Asperger's syndrome is around 5 years, but it can be delayed until adulthood due to compensatory techniques individuals may use.
How does having a sibling with autism affect the risk for Asperger's syndrome?
Having a sibling with autism increases the risk for autism spectrum disorders, which can complicate family dynamics and support systems.
What role do genetic factors play in Asperger's syndrome?
Genetic factors are significant, as monozygotic twins show a 98% concordance for autism, while dizygotic twins have a concordance of 53% to 67%.
What is the importance of thorough evaluations for individuals with autism?
Thorough evaluations, including psychiatric assessments and genetic testing, are vital for establishing effective intervention strategies that can improve the quality of life for individuals with autism.




