Overview
Understanding autism prevalence in the U.S. is crucial for many families. As of 2025, approximately 1 in 36 children are diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This statistic is not just a number; it reflects a significant increase over the years, a change driven by improved diagnostic criteria and greater awareness.
For parents, this increase can be concerning. It highlights the importance of recognizing and addressing demographic disparities in diagnosis and support services. Every child deserves the best possible support, and understanding these challenges is the first step toward making a difference.
We encourage you to share your experiences and thoughts on this topic. Together, we can foster a community of support and understanding, ensuring that every child with ASD receives the care and resources they need.
Introduction
The increasing prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has drawn the attention of researchers, healthcare professionals, and families, revealing a complex tapestry of statistics, definitions, and societal implications. As awareness grows, so does our understanding of how various factors—ranging from demographic disparities to environmental influences—shape the landscape of autism diagnoses.
This article explores critical aspects of autism prevalence, including:
- Historical trends
- The vital role of early diagnosis
- The challenges families face while navigating support systems
By examining these elements, we can better understand not only who is affected by autism but also the urgent need for effective advocacy and resources to improve outcomes for individuals on the spectrum. Together, let’s delve into this important conversation and seek ways to support those in need.
Understanding Autism Prevalence: Key Definitions and Concepts
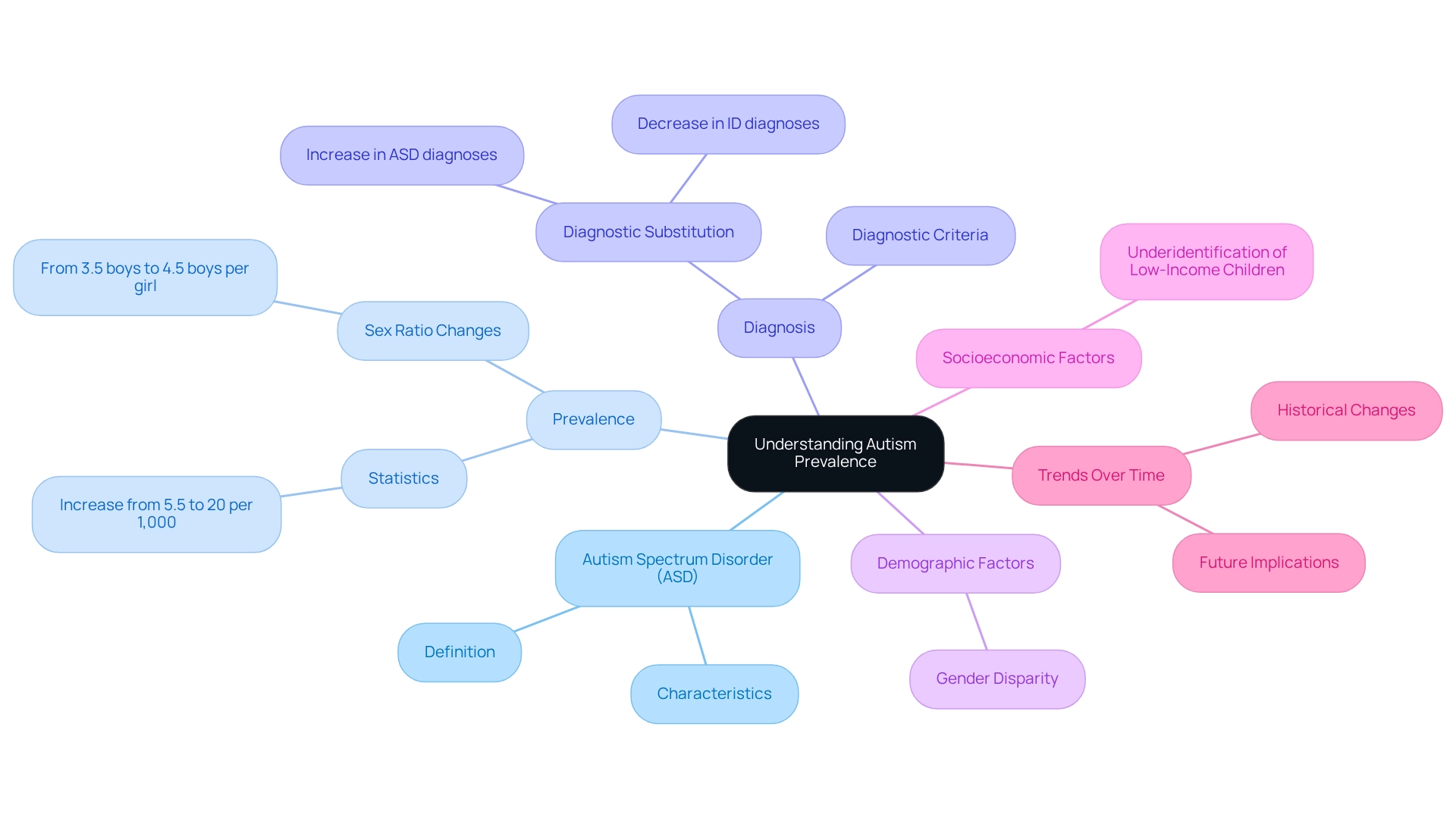
Understanding the prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) begins with clarifying key terms such as 'spectrum disorder (ASD)', 'prevalence', and 'diagnosis'. Autism spectrum disorder encompasses a variety of neurodevelopmental conditions characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. Prevalence refers to how often a condition occurs within a specific population, typically expressed as a percentage or ratio.
Diagnosis involves identifying ASD based on established criteria from diagnostic manuals, which help healthcare professionals recognize the disorder. Recent statistics reveal a concerning rise in autism and developmental disorder identifications in the U.S. For instance, the National Survey of Children's Health reported an increase in developmental disorder cases from 5.5 per 1,000 children in 2003-2004 to 20 per 1,000 by 2011-2012. This upward trend underscores the importance of understanding the nuances of these conditions, particularly regarding demographic factors.
Interestingly, the sex ratio of ASD prevalence has changed significantly, shifting from 3.5 boys for every girl in 2000 to 4.5 boys for every girl by 2010. This shift indicates a growing disparity in diagnosis between genders, which is a crucial point for parents to consider.
Additionally, it is vital to acknowledge the socioeconomic factors that influence the identification of this condition. Research suggests that low-income children with ASD may be underidentified and less likely to receive necessary services compared to their higher-income peers. This disparity can have lasting effects on access to support and intervention, complicating the landscape of autism identification and occurrence.
A poignant quote from Williams AR emphasizes the importance of understanding these trends: "Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years — Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020." This highlights the need for ongoing research and awareness in the field.
Real-world examples illustrate how diagnostic criteria impact prevalence rates. A significant case study reveals a phenomenon known as diagnostic substitution, where an increase in ASD diagnosis corresponds with a decrease in intellectual disability (ID) diagnosis. Data from special education services and SSI indicate that children previously classified with ID may now be more frequently diagnosed with ASD, affecting service eligibility and identification processes.
In summary, comprehending the definitions and implications of autism prevalence in the U.S. is essential for understanding the broader context of ASD. This knowledge not only informs advocacy efforts but also enhances the ability to navigate the complexities of diagnosis and support services related to developmental disorders. As we continue to learn and adapt, let’s foster a community of understanding and support for those affected by these challenges.
Current Statistics: How Many People Are Affected by Autism in the US?
As of 2025, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that approximately 1 in 36 children in the United States is recognized with a spectrum condition (ASD). This statistic raises important concerns about how many people in the US have autism. It signifies a significant rise from prior years, reflecting not only a greater awareness but also enhanced diagnostic methods. Notably, the disparity in prevalence rates between genders is striking; about 1 in 24 boys are diagnosed with ASD, compared to just 1 in 100 girls.
Males are identified with developmental disorders 4.2 times more frequently than females. This may be linked to factors such as symptom concealment in females, leading to postponed or overlooked evaluations, as highlighted by Wiley Online Library. These statistics emphasize the vital need for heightened awareness and accessible resources for families navigating the complexities of developmental disorders. It is essential that they obtain the assistance necessary to promote their children's growth and well-being. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that 36.5% of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders utilize ABA therapy, underscoring the importance of effective interventions in light of rising diagnosis rates.
Understanding the expenses related to services for individuals on the spectrum is crucial. For instance, adaptive behavior services average around $82.25, which is important for families to consider in their financial planning. By being informed about these costs, families can better manage their resources and seek necessary assistance.
Historical Trends: The Evolution of Autism Prevalence Over the Years
Over the last twenty years, we have witnessed a significant rise in developmental disorders, raising important questions about the prevalence of autism in the U.S. In the early 2000s, the estimated prevalence was around 1 in 150 children, prompting ongoing inquiries into how many people in the U.S. have autism. This figure notably increased to 1 in 110 by 2010, and by 2020, it escalated further to 1 in 54, deepening our curiosity about this condition.
This rise can be attributed to several key factors:
- The refinement of diagnostic criteria
- Heightened awareness among healthcare professionals
- Improved screening practices
These advancements not only reflect an increasing awareness of neurodevelopmental disorders but also signify a broader understanding of the various conditions related to them.
Experts emphasize that this increase is not merely a reflection of more individuals being diagnosed; it also represents a shift in societal perceptions and understanding of autism. For instance, Dr. Mary Doherty, a consultant anesthetist, shares how her son's diagnosis illuminated her own experiences, highlighting the personal journeys that accompany these statistics.
Moreover, historical case studies reveal that changes in diagnostic criteria have significantly influenced statistics related to autism. As definitions have expanded, more individuals have been recognized as being on the spectrum, leading to further inquiries about how many people in the U.S. have autism and contributing to rising prevalence rates. This development in understanding resonates with the sentiment expressed by Harvey C. Jenkins: 'It is OK to be different,' underscoring the importance of honoring the unique characteristics of individuals on the spectrum.
It is essential to recognize that every person on the spectrum is unique and deserves celebration. This perspective is beautifully illustrated by humorous quotes from individuals on the spectrum, reflecting their experiences in a light-hearted manner. Such quotes foster a sense of community and acceptance, showing that individuals with developmental differences can embrace their uniqueness and find joy in their distinctive traits.
Ultimately, the historical trends regarding how many people in the U.S. have autism not only provide us with figures but also invite us to reflect on the individual narratives and experiences that lie behind them. This fosters a sense of community and acceptance, encouraging us all to share our stories and support one another.
Demographic Insights: Who is Most Affected by Autism?
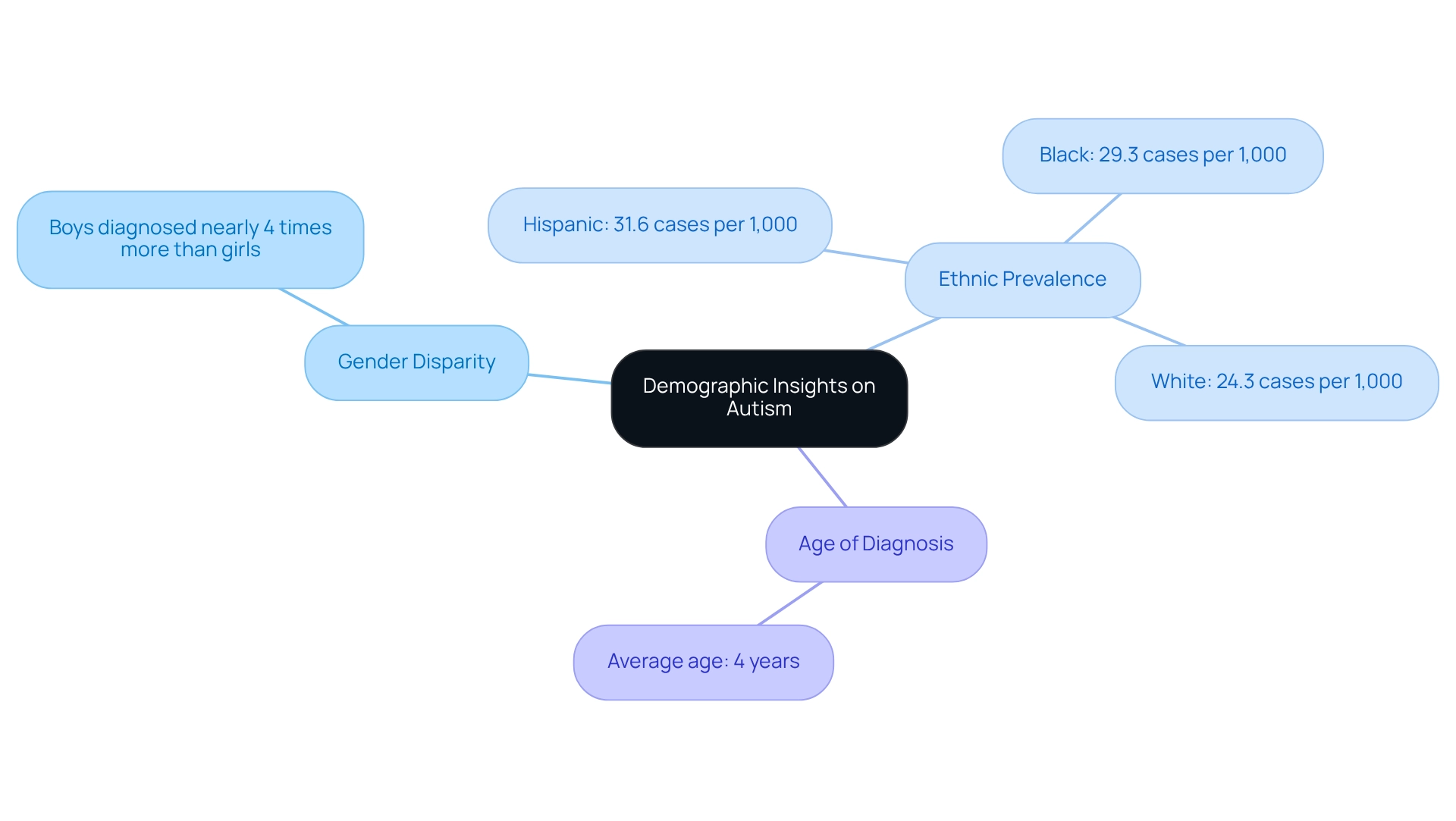
Demographic studies illustrate significant disparities in autism occurrence across various groups, a reality that many parents may find concerning. Notably, boys are diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) at a rate nearly four times higher than that of girls, underscoring a critical gender disparity in diagnosis. Moreover, recent statistics reveal that occurrence rates vary significantly by ethnicity and socioeconomic status, which can impact families in different ways.
For instance, Hispanic youth display a prevalence rate of 31.6 cases per 1,000, while Black youth have a rate of 29.3 per 1,000, in contrast to 24.3 per 1,000 for White youth. This data highlights the growing acknowledgment of developmental disorder assessments among Black and Hispanic children, who often receive their evaluations at later ages compared to their White counterparts. The average age for diagnosis is 4 years, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention for all children, regardless of background.
Additionally, findings from the CDC study indicate that many adults with ASD remain unidentified, illustrating the ongoing need for awareness and support in diagnosing and providing services. Understanding these demographic factors is crucial for developing effective support systems and advocacy efforts that are responsive to the unique needs of diverse communities. By tackling these disparities, we can strive for fairer access to resources and services for all individuals impacted by the condition. This aligns with ASD Media's mission to empower parents and professionals in their advocacy efforts, creating a community where everyone feels supported and understood.
Exploring Causes: What Contributes to Autism Prevalence?
Understanding the factors contributing to developmental disorders can feel overwhelming, but it’s essential to know that you're not alone. The complexities of these conditions are still being unraveled, yet studies reveal that genetic elements play a significant role in the risk of these disorders. For instance, children with a sibling diagnosed with the condition often face a heightened risk of developing it themselves. A pivotal study from 2007 highlighted the potential influence of maternal genetics, suggesting that certain genetic haplotypes, such as the GSTP1*A haplotype, might increase the likelihood of developmental disorders when combined with maternal factors during pregnancy.
This insight underscores the importance of maternal genetics in understanding the risks associated with developmental disorders. However, it’s not just genetics at play; environmental factors also significantly contribute to the prevalence of these conditions. Consider the impact of:
- Prenatal exposure to specific medications
- Complications during birth
- Overall health of the mother during pregnancy
All these elements can affect the likelihood of a child receiving a diagnosis related to autism spectrum disorders.
Additionally, societal changes, such as heightened awareness and evolving diagnostic standards, have led to an increase in autism diagnoses in the US. According to the World Health Organization's Comprehensive Mental Health Action Plan 2013–2030, addressing the gaps in early detection, care, treatment, and rehabilitation for mental and neurodevelopmental conditions is crucial for improving outcomes for families affected by these challenges.
As noted by Daniel H. Geschwind, MD, PhD, in Neurodevelopmental Disorders, grasping both genetic and environmental factors is vital for understanding the occurrence of these conditions. This knowledge not only informs ongoing research but also supports initiatives aimed at enhancing outcomes for individuals and families navigating these complexities. If you’re seeking support or resources, please consider reaching out to local organizations or online communities—together, we can foster understanding and compassion in this journey.
Implications of Rising Rates: What It Means for Families and Society
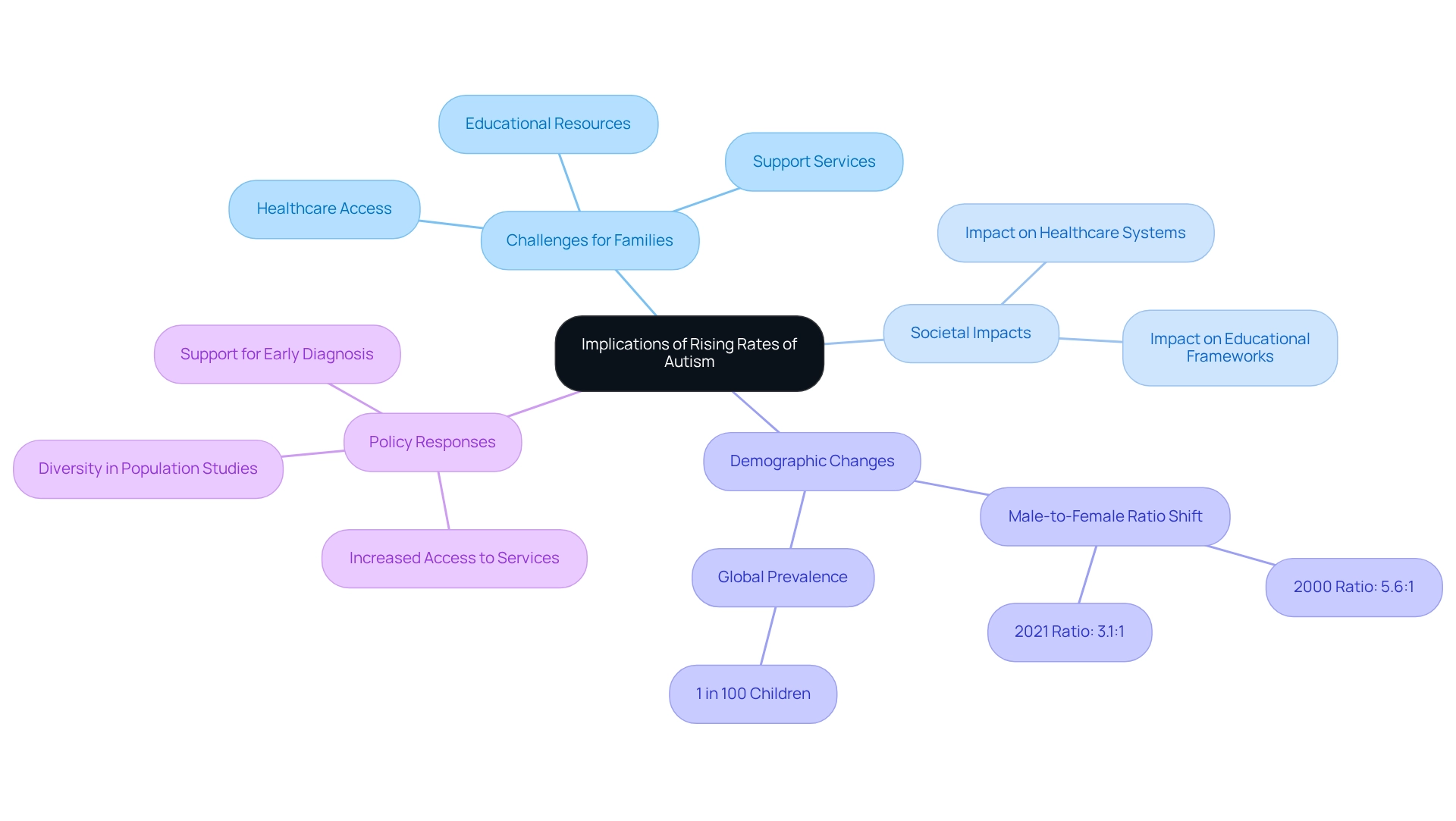
The rising occurrence of autism presents profound implications for families and society at large. Families are facing increased challenges in securing appropriate healthcare, educational resources, and support services. As the number of children identified with autism continues to rise, so too does the demand for trained specialists in both healthcare and education sectors.
This situation calls for a strong response from policymakers to ensure that the needs of this growing population are met. Fair access to services and support systems is vital for fostering inclusion and improving the quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum.
Statistics reveal a significant shift in the male-to-female ratio among adults diagnosed with autism, changing from 5.6:1 in 2000 to 3.1:1 in 2021. This suggests a broader acknowledgment of the condition across genders. Such changes highlight the importance of expanding population data collection, as advocated by the Autism Society, which emphasizes the need for increased diversity in the populations studied. Christopher Banks, President and CEO of the Autism Society of America, stresses the urgency of this issue, noting that while advancements in identification are noteworthy, they underscore the essential need for improved access to quality supports and services at both federal and state levels.
The urgency of this demand is particularly pronounced as families navigate the challenges posed by rising rates of developmental disorders, especially regarding autism.
Globally, it is estimated that approximately 1 in 100 youngsters has autism, prompting inquiries about how many people in the US are affected, and emphasizing the necessity for thorough support systems. Real-world examples illustrate the challenges families face daily. For instance, the significance of early diagnosis and intervention cannot be overstated; experts advocate for supportive measures to commence before the age of three to significantly enhance cognitive, social, and communication skills.
Implementing strategies such as speech therapy and personalized education plans has been shown to improve developmental outcomes for children on the spectrum. As families navigate these complexities, the implications of increasing rates of developmental disorders extend beyond individual households, impacting healthcare systems and educational frameworks, thereby necessitating a collective response to foster a supportive environment for all.
The Role of Early Diagnosis: Improving Outcomes for Individuals with Autism
Recognizing autism early is vital for enhancing the lives of those affected. Research shows that children diagnosed by the age of 2 can significantly benefit from early intervention programs, which help improve their social, communication, and behavioral skills. These interventions can lead to remarkable improvements in their developmental journeys, empowering them to thrive both academically and socially.
As a parent, if you suspect your child may be experiencing developmental delays, reaching out for evaluations and support as soon as possible can truly make a world of difference. Early action is not just beneficial; it can be transformative for your child's future.
Resources for Parents: Navigating Autism Support and Advocacy
Navigating the spectrum environment can be challenging for parents, but there is a wealth of resources available to support them. Organizations such as Autism Speaks and the Autism Society provide comprehensive guides, advocacy tools, and support groups tailored to the needs of families. In 2025, these organizations continue to play a crucial role in shaping policies and systems that address individuals with developmental disorders and their families.
As noted by the National Autism Association, they strive to change policies and systems to better cater to individuals with autism and their families. Local community resources, including autism centers and support networks, offer personalized assistance that can significantly enhance a family's advocacy efforts. For instance, case studies highlight the effectiveness of using shaping principles to reinforce positive changes in school collaboration. Acknowledging and expressing gratitude to school personnel for their collaboration not only inspires them but also cultivates a stronger relationship that benefits the student.
This aligns with the findings of Julie Lounds Taylor, who noted that group-based programs can lead to increases in advocacy ability for parents of youth with autism. Online platforms and forums serve as invaluable spaces for parents to connect, share experiences, and access critical information. These digital communities enable families to advocate effectively for their offspring's needs. Strategies for advocacy involve requesting Individualized Education Program (IEP) meetings and carefully recording communications with school staff, which can result in better outcomes for students.
Statistics indicate that the CSA helps assess the skill levels of students with developmental disorders starting at age 12, highlighting the importance of early intervention and support in relation to how many people in the US have autism.
Support groups for parents of children with developmental disorders are increasingly vital, with many families reporting enhanced advocacy skills and confidence through participation. By leveraging these resources, families can navigate the complexities of autism support more effectively, ensuring their children receive the necessary assistance on their journey.
Conclusion
The examination of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) prevalence reveals essential insights into the factors that influence diagnosis and support. Historical data demonstrates a significant rise in autism diagnoses, largely due to increased awareness and improved diagnostic practices. This trend highlights the urgent need for continued education and advocacy to ensure individuals on the spectrum receive the necessary resources.
Demographic disparities are apparent, particularly in gender and socioeconomic status. Boys are diagnosed with autism at a much higher rate than girls, and children from diverse ethnic backgrounds often face delays in receiving diagnoses. Addressing these disparities is vital for enhancing early detection and ensuring equal access to services.
The rising prevalence of autism carries significant implications for families and society as a whole. As the demand for trained professionals grows, it is crucial for policymakers to prioritize comprehensive support systems. Early diagnosis plays a key role in improving outcomes, emphasizing the importance of prompt evaluations and interventions for families.
Numerous resources are available to assist families navigating autism support. Advocacy organizations offer vital information and foster community connections, empowering parents to advocate effectively for their children’s needs. By utilizing these resources, families can enhance their efforts to ensure that children with autism thrive.
In summary, a collective commitment to understanding autism prevalence and addressing the challenges faced by individuals and families is essential. Through awareness, advocacy, and effective support, society can foster an inclusive environment that celebrates the unique strengths of individuals on the spectrum.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) encompasses a variety of neurodevelopmental conditions characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
What does the term 'prevalence' mean in the context of ASD?
Prevalence refers to how often a condition occurs within a specific population, typically expressed as a percentage or ratio.
How is ASD diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves identifying ASD based on established criteria from diagnostic manuals, which help healthcare professionals recognize the disorder.
What recent statistics indicate about the prevalence of autism in the U.S.?
Recent statistics reveal a concerning rise in autism and developmental disorder identifications, with the National Survey of Children's Health reporting an increase in developmental disorder cases from 5.5 per 1,000 children in 2003-2004 to 20 per 1,000 by 2011-2012.
How has the sex ratio of ASD prevalence changed over the years?
The sex ratio has changed from 3.5 boys for every girl in 2000 to 4.5 boys for every girl by 2010, indicating a growing disparity in diagnosis between genders.
What socioeconomic factors influence the identification of ASD?
Research suggests that low-income children with ASD may be underidentified and less likely to receive necessary services compared to their higher-income peers, affecting access to support and intervention.
What does the term 'diagnostic substitution' refer to in the context of ASD?
Diagnostic substitution refers to a phenomenon where an increase in ASD diagnosis corresponds with a decrease in intellectual disability (ID) diagnosis, affecting service eligibility and identification processes.
What is the current prevalence of ASD among children in the U.S. as of 2025?
As of 2025, the CDC reports that approximately 1 in 36 children in the United States is recognized with a spectrum condition (ASD).
How does the prevalence of ASD differ between genders?
About 1 in 24 boys are diagnosed with ASD, compared to just 1 in 100 girls, indicating that males are identified with developmental disorders 4.2 times more frequently than females.
What percentage of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders utilize ABA therapy?
Approximately 36.5% of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders utilize ABA therapy.
What are the average costs related to services for individuals on the spectrum?
Adaptive behavior services average around $82.25, which is important for families to consider in their financial planning.




