Introduction
Navigating the complexities of autism meltdowns and panic attacks can be a daunting challenge for parents and advocates alike. Understanding the distinct nature of these emotional responses is crucial, as each presents unique triggers and symptoms that can profoundly impact a child's well-being.
Autism meltdowns often arise from sensory overload or disruptions in routine, manifesting as intense emotional outbursts that can leave both children and their families feeling overwhelmed. In contrast, panic attacks strike suddenly, marked by acute fear and physical symptoms that can be just as distressing.
By delving into the underlying causes, recognizing key symptoms, and exploring effective management strategies, parents can empower themselves with the knowledge needed to support their children through these trying moments.
This article aims to illuminate the differences between meltdowns and panic attacks, providing essential insights and practical tools to foster a nurturing environment for emotional growth and resilience.
Defining Autism Meltdowns and Panic Attacks
Autism episodes signify profound emotional reactions usually provoked by overwhelming stimuli, disruptions in routine, or intense frustration. These episodes may manifest as behaviors such as screaming, crying, or physical aggression, often resulting from sensory overload or emotional distress. In contrast, panic attacks emerge as sudden episodes characterized by acute fear or discomfort, frequently accompanied by physical symptoms like heart palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
While both autism meltdowns vs panic attacks can be profoundly distressing for young individuals and their families, understanding their distinct underlying causes is vital for effective management. For instance, a 2017 study indicated that children with private insurance exhibited a prevalence rate of 2.07% for this condition, emphasizing the importance of tailored approaches for these experiences. Significantly, the absence of considerable difference in ASD prevalence by race/ethnicity further emphasizes the need for tailored approaches in addressing the condition.
Recent research investigating the fascinating link between neurodevelopmental disorders and testosterone levels may also affect behavioral results, indicating that hormonal elements could contribute to the severity and occurrence of emotional outbursts. Recognizing these differences not only aids parents in addressing their child's needs but also fosters a more supportive environment for their emotional well-being. Additionally, insights from the case study titled 'Understanding Autism Therapy and Assessment Procedures' illustrate effective management strategies for behavioral outbursts, enhancing practical guidance for parent advocates.
Key Symptoms: Autism Meltdowns vs. Panic Attacks
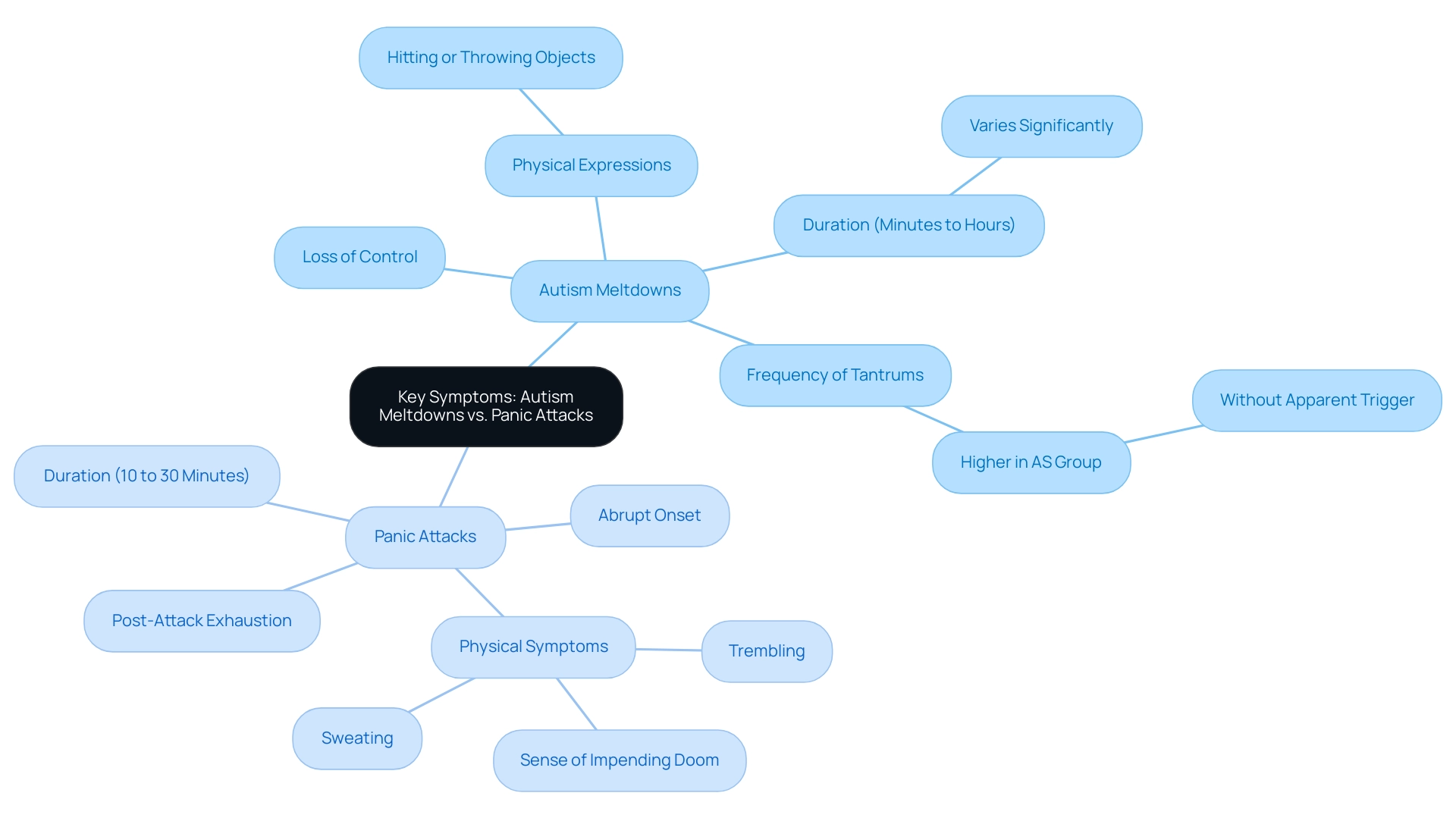
Understanding the key symptoms of autism episodes is crucial for parents and advocates, especially when distinguishing between autism meltdown vs panic attack. These breakdowns often manifest as a loss of control, making effective communication nearly impossible. Physical expressions can include hitting or throwing objects, which serve as a release for overwhelming emotions.
Research indicates that meltdowns can vary significantly in duration, lasting anywhere from a few minutes to several hours. In fact, statistics show that the AS group had a significantly higher frequency of tantrums without an apparent trigger (U = 880, p = 0.032, r = -0.22), highlighting the unpredictability of these episodes. In contrast, the differences between an autism meltdown vs panic attack are marked by an abrupt onset of intense fear or discomfort, frequently accompanied by physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling, or a profound sense of impending doom.
While panic attacks are typically shorter in duration, lasting between 10 to 30 minutes, they can leave young individuals feeling drained and exhausted afterward. Current findings suggest that understanding the distinct features of episodes like autism meltdown vs panic attack is essential for caregivers. A case study titled 'Comparison of Temper Tantrums in Autistic and Non-Autistic Youth' found no significant differences in the frequency, duration, or impact of tantrums between the two groups, emphasizing that both autistic and non-autistic individuals experience tantrums similarly.
This knowledge enables parents to better support their offspring through these challenging moments, fostering a more empathetic and informed approach to their care. As Juergen Hahn, an Academic Editor, notes, understanding these distinctions is vital for effective intervention.
Understanding Triggers: What Causes Meltdowns and Panic Attacks?
Common triggers for autism meltdown vs panic attack often stem from sensory overload, transitions between activities, or unexpected changes in routine. Research indicates that approximately 60% of young individuals experience tantrums daily, highlighting the prevalence of these emotional responses. A case study titled 'Prevalence and Behavioral Profile of Temper Tantrums in Autistic Individuals' reveals that the frequency, duration, and perceived parental impact of tantrums do not significantly differentiate between autistic and non-autistic individuals with other clinical diagnoses.
Furthermore, for many individuals on the spectrum, environments characterized by loud noises or bright lights can significantly heighten anxiety, leading to intense emotional reactions. As noted by experts at Leaf Complex Care, the inability to filter and regulate incoming sensory information can provoke anxiety, stress, and an intense emotional response, ultimately resulting in an outburst. Additionally, research involving 48 autistic preschoolers and 47 preschoolers with other neurodevelopmental conditions emphasizes the need for tailored approaches to managing these emotional responses.
On the other hand, when examining autism meltdown vs panic attack, it can be noted that panic attacks can be triggered by various factors including stress, anxiety, or specific phobias. Situations that evoke feelings of helplessness or a loss of control are often precursors to these attacks. Comprehending these unique triggers is essential for parents, enabling them to create effective strategies to assist their children in navigating these challenging situations, fostering a greater sense of understanding and encouragement within the family dynamic.
Effective Management Strategies for Meltdowns and Panic Attacks
When managing an autism crisis, it is important to understand the differences between an autism meltdown vs panic attack, as several strategies can be highly effective. Creating a calm environment, utilizing visual supports, and implementing sensory breaks are crucial components that can significantly ease the situation. Patience and reassurance are essential during a crisis, as they help the young one feel secure and understood.
Recent research indicates that parents reported a posttest mean aggression score of 13.11 (SD 6.21) after employing these strategies, showcasing their potential effectiveness. Additionally, teacher-reported aggression shows a slight decrease in the treatment group, further supporting the positive impact of these strategies. Insights from therapists emphasize the importance of understanding emotional states, with one expert stating,
Parents gained sociological insights into public order and disorder,
which can guide them in their responses.
Furthermore, recent tips shared on supporting siblings of kids with autism highlight the importance of a supportive family environment, which can also contribute to effectively managing the differences between autism meltdowns vs panic attacks. Grounding techniques, deep breathing exercises, and cognitive-behavioral strategies are essential tools that help individuals regain control during an episode. Encouraging young individuals to articulate their feelings and providing a safe space for emotional processing can significantly alleviate anxiety.
Recent advancements in panic attack management techniques emphasize the importance of these strategies, enabling parents to support their offspring effectively. Case studies, including those from the Attention-Based Intervention for Aggression in Individuals with ASD, demonstrate how increased awareness of emotional states can lead to improved behavioral functioning and enhance the quality of life for youth. This intervention focuses on reducing aggressive behavior through parental psychoeducation, which aligns with the goal of equipping parents with effective management strategies.
By combining effective strategies for both autism meltdown vs panic attack, parents can empower themselves and their children to navigate these emotional crises with confidence.
The Importance of Support: Caregivers and Professional Help
Support systems are essential for effectively managing autism meltdowns vs panic attacks, with caregivers, therapists, and peer networks playing pivotal roles. Caregivers offer not only emotional encouragement but also practical assistance, helping individuals navigate challenging situations. A recent study emphasizes that mothers frequently indicate a greater number of assistance needs than fathers; however, fathers may encounter unmet needs because services are mainly concentrated on mothers.
This highlights the necessity for all caregivers to access comprehensive assistance systems that address their unique challenges. Professional help, including counseling and therapeutic interventions, delivers tailored strategies that empower individuals to cope with their specific circumstances. Therapeutic methods, including Applied Behavior Analysis and Occupational Therapy, have demonstrated effectiveness in providing assistance that addresses the varied needs of individuals with developmental disorders.
The significance of these assistance systems is further emphasized by the alarming statistic that 10% of individuals who died by suicide were likely to have undiagnosed autism, highlighting the critical need for early intervention and aid. Moreover, joining assistance groups allows parents to engage in meaningful conversations, share experiences, and learn from one another, creating a robust sense of community. As Laura Lee McIntyre articulately notes, 'Understanding these variables may help professionals guide families in access to and use of social support.'
Ultimately, embracing both community and professional resources fosters resilience in the face of autism meltdowns vs panic attacks, ensuring that individuals and their families are equipped to thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities surrounding autism meltdowns and panic attacks is essential for fostering a supportive environment for children. As outlined, autism meltdowns typically arise from sensory overload or changes in routine, leading to intense emotional responses that require careful management. In contrast, panic attacks present sudden episodes of acute fear, often accompanied by physical symptoms. Recognizing the distinct triggers and symptoms of each can empower parents and advocates to respond more effectively during these challenging moments.
Effective management strategies play a crucial role in addressing both meltdowns and panic attacks. Creating a calm environment, utilizing visual supports, and employing grounding techniques are just a few methods that can help children navigate their emotions. Additionally, the importance of support systems cannot be overstated. Caregivers, therapists, and peer networks provide vital resources and encouragement, ensuring that families do not face these challenges alone.
Ultimately, equipping parents with knowledge and practical tools is key to promoting emotional growth and resilience in children. By understanding the unique nature of meltdowns and panic attacks, parents can foster a nurturing environment that supports their child's well-being, paving the way for a brighter future filled with understanding and compassion.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are autism episodes and what triggers them?
Autism episodes signify profound emotional reactions typically provoked by overwhelming stimuli, disruptions in routine, or intense frustration. These episodes may manifest as behaviors such as screaming, crying, or physical aggression, often resulting from sensory overload or emotional distress.
How do panic attacks differ from autism episodes?
Panic attacks emerge as sudden episodes characterized by acute fear or discomfort, frequently accompanied by physical symptoms like heart palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness. In contrast, autism episodes are often linked to emotional distress due to sensory overload or disruptions.
Why is it important to distinguish between autism meltdowns and panic attacks?
Understanding the distinct underlying causes of autism meltdowns and panic attacks is vital for effective management. This knowledge helps parents and caregivers address their child's needs appropriately and fosters a supportive environment for their emotional well-being.
What do recent studies indicate about the prevalence of autism?
A 2017 study indicated that children with private insurance exhibited a prevalence rate of 2.07% for autism, highlighting the importance of tailored approaches for managing these experiences. Additionally, there is no significant difference in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) prevalence by race or ethnicity.
How do autism meltdowns manifest physically?
Autism meltdowns often manifest as a loss of control, making effective communication nearly impossible. Physical expressions can include hitting or throwing objects, which serve as a release for overwhelming emotions.
How long do autism meltdowns typically last?
Meltdowns can vary significantly in duration, lasting anywhere from a few minutes to several hours. Research shows that the frequency of tantrums without an apparent trigger is notably higher in individuals with autism.
What are the typical durations of panic attacks?
Panic attacks are typically shorter in duration, lasting between 10 to 30 minutes, but can leave individuals feeling drained and exhausted afterward.
What similarities exist between tantrums in autistic and non-autistic individuals?
A case study found no significant differences in the frequency, duration, or impact of tantrums between autistic and non-autistic youth, indicating that both groups experience tantrums similarly.
How can understanding these distinctions help caregivers?
Recognizing the differences between autism meltdowns and panic attacks enables caregivers to better support their children during challenging moments, fostering a more empathetic and informed approach to care.




