Overview
This article shines a light on the challenges and strategies surrounding emotional dysregulation in individuals with autism, underscoring the vital importance of understanding these issues for parents and advocates. It brings attention to the fact that tailored interventions—like behavioral therapy and mindfulness practices—are essential for effectively managing emotional dysregulation. These approaches can lead to significant improvements in emotional regulation and social interactions among autistic youth, ultimately easing the psychological burden that families often face.
For parents navigating this journey, recognizing the unique emotional landscapes of their children can be both daunting and enlightening. By engaging in supportive practices, families can foster a nurturing environment that encourages growth and understanding. Imagine the positive changes that can unfold when emotional regulation is prioritized—how it can transform not just the lives of children, but the entire family dynamic.
As you explore these strategies, consider reaching out to professionals who can guide you in implementing these interventions. Your role as a parent or advocate is crucial, and together, we can create a more supportive community for those affected by autism. Let's embrace this journey with compassion and commitment.
Introduction
Navigating the emotional landscape of autism is often a complex journey, filled with unique challenges and profound insights. For many parents, understanding emotional dysregulation—a common experience among autistic individuals—can feel overwhelming. It often presents as intense reactions, mood swings, and difficulties in managing feelings. This experience not only impacts the individuals themselves but also significantly affects their families. Alarming studies reveal high rates of depression and anxiety among parents of autistic children, highlighting the emotional toll of this journey.
As researchers delve deeper into the intricacies of emotional dysregulation, the importance of personalized interventions and support systems becomes increasingly clear. By understanding the factors influencing emotional responses and implementing effective strategies, families can foster emotional growth and resilience. This nurturing approach ultimately enhances the quality of life for autistic children and their loved ones, creating a more supportive environment for everyone involved. Together, we can explore these insights and seek out the resources necessary to navigate this emotional landscape with compassion and understanding.
Understanding Emotional Dysregulation in Autism
Affect regulation issues can be particularly challenging for families, often leading to intense feelings, mood swings, or outbursts. For autistic individuals, these challenges may be heightened due to sensory sensitivities and communication barriers. It's essential for parents and advocates to understand the strong link between emotional dysregulation and autism. Recent studies indicate that nearly 50% of mothers with children who have developmental disorders show signs of depression, highlighting the profound psychological impact on families and the urgent need for effective support systems.
Understanding the key characteristics of emotional dysregulation and autism in autistic individuals is vital. Research conducted by Rachel G. McDonald and Erin Kang from Montclair State University, along with Sadaf Khawar from the University of Minnesota Medical School, has categorized preschoolers with emotional dysregulation and autism into low and high affective instability profiles. This analysis uncovered significant differences in behavioral issues, particularly those linked to emotional dysregulation and autism, emphasizing the need for tailored interventions. One-size-fits-all approaches may not be effective. Real-world examples show that parent-mediated interventions can greatly reduce challenging behaviors associated with emotional dysregulation and autism, while also improving social communication.
These strategies not only empower parents but also foster a collaborative environment where young individuals can flourish. Experts emphasize that diverse approaches and therapies are often necessary for each child, especially when multiple conditions coexist.
As we look ahead to 2025 and delve into the complexities of affective instability in individuals with developmental disorders, staying informed about the latest findings and professional insights is crucial. By cultivating a supportive community, parents and advocates can share experiences and strategies, ultimately unlocking the potential of children with developmental differences and ADHD. Understanding affective instability goes beyond merely identifying obstacles; it is about creating pathways for effective management and support.
Core Features and Challenges of Emotional Dysregulation
Emotional dysregulation and autism are core aspects of the condition, characterized by several key behaviors that can significantly affect daily life. Many children with emotional dysregulation and autism struggle to return to a calm state after outbursts, often triggered by seemingly minor events. This heightened emotional response can lead to intense reactions that feel disproportionate to the situation, especially in the context of emotional dysregulation and autism.
Moreover, these individuals often face challenges in expressing their emotions appropriately, which complicates their interactions with peers and family members. It’s important to recognize these struggles, as they can create feelings of isolation and frustration.
Statistics highlight the prevalence of these challenges: a significant portion of mothers of autistic individuals report experiencing symptoms of depression and anxiety. Studies indicate that around 67.1% of mothers experience both. Additionally, approximately 50% of mothers of autistic individuals exhibit symptoms of depression, a stark contrast to the 6% to 13.6% rate for mothers of non-autistic individuals. This psychological burden can exacerbate the difficulties faced by children, creating a cycle of stress and emotional instability.
For instance, a study conducted in China found that 72.5% of mothers of autistic children exhibited symptoms of depression, while 80.2% reported anxiety symptoms. A 2022 study from researchers at the University of California San Francisco revealed that nearly half of all mothers with children who have ASD noticed increased levels of depression symptoms over 18 months. These statistics serve as a reminder of the broader impact of emotional dysregulation and autism on family dynamics.
The challenges of emotional dysregulation and autism extend beyond the young individual, affecting family relationships. Parents often find themselves navigating the complexities of their child’s reactions, which can lead to feelings of frustration and helplessness. Many parents express feeling overwhelmed during their child's emotional outbursts, resulting in disruptions to daily routines and social interactions.
Recent research emphasizes the importance of understanding these features of affective instability. For example, research from Vanderbilt University suggests a potential connection between musical rhythm and language, which could inspire creative methods for teaching children to express themselves and regulate their emotions. By acknowledging and addressing these critical aspects of affective instability, parents can better support their children in developing effective coping strategies and improving their overall emotional well-being.
As we navigate these challenges together, it’s essential to share experiences and seek support. Have you encountered similar situations? How have you managed these emotional ups and downs? Your stories can help foster a community of understanding and resilience.
Factors Influencing Emotional Dysregulation in Autistic Individuals
Emotional dysregulation and autism in individuals are influenced by various factors, including sensory sensitivities, anxiety levels, and communication challenges. For example, children with heightened sensory sensitivities may feel overwhelmed in loud or chaotic environments, triggering significant anxiety and leading to outbursts. This response is not uncommon; recent findings indicate that emotional dysregulation and autism, characterized by limited interests and difficulties with inhibitory control, are strong indicators of parent-reported affective instability.
In fact, a higher Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule-Child Severity Score (ADOS-CSS) alongside emotional dysregulation and autism was predictive of more severe social anxiety disorder (SAD) and panic anxiety disorder (PAD), with p-values of 0.032 and 0.002, respectively.
Moreover, communication barriers can exacerbate psychological challenges. When children struggle to express their feelings, it often leads to emotional dysregulation and autism, making self-regulation even more difficult. This interplay emphasizes the importance of understanding each child's unique sensory profile and psychological needs.
A recent study revealed that emotional instability is closely linked to adaptive functioning, suggesting that further exploration is essential to fully grasp these dynamics. The study's limitations, including its reliance on caregiver reports and cross-sectional design, highlight the necessity for more comprehensive research to inform effective interventions. As Rachel G. McDonald from Montclair State University stated, "Overall, this article underscores the importance of more research into emotional dysregulation and autism to inform areas of challenges related to emotional dysregulation that can be used to better inform treatment targets."
Real-world examples illustrate these challenges vividly. For instance, a young person who is sensitive to bright lights may feel increasingly anxious in a brightly lit classroom, leading to disruptive behavior. Such scenarios underscore the critical role that sensory environments play in regulating emotions.
Experts in the field advocate for tailored strategies that address these factors. Therapists frequently emphasize the necessity for personalized approaches that consider sensory sensitivities and anxiety management techniques, which can significantly enhance the wellbeing of individuals on the autism spectrum. By fostering a deeper understanding of these influences, parents and advocates can better support youth in navigating their emotional landscapes.
ASD Media's commitment to fostering collaboration and growth in the ABA therapy industry further empowers parents and professionals to implement effective strategies in these contexts.
The Impact of Emotional Dysregulation on Daily Life and Relationships
Emotional dysregulation and autism can deeply impact daily life for individuals, creating challenges in school, social interactions, and family dynamics. For instance, young people who struggle to manage their emotions often find it difficult to make friends or participate in group activities, which can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness. This psychological turmoil may hinder their ability to engage in classroom discussions, ultimately affecting their overall school performance.
In 2025, statistics suggest that a significant number of individuals with autism experience difficulties in social interactions due to mood instability, underscoring the urgent need for targeted interventions.
Case studies illustrate how emotional dysregulation and autism can profoundly affect social interactions. Young individuals may misinterpret social cues or respond disproportionately to minor frustrations, which can alienate peers and strain relationships. A study titled "How Emotional Dysregulation and Autism Affect Emotional Development in Youngsters" reveals that these challenges can impede their ability to recognize, express, and regulate emotions, often necessitating additional support.
Understanding these psychological challenges is crucial for both parents and educators, as it empowers them to provide the necessary support to help young individuals develop social skills and navigate interpersonal situations more effectively.
Moreover, difficulties in managing emotions can strain family bonds, as parents may struggle to understand their child's reactions. Real-life examples show how these challenges can lead to misunderstandings and conflict within the family unit. By fostering open communication and utilizing parent-mediated interventions, which have proven effective in reducing challenging behaviors and enhancing social communication, families can collaboratively support their children.
Expert insights emphasize the importance of addressing emotional dysregulation and autism in educational settings. Rivka Hoch, BCBA, LBA, clinical director of Illuminate ABA, notes that young individuals with developmental disorders often face significant hurdles in identifying and articulating their feelings, potentially leading to behavioral issues in the classroom. Dr. Szatmari has also stressed the critical need to understand these psychological challenges, as they play a vital role in the development of young individuals with developmental disorders.
By implementing supportive strategies, schools can create an environment that fosters personal growth, benefiting both the student and their peers. Recognizing the complex influence of emotional dysregulation is essential for parents and advocates striving to assist youth on their journey toward psychological and social well-being.
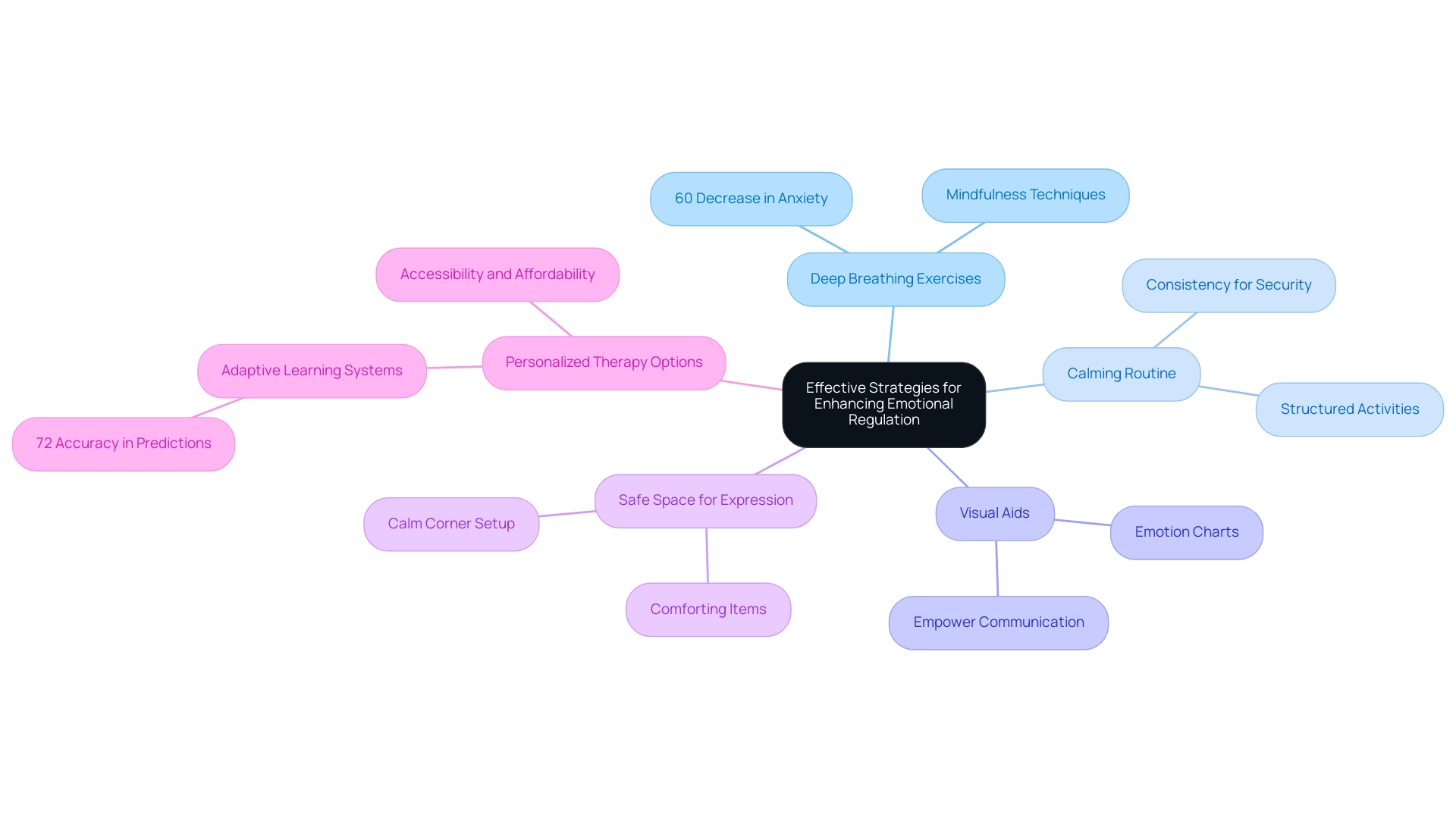
Effective Strategies for Enhancing Emotional Regulation
To effectively improve feelings management in youngsters with developmental differences, parents can adopt a variety of strategies that encourage awareness of feelings and self-regulation. One of the most impactful techniques is teaching deep breathing exercises, which have been shown to significantly enhance regulation of feelings. Research shows that these exercises can result in a 60% decrease in anxiety levels among youth with emotional dysregulation and autism, making them a crucial tool for managing their symptoms.
Establishing a calming routine is another important strategy. Consistency aids youngsters in feeling secure and grasping what to anticipate, which can lessen anxiety and outbursts. Incorporating visual aids, such as emotion charts, can also assist young individuals in identifying and expressing their feelings more effectively.
This visual support not only aids in recognition but also empowers youngsters to communicate their emotions, fostering a deeper understanding of their emotional landscape.
Creating a safe space for youngsters to express their feelings is crucial. This environment promotes open communication and enables youngsters to explore their emotions without fear of judgment. For instance, a dedicated 'calm corner' equipped with comforting items like soft pillows, sensory toys, and calming visuals can provide a retreat for young ones when they feel overwhelmed.
Real-world examples illustrate the effectiveness of these strategies. In one case study, a family implemented a structured routine that included deep breathing exercises and a calm corner. The result was extraordinary: the young person exhibited better management of feelings and a significant reduction in meltdowns over a three-month period.
Expert strategies for enhancing personal regulation also include teaching self-regulation techniques tailored to individual needs, especially for those dealing with emotional dysregulation and autism. For instance, therapists suggest utilizing mindfulness techniques along with deep breathing to assist young individuals in cultivating a deeper understanding of their feelings. This dual approach not only assists in prompt management of feelings but also develops long-term abilities for handling stress and anxiety.
As the landscape of support for individuals on the spectrum evolves, the emphasis on personalized therapy options continues to expand. According to research by Lovaas, adaptive learning systems can predict developmental trajectories with 72% accuracy, highlighting the importance of tailored approaches in therapy. Metin Nacar, COO, emphasizes that the field is moving toward more accessible and affordable therapy options, enhanced technological solutions, and better integration of various support strategies.
By integrating these effective strategies, parents can empower their offspring to navigate their emotions more successfully, ultimately enhancing their overall well-being and quality of life. Furthermore, instructing on recognizing feelings is a crucial step in self-control, as demonstrated in the case study on self-regulation methods for individuals experiencing emotional dysregulation and autism. Moreover, respite care for developmental disorders offers vital relief for parents, enabling them to rejuvenate while ensuring their offspring receives stimulating assistance, which is essential for behavioral regulation.
Interventions and Support for Managing Emotional Dysregulation
Interventions for addressing emotional dysregulation and autism in youth encompass a variety of methods, including:
- Behavioral therapy
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Mindfulness practices
These techniques have shown promise in helping young people develop regulation skills. Research indicates that CBT can significantly improve outcomes for individuals facing emotional dysregulation and autism. A systematic review has identified 572 articles on this topic, highlighting the expanding evidence base supporting these interventions (CRD42024587433).
Parents are encouraged to work closely with educators and therapists to create a comprehensive support plan tailored to their child's unique needs. This collaborative approach not only enhances the effectiveness of the interventions but also ensures that regulation strategies are consistently applied across different environments.
Real-world examples underscore the positive impact of behavioral therapy on mood regulation. One notable case study delved into emotional dysregulation and autism, specifically exploring rejection sensitive dysphoria (RSD) within the autism community. It revealed that heightened awareness and targeted support can lead to improved outcomes for individuals experiencing this condition. The study highlighted that individuals with emotional dysregulation and autism often struggle with affect regulation due to increased sensitivity to perceived rejection, suggesting that tailored interventions can significantly benefit them.
By incorporating insights from behavioral therapists, parents can adopt effective support strategies that address emotional dysregulation and autism, fostering a nurturing environment for their children.
As J.C.-P. wisely noted, "It would be advisable to continue exploring new instruments and approaches to more precisely measure EI in this population to further enhance the effectiveness of interventions." This statement underscores the importance of ongoing research in this area. Additionally, as research evolves, future studies should examine the long-term effects of these interventions and the generalization of social skills across various contexts.
This ongoing investigation will be crucial in improving and augmenting the effectiveness of regulation strategies for young individuals with developmental disorders. Furthermore, understanding the genetic and environmental factors, such as those observed in twins, can provide valuable insights into behavioral challenges faced by youth with autism.
Building Emotional Awareness and Empathy in Autism
Promoting awareness and empathy in autistic individuals is vital for improving their social connections and addressing emotional dysregulation. Engaging in activities such as role-playing, discussing emotions through storytelling, and utilizing emotion cards can significantly aid in this development. These methods encourage individuals to recognize and articulate their own feelings while also understanding the emotions of others.
Recent studies underscore the importance of these practices. For instance, a report from UC San Francisco revealed that roughly 50% of mothers of autistic children experience symptoms of depression, highlighting the psychological challenges encountered by families. This situation emphasizes the necessity for effective strategies that not only assist the youth but also offer relief for parents.
As Charlotte F Huggins observes, "it is important to find out more about, and subsequently support, the self-awareness challenges that autistic adolescents may encounter."
Role-playing, in particular, has proven to be an effective tool in teaching empathy to individuals with autism. By simulating real-life scenarios, children can practice responding to various feelings, which helps them develop a deeper understanding of social cues and reactions. Activities designed to foster empathy, such as collaborative games or group discussions about feelings, can further enhance these skills.
In 2025, experts continue to advocate for the integration of awareness training in therapeutic settings. The CDC is committed to providing essential data on Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and developing resources for early identification, underscoring the importance of these initiatives. Psychologists emphasize that developing self-awareness is essential for autistic individuals, as it lays the groundwork for healthier interactions and helps manage emotional dysregulation.
Additionally, social workers require education to assist parents in planning and breaking down the process into manageable steps.
By implementing these strategies, parents and advocates can create supportive environments that empower autistic individuals to navigate their emotions and relationships more effectively. The prevalence of autism in Maryland, which rose to 1 in 48 by 2016, further highlights the necessity for training and support systems addressing emotional dysregulation for families.
Conclusion
Navigating the emotional landscape of autism can be daunting, especially when it comes to emotional dysregulation, which deeply affects both autistic individuals and their families. It is vital to grasp the complexities of emotional dysregulation—marked by intense reactions, mood swings, and challenges in managing feelings—to nurture resilience and emotional growth. The distressing rates of depression and anxiety among parents of autistic children highlight the urgent need for effective support systems that can ease these emotional burdens.
Research underscores the significance of tailored interventions that cater to individual profiles of emotional dysregulation, as a one-size-fits-all approach often falls short. Simple strategies, such as:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Establishing calming routines
- Creating safe spaces for emotional expression
can empower children and enhance their emotional regulation skills. Additionally, fostering emotional awareness and empathy through engaging activities can strengthen social connections and aid children's development in navigating their emotional landscapes.
Ultimately, a collaborative approach involving parents, educators, and therapists is essential for implementing these strategies effectively. By embracing personalized interventions and cultivating a supportive environment, families can significantly improve the quality of life for autistic individuals. This commitment to understanding and addressing emotional dysregulation lays the foundation for healthier emotional development, stronger family dynamics, and a more inclusive society where autistic individuals are equipped to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are affect regulation issues and how do they affect families with autistic individuals?
Affect regulation issues can lead to intense feelings, mood swings, or outbursts, particularly challenging for families of autistic individuals. These challenges may be heightened due to sensory sensitivities and communication barriers.
What is the link between emotional dysregulation and autism?
There is a strong link between emotional dysregulation and autism, with research indicating that many autistic individuals struggle to return to a calm state after emotional outbursts, often triggered by minor events.
How prevalent are mental health issues among mothers of children with autism?
Nearly 50% of mothers with children who have developmental disorders show signs of depression, and around 67.1% experience both depression and anxiety. This psychological burden can exacerbate the emotional difficulties faced by their children.
What did recent studies reveal about emotional dysregulation profiles in preschoolers with autism?
Research categorized preschoolers with emotional dysregulation and autism into low and high affective instability profiles, uncovering significant differences in behavioral issues and emphasizing the need for tailored interventions.
What types of interventions can help manage emotional dysregulation in autistic children?
Parent-mediated interventions have been shown to reduce challenging behaviors associated with emotional dysregulation and autism while also improving social communication. Diverse approaches and therapies are often necessary, especially when multiple conditions coexist.
How do emotional dysregulation challenges impact family dynamics?
The challenges extend beyond the individual, affecting family relationships and often leading parents to feel overwhelmed during their child's emotional outbursts, which can disrupt daily routines and social interactions.
What role does community support play in managing emotional dysregulation and autism?
Cultivating a supportive community allows parents and advocates to share experiences and strategies, which can help unlock the potential of children with developmental differences and ADHD.
What is the importance of staying informed about affective instability in individuals with developmental disorders?
Staying informed about the latest findings and professional insights is crucial for understanding and managing affective instability, enabling parents and advocates to create effective management pathways and support systems.




