Overview
This article seeks to illuminate the nuances of hypersensitivity in autism, focusing on its signs, supportive strategies, and the vital role of creating accommodating environments for those affected. By recognizing and addressing sensory sensitivities—like auditory, visual, tactile, and olfactory reactions—we can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals with autism. Effective coping strategies and professional therapies play a crucial role in fostering emotional regulation and helping them adapt to various stimuli.
As we explore these topics, it's essential to consider the experiences of parents and caregivers. Many face challenges in navigating the complexities of sensory sensitivities, and sharing personal stories can help us understand these struggles better. If you have faced similar situations, we encourage you to share your experiences in the comments or through our newsletter. Your insights can foster a supportive community.
Ultimately, our goal is to provide specific resources and support that can make a difference. By creating understanding and accommodating environments, we can empower individuals with autism to thrive. Let's work together to enhance their experiences and well-being.
Introduction
Understanding hypersensitivity in autism is crucial, as it affects many individuals on the spectrum, leading to significant challenges in their everyday lives. This article explores the signs of hypersensitivity in autism, providing valuable strategies for parents and caregivers. These strategies aim to create supportive environments that cater to these unique sensitivities. How can we effectively navigate the complexities of hypersensitivity to foster a more inclusive and understanding atmosphere for those affected?
Define Hypersensitivity in Autism
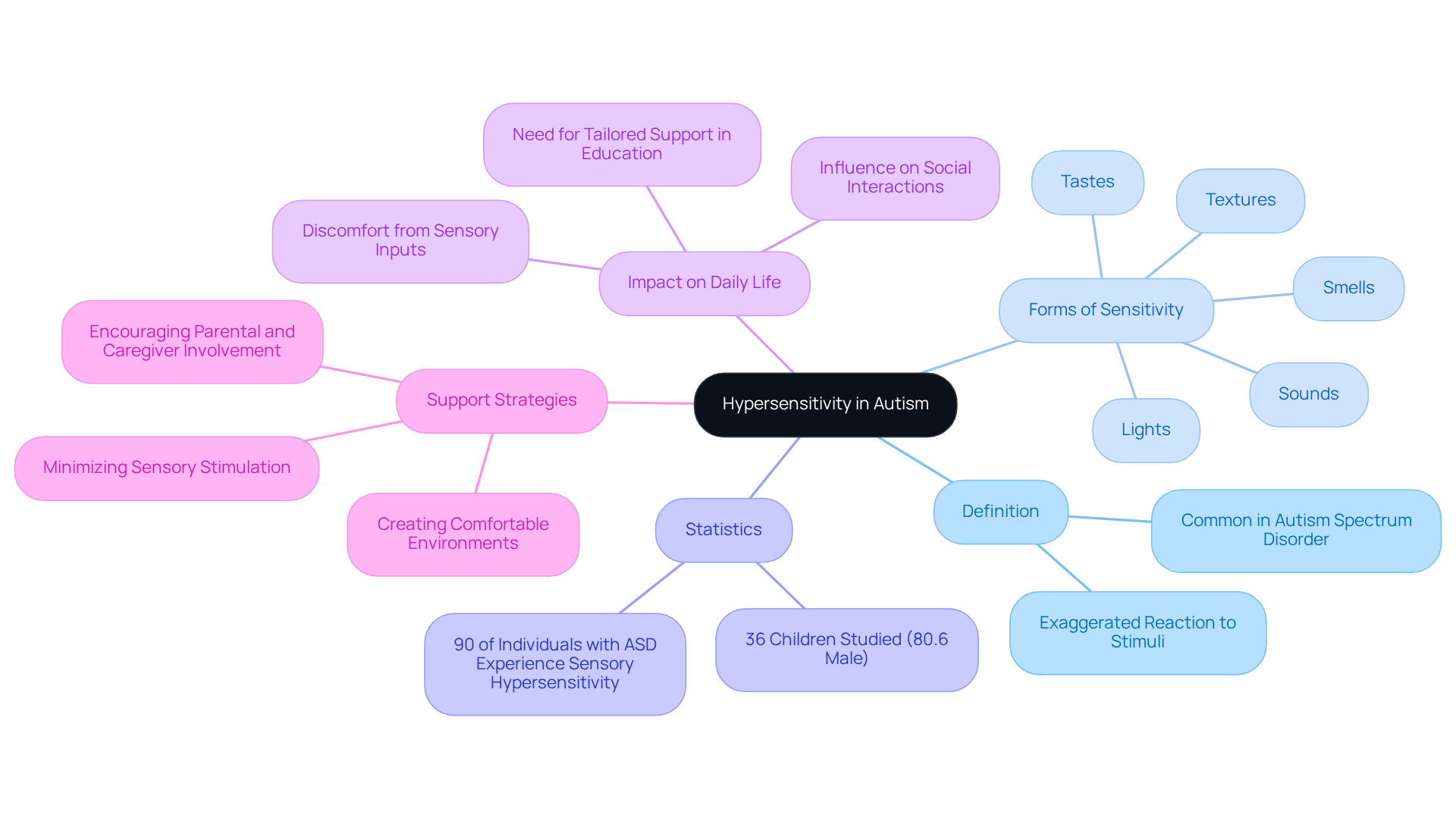
Hypersensitivity autism often results in an exaggerated reaction to stimuli, leading to discomfort or distress from inputs that others may find tolerable or even pleasant. This heightened sensitivity can take many forms, such as aversion to sounds, lights, textures, tastes, and smells. For example, a child may cover their ears in response to loud noises or refuse to wear certain fabrics because of their texture. Remarkably, studies indicate that up to 90% of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience some form of hypersensitivity autism, significantly influencing their daily experiences and interactions.
Recent research has revealed that children with ASD exhibit notable differences in processing patterns when compared to their neurotypical peers. This underscores the necessity for tailored support within educational settings. Understanding these sensitivities is crucial for parents and professionals alike, as it enables them to create supportive environments that address the unique needs of individuals with hypersensitivity autism.
By implementing strategies such as establishing comfortable environments and minimizing sensory stimulation in classrooms, caregivers can foster greater involvement and participation in various activities. Ultimately, these efforts contribute to enhancing the quality of life for those affected by autism. We encourage parents and caregivers to share their experiences and insights, as together we can build a more understanding and supportive community.
Identify Manifestations and Triggers of Hypersensitivity
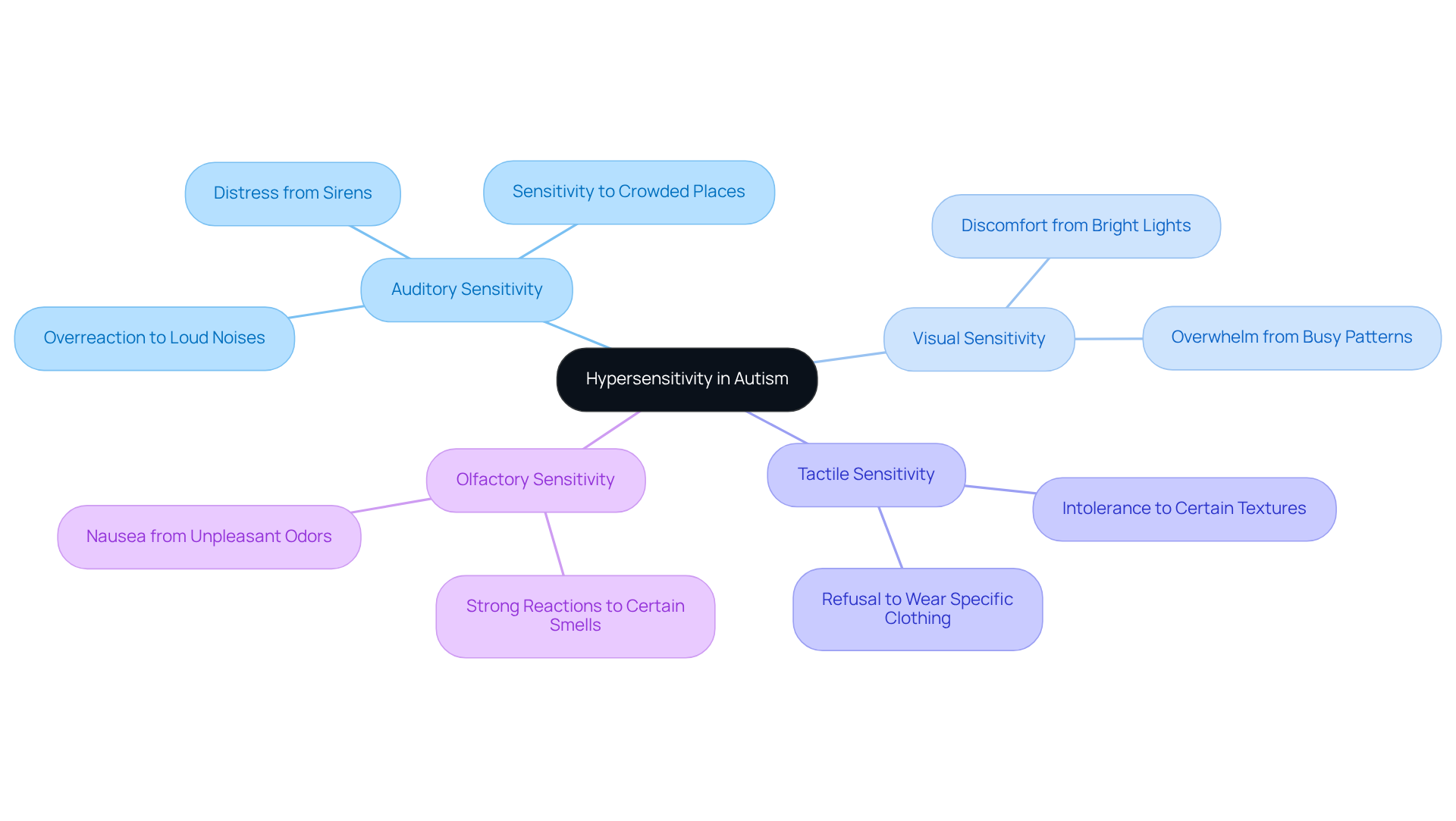
Understanding hypersensitivity autism can be crucial for parents navigating their child's experiences. Here are some common manifestations:
- Auditory Sensitivity: Many children may overreact to loud noises, like sirens or crowded places. This can often lead them to cover their ears or show signs of distress.
- Visual Sensitivity: Bright lights or busy patterns can be overwhelming, causing discomfort or anxiety for some children.
- Tactile Sensitivity: Certain textures, such as clothing tags or specific food textures, may be intolerable, resulting in refusal to wear or eat those items.
- Olfactory Sensitivity: Some children have strong reactions to certain smells, which can lead to nausea or a desire to avoid particular environments.
Recognizing these triggers is essential for developing effective strategies to manage sensory overload associated with hypersensitivity autism. By understanding and addressing these sensitivities, we can create a more supportive environment for our children.
Implement Coping Strategies and Create a Supportive Environment
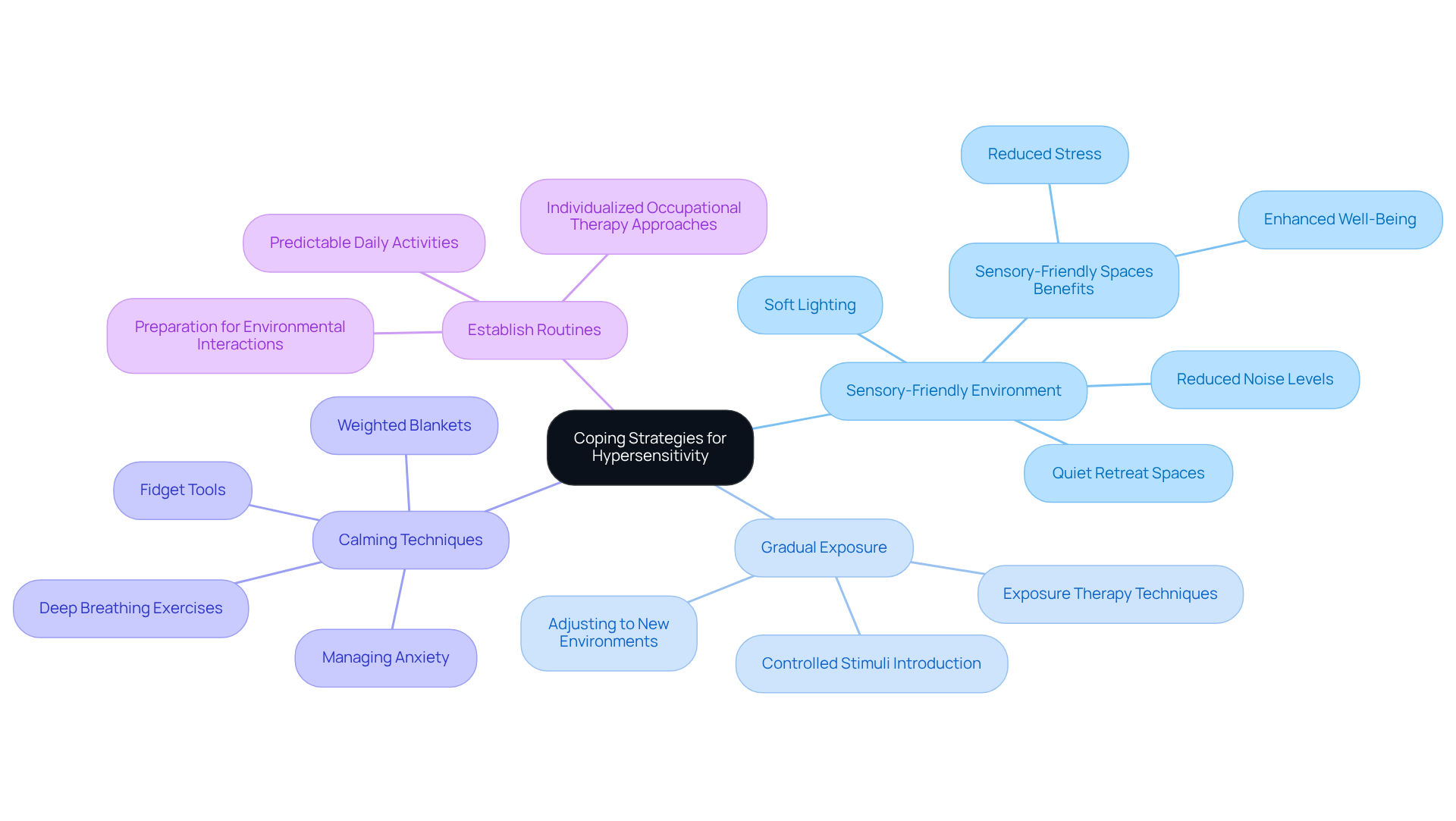
Supporting individuals with hypersensitivity requires a thoughtful approach. Here are some effective strategies caregivers can implement:
- Create a Sensory-Friendly Environment: Consider soft lighting, reduced noise levels, and quiet spaces where individuals can retreat when feeling overwhelmed. Research shows that sensory-friendly spaces can significantly reduce stress and enhance overall well-being for children on the autism spectrum. As noted by ABA Centers of America, "Sensory-friendly spaces can help those on the spectrum adjust to new environments in bite-sized pieces."
- Introduce Gradual Exposure: Gradually present stimuli in a controlled manner to help develop tolerance. This method, known as exposure therapy, allows individuals to adjust to stimuli without feeling overwhelmed. It's important to clarify that this involves the gradual introduction of experiential stimuli, as highlighted in recent studies.
- Use Calming Techniques: Incorporate calming strategies like deep breathing exercises, weighted blankets, and fidget tools. These tools can effectively manage anxiety during overwhelming situations, providing immediate relief and promoting emotional regulation. Research indicates that about 90% of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) display hypersensitivity autism to stimuli, making these techniques essential for managing anxiety.
- Establish Routines: Predictable routines can provide a sense of security and help lower anxiety related to unforeseen experiences. Regularity in everyday tasks enables individuals to foresee and prepare for environmental interactions. Individualized approaches in occupational therapy for children with autism can further enhance the effectiveness of these routines.
By applying these approaches, caregivers can empower individuals with hypersensitivity autism to manage their condition more effectively, fostering a supportive atmosphere that enhances their quality of life. Moreover, research has shown considerable decreases in autistic behaviors among children undergoing integration therapies, underscoring the importance of these strategies.
Seek Professional Support and Therapy Options
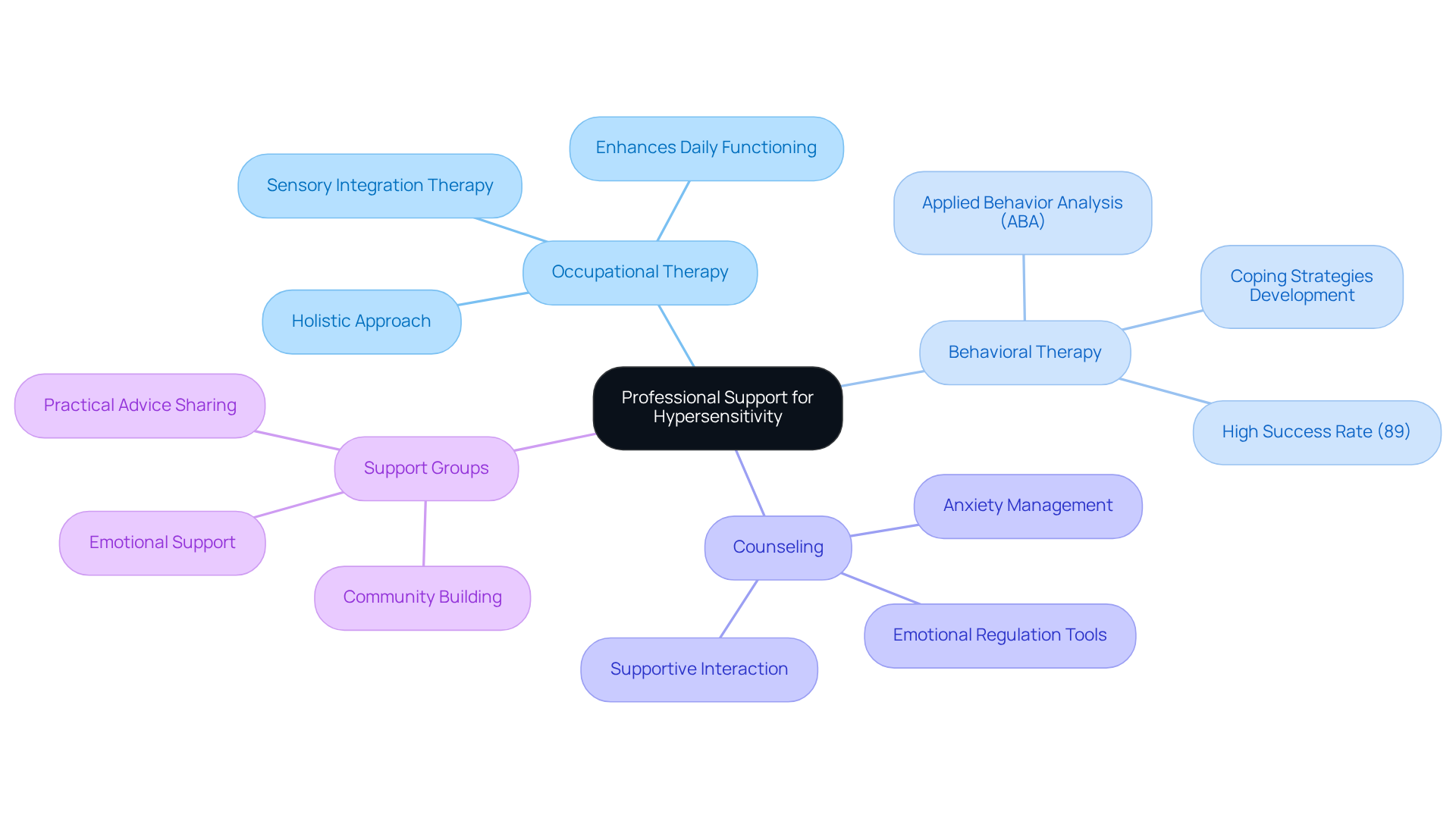
Professional support plays a crucial role for individuals navigating hypersensitivity. It's essential to explore effective options that can truly make a difference:
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapists focus on sensory integration therapy, helping individuals process sensory information more effectively. As Jessica Kensky beautifully articulates, occupational therapy intertwines science, creativity, and compassion, leading to significant improvements in daily functioning and overall quality of life.
- Behavioral Therapy: Techniques like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) empower individuals to develop effective coping strategies. Research indicates that ABA therapy boasts a success rate exceeding 89% in supporting children with ASD, primarily by reducing negative responses to environmental stimuli and promoting more adaptive behaviors across various settings.
- Counseling: Engaging with a psychologist can be invaluable for managing anxiety and emotional responses tied to sensory input. This supportive interaction equips individuals with essential tools for emotional regulation, enabling them to handle overwhelming stimuli more effectively.
- Support Groups: Connecting with other families facing similar challenges can provide both emotional support and practical advice. These groups cultivate a sense of community, allowing individuals to share their experiences and learn from one another, reinforcing the collaborative spirit of support.
By exploring these professional avenues, individuals can access tailored strategies that effectively address their sensory sensitivities associated with hypersensitivity autism, paving the way for improved outcomes and enriched daily living. If you have experiences or insights to share, we invite you to connect with us and join the conversation.
Conclusion
Understanding hypersensitivity in autism is crucial for creating a nurturing environment for individuals on the spectrum. This heightened sensitivity can present itself in various forms, impacting daily interactions and overall quality of life. By recognizing and addressing these unique challenges, caregivers and professionals can profoundly enhance the experiences of those with hypersensitivity autism.
Key insights from this article underscore the significance of identifying specific sensory triggers, including:
- Auditory sensitivities
- Visual sensitivities
- Tactile sensitivities
- Olfactory sensitivities
By implementing effective coping strategies—such as crafting sensory-friendly spaces, gradually introducing exposure to stimuli, and establishing routines—individuals can feel empowered to manage their sensitivities more effectively. Additionally, seeking professional support through therapies like:
- Occupational therapy
- Behavioral therapy
- Counseling
can offer tailored strategies that improve emotional regulation and daily functioning.
Ultimately, awareness and understanding of hypersensitivity in autism are vital for fostering a more inclusive community. By sharing experiences and insights, caregivers can build a collaborative network that supports individuals facing these challenges. Emphasizing the importance of personalized approaches and professional guidance can lead to better outcomes and enriched lives for those affected by hypersensitivity autism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is hypersensitivity in autism?
Hypersensitivity in autism refers to an exaggerated reaction to stimuli, resulting in discomfort or distress from inputs that others may find tolerable or pleasant. This can include aversions to sounds, lights, textures, tastes, and smells.
How common is hypersensitivity among individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Studies indicate that up to 90% of individuals with autism spectrum disorder experience some form of hypersensitivity, which significantly influences their daily experiences and interactions.
How do children with ASD process sensory information differently than neurotypical peers?
Recent research has shown that children with ASD exhibit notable differences in processing patterns compared to their neurotypical peers, highlighting the need for tailored support in educational settings.
Why is it important for parents and professionals to understand hypersensitivity in autism?
Understanding hypersensitivity is crucial for parents and professionals as it enables them to create supportive environments that address the unique needs of individuals with hypersensitivity autism.
What strategies can caregivers implement to support individuals with hypersensitivity autism?
Caregivers can establish comfortable environments and minimize sensory stimulation in classrooms to foster greater involvement and participation in various activities.
How can the community support individuals with hypersensitivity autism?
The community can support individuals by sharing experiences and insights, which helps build a more understanding and supportive environment for those affected by autism.




