Overview
Supporting children with dyspraxia and dysgraphia can feel overwhelming, but tailored interventions can make a significant difference. Encouraging physical activity, utilizing assistive technology, and implementing visual aids are effective strategies that enhance their motor skills and writing abilities. It's crucial to recognize the importance of early intervention and customized support, as these approaches address the unique challenges these children face. By fostering their independence and confidence, we can help them navigate daily tasks and excel in their academic pursuits.
As parents, you may often wonder how to best support your child. Imagine a world where your child feels empowered to express themselves through writing or confidently engages in physical activities. This vision can become a reality with the right resources and support. Sharing personal experiences, whether through comments or newsletters, can create a community of understanding and encouragement.
Take action today by exploring specific resources that align with your child's needs. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Together, we can foster an environment where children with dyspraxia and dysgraphia thrive, gaining the confidence they need to succeed in every aspect of their lives.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of developmental challenges like dyspraxia and dysgraphia can feel overwhelming for both children and their families. Dyspraxia, a neurological condition that impacts motor skills, and dysgraphia, a specific learning disability affecting writing abilities, introduce unique hurdles that can obstruct academic success and daily life.
As awareness of these conditions increases, so does the need for effective strategies and interventions that can empower affected children. By exploring the symptoms, challenges, and tailored support mechanisms available, parents and educators can create an environment that nurtures independence, confidence, and academic achievement.
This article delves into the intricacies of dyspraxia and dysgraphia, offering insights and practical advice to support children as they navigate their educational journeys.
Define Dyspraxia and Dysgraphia
Dyspraxia and dysgraphia, clinically known as Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), are neurological conditions that profoundly affect motor skill development, leading to challenges with coordination and movement. For children grappling with dyspraxia and dysgraphia, everyday tasks—like tying shoelaces, riding a bike, or participating in sports—can feel particularly daunting due to their difficulties with motor planning and execution. The prevalence of DCD is significant, underscoring the necessity for interprofessional strategies aimed at ensuring the best educational outcomes for these children.
In contrast, dysgraphia is a specific learning disability that primarily impacts writing skills, similar to how dyspraxia and dysgraphia affect motor skills. This condition often manifests as struggles with handwriting, spelling, and organizing thoughts on paper. Children with dyspraxia and dysgraphia may find even basic tasks, such as holding a pencil, forming letters, or keeping a straight line while writing, to be challenging. The challenges posed by dyspraxia and dysgraphia can greatly affect their academic performance and self-esteem, which highlights the critical importance of early intervention and tailored support strategies.
Recent research reveals that individuals with a birth weight of less than 750 grams face an increased risk for perceived motor difficulties, further emphasizing the need for targeted interventions. For example, task-oriented approaches in DCD therapy have proven effective in enhancing independence in daily activities, especially when they are goal-oriented and actively involve the child. Such interventions can lead to improved functionality and greater confidence in managing everyday tasks.
As we approach 2025, understanding the definitions and signs of motor coordination disorders, specifically dyspraxia and dysgraphia, remains essential. Symptoms of dyspraxia and dysgraphia may include clumsiness, difficulty with fine motor tasks, and challenges in spatial awareness. Meanwhile, symptoms of dysgraphia and dyspraxia often appear as inconsistent handwriting, spelling difficulties, and trouble organizing written work. By recognizing these signs of dyspraxia and dysgraphia and implementing effective strategies, parents and educators can better support youth facing these challenges.
Moreover, near-infrared spectroscopy has emerged as a valuable method for exploring cortical activity during fine motor tasks in youth with DCD, offering insights into the neurological foundations of these conditions. As noted by the authors, "The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors." This highlights the ongoing research initiatives focused on understanding and addressing the complexities of both dyspraxia and dysgraphia. By prioritizing early intervention and customized assistance, we can create a more inclusive environment for young individuals facing these difficulties.
Identify Challenges Associated with Dyspraxia and Dysgraphia
Children facing motor coordination difficulties, including dyspraxia and dysgraphia, navigate a landscape filled with challenges that can significantly impact their daily lives and academic performance. These hurdles often include:
- Struggles with both fine and gross motor skills, making everyday tasks like writing, buttoning shirts, or participating in sports particularly tough.
- Limited spatial awareness, which can lead to clumsiness and difficulties in moving through their environment, potentially causing social isolation.
- Challenges with organization and planning, making it hard for them to manage schoolwork and meet assignment deadlines.
On the other hand, children with dyspraxia and dysgraphia face unique obstacles that can impede their educational journey, such as:
- Handwriting that is inconsistent and often illegible, posing challenges for teachers and peers trying to read their work.
- Difficulties with spelling and grammar, which can result in feelings of frustration and anxiety during writing tasks, ultimately affecting their confidence.
- Trouble organizing thoughts on paper, complicating their ability to express ideas clearly and effectively complete assignments.
Research indicates that approximately 2% to 7% of children are affected by auditory processing disorders, which share similarities with the difficulties encountered by those with dyspraxia and dysgraphia. This underscores the urgent need for targeted interventions within academic settings, as these conditions can significantly disrupt essential skills such as reading, writing, and mathematics.
As Steven Zauderer, CEO of CrossRiverTherapy, insightfully notes, 'Understanding the specific challenges faced by children with learning disabilities is crucial for developing effective support strategies.' These challenges underscore the importance of implementing focused interventions and support strategies in educational environments, ensuring that individuals with dyspraxia and dysgraphia receive the assistance they need to thrive.
Implement Effective Support Strategies for Your Child
Supporting a young person with dyspraxia and dysgraphia can feel daunting, but with the right approach, you can make a significant difference.
- Encourage Physical Activity: Involve your child in activities that enhance motor skills, such as swimming, dancing, or martial arts. Research shows that structured physical activities can greatly improve motor performance and social abilities in young individuals. A notable meta-analysis of 29 studies revealed that youth engaged in structured activities—like exergaming, aquatic exercises, and horseback riding—demonstrated considerable gains in social skills and motor performance. This support is crucial, especially since self-efficacy in youth with Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD) tends to be lower than their peers, highlighting the need for tailored interventions.
- Use Visual Aids: Implement visual schedules and step-by-step instructions to help them navigate daily tasks more easily.
- Practice Fine Motor Skills: Engage your child in fun activities like playdough, threading beads, or using scissors to strengthen hand muscles and improve dexterity, particularly for children with dyspraxia and dysgraphia, where supportive strategies can be useful.
- Utilize Assistive Technology: Encourage the use of typing or speech-to-text software to ease the challenges of handwriting, enhancing their writing experience.
- Modify Writing Tasks: Allow alternative forms of expression, such as drawing or using graphic organizers, to help them organize their thoughts without the stress of traditional writing. This is particularly important, as youngsters with learning disabilities are 31% more likely to face bullying compared to their peers without disabilities, underscoring the need to cultivate social skills through diverse methods of expression.
- Provide Handwriting Support: Use specialized grips or slant boards to improve writing posture and control, making the writing process more manageable and less frustrating. Additionally, aerobic training has been shown to enhance quality of life and reduce anxiety levels, further supporting the emotional well-being of young individuals as they navigate their learning challenges.
Access Resources and Tools for Ongoing Support
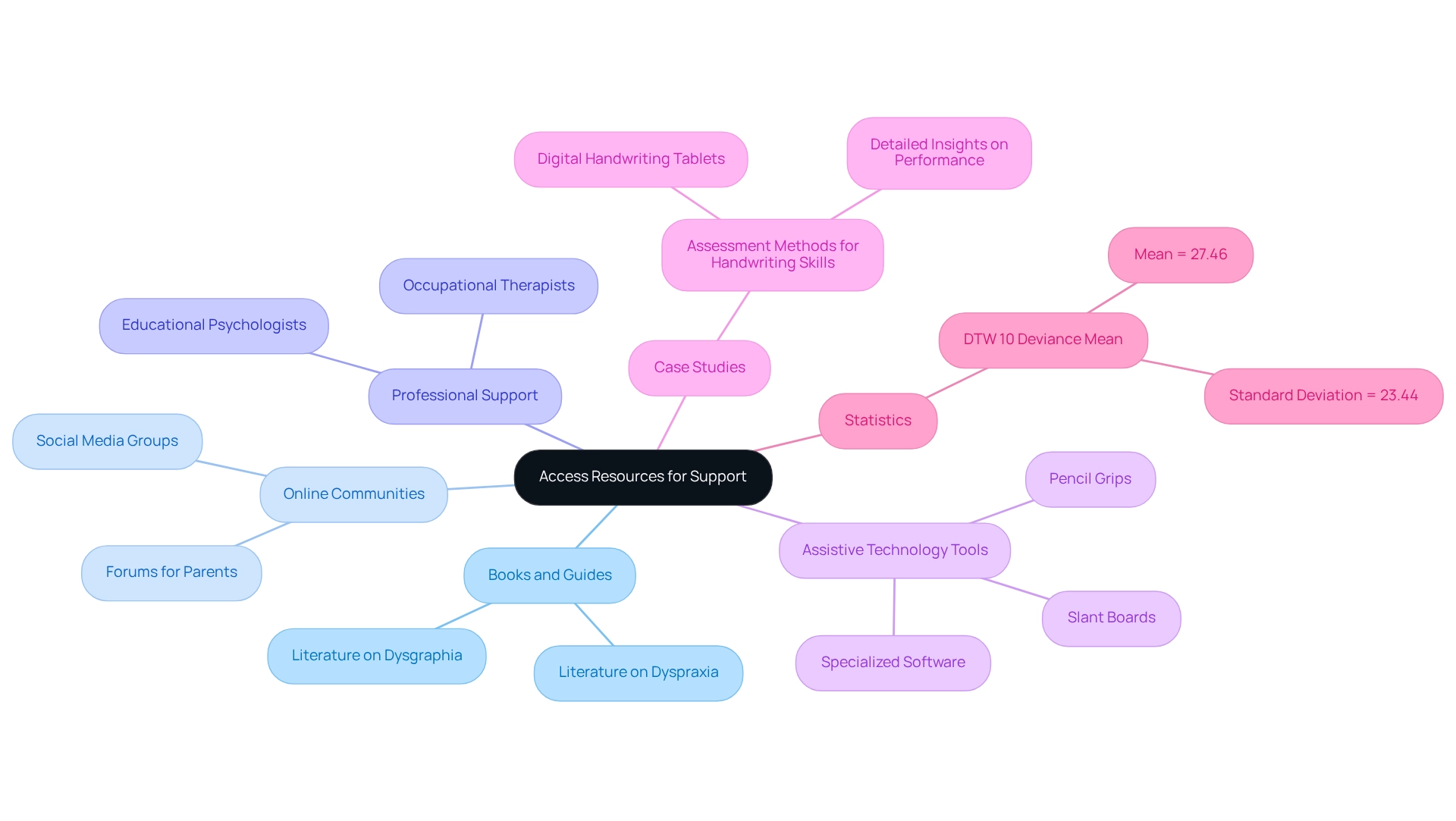
Accessing the right resources is essential for supporting children with motor coordination and writing difficulties. As a parent, it’s natural to seek out valuable tools and strategies that can make a difference in your child's life.
Books and guides should include literature specifically addressing dyspraxia and dysgraphia. These resources offer practical insights and strategies tailored for both parents and educators, helping you navigate the challenges ahead.
- Online Communities: Engaging with forums and social media groups dedicated to these conditions can be incredibly beneficial. These platforms provide a space for parents to share their experiences, exchange advice, and foster a sense of community.
Professional support from occupational therapists or educational psychologists who specialize in motor coordination disorders, including dyspraxia and dysgraphia, can provide personalized strategies and interventions that cater to your child's individual needs.
- Assistive Technology Tools: Consider utilizing tools such as pencil grips, slant boards, and specialized software designed to enhance writing skills and organizational abilities. These technologies can significantly assist young individuals in overcoming challenges related to their conditions.
- Case Studies: Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of occupational therapy in enhancing fine motor skills among young individuals with dyspraxia. For instance, assessments using digital handwriting tablets have provided detailed insights into handwriting performance, allowing for targeted interventions. The research named 'Assessment Methods for Handwriting Skills' emphasized that advanced evaluation tools can result in a more detailed understanding of students' progress and areas requiring enhancement.
- Statistics: Current data indicates that tailored therapeutic interventions are essential for young individuals facing handwriting difficulties, with a DTW 10 Deviance mean of 27.46 and a standard deviation of 23.44. This highlights the importance of individualized planning in therapy.
Experts recommend a variety of resources, including online platforms and community support, to empower parents in navigating the complexities of dyspraxia and dysgraphia. W.W. noted that "the reasons for the increase in fine motor skills still need to be substantiated by the differentiated analysis of the protocol data," underscoring the importance of thorough evaluation. By leveraging these resources, you can better support your child's development and learning.
Conclusion
Addressing the challenges of dyspraxia and dysgraphia requires a compassionate understanding of these conditions and the unique hurdles they present to affected children. Dyspraxia can impair motor skills, leading to difficulties in coordination and everyday tasks, while dysgraphia hinders writing abilities, impacting academic performance and self-esteem. For parents and educators, recognizing the symptoms of both conditions is essential in providing the necessary support and interventions.
Implementing effective support strategies is vital for fostering independence and confidence in children facing these challenges. Encouraging physical activity, utilizing visual aids, and integrating assistive technology can significantly enhance their daily experiences and academic success. The importance of tailored interventions cannot be overstated, as they not only improve motor and writing skills but also contribute to the emotional well-being of children.
Accessing appropriate resources and professional support further empowers families to navigate the complexities of dyspraxia and dysgraphia. By engaging with literature, online communities, and specialists, parents can gain valuable insights and strategies that cater to their child's unique needs. Ultimately, a collaborative approach involving parents, educators, and professionals can create a nurturing environment that promotes growth, resilience, and achievement for children with these developmental challenges. Together, we can make a meaningful difference in their lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are dyspraxia and dysgraphia?
Dyspraxia and dysgraphia, clinically known as Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), are neurological conditions that significantly affect motor skill development, leading to challenges with coordination and movement.
How do dyspraxia and dysgraphia impact children in daily life?
Children with dyspraxia and dysgraphia may struggle with everyday tasks such as tying shoelaces, riding a bike, or participating in sports due to difficulties with motor planning and execution.
What specific challenges do children with dysgraphia face?
Dysgraphia primarily impacts writing skills, leading to struggles with handwriting, spelling, and organizing thoughts on paper. Basic tasks like holding a pencil or forming letters can be particularly challenging.
How do dyspraxia and dysgraphia affect academic performance?
The challenges posed by dyspraxia and dysgraphia can significantly affect academic performance and self-esteem, making early intervention and tailored support strategies crucial.
What recent research findings are relevant to dyspraxia and dysgraphia?
Recent research indicates that individuals with a birth weight of less than 750 grams are at an increased risk for perceived motor difficulties, highlighting the need for targeted interventions.
What types of interventions are effective for children with DCD?
Task-oriented approaches in DCD therapy, especially those that are goal-oriented and actively involve the child, have proven effective in enhancing independence in daily activities.
What are some common symptoms of dyspraxia and dysgraphia?
Symptoms may include clumsiness, difficulty with fine motor tasks, challenges in spatial awareness, inconsistent handwriting, spelling difficulties, and trouble organizing written work.
How can parents and educators support children with dyspraxia and dysgraphia?
By recognizing the signs of dyspraxia and dysgraphia and implementing effective strategies, parents and educators can better support youth facing these challenges.
What role does near-infrared spectroscopy play in understanding DCD?
Near-infrared spectroscopy is a valuable method for exploring cortical activity during fine motor tasks in youth with DCD, providing insights into the neurological foundations of these conditions.
Why is early intervention important for children with dyspraxia and dysgraphia?
Prioritizing early intervention and customized assistance is essential for creating a more inclusive environment and improving the functionality and confidence of young individuals facing these difficulties.




