Overview
Visual stimming, or visual self-stimulation, is more than just a behavior; it's a common coping mechanism for many individuals on the autism spectrum. Engaging in repetitive sight-related activities can help manage sensory input and provide comfort, making it a vital part of their daily lives. It’s important to recognize these behaviors as legitimate strategies for self-soothing. Research shows their prevalence and benefits in enhancing focus and emotional regulation. This understanding can empower parents and caregivers to create supportive environments that nurture their children’s unique needs.
As a parent, witnessing your child engage in visual stimming might raise questions. You may wonder how to best support them or if these behaviors are truly helpful. The reality is that these actions can serve as a bridge to emotional calmness and concentration. By embracing and validating these behaviors, you can foster an environment where your child feels understood and accepted.
Consider sharing your experiences or seeking advice from other parents who have navigated similar journeys. Your insights can be invaluable, not just for you, but for others in the community. Together, we can cultivate a space where every child’s coping mechanisms are recognized and celebrated, paving the way for their growth and happiness.
Introduction
In the intricate world of autism, visual stimming stands out as a fascinating and essential aspect of sensory processing. This self-stimulatory behavior, often characterized by repetitive visual activities, serves as a coping mechanism for many children on the autism spectrum, helping them navigate overwhelming environments and manage their sensory experiences. As research continues to unfold, our understanding of visual stimming deepens, revealing its prevalence and significance in the lives of autistic children.
Consider the calming effects of watching spinning objects or the focus-enhancing benefits of repetitive eye movements. These behaviors are not merely distractions; they are vital tools for self-soothing and emotional regulation. For parents and caregivers, recognizing the nuances of visual stimming can empower them to create supportive environments that foster growth, understanding, and acceptance in their children's unique journeys.
By embracing the importance of visual stimming, we can better support our children. Let’s explore how these behaviors play a crucial role in their lives and discover ways to nurture their emotional well-being together.
What is Visual Stimming? An Overview
Visual self-stimulation, often referred to as visual stim, encompasses a range of repetitive sight-related activities that individuals, particularly those on the autism spectrum, engage in to soothe themselves or manage sensory input. These behaviors can take various forms, such as:
- Gazing at lights
- Observing spinning objects
- Flicking fingers in front of the eyes
Each of these actions serves important purposes, providing comfort in overwhelming situations or aiding in focus and concentration.
As we move into 2025, our understanding of sensory behaviors has deepened, with recent research highlighting their prevalence among autistic youth. Studies show that self-stimulatory behaviors are quite common, with a notable percentage of children using these actions as coping mechanisms. For example, a study indicated that all participants achieved a data quality rate of 65%, with variability ranging from 42% to 93%. This underscores the diverse experiences of individuals with autism.
The credibility of this research is bolstered by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from JSPS, affirming the significance of these findings.
Experts in the field stress the importance of recognizing sensory self-stimulation as a legitimate coping strategy. Laura NG, a Clinical Operations Manager, notes, "it is important to view sensory self-soothing as a genuine method to cope for those on the autism spectrum." This perspective is crucial for parents and caregivers, as it validates the experiences of their children and encourages supportive responses.
Real-life examples of visual stim activities highlight their positive impact on daily life. For instance, a child might find comfort in watching a spinning toy, which not only calms them but also aids in navigating their environment more effectively. Understanding these behaviors can lead to better strategies for managing challenging situations and fostering social skills development.
Moreover, it is essential to consider the broader challenges faced by individuals with autism, such as feeding difficulties. On March 5, 2025, insights were shared regarding feeding challenges in youths with autism, including implications for nutrition and effective family strategies. These challenges often intersect with sensory-seeking behaviors, as both are integral to the complex sensory experiences individuals with autism navigate.
Recent correlation analyses have also examined the relationship between observation ratios of predictable movements and parent-reported scores. Findings suggest that a higher observation ratio correlates with increased autistic traits and lower language comprehension, indicating a meaningful connection between attention patterns and developmental metrics. This link is particularly significant for understanding how sensory-seeking behaviors relate to overall development in young individuals with autism.
As we continue to explore sensory behaviors, it becomes clear that these actions are not merely distractions but essential components of how many individuals with autism interact with their surroundings. By fostering an understanding of visual stim and self-soothing behaviors, parents and caregivers can better support their children in navigating their unique sensory experiences.
Causes of Visual Stimming in Children with Autism
Visual stimming in individuals with autism often emerges from various triggers, such as sensory overload, anxiety, and the need for self-regulation. Research reveals that up to 40% of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may experience chromosomal, DNA, or mitochondrial-related anomalies, contributing to increased sensory sensitivities. For instance, a child might find comfort in fixating on the movement of a ceiling fan during moments of anxiety or overstimulation. This behavior serves as a vital coping mechanism, enabling them to navigate overwhelming sensory experiences.
Understanding these triggers is crucial for caregivers, as it allows them to provide tailored support. By recognizing the signs of sensory overload, caregivers can develop effective strategies to alleviate its impact. For example, creating a calm environment with reduced sensory input can significantly minimize instances of visual stimming.
Laura NG, Clinical Operations Manager, emphasizes, "Discover strategies for promoting neurodiversity in autism education. Learn how inclusive practices foster a supportive learning environment for all students." This statement underscores the importance of inclusive practices in educational settings, as highlighted in the case study titled 'Cultivating Neurodiversity in Autism Education.'
By promoting understanding and acceptance of neurodiversity, caregivers can help create an environment where young individuals feel safe and understood. This, in turn, enhances their ability to manage sensory challenges. ASD Media's commitment to fostering collaboration and development in the ABA therapy sector further supports this mission, empowering parents and professionals to devise effective strategies for their children.
Types of Visual Stimming: Recognizing the Signs
Visual stimming behaviors can manifest in a variety of ways, each reflecting the unique sensory needs of individuals with autism. For many children, the world is a canvas of sensory experiences, and understanding these behaviors is essential. Common examples include:
- Staring at lights or moving objects: Many children may become captivated by ceiling fans, spinning toys, or flickering lights, often finding comfort in the visual stimulation these elements provide.
- Repetitive eye movements: This can encompass a range of actions, such as rapid blinking, rolling, or darting of the eyes, which may serve as a self-soothing mechanism.
- Hand movements: Children might engage in actions like waving their fingers in front of their eyes or flicking them, which can help regulate their sensory input.
Recognizing these signs is crucial for caregivers, as it allows them to better understand and respond to their offspring's sensory needs. Addressing the root causes of visual stimming can significantly enhance a young person's independence and reduce anxiety. For instance, a case study titled "Therapeutic Approaches to Managing Visual Stim" highlights the effectiveness of individualized therapeutic plans, including Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), in addressing these behaviors.
The findings suggest that with professional support, young individuals can enhance their social skills and emotional regulation, leading to better overall functioning in daily life. As we look ahead to 2025, statistics indicate that visual stimming behaviors are increasingly recognized, with a growing emphasis on developing strategies to support young individuals in navigating their sensory experiences. Additionally, the use of ABA therapy toys has been shown to enhance development and promote learning through play, which is particularly beneficial for kids with autism. Furthermore, setting SMART goals can unlock the potential for functional communication, providing youngsters with the tools they need to express themselves effectively.
By understanding and acknowledging these actions, caregivers can create a more supportive environment that fosters growth and development. What strategies have you found helpful in supporting your child? Share your experiences and insights, as they may inspire others on a similar journey.
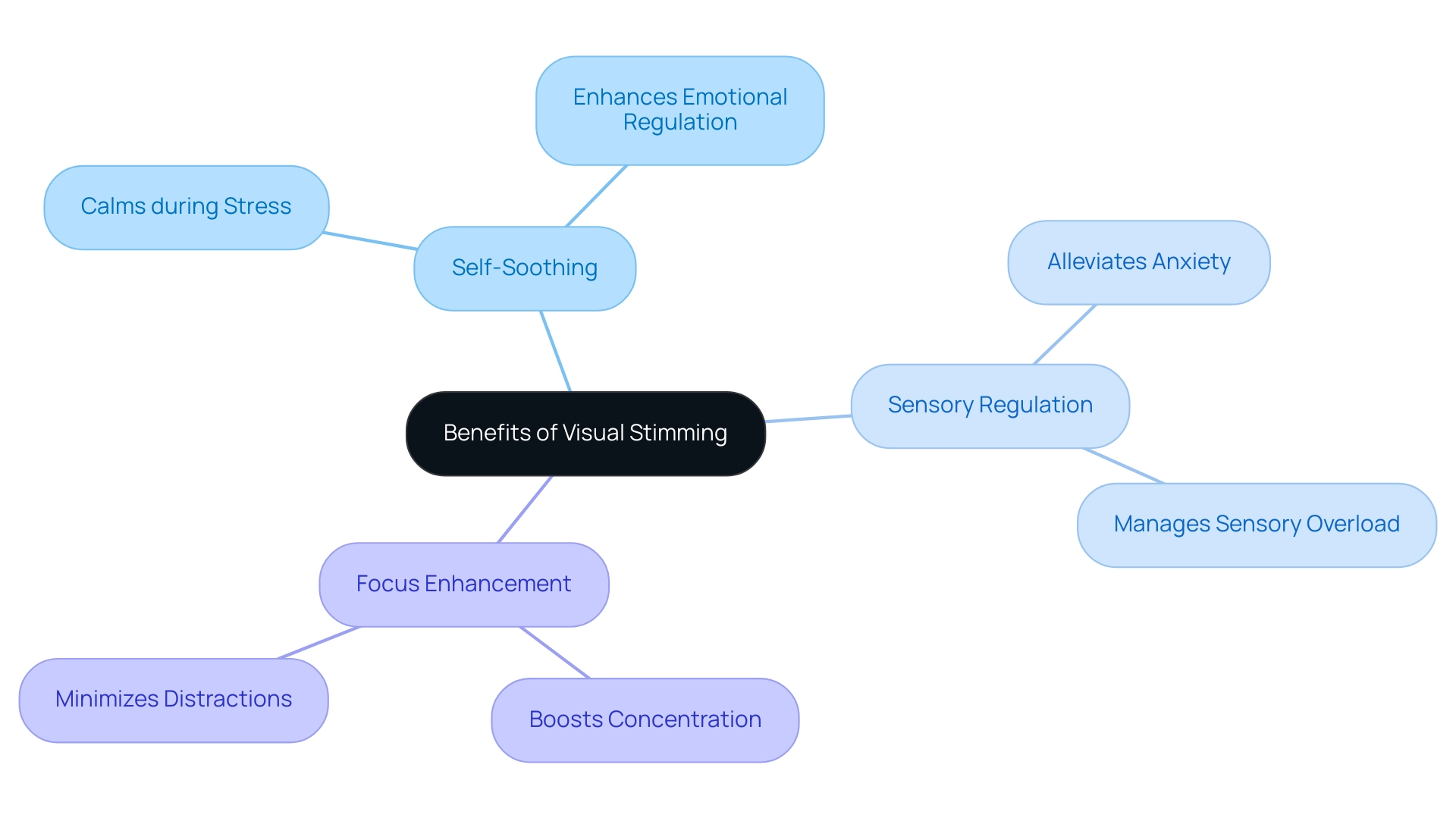
The Benefits of Visual Stimming: Understanding Its Role
Visual stimming offers a range of significant benefits for children with autism, which can be crucial for their development and well-being.
- Self-soothing: Engaging in visual stimming behaviors allows children to calm themselves during stressful situations. This self-regulation is vital, especially in environments that may feel overwhelming.
- Sensory regulation: These behaviors play a key role in managing sensory overload. By concentrating on familiar sensory cues, youngsters can navigate their environment more easily, alleviating anxiety and unease.
- Focus enhancement: For numerous youngsters, sensory repetition functions as a means to boost concentration. By providing a focal point, it helps minimize distractions, enabling them to engage more fully with tasks or activities.
Understanding the triggers and causes of sensory behaviors is crucial for creating effective support strategies. Recent statistics suggest that self-soothing actions, including visual stim, are common among autistic individuals, with studies demonstrating that these actions can significantly improve their quality of life. A 2025 study highlights the potential utility of predictable movement stimuli as a behavioral marker for early ASD screening, underscoring the importance of recognizing and understanding these behaviors early on.
Mikimasa Omori, the author of the study, stated, "This study’s results highlight the potential of predictable stimuli as an early screening tool, offering promise for improving early diagnosis and intervention for individuals at risk for ASD."
Real-world instances demonstrate how sensory self-stimulation can be advantageous. In a single case study, youngsters who engaged in sensory stimulation reported feeling more in control of their sensory experiences, leading to enhanced emotional regulation and social interactions. The case study titled 'Intervention Options' discusses how professional support can assist in managing sensory-seeking actions, focusing on behavioral therapy and the potential use of medications under professional supervision.
Occupational therapists emphasize that these self-soothing techniques can be instrumental in assisting youngsters navigate their sensory needs effectively.
Overall, sensory self-soothing not only helps in calming and sensory regulation but also incorporates visual stim to create an environment where young ones can flourish, emphasizing the necessity for supportive approaches that embrace these behaviors.
Challenges of Visual Stimming: What Parents Should Know
While visual stimulation can often be beneficial for sensory management and emotional expression, it also presents several challenges for individuals with autism and their caregivers. These challenges include:
- Distraction: Excessive visual stimming can sometimes impede learning and social interactions. For instance, children may become so engrossed in their self-soothing actions that they miss important visual cues in their environment, which can lead to difficulties in classroom settings or during social interactions. Recent studies indicate that a significant percentage of children with autism face attentional deficits, which may be exacerbated by distracting self-soothing behaviors that serve as visual stimulation. Alarmingly, 67.1% of mothers have reported experiencing symptoms of both depression and anxiety, highlighting the emotional burdens caregivers bear in managing these challenges.
- Safety Concerns: Certain repetitive behaviors may involve objects or actions that pose risks. For example, if a child engages in sensory behaviors with sharp or heavy objects, there is a potential for injury. Caregivers need to be vigilant in creating safe environments that allow for self-soothing behaviors while minimizing hazards.
- Social Stigma: Children who engage in visual stimulation might encounter misunderstanding or stigma from peers and adults, which can lead to feelings of isolation or anxiety. It is essential for caregivers to prepare for these situations by fostering empathy and understanding, both within themselves and in the broader community. By educating others about the nature of self-stimulatory behavior and its role in sensory processing, caregivers can help reduce stigma and promote acceptance. As Bilal Mansoor noted, "The analysis of facial expressions recently emerged as an objective method of measuring attention and participation levels of typical learners," underscoring the importance of understanding attentional dynamics in individuals with autism.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that includes professional evaluations to understand the context of visual stimulation behaviors and the development of coping strategies tailored to the individual's unique sensory needs. The case study titled "Understanding Visual Stim in Neurodiversity" emphasizes the necessity of professional assessment and advocates for creating sensory-friendly environments. Furthermore, ongoing research suggests further exploration into attention assessment methodologies in realistic classroom settings to gain a better understanding of attentional deficits in individuals with ASD.
Creating sensory-friendly spaces can be crucial in helping youth manage their self-soothing behaviors safely and effectively.
Effective Strategies for Managing Visual Stimming
To effectively manage sensory behaviors in youngsters, caregivers can implement several key strategies that foster understanding and support:
- Create a Calming Environment: Establish spaces that minimize distractions. Research indicates that sensory-friendly spaces with dim lighting and calming stimuli can significantly enhance comfort for individuals with autism. Keeping these areas tidy and reducing clutter contributes to overall wellness, creating a nurturing atmosphere.
- Introduce Visual Stim Tools: Providing youngsters with soothing sensory toys or tools can serve as positive alternatives to sight-related stimulation activities. These tools not only offer sensory input but also help children self-regulate their sensory needs and emotions, nurturing a sense of control and independence.
- Set Clear Boundaries: It’s crucial to create guidelines regarding when and where sensory behaviors are appropriate. This helps children understand the context of their actions, fostering self-awareness and social comprehension, which are vital for their development.
- Educate and Normalize: Supporting individuals who engage in sensory activities, especially in social settings, requires a compassionate approach. Informing peers and adults about these behaviors can help normalize them, reducing stigma and encouraging acceptance. It’s essential to avoid negative reinforcement, as it can further isolate those who engage in repetitive actions.
- Utilize ABA Therapy: Case studies have shown that targeted ABA interventions can effectively address repetitive actions linked to sensory stimulation. These interventions can lead to significant reductions in such behaviors, demonstrating their effectiveness. By focusing on specific behaviors, caregivers can witness improvements in social interactions and emotional control.
By applying these techniques, caregivers can cultivate a supportive environment that not only nurtures sensory behaviors but also empowers young individuals to thrive. Together, let’s create spaces where every child feels understood and valued.
Creating Supportive Environments for Visual Stimming
Creating a nurturing environment for children who rely on visual stimulation for self-soothing is essential for their comfort and development. Here are several strategies that can help:
- Minimizing sensory overload: Adjusting lighting and reducing noise can greatly enhance a child's sense of calm. Soft, natural lighting and tranquil spaces foster relaxation, allowing children to engage in self-soothing activities without feeling overwhelmed.
- Incorporating sensory-friendly elements: Adding soft textures, calming colors, and gentle sounds to a child's surroundings can significantly boost their comfort. For instance, plush rugs, muted color palettes, and soothing background music can create a supportive space that encourages exploration and self-soothing.
- Establishing routines: Consistent daily schedules provide the predictability that is crucial for individuals with autism. By setting clear routines, parents can help their children feel secure, reducing anxiety and the need for stimming behaviors. This structure not only supports emotional well-being but also provides visual stimulation that fosters independence as children learn to anticipate and navigate their daily activities. Task analysis in ABA therapy can further enhance this process by breaking down skills into small, manageable steps, making learning more accessible for children.
Research shows that access to information and connections with other families can offer vital support for those facing autism challenges. For example, case studies reveal that parents often feel overwhelmed by treatment options, yet those who connect with supportive communities report significant improvements in their children's daily lives. This underscores the importance of community support in navigating the complexities of autism treatment. Experts also emphasize the role of visual stimulation in creating sensory-friendly spaces. Tova Leibowitz, a BCBA and Clinical Director, highlights that crafting engaging and enjoyable environments during ABA sessions can greatly enhance the therapeutic experience for autistic children. By focusing on these elements, parents can cultivate spaces that not only support visual engagement but also promote overall well-being and development.
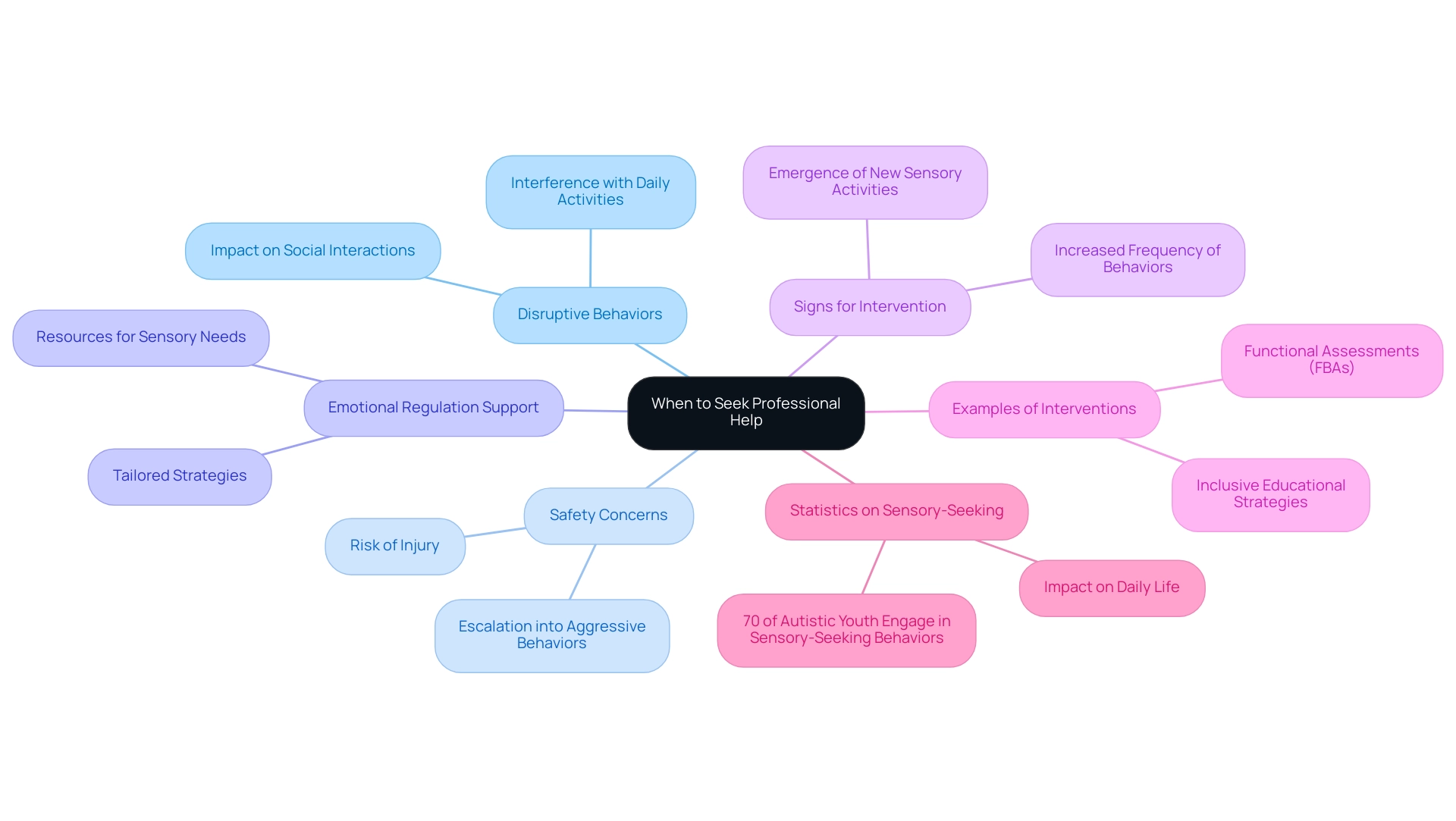
When to Seek Professional Help: Guidance for Parents
As a parent, it’s important to know when to seek professional help for your child’s visual stimming behaviors. Here are some key considerations:
-
Disruptive visual stimming behaviors: If your child’s stimming begins to interfere with daily activities or social interactions, it’s essential to reach out to a specialist. Disruptive self-soothing behaviors can hinder their ability to engage in learning and socialization, making professional guidance vital.
-
Safety concerns: Should your child’s self-stimulatory actions pose risks to themselves or others—such as causing injury or escalating into aggressive behaviors—professional intervention becomes crucial. Addressing these safety concerns promptly can prevent potential harm and create a supportive environment.
-
Support for emotional regulation: Professionals can offer tailored strategies and resources to help young individuals manage their sensory needs effectively. This support is particularly important, especially considering a meta-analysis published in 2024 that highlighted the variability in cognitive profiles among individuals with autism and ADHD. It underscores the necessity for a holistic, family-centered approach in evaluations.
-
Signs that sensory stimulation activities require specialist intervention: Look for indicators such as increased frequency, intensity, or the emergence of new sensory activities. Recognizing these signs can empower you to take proactive steps in your child’s development.
-
Examples of professional interventions for disruptive visual stim: Interventions may include functional assessments (FBAs) to identify underlying triggers and develop effective strategies. As highlighted by the U.S. Department of Education, "By using FBAs, educators can gain a better understanding of a student’s needs by identifying factors that contribute to the occurrence, allowing them to create more inclusive, developmental, and educational experiences, without having to resort to removals from the classroom." These assessments assist educators and parents in understanding a young person's needs, fostering more inclusive and supportive experiences.
-
Statistics on disruptive sensory-seeking behaviors in autistic youth: Recent data shows that approximately 70% of individuals on the autism spectrum engage in sensory-seeking behaviors, with many exhibiting actions that can disrupt their daily lives. Understanding these statistics can help you assess the seriousness of your child’s repetitive behaviors and the potential need for professional assistance.
In summary, recognizing when to seek professional help for visual stimming is crucial for ensuring the well-being and development of young individuals on the autism spectrum. By being attentive to the signs and understanding the available interventions, you can better support your child’s journey.
Conclusion
Visual stimming is a vital part of the lives of children on the autism spectrum, serving as a crucial coping mechanism for navigating sensory experiences. By engaging in repetitive visual activities—like watching spinning objects or focusing on lights—children can self-soothe, manage anxiety, and enhance their concentration. Understanding the nuances of visual stimming is essential for parents and caregivers, as it empowers them to create supportive environments that acknowledge and validate these behaviors.
Exploring visual stimming reveals its multifaceted nature, including its triggers, benefits, and potential challenges. While these behaviors can provide comfort and aid emotional regulation, they may also lead to distractions or safety concerns. Recognizing when these behaviors become disruptive is crucial, allowing parents to seek professional guidance and develop tailored strategies to support their children effectively.
Fostering an understanding of visual stimming emphasizes creating sensory-friendly spaces, establishing routines, and utilizing therapeutic interventions as key strategies for enhancing the well-being of children with autism. By prioritizing these approaches, caregivers can help children thrive, embracing their unique sensory needs while promoting growth and acceptance. Ultimately, acknowledging the significance of visual stimming enriches the lives of children on the spectrum and cultivates a more inclusive and empathetic community. Together, let’s embrace these unique experiences and support one another in this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is visual self-stimulation, or visual stim?
Visual self-stimulation, often referred to as visual stim, includes a range of repetitive sight-related activities that individuals, particularly those on the autism spectrum, engage in to soothe themselves or manage sensory input.
What are some examples of visual stim activities?
Examples of visual stim activities include gazing at lights, observing spinning objects, and flicking fingers in front of the eyes. These actions provide comfort in overwhelming situations or assist in focus and concentration.
How prevalent are self-stimulatory behaviors among autistic youth?
Recent research indicates that self-stimulatory behaviors are common among autistic youth, with many using these actions as coping mechanisms. A study showed that all participants achieved a data quality rate of 65%, with variability ranging from 42% to 93%.
Why is it important to recognize sensory self-stimulation as a coping strategy?
Experts stress that recognizing sensory self-stimulation as a legitimate coping strategy validates the experiences of individuals on the autism spectrum, encouraging supportive responses from parents and caregivers.
How can visual stim activities positively impact daily life?
Visual stim activities, such as watching a spinning toy, can provide comfort and help individuals navigate their environment more effectively, which can lead to better management of challenging situations and foster social skills development.
What are some broader challenges faced by individuals with autism?
Individuals with autism often face challenges such as feeding difficulties, which can intersect with sensory-seeking behaviors. Addressing these challenges is crucial for effective nutrition and family strategies.
What insights have been gained regarding the relationship between observation ratios and autistic traits?
Recent correlation analyses suggest that a higher observation ratio of predictable movements correlates with increased autistic traits and lower language comprehension, indicating a meaningful connection between attention patterns and developmental metrics.
How can caregivers support individuals with autism in managing sensory experiences?
Caregivers can support individuals by recognizing signs of sensory overload and creating a calm environment with reduced sensory input, which can help minimize instances of visual stimming.
What is the importance of promoting neurodiversity in autism education?
Promoting neurodiversity in autism education fosters understanding and acceptance, creating a supportive learning environment that enhances individuals' ability to manage sensory challenges.




