Overview
The article focuses on understanding the signs of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in adults, highlighting the distinct challenges they face in social communication and daily life. It emphasizes the importance of early identification and tailored support strategies, as many adults with ASD experience difficulties that can lead to isolation and underemployment, underscoring the need for accurate diagnosis and effective intervention to improve their quality of life.
Introduction
In a world increasingly aware of neurodiversity, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in adults often remains shrouded in misunderstanding and stigma. This complex condition, which affects social communication and behavior, is frequently underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed, leaving many adults without the support they need.
As the prevalence of autism rises, understanding its manifestations in adulthood becomes crucial, not only for those living with the condition but also for their families and communities.
This article delves into the intricacies of ASD in adults, exploring:
- Identification
- Diagnosis
- Effective support strategies
These strategies can empower individuals to thrive in a society that often overlooks their unique challenges and strengths.
1. What is Autism Spectrum Disorder in Adults?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that presents significant challenges in social communication and is often accompanied by restrictive or repetitive behaviors. In grown individuals, the signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults can differ markedly from those observed in children, leading to a concerning trend of underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis. Symptoms in individuals may include signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults, such as:
- Difficulties with social interactions
- An increased likelihood of feeling overwhelmed in social environments
- A strong preference for structured routines
Current research indicates that about 1 in 6 children aged 3–17 years have been diagnosed with a developmental disability, emphasizing the need for greater awareness and understanding of ASD across all ages. Furthermore, the prevalence of cases related to developmental disorders has risen from 23 per 1,000 children in 2018 to 27.6 in 2020, highlighting the growing concern surrounding this disorder. Additionally, the co-occurrence of ASD with other neurodevelopmental disorders is significant, stemming from genetic and structural brain differences that characterize them, as noted in studies from Practical Neurology.
Recognizing the signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults is essential for understanding the profound impact of ASD on the lives and relationships of grown individuals, enabling more effective support and intervention strategies. Social workers need education to assist parents in planning for their child's future, thereby breaking down the planning process into manageable steps.
2. Identifying the Signs of Autism in Adults
Typical indicators, or signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults, appear in diverse forms, greatly affecting their everyday existence. Individuals may struggle with interpreting social cues or engaging in small talk, which can lead to feelings of isolation. A strong preference for routines often accompanies a resistance to change, making transitions particularly challenging.
Furthermore, adults with this condition may exhibit an intense focus on specific interests or hobbies, sometimes to the exclusion of other activities. Emotional regulation is another area where difficulties arise; understanding their own emotions and those of others can be particularly tough. Sensitivity to sensory inputs, such as noise or bright lights, can also complicate social situations.
Identifying the signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults is essential, as they can act as a gateway for individuals or their loved ones to seek the needed assistance. Notably, statistics reveal that around 8% of autistic students in the U.S. do not finish high school—significantly higher than the 5% dropout rate for all students. This underscores the importance of early identification and intervention.
Temple Grandin famously stated,
It is part of who I am,
reflecting the reality that understanding this condition is essential not only for assistance but also for celebrating the unique strengths that accompany it. Furthermore, real-life instances demonstrate that almost 60% of individuals on the autism spectrum secure jobs after obtaining vocational rehabilitation services, emphasizing the effectiveness of tailored assistance in navigating social and professional environments. However, it is important to note that only 21% of individuals with disabilities, including those on the spectrum, are employed, which emphasizes the significant challenges faced by grown individuals with developmental disorders in the workforce.
Additionally, regions such as California and Texas have the highest projected figures of individuals living with signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults, indicating the prevalence of autism among grown individuals and the urgent need for assistance services.
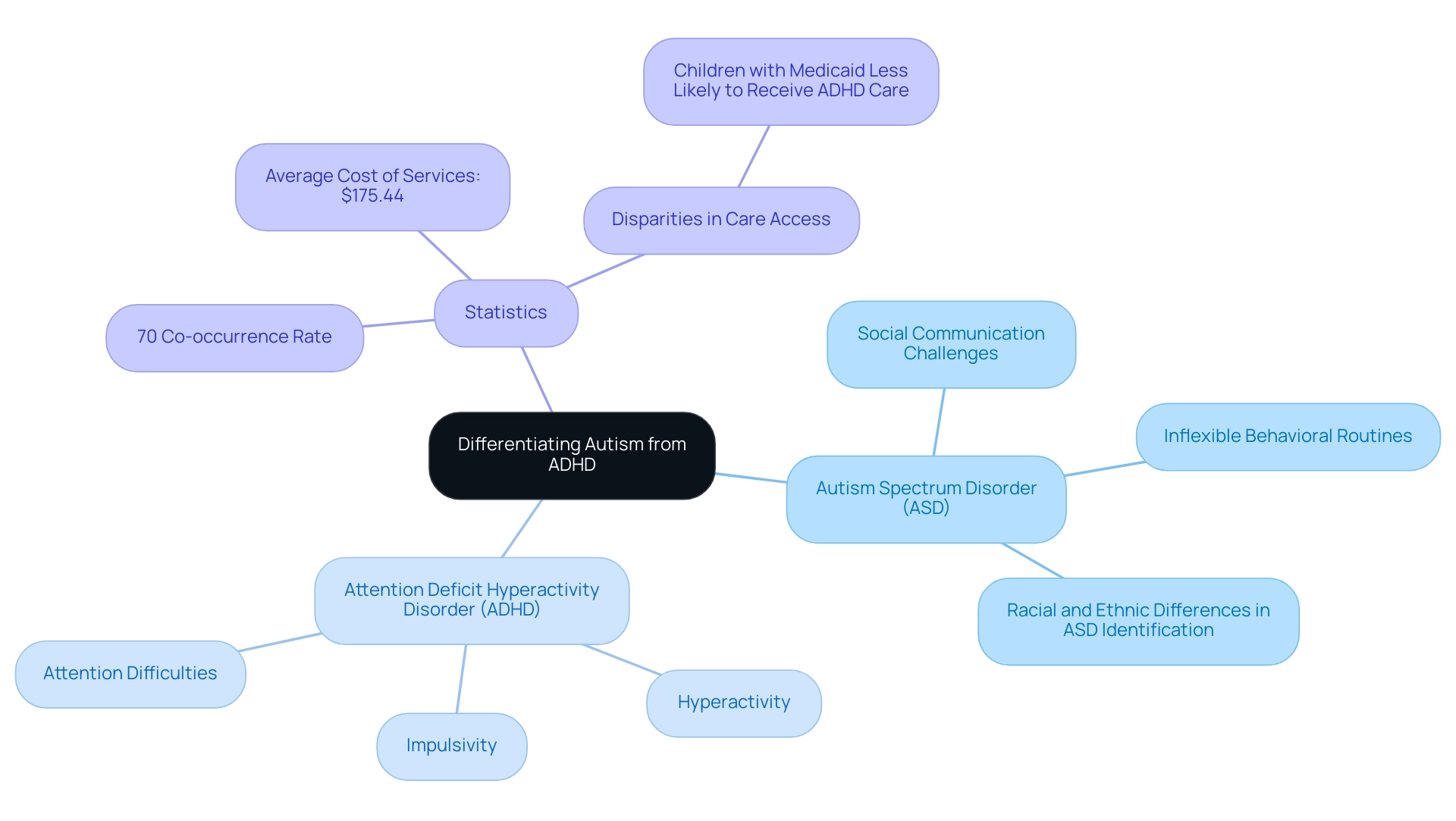
3. Differentiating Autism from ADHD and Other Conditions
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are often confused due to some overlapping traits, yet they represent distinct neurodevelopmental conditions. Individuals with ADHD commonly display impulsivity, hyperactivity, and attention difficulties, which are less pronounced in those with ASD. In contrast, individuals exhibiting signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults typically face challenges in social communication and may engage in inflexible behavioral routines.
Understanding these differences is critical, particularly given the high co-occurrence rates of up to 70% between ADHD and signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults. This complexity underscores the necessity for precise diagnostic practices that inform effective treatment strategies. Mental health professionals emphasize that recognizing the signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults is essential for developing individualized support plans that cater to the unique needs of each individual.
The average cost of therapeutic behavioral services is $175.44, which can be a significant consideration for families seeking help. Furthermore, disparities in care access are highlighted by the observation that children with Medicaid were less likely to receive ADHD care from healthcare specialists, such as psychologists or psychiatrists. As research progresses into 2024, ongoing studies will continue to enhance clarity around the diagnostic processes, ultimately benefiting those affected by both conditions.
Additionally, a recent case study has identified racial and ethnic differences in ASD identification, suggesting potential disparities in how these conditions are diagnosed across different demographic groups.
4. Navigating the Diagnosis of Autism in Adults
The diagnostic process for adults suspected of showing signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults involves several critical steps that ensure a thorough evaluation. First, an initial evaluation is conducted, where the individual meets with a healthcare professional specializing in developmental disorders. This meeting concentrates on addressing particular issues and signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults that may suggest the existence of a developmental disorder.
Next, a comprehensive assessment is performed, which includes standardized tests and interviews designed to evaluate behavior, communication skills, social interactions, and signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults. This thorough examination is crucial as it results in a clearer comprehension of the person's difficulties and advantages. After the evaluation, a diagnosis is established based on the outcomes, enabling conversations regarding possible assistance and treatment alternatives customized to the individual's requirements.
According to recent data, the average time to diagnose this condition in adults can vary widely, emphasizing the necessity for timely and accurate evaluations. Dr. Stephanie Collier emphasizes the significance of accurate diagnoses, stating,
A precise diagnosis is crucial as it directly influences the quality of life and the support available to individuals with developmental disorders.
Furthermore, a recent analysis highlighted variability in ASD prevalence by state, ranging from 1.97% to 2.42%, which underscores how differences in the availability of diagnostic services can impact reported prevalence rates.
Significantly, the prevalence of this condition rises to 2.7% of children in the U.S., illustrating the broader context of it within the population. Additionally, the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services for individuals with developmental disorders in the U.S. is $175.44, highlighting the financial implications associated with diagnosis and treatment. This variability and the related costs emphasize the significance of thorough evaluations in improving the comprehension and management of diagnosis in grown individuals, aligning with the study's goal to inform planning for services and programs for individuals with ASD.
5. Support Strategies for Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Support strategies for individuals with developmental disorders encompass a variety of approaches aimed at fostering connection and enhancing quality of life. Key strategies include:
- Joining assistance groups: Engaging with others who share similar experiences can provide emotional encouragement and practical advice. Recent statistics show that involvement in groups for individuals with developmental disorders has increased, reflecting heightened awareness of their advantages.
- Engaging in therapy: Therapeutic approaches such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) are essential for developing effective coping mechanisms. Therapists emphasize that tailored therapeutic strategies can significantly improve emotional regulation and interpersonal skills.
- Utilizing organizational tools or apps: These resources assist individuals with autism in managing daily tasks and schedules, promoting greater independence and productivity.
- Seeking vocational training and employment support: These initiatives are crucial for enhancing work-related skills and facilitating successful integration into the workplace. Liu et al.'s recent quasi-experimental study demonstrated that workplace training programs can lead to significant improvements in social behavior among autistic individuals; however, the absence of a control group highlights the need for further research. Moreover, it is important to acknowledge the challenges faced by autistic individuals, particularly the signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults, as noted by Cassidy et al., who reported that non-suicidal self-inflicted injuries and suicidal tendencies rates in autistic adolescents and grown individuals are higher than their non-autistic peers. Additionally, statistics indicate that 15% of autistic individuals cared for by caregivers required institution-like care, and a study by Lugnegard et al. found that 70% of individuals with ASD experienced at least one episode of major depression. By leveraging these strategies and resources, adults with autism can build fulfilling lives, foster meaningful connections, and navigate their unique challenges more effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in adults is essential for breaking down barriers of stigma and misunderstanding. The complexities of ASD manifest differently in adults compared to children, leading to significant challenges in social communication and behavior. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of autism, individuals and their families can seek appropriate support, allowing for better quality of life and integration into society.
The diagnostic process is a critical step toward obtaining the necessary resources and interventions. Accurate identification and differentiation from other conditions, such as ADHD, are vital for developing personalized support plans. Timely and thorough evaluations can significantly influence the effectiveness of treatment and support services, ultimately impacting the overall well-being of individuals with autism.
Implementing effective support strategies is crucial for empowering adults with ASD. From joining support groups and engaging in therapy to utilizing organizational tools and seeking vocational training, these strategies can foster independence and enhance social connections. As awareness of autism grows, so too does the potential for positive change in the lives of those affected. By embracing and celebrating neurodiversity, society can create an inclusive environment that acknowledges the unique strengths and challenges faced by individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that presents challenges in social communication and is often accompanied by restrictive or repetitive behaviors.
How do the signs of ASD differ in adults compared to children?
The signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults can differ significantly from those in children, leading to a concerning trend of underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis.
What are some common symptoms of ASD in adults?
Common symptoms of autism spectrum disorder in adults include difficulties with social interactions, feeling overwhelmed in social environments, and a strong preference for structured routines.
What is the prevalence of developmental disabilities in children?
Current research indicates that about 1 in 6 children aged 3–17 years have been diagnosed with a developmental disability, with the prevalence of such cases rising from 23 per 1,000 children in 2018 to 27.6 in 2020.
Why is recognizing the signs of ASD in adults important?
Recognizing the signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults is crucial for understanding its impact on their lives and relationships, which enables more effective support and intervention strategies.
What challenges do adults with ASD face in social situations?
Adults with ASD may struggle with interpreting social cues, engaging in small talk, and may experience feelings of isolation. They often have a strong preference for routines and may resist change, making transitions difficult.
How does ASD affect emotional regulation in adults?
Adults with ASD may have difficulties in understanding their own emotions and those of others, which complicates social interactions.
What are some educational challenges faced by autistic students?
Statistics reveal that around 8% of autistic students in the U.S. do not finish high school, which is significantly higher than the 5% dropout rate for all students, highlighting the importance of early identification and intervention.
What is the employment situation for individuals with ASD?
Although almost 60% of individuals on the autism spectrum secure jobs after obtaining vocational rehabilitation services, only 21% of individuals with disabilities, including those on the spectrum, are employed, indicating significant workforce challenges.
Which regions have the highest projected figures of adults with ASD?
Regions such as California and Texas have the highest projected figures of individuals living with signs of autism spectrum disorder in adults, indicating a need for assistance services.




