Overview
Microarray genetic testing serves as a vital resource for families navigating the complexities of developmental delays and health conditions. This powerful tool identifies genetic variations, offering insights that can guide meaningful interventions and support. As technology advances, the accuracy and accessibility of these tests continue to improve, which is empowering for parents and advocates alike. With this knowledge, families can make informed decisions regarding their children's health and well-being.
The growing importance of microarray genetic testing in clinical practice cannot be overstated. It not only provides clarity but also fosters hope for many families facing uncertainties. Imagine being able to pinpoint the genetic factors that may be influencing your child's development. This understanding can lead to tailored support and interventions, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
As you explore the possibilities that microarray genetic testing offers, consider how it can transform your family's journey. If you have experiences or questions about genetic testing, we invite you to share them in the comments or through our newsletter. Together, we can build a supportive community that empowers families to advocate for their children's health.
Introduction
In the intricate world of genetics, microarray genetic testing emerges as a groundbreaking tool that illuminates the subtle variations within our DNA. This advanced technique not only aids in detecting chromosomal abnormalities but also plays a pivotal role in diagnosing developmental delays and intellectual disabilities.
As more families turn to this testing method, its significance in understanding complex health conditions, especially in children, continues to grow. Recent advancements have enhanced both its accuracy and accessibility, transforming the landscape of genetic diagnostics and providing families with vital insights that guide their care decisions.
This article explores the nuances of microarray genetic testing, delving into its methodology, the implications of results, and the ongoing need for additional testing. It also emphasizes the importance of community support for families navigating these challenges, inviting readers to share their experiences and seek guidance together.
What is Microarray Genetic Testing?
Microarray genetic testing represents a groundbreaking laboratory technique that can detect subtle variations in DNA, including deletions or duplications of chromosome segments. This innovative testing method unveils hereditary abnormalities linked to developmental delays, intellectual disabilities, and various health conditions. By examining thousands of genes simultaneously, microarray genetic testing offers a comprehensive overview of a person's hereditary profile, helping to identify potential health concerns that traditional assessment techniques might overlook.
In recent years, the use of DNA analysis has surged, with approximately 1 in 10 children undergoing this evaluation annually. This increase reflects a growing acknowledgment of its critical role in diagnosing conditions such as autism spectrum disorders and other developmental disabilities. Notably, a study revealed that exome sequencing yielded positive outcomes in 47% of cases (7 out of 15; 95% CI: 21%, 74%), highlighting the effectiveness of genetic analysis in uncovering underlying causes of developmental delays.
Recent advancements in chip technology have significantly enhanced the utility of this testing. For instance, the 2025 updates in evaluation methodologies have improved accuracy and reduced turnaround times, making it a more accessible option for families seeking answers. Real-world experiences illustrate the profound impact of microarray genetic testing; families have shared how it has provided crucial insights into their children's conditions, leading to tailored interventions and support strategies.
Case studies from 2025 emphasize the ongoing need for research to address existing evidence gaps regarding the clinical utility of hereditary tests for developmental disabilities. The Technical Brief summarizes these gaps and guides future research, underscoring the importance of connecting test results to patient-centered outcomes. This ensures that families receive actionable information that can inform their care decisions.
Experts in the field advocate for the advantages of array analysis, emphasizing its role in providing insight and guidance for families navigating the challenges of developmental delays. Geneticists assert that microarray genetic testing is now recognized as the standard for diagnosing patients with global developmental delays and intellectual disabilities. As noted by Moeschler & Shevell: "CMA is now the standard for diagnosis of patients with GDD/ID, along with other conditions, such as autism spectrum disorders or multiple congenital anomalies." This statement highlights the validity and significance of array-based analysis in this important conversation.
In summary, microarray genetic testing serves as an invaluable resource for parents and advocates, offering a means to understand the hereditary factors that may influence a child's development. Its importance lies not only in identifying abnormalities but also in empowering families with knowledge that can lead to improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life. If you are a parent seeking answers, consider exploring microarray genetic testing as a pathway to understanding your child's unique needs.
How is Microarray Testing Conducted?
Microarray DNA analysis begins with the careful gathering of a DNA sample, which can be obtained through a blood draw, saliva, or tissue sample. This initial step is crucial, as the quality of the sample directly impacts the precision of the findings. Once collected, the sample is sent to a specialized laboratory where advanced technology is used to analyze the DNA.
In the laboratory, the patient's genetic material is compared with a reference sample, meticulously detecting any chromosomal imbalances that may be present. The average processing time for obtaining results from array analysis typically ranges from a few weeks. However, this timeframe can vary depending on the laboratory's workload and the complexity of the analysis. Once the evaluation is complete, healthcare providers play a vital role in discussing the findings with the family, ensuring that the implications of the results are clearly understood.
A significant aspect of this analysis is its ability to identify chromosomal imbalances in approximately 15-20% of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This statistic underscores the importance of array analysis in providing insights that can guide further interventions and support. Additionally, the projected incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of chromosomal array analysis (CMA) compared to karyotype evaluation highlights the economic significance of this analysis method in clinical practice.
In a recent case study titled 'Reporting Array Analysis Results,' the importance of thorough reporting was emphasized. The study stressed that clear communication of both normal and abnormal findings is essential for effective clinical interpretation and patient management. It also noted that the limitations of the test should be clearly indicated, as these can influence the interpretation of findings and subsequent choices.
Importantly, the study's retrospective nature and small group sizes may affect the interpretation of its findings, which is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the results.
As the field of hereditary analysis evolves, the latest methods in microarray assessment are continuously being refined. Experts advocate for standardized protocols in DNA sample collection to enhance the reliability of findings. By adhering to a structured approach, healthcare professionals can ensure that families receive the most accurate and actionable information possible, ultimately empowering them in their journey with autism and related challenges.
Types of Samples Used in Microarray Testing
Microarray testing offers a variety of sample types, each with its own unique advantages and considerations that can significantly impact families:
- Blood Samples: These are the most common choice for genetic testing, largely due to their ease of collection and the ample DNA they provide for analysis. In clinical environments, blood samples are especially preferred as they yield reliable results and are well-established in evaluation protocols.
- Saliva Samples: Increasingly recognized as a viable alternative, saliva samples are particularly beneficial for children who may feel anxious or uncomfortable during blood draws. This non-invasive option can make the collection process easier and more accessible for families, fostering a sense of comfort.
- Tissue Samples: While less common, tissue samples are utilized in specific circumstances where blood or saliva cannot be obtained. These samples can provide essential hereditary information, particularly in complex cases where other sample types may not suffice.
As we look ahead to 2025, the landscape of DNA analysis continues to evolve. The Genetic Analysis Registry (GTR) is being updated with new examination submissions and alterations. Notably, in the United States, a mere 10 of over 250 laboratories dominate the market, accounting for 81% of new genetic tests. This concentration underscores the importance of understanding the types of samples used in microarray genetic testing and their implications for diagnosis and treatment.
Expert opinions increasingly highlight the growing preference for saliva samples, especially among pediatric populations. Genetic counselors share that while blood samples remain the gold standard, saliva offers a practical alternative that can enhance patient comfort and compliance. Case studies illustrate successful outcomes utilizing both blood and saliva samples, showcasing their effectiveness in various assessment scenarios.
As the number of hereditary tests expands, the need for mandatory reporting to the GTR becomes increasingly critical. This will help clarify the landscape of assessments and ensure that families have access to the most relevant and effective options available. Furthermore, recent research emphasizes the significance of worldwide cooperation in DNA analysis, indicating that understanding the global environment of DNA examinations is essential as the quantity of assessments continues to rise.
As Giovanni Montana observes, "A distinct type of regression model that has been recently created to investigate these interactions is the logic regression," highlighting the continuous progress in this field that can influence testing methodologies.
We encourage families to stay informed and engaged in this evolving landscape, sharing their experiences and seeking support as needed.
Interpreting Microarray Test Results: What Do They Mean?
Microarray test results are generally classified into three primary categories, each carrying distinct implications for families:
- Normal Results: These results indicate that no significant chromosomal abnormalities were detected, providing reassurance to families that the tested individual does not have identifiable genetic issues.
- Pathogenic Results: This category suggests the presence of a genetic alteration that may be associated with specific health conditions. Understanding these findings is essential, as they can guide families toward suitable medical interventions and support services.
- Variants of Uncertain Significance (VUS): VUS findings indicate changes in the DNA that are not yet fully understood. Approximately 3.9% of microarray genetic testing results yield VUS, underscoring the need for further investigation and discussions with healthcare providers. These outcomes can be particularly challenging for families, as they may not provide clear answers but indicate the potential for future discoveries.
Healthcare providers play a vital role in helping families understand these outcomes, discussing the implications of pathogenic findings, and outlining potential next steps. For instance, if initial CMA findings are unfavorable, additional hereditary assessments may be recommended, especially if there are clinical signs or a family history suggesting a hereditary disorder. This approach can help families navigate the complexities of DNA analysis and ensure they receive the most accurate information available.
Recent advancements in DNA testing have significantly enhanced our understanding of microarray genetic testing outcomes. For example, the significance analysis of microarrays (SAM) method has successfully recovered 94.7% of differentially expressed genes, thereby improving the accuracy of interpretations in microarray genetic testing. As we approach 2025, ongoing studies in microarray genetic testing continue to enhance our understanding of pathogenic outcomes, providing families with clearer insights into their hereditary health.
Real-world examples illustrate the importance of accurately interpreting microarray genetic testing findings. In one case study, a family received unfavorable CMA results but later pursued further genetic analysis due to persistent clinical symptoms, ultimately leading to a diagnosis that significantly influenced their care strategy. Such scenarios highlight the necessity of thorough follow-up and the potential for uncovering critical health information through continued investigation.
Additionally, it is important to recognize that the yield of CMA analysis in prenatal microcephaly is lower than in postnatal cases, with rates of 4.6% versus 15%, respectively, emphasizing the significance of microarray genetic testing. This statistic highlights the disparities in assessment outcomes and the importance of the context of microarray genetic testing when interpreting findings. As Giovanni Ferrara noted, "The normalization process was performed using the simple linear model, as described previously," which underscores the methodologies that enhance the reliability of genetic testing outcomes.
Furthermore, the prediction analysis of microarrays (PAM) classifies samples based on gene expression profiles, and microarray genetic testing can assist in understanding the broader implications of VUS and other findings.
Understanding Negative or Normal Microarray Results
A negative or normal test result may suggest that no significant chromosomal abnormalities were detected. However, it’s important for parents to understand that this outcome does not completely rule out the possibility of an underlying hereditary condition. Research indicates that approximately 30% of hereditary conditions can remain undetectable through microarray genetic testing, which highlights the limitations of this diagnostic tool.
For instance, specific single-gene disorders or rare syndromes might not be identified, even when the array findings appear normal.
Given these limitations, it’s vital for parents to keep open lines of communication with their healthcare providers. If clinical symptoms persist despite a normal test result, further assessment may be necessary. Genetic advisors often emphasize the importance of considering additional examination options, such as microarray genetic testing and whole exome sequencing, which can offer a more thorough analysis of hereditary factors.
Furthermore, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) identifies chromosomal analysis (CMA) as a first-line test for children with intellectual disabilities of unknown origin, underscoring its significance in clinical practice. Real-life stories illustrate the challenges families face; there have been cases where children with significant developmental delays and autism spectrum disorders received typical findings, only to later be diagnosed with previously undetected hereditary conditions through more comprehensive evaluations. This highlights the necessity for vigilance and advocacy in the quest for a definitive diagnosis.
As noted by Moeschler & Shevell, "CMA is now the standard for diagnosis of patients with GDD/ID, as well as other conditions, such as autism spectrum disorders or multiple congenital anomalies." Ultimately, while a standard array outcome can provide some reassurance, it is essential for parents to remain proactive and informed, recognizing that further examination may be needed to uncover the full spectrum of potential hereditary conditions.
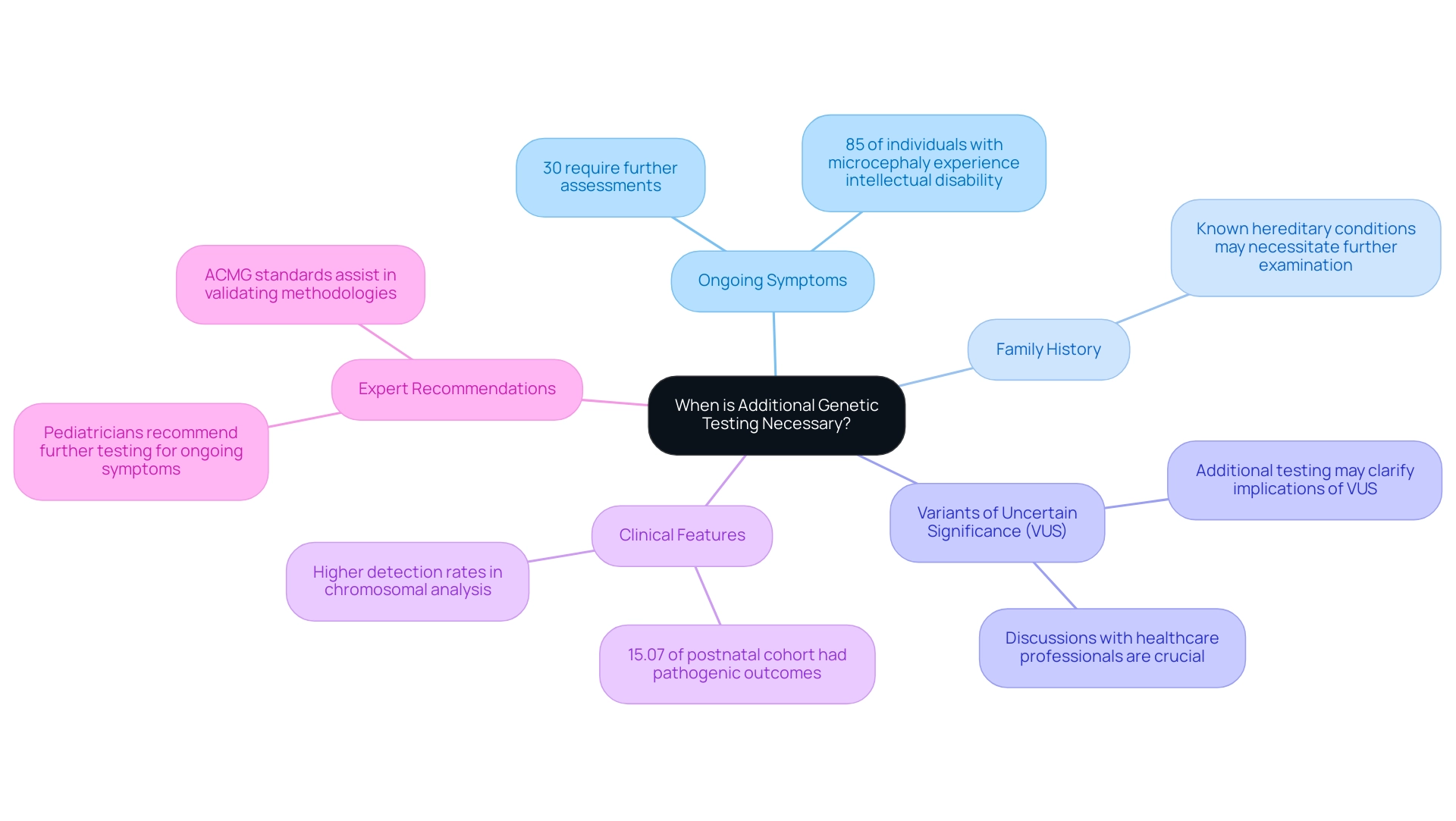
When is Additional Genetic Testing Necessary?
In various situations, further analysis may be necessary, particularly when certain signs become apparent:
-
Ongoing Symptoms: If a child continues to experience developmental delays or health issues, even with normal microarray results, additional examination is crucial. Research indicates that a significant number of children—up to 30%—might require further assessments, including microarray genetic testing, despite initial normal results, especially if they show persistent symptoms such as intellectual disability or microcephaly. Notably, 85% of individuals with microcephaly have faced intellectual disability, underscoring the importance of addressing ongoing symptoms.
-
Family History: If there is a known hereditary condition in the family, this may necessitate further examination. Understanding the family's hereditary landscape can provide valuable insights into potential risks and guide the evaluation process.
-
Variants of Uncertain Significance (VUS): When initial examination findings reveal VUS, additional testing may be required to clarify their implications. Engaging in discussions with healthcare professionals about these variants can help parents navigate the complexities of hereditary information and determine the most appropriate next steps.
-
Clinical Features: Certain clinical characteristics, such as dysmorphism or congenital heart malformations, are associated with higher detection rates in chromosomal analysis. For instance, a postnatal cohort examination found that 15.07% of cases presented pathogenic outcomes, highlighting the importance of considering clinical context when analyzing findings. Additionally, variability around breakpoints due to genomic structure should be noted, as it can influence the interpretation of hereditary testing results.
-
Expert Recommendations: Pediatricians often recommend further hereditary testing, like microarray genetic testing, when ongoing symptoms are observed, even after normal array results. As Lina Shao pointed out, the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics has established updated technical laboratory standards to assist clinical laboratories in validating chromosomal microarray methodologies. Their insights stress the significance of a thorough assessment to ensure that no underlying hereditary conditions are overlooked. Furthermore, identifying chimerism is essential in both constitutional and cancer samples, impacting data interpretation and the overall evaluation process.
In conclusion, the decision to pursue additional analysis should be a collaborative effort between parents and healthcare providers, taking into account the child's unique circumstances and any ongoing health challenges.
Types of Additional Genetic Tests and Their Importance
Navigating the complexities of DNA analysis for autism can feel overwhelming, but several additional assessments can provide a clearer picture of your child's hereditary profile. These include:
- Whole Exome Sequencing (WES): This advanced technique analyzes all coding regions of genes, allowing for the identification of mutations that may elude traditional microarray testing. Research suggests WES is especially efficient, revealing hereditary variants in many cases where array results are inconclusive. A systematic review conducted in December 2022 highlighted WES's superior diagnostic capabilities compared to traditional methods, particularly in cases involving congenital anomalies.
- Targeted Gene Panels: These panels focus on specific genes known to be associated with particular conditions. By honing in on these genes, targeted panels provide a more detailed analysis, which can be essential for diagnosing hereditary disorders that broader evaluation methods might miss.
- Chromosomal Karyotyping: This method examines the number and structure of chromosomes, helping to identify larger chromosomal abnormalities. While gene chip analysis excels at identifying smaller genetic changes, karyotyping remains crucial for detecting significant chromosomal alterations. It's important to note that only 1.08% of cases with normal chromosomal analysis (CMA) showed abnormalities on chromosomal examination, underscoring the limitations of this testing and the importance of additional tests.
Each of these tests plays a vital role in complementing the results of microarray genetic testing, ultimately aiding in a more accurate diagnosis. The significance of these additional hereditary tests cannot be overstated, especially as advancements in research continue to evolve. For instance, the prevalence of WES and targeted gene panels is on the rise, reflecting their growing recognition as essential tools in the diagnostic process.
In 2025, the integration of whole exome sequencing and targeted gene panels is increasingly regarded as a standard procedure in evaluating autism. Real-life examples illustrate their effectiveness; geneticists emphasize that WES, in particular, is championed for its cost-effectiveness and diagnostic breadth, making it a first-tier strategy for children suspected of having rare diseases. As Mario Cesare Nurchis stated, "This study champions WGS over WES as a first-tier diagnostic strategy for its cost-effectiveness, especially for children with suspected rare diseases."
As parents and advocates, understanding these options empowers you to engage in informed discussions with healthcare providers, ensuring your child receives the most comprehensive hereditary evaluation possible. Moreover, the presence of specific phenotypes can guide clinicians to suggest more intensive analysis, further highlighting the necessity for a comprehensive approach to evaluation.
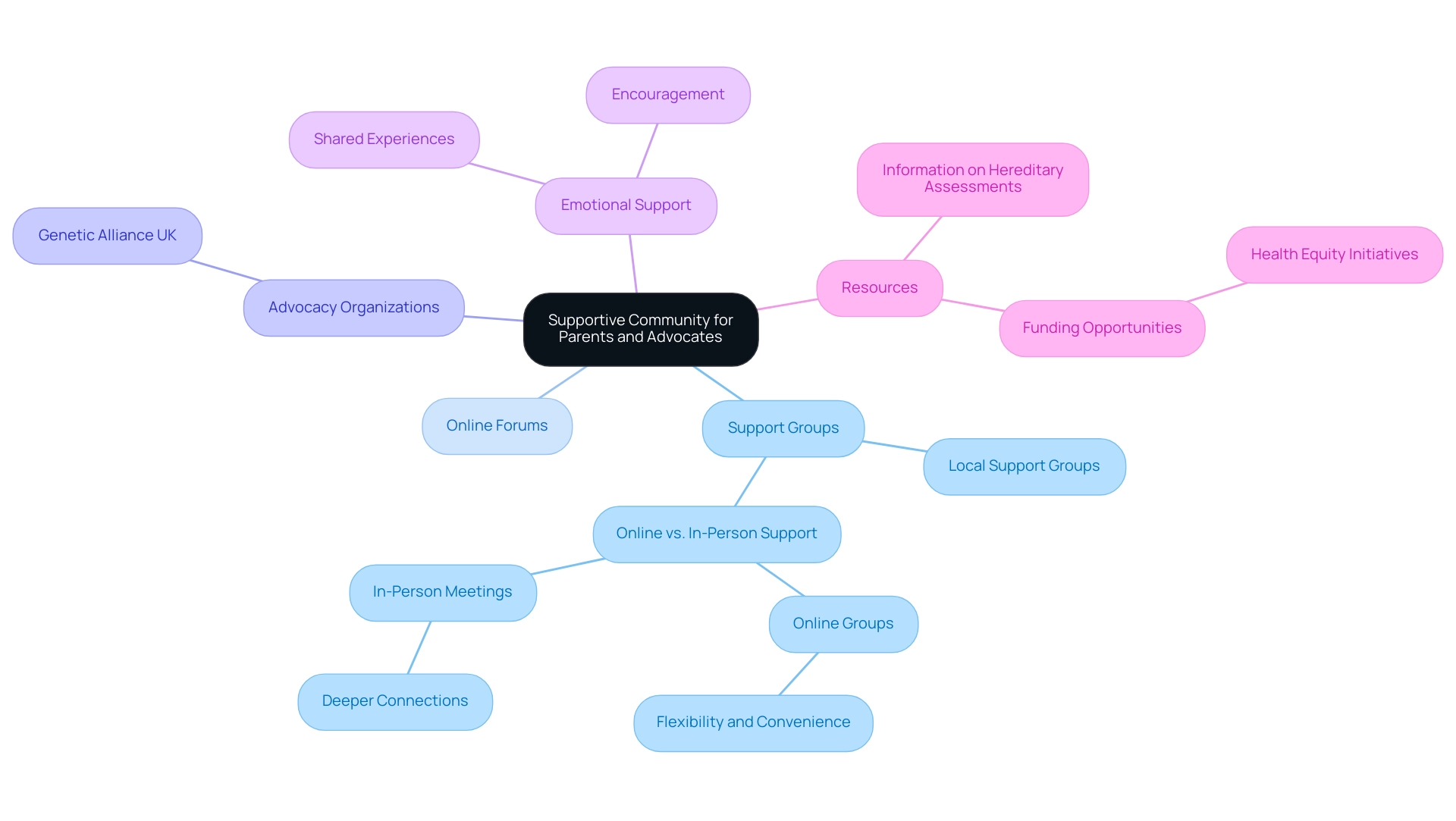
Building a Supportive Community for Parents and Advocates
Establishing a nurturing community is essential for parents and supporters as they navigate the intricacies of DNA analysis. Local support groups, online forums, and advocacy organizations dedicated to hereditary conditions serve as invaluable resources. These communities not only provide a platform for sharing personal experiences but also facilitate access to essential resources and emotional support.
Engaging with others who face similar challenges can significantly empower parents, enhancing their ability to advocate effectively for their child's needs while fostering a profound sense of belonging.
Research indicates that participation in support groups can lead to improved mental health outcomes for parents. Studies show that 70% of participants report feeling less isolated and more informed after joining such communities. For instance, families in the U.S. can choose between online and in-person support groups. While online groups offer flexibility and convenience, in-person meetings often foster deeper connections and a stronger sense of community, as highlighted in the case study titled "Online vs. In-Person Support Groups."
Expert opinions underscore the importance of these networks. Advocates highlight that support groups not only offer emotional encouragement but also function as a venue for exchanging essential information about hereditary assessments and available resources. As Ashley Dalton, Parliamentary Under Secretary of State for Health and Social Care, noted, "The strength of our community lies in our shared experiences and the support we provide each other," praising organizations like Genetic Alliance UK for their role in fostering these connections.
To build a supportive community for parents of children with hereditary conditions, it is essential to create inclusive spaces where individuals can share their stories and access vital information. This can be achieved through regular meetings, workshops, and online discussions that encourage participation and collaboration. By fostering these connections, parents can enhance their advocacy efforts, ensuring they are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of microarray genetic testing and support their children's needs effectively.
Additionally, current funding opportunities aimed at promoting health equity can further bolster these community initiatives, providing essential resources for parents and advocates.
Conclusion
Microarray genetic testing represents a significant advancement in the field of genetics, offering families critical insights into their children's health by identifying subtle genetic variations and chromosomal abnormalities. This innovative testing method plays a vital role in diagnosing developmental delays and intellectual disabilities, empowering families to make informed decisions about their care.
The journey begins with the collection of DNA samples and culminates in the interpretation of results that guide necessary medical interventions. While receiving normal results can offer reassurance, it is essential for families to remain vigilant, as approximately 30% of genetic disorders may go undetected. This reality underscores the importance of ongoing communication with healthcare providers and the possibility of further testing should symptoms persist.
Equally important is the support from the community for families navigating these challenges. Connecting with other parents and advocates can foster resilience, providing valuable resources and shared experiences that enhance advocacy efforts.
In conclusion, microarray genetic testing is more than just a diagnostic tool; it brings hope to families seeking clarity in genetic health. By understanding the testing process, acknowledging its limitations, and engaging in supportive communities, parents can confidently navigate this journey, striving for the best outcomes for their children.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is microarray genetic testing?
Microarray genetic testing is a laboratory technique that detects subtle variations in DNA, such as deletions or duplications of chromosome segments, and identifies hereditary abnormalities linked to developmental delays, intellectual disabilities, and various health conditions.
How does microarray genetic testing benefit families?
It offers a comprehensive overview of a person's hereditary profile by examining thousands of genes simultaneously, helping to identify potential health concerns that traditional assessment techniques might overlook.
What has contributed to the increase in DNA analysis among children?
Approximately 1 in 10 children undergo DNA analysis annually, reflecting a growing acknowledgment of its critical role in diagnosing conditions like autism spectrum disorders and other developmental disabilities.
What recent advancements have been made in microarray genetic testing?
Advancements in chip technology and evaluation methodologies have improved the accuracy and reduced turnaround times for results, making it more accessible for families.
What is the significance of the studies related to microarray genetic testing?
Studies emphasize the effectiveness of genetic analysis in uncovering underlying causes of developmental delays, with findings indicating positive outcomes in a notable percentage of cases.
How does microarray genetic testing impact the diagnosis of developmental disabilities?
Experts recognize microarray genetic testing as the standard for diagnosing patients with global developmental delays and intellectual disabilities, including conditions like autism spectrum disorders.
What is the process of microarray DNA analysis?
The process begins with collecting a DNA sample through a blood draw, saliva, or tissue sample, which is then analyzed in a specialized laboratory to detect chromosomal imbalances.
How long does it typically take to receive results from microarray genetic testing?
The average processing time for results typically ranges from a few weeks, but it can vary based on the laboratory's workload and the complexity of the analysis.
What percentage of individuals with autism spectrum disorder exhibit chromosomal imbalances identified by this analysis?
Chromosomal imbalances are identified in approximately 15-20% of individuals with autism spectrum disorder through microarray analysis.
Why is clear communication of test results important?
Clear communication of both normal and abnormal findings is essential for effective clinical interpretation and patient management, ensuring families understand the implications of the results.
What recommendations do experts have for enhancing the reliability of microarray testing?
Experts advocate for standardized protocols in DNA sample collection to improve the reliability of findings and ensure families receive accurate and actionable information.




