Overview
Autistic Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is defined as a range of neurodevelopmental challenges that significantly affect social interaction, communication, and behavior, with variability in both difficulties and strengths among individuals. The article supports this definition by detailing the complexities of ASD, including its prevalence, diagnostic criteria, co-occurring conditions, and the importance of tailored interventions, emphasizing the need for comprehensive understanding and support for affected individuals and their families.
Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) represents a complex tapestry of neurodevelopmental challenges that affect individuals in diverse ways, influencing their social interactions, communication skills, and behaviors. With an increasing prevalence and a shifting demographic landscape, understanding the nuances of ASD has never been more critical for parents, educators, and professionals.
This article delves into the intricacies of ASD, including:
- Recognizing early signs and symptoms
- Exploring the underlying causes and risk factors
- Examining the diagnostic process
- Various treatment options
- Importance of social and educational integration
By fostering a supportive community for families affected by ASD, this comprehensive overview aims to equip readers with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the complexities surrounding autism, ultimately enhancing the lives of those on the spectrum and their families.
Defining Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Overview
The definition of autistic spectrum disorder highlights a broad range of neurodevelopmental challenges, particularly impacting social interaction, communication, and behavior. The term 'spectrum' emphasizes the considerable variability in both difficulties and strengths displayed by people with ASD. While some may face profound challenges in everyday activities, others may display exceptional abilities in specific domains.
Understanding the definition of autistic spectrum disorder is essential for parents, educators, and professionals who strive to deliver effective support and interventions tailored to individual needs. Recent data highlights the increasing awareness of ASD, indicating that in 2020, the prevalence among youth aged eight rose from 6.7 per 1,000 in 2000 to 27.6 per 1,000. Notably, the demographic landscape of those diagnosed is shifting, with higher rates observed among Black and Hispanic youth compared to their White counterparts.
Additionally, 3.9% of all individuals with ASD had an evaluation ruling out ASD more recently than one confirming ASD, highlighting the complexities within the diagnostic landscape. As highlighted in research from Practical Neurology, "the co-occurrence of these two disorders stems from genetic and structural brain differences that characterize them," further emphasizing the necessity for specialized approaches to assist those on the autism spectrum. These insights highlight the essential role of education for social workers and advocates, enabling them to support families in navigating the complexities of planning for their offspring's future in manageable, informed steps.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of ASD
The signs and symptoms of the definition autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) can show significant variability, often manifesting as difficulties in social communication. Individuals may struggle to interpret social cues, maintain conversations, and build relationships, which are critical components of social interaction. Furthermore, many with ASD engage in repetitive behaviors or display restricted interests, alongside potential sensory sensitivities that can lead to unusual responses to sensory stimuli.
Identifying these indicators promptly is crucial, as it enables families to understand the definition of autistic spectrum disorder and obtain the required assistance and interventions that can significantly impact the individual's developmental path. Statistics reveal that as of 2002, the prevalence of autism was estimated at 6-7 per 1,000 children, highlighting the importance of awareness and early detection. Psychologists emphasize that identifying these symptoms promptly can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected, paving the way for more effective treatment strategies and support systems.
Additionally, the co-occurrence of conditions such as:
- epilepsy
- gastrointestinal disorders
- sleep problems
- ADHD
- anxiety
complicates the challenges encountered by people with ASD, as noted in 'Practical Neurology': 'The co-occurrence of these two disorders stems from genetic and structural brain differences that characterize them.' Recent studies continue to shed light on the early indicators of ASD, and understanding the definition of autistic spectrum disorder is vital, along with the ongoing commitment from organizations like the CDC to provide data and resources for improving outcomes for children with ASD. Moreover, despite being college-educated, only around 15% of autistic adults are fully employed, illustrating the significant employment gap that persists even among those with higher education.
This highlights the critical significance of early detection and intervention in shaping a more favorable future for those with the definition of autistic spectrum disorder.
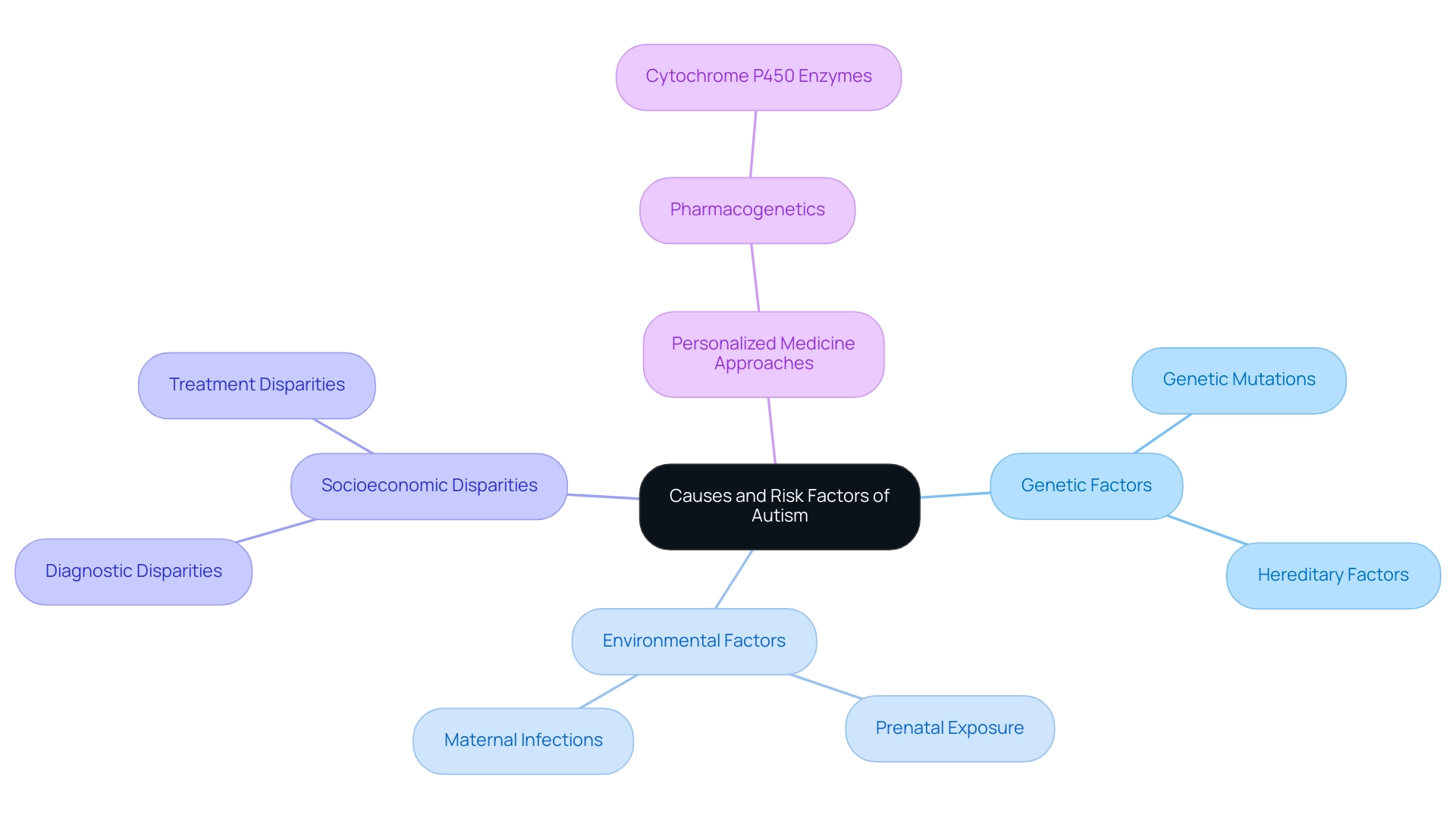
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors of Autism
The definition of autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) reveals complex and multifaceted origins, with recent research highlighting a significant interplay between genetic and environmental influences. Genetic studies have identified specific mutations that may heighten the risk of developing ASD, suggesting that hereditary factors play a crucial role. Concurrently, environmental risk factors—such as prenatal exposure to certain medications or maternal infections—have also been implicated in ASD development, as evidenced by various research studies that explore these associations.
These insights are vital for both parents and professionals, as recognizing these risk factors can facilitate early intervention strategies. As highlighted by Dr. Daniel H. Geschwind, a prominent authority in the field,
There are also significant diagnostic and treatment disparities based on socioeconomic status, indicating the necessity for fair access to assessment and assistance.
Emerging personalized medicine approaches, particularly in pharmacogenetics, underscore the importance of tailoring treatments based on genetic variations that affect drug metabolism.
Notably, about 90% of all drugs are metabolized by seven different cytochrome P450 enzymes, which highlights the significance of understanding pharmacogenomics in improving treatment efficacy and reducing adverse effects. A case study titled 'Pharmacogenetics in ASD Treatment' illustrates how these personalized medicine approaches can enhance outcomes by considering genetic variations that influence drug responses. Understanding these genetic and environmental components not only enhances treatment efficacy but also minimizes adverse effects, particularly as many individuals with the definition autistic spectrum disorder do not respond predictably to standard dosages.
This evolving knowledge can guide proactive measures, ensuring that those at risk receive the necessary support and resources.
The Diagnostic Process: How Autism is Identified
The diagnosis of the definition autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) generally requires a thorough evaluation conducted by a multidisciplinary team, which often includes psychologists, speech-language pathologists, and developmental pediatricians. This comprehensive approach typically integrates standardized assessments, behavioral observations, and detailed parent interviews to form a holistic understanding of the individual's developmental trajectory and behavioral patterns. According to the DSM-5, the definition of autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) includes specific criteria that highlight symptoms must manifest during early childhood and significantly disrupt daily functioning.
In Arizona, the site-specific prevalence for AI/AN autism spectrum disorder in 2020 was reported at 26.8 per 1,000, emphasizing the importance of understanding the local context of ASD prevalence. Moreover, a significant percentage of children and adolescents with the definition autistic spectrum disorder (91%) are diagnosed with co-occurring psychiatric disorders, with ADHD being the most common. This highlights the intricacy of the diagnostic process and the significance of customizing assistance to personal needs.
As pointed out by Chiugo Okoye, as we progress in comprehending and identifying ASD, it is essential to balance acknowledging neurodiversity and offering timely and effective assistance for those with ASD and their families. Ongoing research into developing objective biomarkers for early diagnosis, including neuroimaging and machine learning applications, further illustrates the evolving landscape of ASD diagnostics.
Exploring Treatment Options and Intervention Strategies for ASD
Treatment for the definition autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) requires a personalized method customized to each person's unique strengths and challenges. Among various interventions, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) stands out as one of the most recognized therapies. It focuses on enhancing specific behaviors and skills through targeted reinforcement strategies.
In addition to ABA, other valuable interventions include:
- Speech therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Social skills training
Each contributes to a well-rounded treatment plan. Research underscores the critical nature of early intervention; statistics reveal that approximately 66% of children referred for ABA therapy commence treatment and remain in services for an average of 12 months. This prompt assistance is crucial in promoting significant advancements in communication and social skills, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of life for those with the definition of autistic spectrum disorder.
Weihong Xu, who collected and analyzed relevant data, emphasizes that 'the study was conducted by the Declaration of Helsinki, and the IRB of Wuhan Sports University approved the protocol.' However, real-world implementation of these therapies often encounters challenges. A study addressing the complexities of delivering ABA within mandated insurance coverage frameworks highlights issues such as provider availability and reimbursement rates, which can hinder effective treatment.
Discontinuation data indicates that reasons for service termination often stem from these systemic challenges, emphasizing the need for improved strategies in service delivery to optimize patient outcomes. Moreover, the case study titled 'Challenges in Implementing ABA for ASD' reveals that despite existing autism mandates, real-world implementation frequently leads to lower service utilization and modest patient outcomes compared to controlled research settings, highlighting the importance of understanding the definition of autistic spectrum disorder to address these barriers.
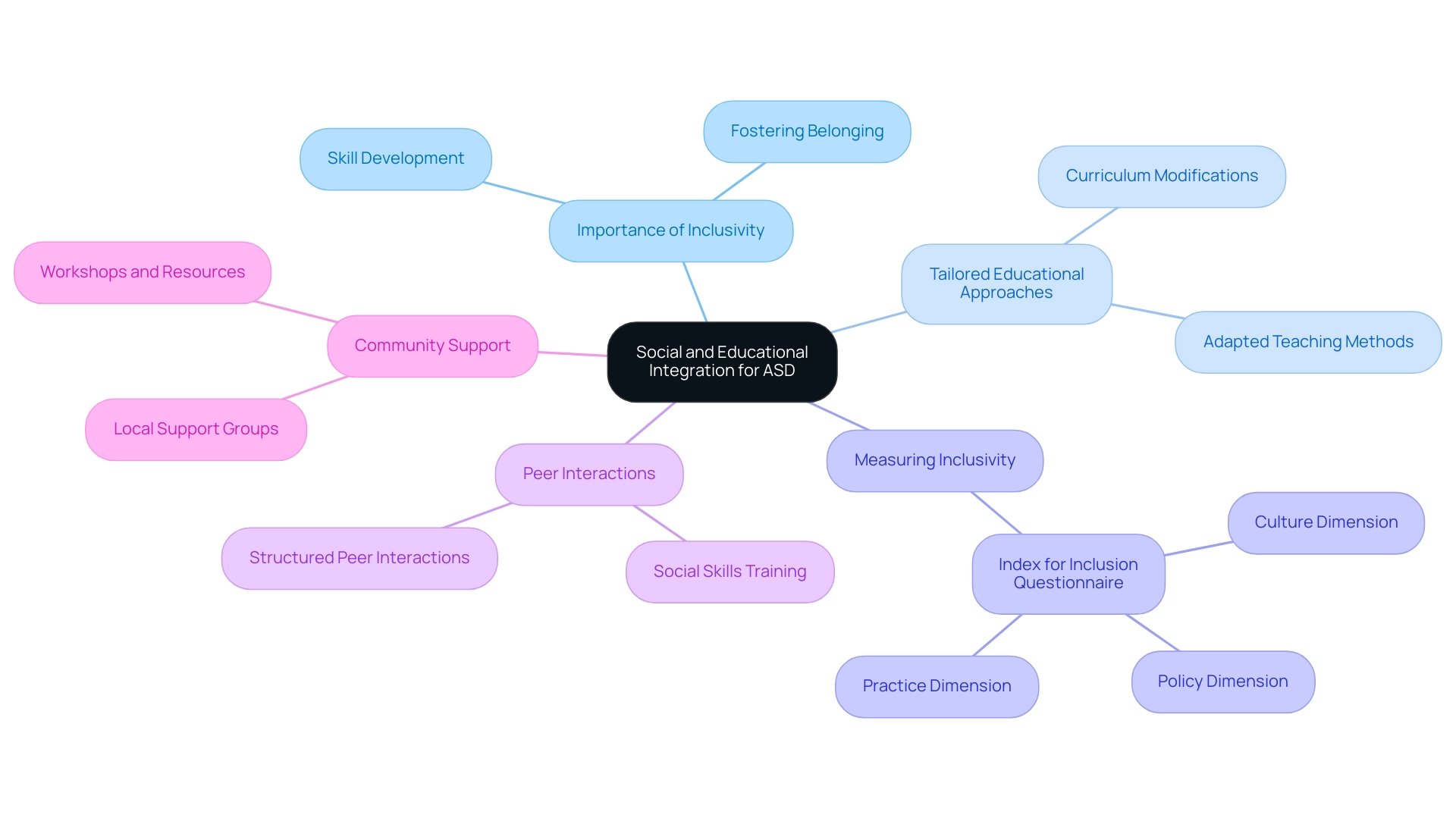
Social and Educational Integration: Supporting Individuals with ASD
Social and educational integration for people with the definition autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) is essential for fostering a sense of belonging and facilitating skill development. Inclusive practices in educational settings involve adapting teaching methods and curricula to meet diverse learning needs, ensuring that students, as defined by the definition autistic spectrum disorder, can thrive alongside their typically developing peers. Research indicates that as the severity of autism increases, engagement levels decrease, highlighting the need for tailored approaches to assist these students effectively.
For instance, the Index for Inclusion questionnaire serves as a valuable tool for measuring school inclusivity across culture, policy, and practice dimensions, guiding educators in creating more inclusive environments. Structured peer interactions, complemented by social skills training, can significantly enhance social integration, empowering students to build meaningful relationships in school environments. Community programs, including local support groups and workshops, play a crucial role in connecting families, providing resources and shared experiences that benefit both those with ASD and their families.
CYP4 beautifully encapsulates this resilience, stating,
Even if life brings you down, you can always put it back up…and maybe, if you're lucky, you can be successful with your autism.
Furthermore, case studies reveal that individuals with ASD often view their condition as a unique strength rather than a limitation, fostering creativity and resilience when placed in supportive environments. These insights highlight the profound impact that inclusive educational practices can have on the lives of individuals with the definition autistic spectrum disorder, thereby reinforcing the importance of social and educational integration.
Building a Supportive Community for Families Affected by ASD
Creating a robust community for families impacted by the definition autistic spectrum disorder is crucial for fostering knowledge exchange, sharing experiences, and accessing essential resources. Support groups, online forums, and community organizations serve as vital lifelines for parents navigating the intricate landscape of ASD. These platforms enable families to connect, collaborate, and share effective strategies that empower them to advocate vigorously for their offspring.
Significantly, parents of youth with ADHD experience higher levels of anxiety compared to those with ASD, highlighting the emotional challenges faced by these families. A recent study on the Parent Psychoeducation Support Group (PPSG) utilized a quasi-experimental, single-group prepost design and revealed that participation significantly reduced stress and anxiety levels among parents of children with the definition autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) and ADHD, underscoring the effectiveness of such interventions. As R Alibekova from the Department of Medicine at Nazarbayev University aptly points out, further research is warranted to explore the benefits of involvement in groups, and interventions are needed to strengthen the role of these groups in meeting the needs of parents.
Parents can locate support groups through:
- Nonprofit organizations
- Facebook pages
- Meetup groups
- Local listservs
This provides them with practical resources to enhance their support network. By cultivating a collaborative environment, families can join forces to enhance the quality of life for individuals with the definition of autistic spectrum disorder and promote positive developmental outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential for fostering a supportive environment for individuals and families affected by its complexities. The article highlights the spectrum nature of ASD, emphasizing the variability in challenges and strengths that individuals may exhibit. Recognizing early signs and symptoms, understanding the causes and risk factors, and navigating the diagnostic process are crucial steps in ensuring timely support and intervention.
Various treatment options, including:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- speech therapy
- occupational therapy
demonstrate the importance of personalized approaches to intervention. The significance of early intervention cannot be overstated, as it plays a pivotal role in enhancing communication and social skills, ultimately improving quality of life. Moreover, social and educational integration is vital to help individuals with ASD thrive alongside their peers, fostering a sense of belonging and promoting skill development.
Building a supportive community for families impacted by ASD is equally critical. Support groups and community organizations offer invaluable resources and opportunities for connection, allowing families to share experiences and strategies. By cultivating such environments, families can enhance the overall quality of life for individuals with ASD and empower them to navigate their unique journeys with resilience and strength.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of Autism Spectrum Disorder equips parents, educators, and professionals with the necessary tools to support individuals on the spectrum. Through awareness, early intervention, and community support, it is possible to create inclusive environments that celebrate the diverse abilities of individuals with ASD, ultimately leading to more positive outcomes for all involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is autistic spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) is a broad range of neurodevelopmental challenges that primarily affect social interaction, communication, and behavior. The term 'spectrum' indicates the variability in difficulties and strengths among individuals with ASD.
Why is understanding the definition of ASD important?
Understanding the definition of ASD is crucial for parents, educators, and professionals to provide effective support and interventions tailored to the individual needs of those with ASD.
How has the prevalence of ASD changed over the years?
The prevalence of ASD among youth aged eight increased from 6.7 per 1,000 in 2000 to 27.6 per 1,000 in 2020, indicating a growing awareness of the disorder.
Are there demographic differences in ASD diagnosis?
Yes, there are demographic differences, with higher rates of ASD observed among Black and Hispanic youth compared to their White counterparts.
What complexities exist within the diagnostic landscape of ASD?
Approximately 3.9% of individuals with ASD had an evaluation that ruled out ASD more recently than one that confirmed it, highlighting the complexities in diagnosing the disorder.
What are some common signs and symptoms of ASD?
Common signs and symptoms of ASD include difficulties in social communication, such as interpreting social cues and maintaining conversations, as well as repetitive behaviors, restricted interests, and potential sensory sensitivities.
Why is early identification of ASD symptoms important?
Early identification of ASD symptoms is crucial as it allows families to seek the necessary assistance and interventions that can significantly impact the individual's developmental trajectory.
What co-occurring conditions are often found with ASD?
Conditions that often co-occur with ASD include epilepsy, gastrointestinal disorders, sleep problems, ADHD, and anxiety.
How does the employment situation look for autistic adults?
Despite being college-educated, only about 15% of autistic adults are fully employed, indicating a significant employment gap that persists even among those with higher education.
What role do organizations like the CDC play in relation to ASD?
Organizations like the CDC provide data and resources aimed at improving outcomes for children with ASD, emphasizing the importance of ongoing support and research.




