Overview
Understanding the behaviors associated with autism is essential for parents and advocates striving to support individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). By recognizing key symptoms—such as challenges in social interactions and heightened sensory sensitivities—families can better navigate the complexities of this journey. Early diagnosis plays a pivotal role, and tailored interventions, like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, can significantly enhance developmental outcomes. \n\nAs you learn more about these important aspects, consider how they relate to your experiences. Each child is unique, and understanding their specific needs can foster a nurturing environment. The journey may seem daunting, but with the right support and resources, improvement is within reach. \n\nWe invite you to explore these insights further. Share your experiences in the comments or connect with others who are on a similar path. Together, we can create a community that uplifts and empowers those navigating the challenges of ASD.
Introduction
In a world where understanding and acceptance of neurodiversity are increasingly prioritized, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) takes center stage in discussions about developmental challenges. This multifaceted condition impacts countless individuals, yet it continues to be clouded by misconceptions and stigma. Recognizing the signs of autism and exploring effective interventions, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, reveals a journey that is both complex and critical.
As research uncovers the nuances of autism, parents and advocates gain valuable knowledge and resources to navigate this landscape, ensuring that children with ASD receive the understanding and support they need to thrive. This article aims to illuminate the key aspects of autism, shedding light on:
- Symptoms
- Effective management strategies
- The essential role of community and professional resources in fostering a brighter future for individuals with autism.
1. What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by ongoing challenges in social communication, limited interests, and behaviors associated with autism. The term 'spectrum' beautifully reflects the wide array of symptoms and severity levels that individuals may experience. It's worth noting that boys often encounter motor skill challenges earlier than girls, which can lead to earlier diagnoses in males.
Recent statistics show a prevalence rate of 27.6 per 1,000 children aged 8 years, with a notable male-to-female ratio of 11.4. This indicates that ASD is significantly more prevalent among males, with diagnoses occurring at a rate of 43.0 for boys compared to 3.8 for girls. These findings are supported by the case study titled 'Overall Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder,' which presents these statistics across various sites. Furthermore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention highlights the importance of improved outreach and de-stigmatization efforts, stating, 'These changes reflect an improvement in outreach, screening, and de-stigmatization of diagnosis among minority communities.' This emphasizes the critical role of such initiatives in enhancing autism screening.
Additionally, among youths with ASD, 37.4% undergo evaluations where ASD is suspected but not confirmed. Notably, 3.9% of all individuals with ASD had an evaluation that ruled out ASD more recently than one that confirmed it, highlighting the complexities involved in diagnostics. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve developmental outcomes for individuals with ASD, making it essential for parents to recognize and understand the characteristics and impacts of autistic behaviors associated with this disorder.
By being informed, parents can advocate more effectively for their children and seek the necessary support.
2. Recognizing the Signs: Key Symptoms of Autism
Understanding the key symptoms of autism and identifying autistic behaviors is essential for parents and advocates. These symptoms can manifest in various ways, particularly in interactions with others. Common indicators include:
- Difficulty with interactions, such as limited eye contact or challenges in interpreting cues. Many individuals with autistic behaviors struggle to engage in reciprocal conversations, highlighting the importance of recognizing these social interaction difficulties.
- Delayed language skills or atypical speech patterns, such as echolalia, where individuals might repeat phrases or sentences they hear. Repetitive movements or behaviors, like hand-flapping or arranging toys in a specific order, are also considered autistic behaviors that can serve as coping mechanisms.
- An intense focus on particular interests or subjects, often leading to conversations dominated by these topics.
- Sensory sensitivities, where an individual may exhibit heightened reactions to sounds, lights, or textures that others find tolerable. Recognizing these signs is vital. Experts emphasize that early identification can significantly improve a young person's access to necessary supports and services.
By understanding these symptoms, parents can take proactive measures toward advocacy and support, ultimately fostering a more inclusive atmosphere for individuals with developmental disorders. Recent data from the CDC highlights that prevalence estimates for the condition are based on 8-year-old children across 11 monitoring sites, underscoring the importance of comprehensive research to illuminate the diverse needs of the neurodiverse community. The CDC reports that the cost of therapeutic behavioral services is approximately $175.44, emphasizing the financial implications of support for individuals with developmental disorders.
Additionally, advocates Alison Singer and Judith Ursitti have pointed out the exclusion of individuals with profound developmental disorders from research studies, advocating for more inclusive research that addresses their specific needs. Together, we can work towards a better understanding and support system for all individuals on the spectrum.
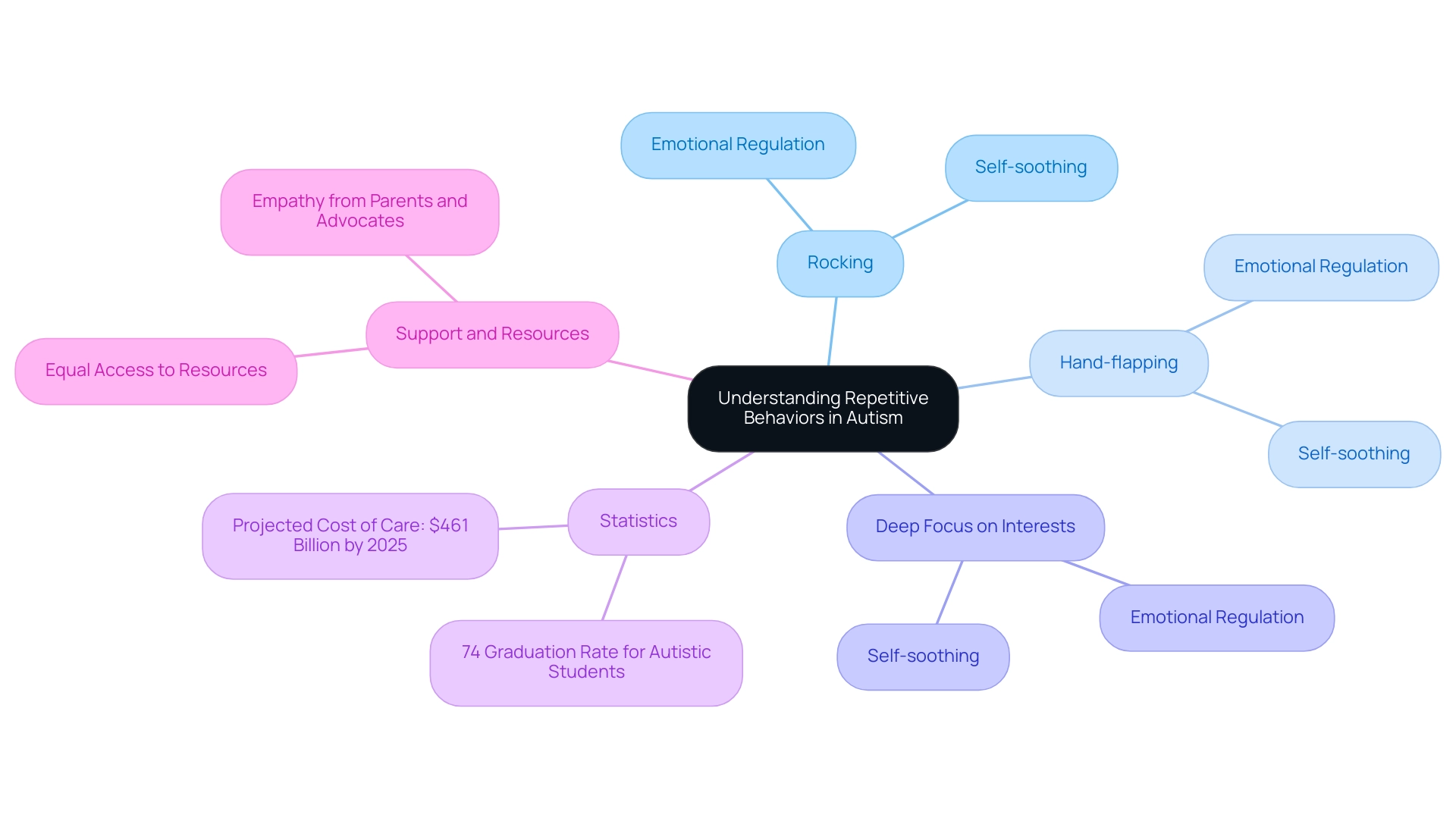
3. Understanding Repetitive Behaviors and Obsessions in Autism
Repetitive actions, often referred to as 'stimming,' are vital behaviors for individuals on the autism spectrum, playing a crucial role in their daily lives. These actions can manifest in various forms, such as:
- Rocking
- Hand-flapping
- A deep focus on specific interests
Research shows that these behaviors are not just quirks; they serve essential functions for emotional regulation and self-soothing.
As Laura NG, a Clinical Operations Manager, observes,
The current prevalence rates of developmental disorders in 2024 align with earlier estimates, underscoring the ongoing visibility of these behaviors.
Studies indicate that engaging in stimming can significantly assist those exhibiting autistic behaviors in managing overwhelming emotions, offering a necessary outlet during stressful situations. Understanding stimming in relation to autistic behaviors is crucial, as it acknowledges these actions as a natural aspect of the condition, fostering a supportive environment rather than one of discouragement.
Encouraging constructive outlets for these actions not only supports emotional regulation but also nurtures a more empathetic response from parents and advocates. Moreover, with the cost of caring for individuals with developmental disorders projected to reach $461 billion by 2025, recognizing the economic implications of such care becomes essential. The graduation rates for autistic students reveal that 74% graduate with a diploma, compared to 86% of all students, emphasizing the need for robust support systems.
Ensuring equal access to resources that promote understanding and acceptance of stimming actions is vital for individuals from all demographic backgrounds, as it connects to the broader challenges faced by this population. Together, we can create a more inclusive and supportive community.
4. The Role of ABA Therapy in Supporting Autistic Children
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy stands out as a highly esteemed intervention for children with autism, primarily due to its systematic approach to transforming autistic behaviors through reinforcement strategies. This evidence-based method not only enhances communication skills and social interactions but also effectively reduces challenging behaviors associated with autism. Among the key techniques in ABA therapy are:
- Breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps
- Employing positive reinforcement to encourage desirable actions
Research underscores the importance of early and consistent ABA intervention, revealing that children with autistic behaviors who receive tailored treatment can experience significant improvements in their overall functioning and quality of life. For instance, young individuals may benefit from up to 40 hours of therapy each week, highlighting the intensity of ABA therapy and its potential to make a meaningful difference. A recent study titled "Adaptive Behavior Gains from ABA" found that youngsters with the lowest initial adaptive levels exhibited clinically significant improvements, averaging an increase of 4.46 points for each year spent in ABA services, despite the challenges of maintaining full treatment dosages.
Moreover, ongoing evaluations of a data-driven, client-centric ABA approach during the COVID-19 pandemic emphasize the effectiveness of telehealth supervision in enhancing treatment outcomes. As expert Andrey Ostrovsky points out,
By iteratively tuning treatment dosage to the individual client’s needs, providers may be able to better maximize functional progress of the client, to preserve family time, and to utilize health plan dollars more efficiently.
This principle reinforces the vital role of personalized ABA interventions in achieving optimal results for children with developmental disorders who display autistic behaviors.
As you navigate this journey, remember that support is available. Consider reaching out to professionals who can provide guidance tailored to your child’s unique needs. Your involvement and understanding can make all the difference in their progress and happiness.
5. Empowering Parents: Navigating Resources and Support for Autism
For parents navigating the complexities of resources related to developmental disorders, the landscape can often feel daunting. It’s important to know that you are not alone. Organizations such as Autism Speaks and the Autism Society, along with local centers for developmental disorders, provide invaluable support. These entities not only assist in locating essential resources like support groups, educational materials, and therapy options but also empower parents through shared knowledge and experience.
Engaging with other families through online forums or local meet-ups cultivates a strong sense of community. This connection offers emotional support and practical advice from those who understand the challenges firsthand. Moreover, advocating for your child’s needs within educational and healthcare systems is paramount. Being informed about your rights and available services can profoundly influence their developmental journey. It is essential to recognize that 5% of all students in the U.S. do not complete high school, highlighting the significance of educational advocacy for individuals who display autistic behaviors.
Furthermore, the expenses linked to services addressing autistic behaviors can be considerable. For instance, adaptive assistance costs around $82.25, and emergency department visits average $1,397.22, emphasizing the financial impact for families. The recent identification trends indicate that, for the first time in 2020, the percentage of 8-year-old Asian or Pacific Islander, Hispanic, and Black youths diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) surpassed that of their White peers. This finding suggests disparities in how ASD is recognized and diagnosed across different demographic groups, emphasizing the need for equitable access to resources and support.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for parents as they seek to navigate the available support systems effectively. Remember, reaching out for help is a sign of strength, and together we can advocate for the resources our children need.
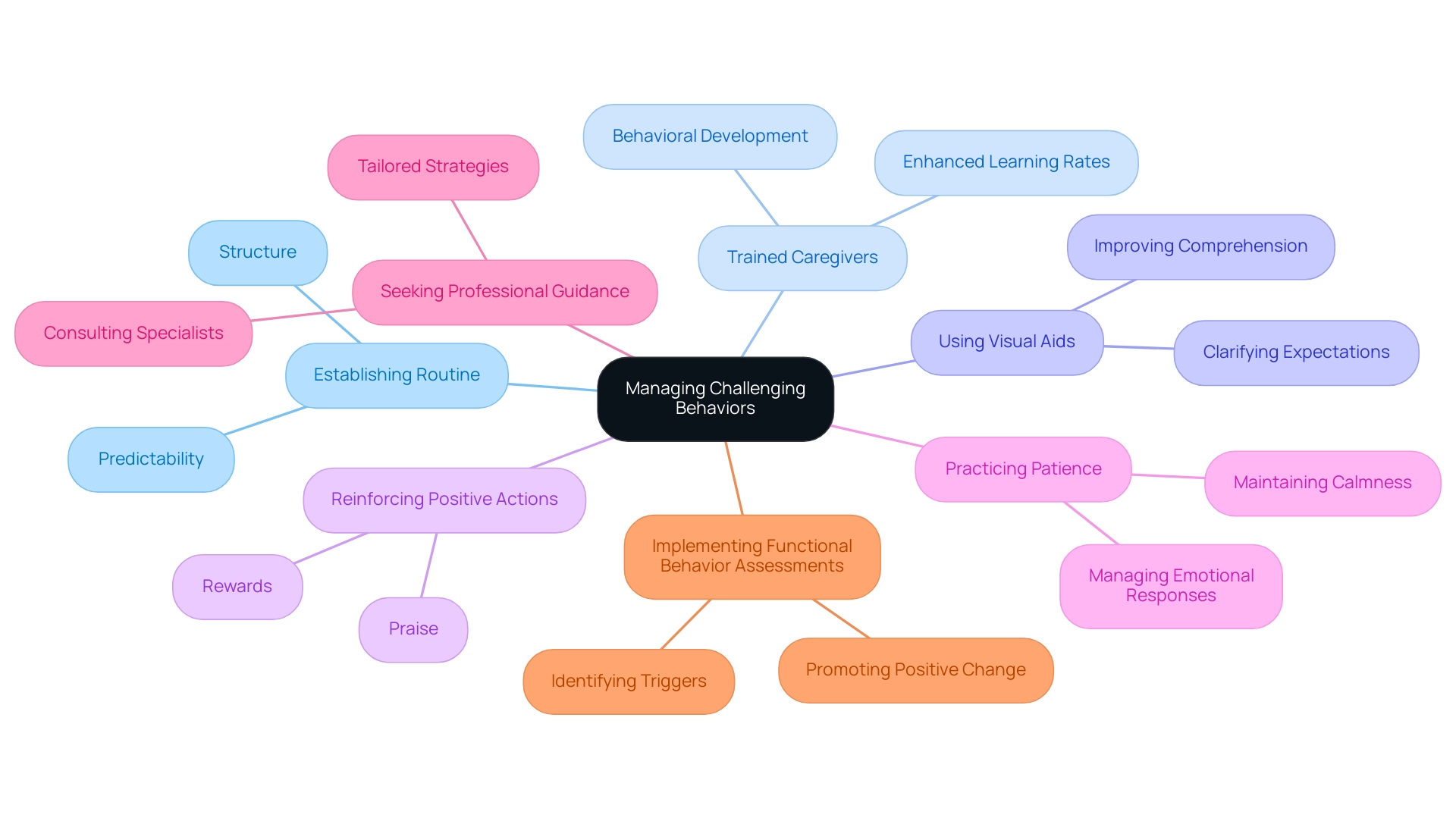
6. Effective Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors
Addressing difficult behaviors, including those associated with autism, in youth with developmental disorders requires a thoughtful and compassionate approach. Establishing a consistent routine is crucial, as it offers the structure and predictability that many young individuals thrive on. Research shows that trained caregivers can significantly enhance learning rates and behavioral development, with studies indicating improvements of up to 30% in skill acquisition when caregivers are properly trained, underscoring the importance of routine.
As Dr. Naomi L. Rahn emphasizes, "A structured routine is not just beneficial; it is essential for young individuals with autism to feel secure and understood." Utilizing visual aids and social narratives can further clarify expectations and outcomes, making it easier for children to comprehend what is required of them. Reinforcing positive actions through praise and rewards fosters a positive feedback loop, encouraging children to repeat desired activities.
Practicing patience and maintaining calmness during challenging moments is vital, as heightened emotional responses can escalate situations. Seeking professional guidance, such as consulting with a specialist or therapist, ensures that caregivers have access to tailored strategies that meet individual needs. A poignant case study titled 'Link Between Actions and Communication' illustrates how challenging behaviors can manifest as autistic behaviors that serve as a form of communication for unmet needs.
Implementing Functional Behavior Assessments (FBAs) can help identify triggers and motivations, leading to strategies that promote positive behavioral change. For those looking for further reading and resources, caregivers can explore additional materials available through SAGE, including the CQ Library and Sage Data, which provide valuable insights into effective behavior management techniques. By nurturing a supportive atmosphere, caregivers and educators can significantly enhance the overall quality of life for individuals with developmental disorders.
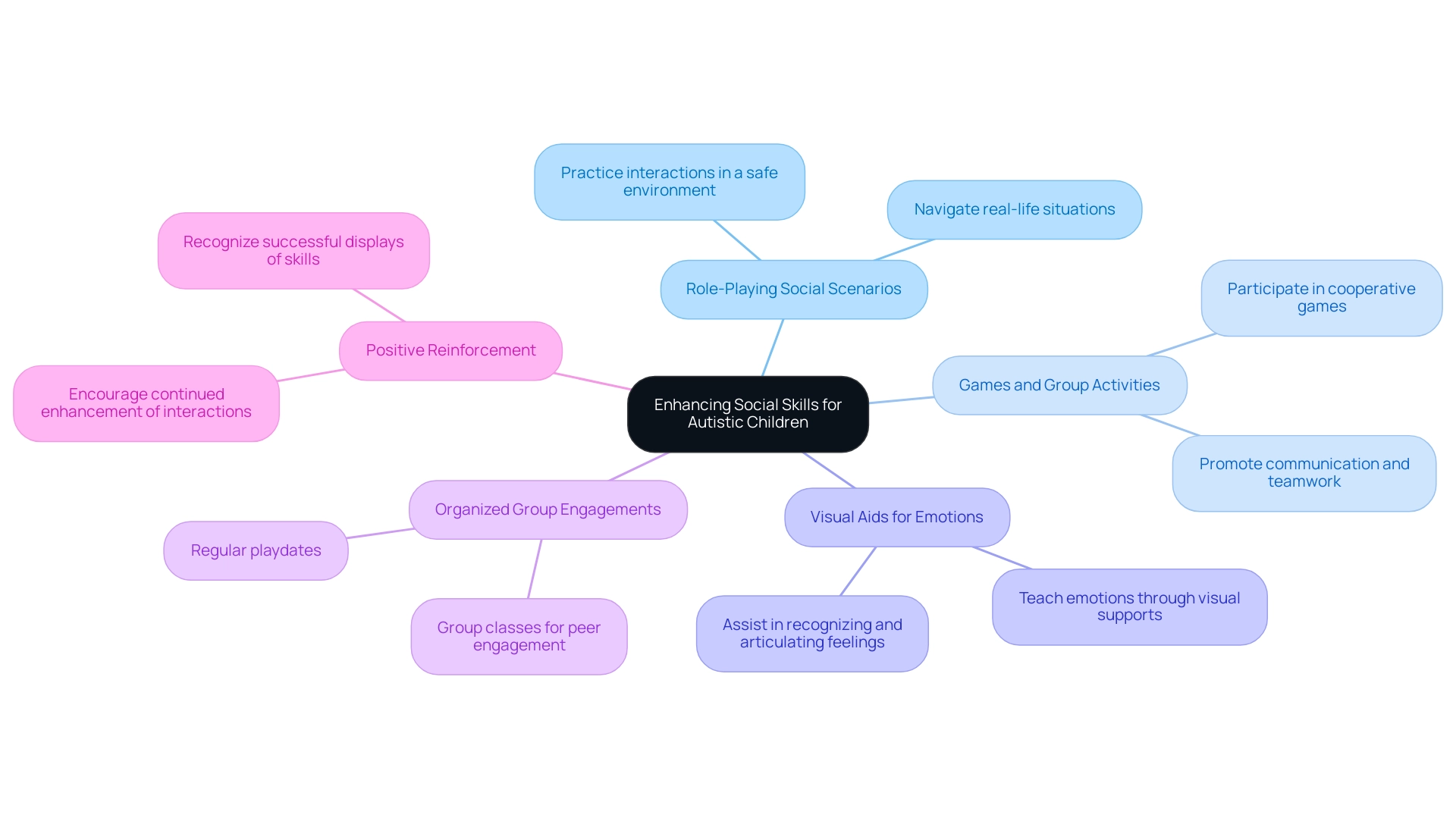
7. Enhancing Social Skills: Building Connections for Autistic Children
Improving interpersonal abilities in youth with autism is essential for nurturing significant relationships with peers and adults, while also addressing their unique behaviors. As a caring parent, you may wonder how best to support your child in this journey. Here are some effective strategies that can help foster their development:
- Role-Playing Social Scenarios: This technique allows youngsters to practice interactions in a safe environment, helping them navigate real-life situations with greater ease.
- Games and Group Activities: Participating in cooperative games promotes communication and teamwork, offering children practical experiences in communal settings.
- Visual Aids for Emotions: Teaching emotions through visual supports assists young individuals in recognizing and articulating their feelings, which is vital for interpersonal interaction.
- Organized Group Engagements: Regular playdates or group classes provide opportunities for children to engage with peers, promoting interpersonal skills in an organized manner.
- Positive Reinforcement: Recognizing and supporting successful displays of interpersonal skills can encourage young individuals to keep enhancing their interactions.
Research continues to support the efficacy of these strategies, with recent findings indicating statistically significant improvements in reciprocity and participation, as well as in autistic behaviors, following targeted interventions. Blythe Lagasse highlights the promise of music therapy, stating, "Preliminary evidence supports the use of music therapy intervention for youth with ASD, with a 2014 Cochrane review indicating that music therapy interventions are effective for enhancing interaction, verbal communication, initiating behavior, and emotional reciprocity."
Furthermore, the MUSAD assessment has shown high validity and reliability, reinforcing the credibility of these strategies. Additionally, case studies, such as the one titled "Impact of Music Therapy on Cognitive and Emotional Skills," reveal that music therapy interventions have positively impacted cognitive and emotional processing skills, leading to better selective attention and emotional understanding.
By actively promoting and implementing these strategies, you can empower your child to develop vital social competencies, ultimately enriching their social lives. Your involvement is key—consider exploring these approaches and sharing your experiences, as together we can foster a supportive community for our children.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential for fostering a supportive environment for individuals affected by this complex condition. This article highlights the multifaceted nature of autism, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and recognition of key symptoms. By identifying behaviors such as challenges in social interaction and repetitive actions, parents and advocates can navigate the landscape of support available, significantly improving outcomes for children.
Effective interventions, particularly Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, play a crucial role in helping autistic children develop essential skills and manage their behaviors. The evidence-based strategies used in ABA therapy demonstrate the potential for meaningful improvements in communication and social interaction. This underscores the importance of tailored approaches to meet individual needs, ensuring that each child receives the support they deserve.
Moreover, empowering parents through access to resources and community support fosters a collaborative atmosphere, essential for advocating for children with autism. Consistent strategies in managing challenging behaviors and enhancing social skills are vital, and this article provides practical insights for caregivers, encouraging them to seek out and utilize available resources.
Ultimately, the journey toward understanding autism and supporting those affected by it requires a commitment to education, advocacy, and empathy. By prioritizing awareness and acceptance, we can work together as a society to dismantle stigma and create a more inclusive environment where individuals with autism can thrive and connect meaningfully with their communities. Let us take action, share our experiences, and support one another in this important endeavor.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social communication, limited interests, and specific behaviors associated with autism. The term 'spectrum' reflects the wide range of symptoms and severity levels experienced by individuals.
How prevalent is ASD among children?
Recent statistics indicate a prevalence rate of 27.6 per 1,000 children aged 8 years, with a significant male-to-female ratio of 11.4. This means that ASD is much more common in males, with diagnoses occurring at a rate of 43.0 for boys compared to 3.8 for girls.
What factors contribute to the earlier diagnosis of boys with ASD?
Boys often encounter motor skill challenges earlier than girls, which can lead to earlier diagnoses in males.
What role do outreach and de-stigmatization efforts play in autism diagnosis?
Improved outreach and de-stigmatization efforts are critical in enhancing autism screening and diagnosis, particularly in minority communities, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
What percentage of youths with ASD undergo evaluations where ASD is suspected but not confirmed?
Among youths with ASD, 37.4% undergo evaluations where ASD is suspected but not confirmed.
Why is early diagnosis and intervention important for individuals with ASD?
Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve developmental outcomes for individuals with ASD, making it essential for parents to recognize and understand the characteristics of autistic behaviors.
What are common symptoms of autism that parents should be aware of?
Common symptoms include: 1. Difficulty with social interactions, such as limited eye contact and challenges in interpreting cues. 2. Delayed language skills or atypical speech patterns, including echolalia. 3. Repetitive movements or behaviors, like hand-flapping. 4. Intense focus on specific interests or subjects. 5. Sensory sensitivities to sounds, lights, or textures.
How can understanding these symptoms help parents?
By recognizing these symptoms, parents can take proactive measures toward advocacy and support, fostering a more inclusive environment for individuals with developmental disorders.
What are the financial implications of support for individuals with developmental disorders?
The cost of therapeutic behavioral services is approximately $175.44, highlighting the financial burden associated with support for individuals with developmental disorders.
What advocacy efforts are being made for individuals with profound developmental disorders?
Advocates like Alison Singer and Judith Ursitti emphasize the need for more inclusive research that addresses the specific needs of individuals with profound developmental disorders, as they are often excluded from studies.




