Overview
This article delves into the understanding of dyspraxia and dyslexia, highlighting the crucial role of awareness and support for parents and educators. It brings to light the prevalence of these learning disabilities and their significant impact on children's academic and social development. By sharing effective strategies for intervention, it underscores the importance of collaborative approaches that can foster a nurturing and supportive educational environment. Together, we can create a space where every child has the opportunity to thrive.
Introduction
In the landscape of education, understanding learning disabilities such as dyslexia and dyspraxia is more crucial than ever. These conditions affect millions of children worldwide and present unique challenges that can significantly impact academic performance and self-esteem.
Dyslexia, which is characterized by difficulties in reading and writing, and dyspraxia, which hinders motor skills and coordination, often co-occur. This complicates the educational journey for those affected.
As awareness grows, so does the need for effective strategies and collaborative approaches among parents, educators, and specialists to foster an inclusive learning environment.
This article delves into the definitions, symptoms, impacts, and support strategies for children with these learning disabilities. It aims to equip readers with the knowledge to advocate for and empower those facing these challenges.
Defining Dyslexia and Dyspraxia: Key Concepts and Terminology
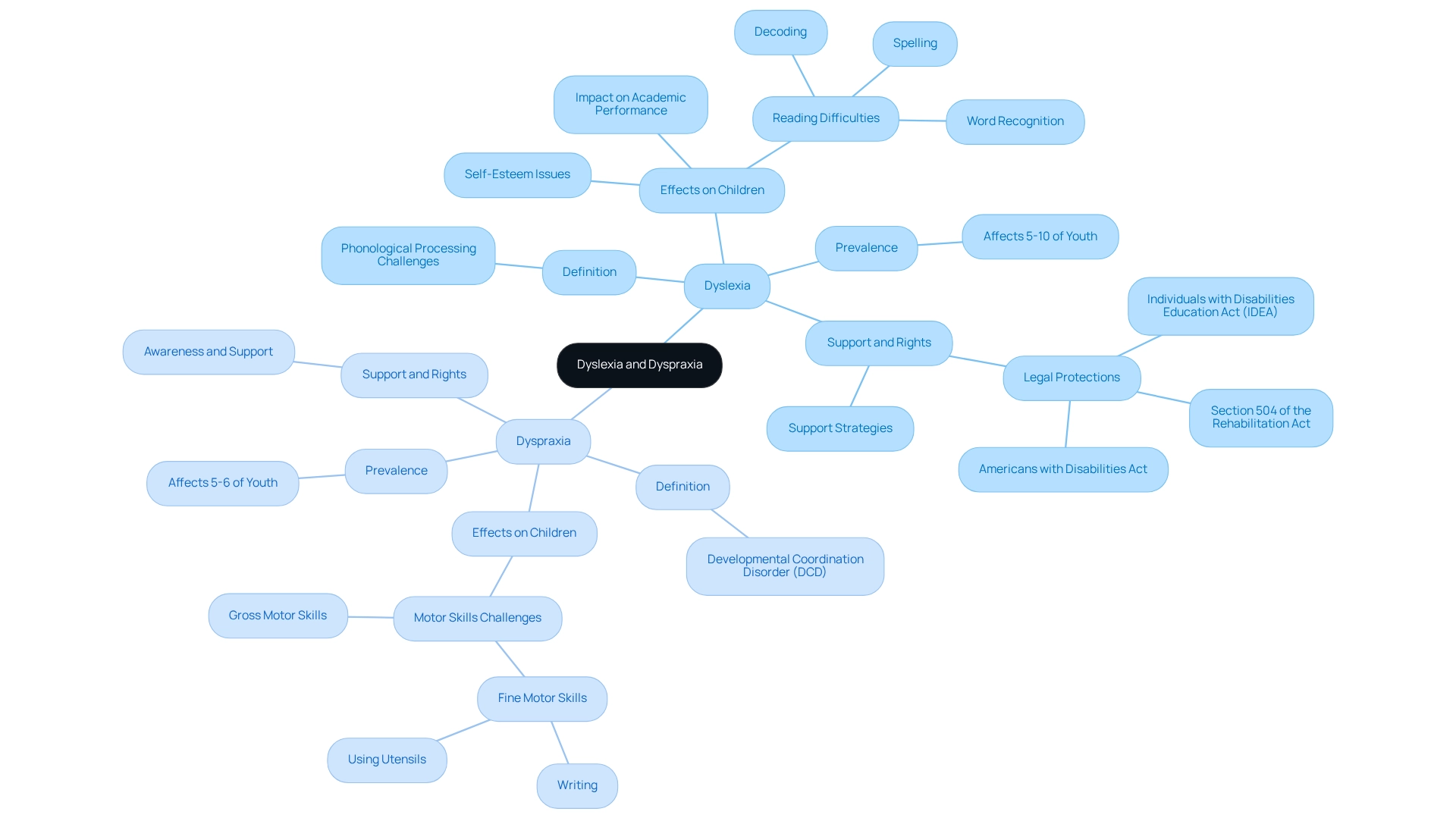
Dyslexia, often linked with dyspraxia, is a significant educational disability that profoundly affects reading, writing, and spelling, primarily due to challenges in phonological processing. Children with dyslexia frequently face reading difficulties, such as word recognition, decoding, and spelling, which can impact their academic performance and self-esteem. It's estimated that dyslexia affects around 5-10% of youth, making it one of the most common learning disabilities across various backgrounds and intellectual levels.
Additionally, this condition, known as Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), is associated with dyspraxia and affects the development of motor skills. This can lead to challenges in coordination and movement planning. For instance, children may struggle with fine motor tasks like writing or using utensils, as well as gross motor skills, which can hinder overall physical coordination. Research shows that dyspraxia impacts approximately 5-6% of young individuals, highlighting the importance of awareness and support in educational settings.
Understanding these definitions is crucial for parents and educators, as it allows them to identify and provide the right support for children facing these challenges. Recent research, including a meta-analysis titled 'Meta-Analysis of Listening and Reading Comprehension,' reveals a significant connection between listening and reading comprehension, suggesting that discrepancies may indicate reading difficulties. Such insights can guide identification practices and intervention strategies, ultimately fostering a supportive learning environment.
Moreover, the rights of individuals with reading difficulties and dyspraxia are protected under various laws, including the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, and the Americans with Disabilities Act. These regulations ensure that children receive the necessary services and accommodations to thrive in educational settings, protecting them from discrimination and promoting equitable access to learning opportunities. As Steven Zauderer noted, "Individuals with reading difficulties have a 60% higher likelihood of being able to connect ideas effectively and utilize alternative approaches to address challenges."
By fostering a deeper understanding of reading difficulties and coordination challenges, including dyspraxia, parents and educators can more effectively support the needs of affected youth. This nurturing approach can significantly enhance their educational experiences and outcomes, creating a brighter future for them.
Recognizing the Symptoms: How to Identify Dyslexia and Dyspraxia
Dyspraxia dyslexia manifests through a variety of symptoms that can profoundly affect a young person's educational journey. Common signs include difficulty reading aloud, a slower reading pace, challenges with spelling, and struggles in understanding written material. These challenges arise from the brain's processing of linguistic codes and symbols, making it essential for educators and parents to recognize these signs early on.
Importantly, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) protects individuals with dyslexia from discrimination, ensuring that affected youth receive the necessary support they need.
In a similar vein, dyspraxia dyslexia presents its own unique challenges. Symptoms often encompass clumsiness, difficulties with fine motor skills—such as handwriting—and trouble with coordination tasks, like participating in sports. Swiftly recognizing the symptoms of dyspraxia dyslexia is vital, as it allows for timely intervention and support strategies that can greatly enhance a young person's learning experience.
Statistics reveal that approximately 5-10% of children are affected by dyslexia, with many exhibiting symptoms by the time they reach school age. Regarding dyspraxia, research suggests that around 5-6% of children may face significant challenges related to coordination and motor skills. Identifying symptoms of dyspraxia dyslexia in educational settings not only aids in providing the necessary support but also empowers young individuals to advocate for their needs, fostering a more inclusive environment.
ASD Media is dedicated to nurturing a community that promotes collaboration and growth within the ABA therapy industry, aligning with the mission of empowering parents and professionals to better understand learning disabilities. Real-life examples underscore the importance of early identification. For instance, a case study titled "Empowering Autistic Youth: The Role of Self-Advocacy and ABA Therapy" highlights how individuals who learn to recognize their challenges gain confidence in seeking assistance, resulting in improved outcomes in both personal and social realms.
By understanding and addressing the signs of reading difficulties and dyspraxia dyslexia, parents and educators can build a supportive framework that encourages growth and development.
The Impact of Dyslexia and Dyspraxia on Learning and Development
Dyslexia presents significant challenges in literacy, deeply impacting a young person's confidence and academic performance. Many studies indicate that individuals with reading difficulties often experience a notable gap between their listening and reading comprehension skills. This gap serves as a crucial indicator for recognizing the condition, highlighting the need for early intervention and personalized support strategies to improve learning outcomes.
Importantly, findings suggest that this discrepancy could be a valuable tool for identifying reading difficulties at the population level.
Similarly, children with motor coordination challenges face hurdles that can limit their participation in physical activities, affecting their social interactions. The implications of motor coordination difficulties extend beyond physical engagement; they can create barriers in communication and teamwork with peers, complicating a young person's social development. Statistics show that dyspraxia dyslexia can significantly influence a child's academic performance, with educators noting that these students often require additional support to thrive in a classroom setting.
Both learning difficulties and dyspraxia dyslexia can lead to feelings of frustration and a decline in self-esteem, making it vital for parents and teachers to adopt supportive strategies. Raising awareness about dyspraxia dyslexia and implementing diverse interventions are crucial steps in enhancing outcomes for affected children. For instance, a meta-analysis exploring the link between listening and reading comprehension reveals that addressing these gaps can foster more effective educational approaches.
As Bethany Beal highlights, one effective way to reduce measurement error is by employing hybrid models that integrate various indicators or criteria, which can refine assessment strategies for reading difficulties. Additionally, the Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) is conducted in 24,500 schools across 5,800 districts in the United States, underscoring the prevalence of assessments related to reading challenges. By nurturing an inclusive environment and providing essential resources, parents and educators can empower young learners to overcome the obstacles posed by these learning disabilities.
Exploring the Connection: Dyslexia and Dyspraxia Co-Occurrence
Research shows that many children facing reading difficulties, such as dyspraxia and dyslexia, also struggle with coordination challenges. Conversely, numerous children with coordination issues exhibit signs of reading difficulties. This overlap can complicate both diagnosis and intervention, as the symptoms of dyspraxia may obscure or amplify the challenges associated with dyslexia. For instance, studies reveal that concordance rates for dyslexia are significantly higher among monozygotic (MZ) twins, at about 60-80%, compared to dizygotic (DZ) twins, which range from 20-30%. This suggests a genetic component that may also affect the expression of dyspraxia.
Furthermore, recent findings highlight that nearly half of all youth with Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) encounter writing challenges, with dysgraphia often emerging as a related concern. This underscores the necessity of recognizing and addressing the overlapping symptoms of dyspraxia and dyslexia within educational environments.
Case studies suggest that educational programs focusing on the social context of DCD, rather than solely on medical models, can significantly enhance outcomes for affected youth. Early identification and customized educational support have been proven to improve coordination and motor skills, fostering greater self-esteem and social interactions.
Expert insights indicate that the relationship between reading difficulties, such as dyspraxia and dyslexia, and coordination disorders often stems from shared etiologies, resulting in overlapping symptoms that demand a nuanced approach to diagnosis and intervention. As noted by Lundström et al., "the existence of overlapping symptoms is often due to partly shared etiologies." By understanding this intricate relationship, parents and educators can develop more effective, comprehensive support strategies tailored to the unique needs of young individuals facing these challenges.
Effective Strategies for Supporting Children with Dyslexia and Dyspraxia
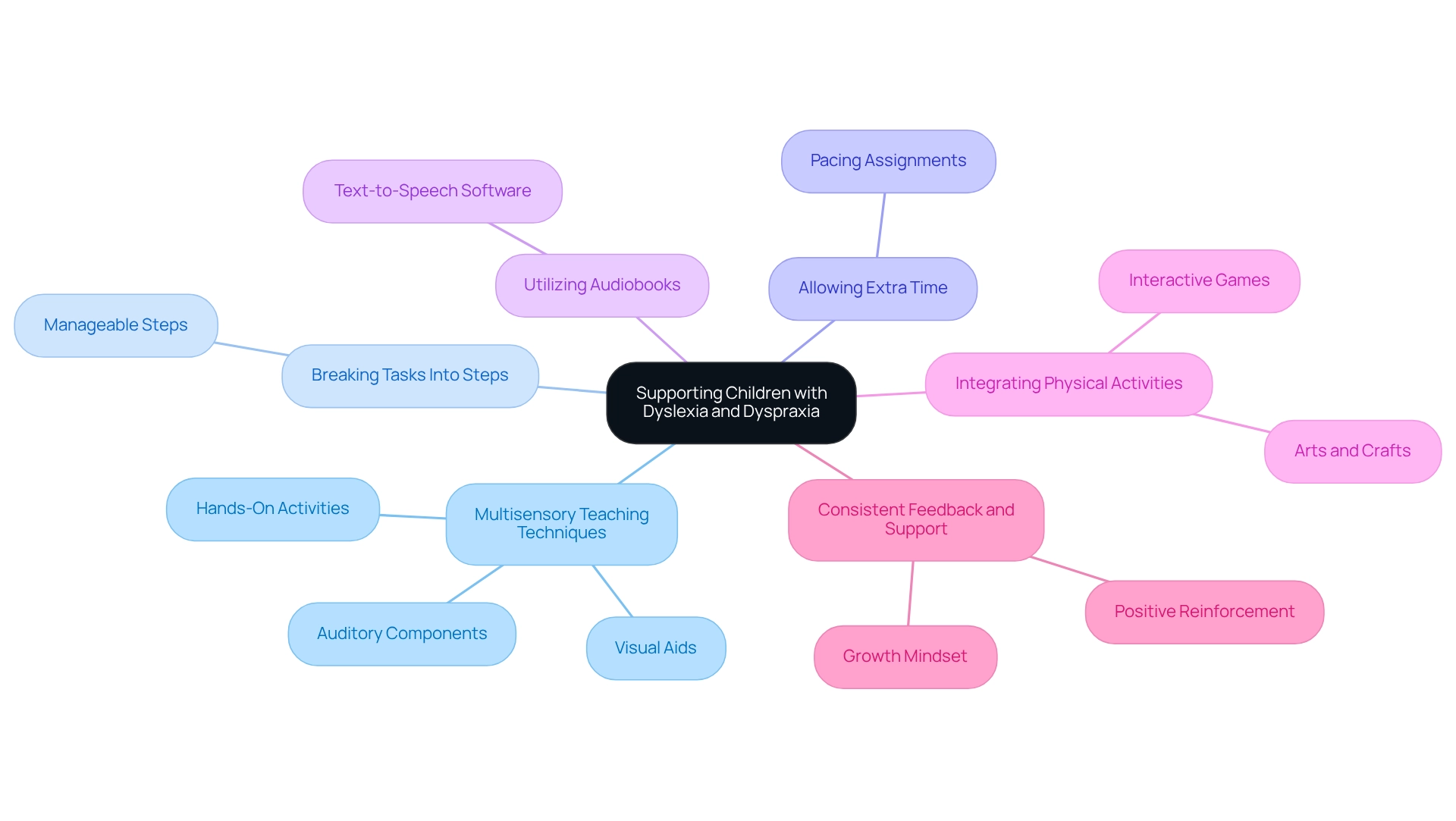
To effectively assist children facing reading difficulties and dyspraxia, a variety of nurturing strategies can be employed. Multisensory teaching techniques stand out as particularly effective, engaging multiple senses to deepen understanding. Research shows that these approaches significantly enhance learning outcomes for students struggling with reading, particularly in areas like reading and spelling.
For instance, incorporating visual aids, hands-on activities, and auditory components can transform the learning experience for young individuals grappling with reading challenges. However, it’s crucial to recognize that the success of these methods can vary depending on how faithfully they are implemented, a factor that has often been inadequately reported in studies, raising concerns about their overall quality.
Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps is another vital strategy. This approach not only aids young learners with reading difficulties in grasping complex tasks but also supports those with dyspraxia in managing their physical coordination challenges.
Allowing extra time for assignments empowers students to absorb information at their own pace, alleviating anxiety and fostering a more supportive educational environment.
For children with dyslexia, utilizing audiobooks and text-to-speech software can significantly enhance reading comprehension. These tools allow students to engage with texts in ways that align with their learning preferences, making literature more accessible. Similarly, for those facing coordination challenges, integrating physical activities that improve coordination and fine motor skills—such as arts and crafts or interactive games—can be beneficial in developing essential abilities.
Consistent feedback and support play a crucial role in nurturing confidence and motivation. Positive reinforcement helps students recognize their progress and fosters a growth mindset, which is essential for overcoming educational challenges associated with disabilities. By implementing these strategies, parents and educators can cultivate a supportive learning atmosphere that empowers individuals with reading and coordination difficulties to flourish.
As Dr. Jack Fletcher pointed out, the ongoing discussion regarding the necessity of multisensory instruction underscores the importance of further investigation into how these methods are applied and their true benefits for students with word learning and reading difficulties. Current research does not definitively establish that multisensory instruction significantly enhances reading outcomes, indicating a pressing need for additional studies to clarify its effectiveness in interventions for students with word-related challenges.
Collaborative Approaches: Working Together for Better Outcomes
Cooperation among parents, educators, and specialists is essential for effectively supporting children with dyspraxia and dyslexia. Regular meetings to discuss each child's progress, share insights, and adjust intervention strategies can significantly improve outcomes. A team approach not only fosters a deep understanding of each individual's unique needs but also creates a supportive network that nurtures their growth and development.
Research shows that structured collaboration can enhance student engagement and achievement. For example, a significant 37.5% of teachers in a recent study reported the positive effects of collaborative efforts on their students, underscoring the power of teamwork in educational settings. Additionally, specialists emphasize that pediatricians and educators are vital in the early detection and intervention of learning disabilities, particularly dyspraxia and dyslexia, especially when they work together to monitor at-risk children.
As Nadine Gaab, PhD, wisely notes, "Pediatricians can contribute to a collaborative effort to screen for youngsters at risk by capitalizing on their unique role in a youth’s early developmental trajectory and by taking advantage of their network of health and educational resources."
Case studies, such as those examining family history as a predictor of dyspraxia and dyslexia risk, highlight the importance of early intervention strategies informed by collaborative insights. Understanding a child's familial risk can promote closer monitoring and tailored support, ultimately aiding literacy development.
Moreover, there is an urgent need for more structured opportunities for collaboration and professional development training for teachers working with students with special needs. Real-life examples of successful parent-teacher collaboration showcase the potential for teamwork to enhance intervention effectiveness. By leveraging the strengths of each participant in the educational process, families and educators can create a more inclusive environment that addresses the challenges faced by individuals with learning disabilities, including dyspraxia and dyslexia.
Experts agree that nurturing these cooperative connections is crucial for unlocking the full potential of young individuals with learning difficulties. Together, we can make a difference in their educational journey.
Resources and Tools: Empowering Parents and Educators
An abundance of resources is available to empower parents and educators in supporting individuals with dyspraxia and dyslexia. Organizations such as the International Dyslexia Association and the Dyspraxia Foundation offer comprehensive information, toolkits, and access to invaluable support networks that can help navigate the challenges associated with these conditions. With dyslexia affecting around 10-15% of the population, raising awareness and providing support is crucial.
Educational apps like 'Ghotit' and 'Voice Dream Reader' present interactive platforms designed to assist dyslexic learners in enhancing their reading and writing skills through engaging, tailored activities.
Beyond digital tools, workshops and training sessions play a vital role in equipping parents and educators with effective strategies to support children. These sessions often delve into best practices in teaching techniques and share insights from the latest studies on learning difficulties, including dyspraxia and dyslexia. Moreover, expert recommendations highlight the importance of early intervention. As Yitz Diena noted, "While there is no cure for dyslexia, early intervention and support can help people with dyslexia succeed in school, work, and life."
Prompt assistance can significantly improve educational outcomes for young individuals facing these challenges.
Real-world examples, such as the use of weighted blankets, have shown promising results in alleviating anxiety and enhancing concentration among individuals with autism. This approach can also benefit those with dyspraxia and dyslexia by fostering a more supportive educational environment. By leveraging these resources and tools, parents and educators can create a nurturing atmosphere that promotes growth and learning for children with these learning disabilities, while also understanding and supporting individuals with autism throughout their lives.
Conclusion
Dyslexia and dyspraxia pose significant challenges for millions of children, deeply affecting their academic performance and self-esteem. It is essential for parents and educators to understand these learning disabilities, as early identification and tailored support can profoundly impact a child's educational journey. This article has outlined the definitions, symptoms, and impacts of both dyslexia and dyspraxia, highlighting the importance of recognizing their co-occurrence and the complexities it introduces in diagnosis and intervention.
Effective strategies, such as:
- multisensory teaching methods
- breaking tasks into manageable steps
- fostering collaboration among parents, teachers, and specialists
can create a nurturing learning environment. By employing these approaches, children can thrive despite their challenges, building confidence and motivation along the way. The role of resources and tools further empowers parents and educators to advocate for their children, ensuring they receive the necessary support and accommodations in educational settings.
Ultimately, fostering awareness, understanding, and proactive intervention for children with dyslexia and dyspraxia is vital. By working together, families and educators can help these children unlock their full potential, transforming their educational experiences and paving the way for future success. Now is the time to prioritize inclusivity and empower those facing learning disabilities, ensuring that every child has the opportunity to flourish.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dyslexia and how does it affect children?
Dyslexia is a significant educational disability that impacts reading, writing, and spelling due to challenges in phonological processing. Children with dyslexia often experience difficulties with word recognition, decoding, and spelling, which can negatively affect their academic performance and self-esteem. It is estimated to affect around 5-10% of youth.
What is dyspraxia and how is it related to dyslexia?
Dyspraxia, also known as Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), affects the development of motor skills and is often linked with dyslexia. Children with dyspraxia may struggle with coordination and movement planning, impacting both fine motor tasks (like writing) and gross motor skills. Approximately 5-6% of young individuals are affected by dyspraxia.
Why is it important for parents and educators to understand dyslexia and dyspraxia?
Understanding dyslexia and dyspraxia is crucial for parents and educators as it helps them identify the challenges faced by affected children and provide appropriate support. Early recognition can lead to effective intervention strategies that enhance educational experiences and outcomes.
What research connects listening and reading comprehension to dyslexia?
Recent research, including a meta-analysis titled 'Meta-Analysis of Listening and Reading Comprehension,' indicates a significant connection between listening and reading comprehension. Discrepancies in these areas may signal reading difficulties, guiding identification practices and intervention strategies.
What legal protections exist for individuals with dyslexia and dyspraxia?
Individuals with dyslexia and dyspraxia are protected under various laws, including the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). These laws ensure that children receive necessary services and accommodations to support their educational needs.
What are common symptoms of dyslexia in children?
Common symptoms of dyslexia include difficulty reading aloud, a slower reading pace, challenges with spelling, and struggles with understanding written material. These symptoms arise from difficulties in processing linguistic codes and symbols.
What are the symptoms of dyspraxia dyslexia?
Symptoms of dyspraxia dyslexia include clumsiness, difficulties with fine motor skills (such as handwriting), and trouble with coordination tasks (like participating in sports). Early recognition of these symptoms is vital for timely intervention and support.
How can understanding reading difficulties and dyspraxia dyslexia empower young individuals?
By recognizing their challenges, young individuals can gain confidence in seeking assistance, which can lead to improved outcomes in both personal and social realms. This empowerment fosters a more inclusive environment and helps them advocate for their needs.




