Overview
This article sheds light on the various types of stimming behaviors in individuals with autism, highlighting their vital role in self-regulation and emotional expression. Understanding these behaviors—whether they are vocal, visual, tactile, auditory, movement-based, or social—is essential for caregivers and professionals alike. By recognizing the significance of stimming, we can better support individuals in navigating their unique emotional landscapes.
Imagine a child who hums softly or flaps their hands in excitement. These actions are not merely quirks; they serve as important tools for self-soothing and communication. As caregivers, it’s crucial to appreciate these behaviors, as they can provide insight into the child’s feelings and needs.
By fostering an environment that acknowledges and respects stimming, we can create effective intervention strategies tailored to each individual's unique requirements. Let’s work together to ensure that every person receives the support they deserve, allowing them to thrive in their own way.
If you have experiences or thoughts on this topic, we encourage you to share them in the comments or through our newsletter. Your insights could help others on similar journeys, creating a community of understanding and support.
Introduction
In the intricate world of autism, stimming behaviors emerge as vital expressions of self-regulation and emotional communication. These behaviors, ranging from the rhythmic flapping of hands to the soothing repetition of phrases, play essential roles for individuals navigating sensory overload and emotional challenges. As awareness grows around the spectrum of stimming—from vocal and visual to tactile and auditory—understanding these behaviors becomes crucial for caregivers and professionals alike.
This article delves into the various forms of stimming, exploring their significance and impact on communication. It highlights the need for tailored interventions that respect individual sensory preferences. By fostering supportive environments and recognizing the unique needs of those with autism, caregivers can enhance emotional well-being and promote positive interactions. Ultimately, this empowers individuals to thrive in their daily lives. We invite you to join us in this exploration, sharing your experiences and insights as we work together to support those on the autism spectrum.
About ASD Media: Resources for Understanding Stimming in Autism
ASD Media is committed to enhancing the application of ABA therapy by providing essential resources that help parents and professionals understand the type of stimming behaviors in autism. Stimming, or a type of stimming known as self-stimulatory actions, is common among children with autism and serves crucial functions like self-regulation and sensory processing. Recent research indicates that incorporating adaptive skills into therapy programs can significantly improve social interactions, underscoring the importance of addressing these actions in therapeutic settings.
ASD Media offers a wealth of articles, guides, and community support designed to empower individuals in effectively managing sensory activities. For example, case studies demonstrate how ABA therapy can uncover functional alternatives to repetitive behaviors by recognizing individual sensory needs and crafting tailored intervention strategies. These approaches not only teach alternative actions but also enhance communication skills, leading to reduced reliance on self-stimulatory activities and an improved quality of life.
Ralph Moller emphasizes, "By focusing on the specific needs of the individual with autism, rather than just the diagnostic label, therapy can be adapted to address the individual's specific goals and promote progress." This perspective highlights the importance of personalized therapeutic approaches in understanding and managing a type of stimming related to repetitive actions.
Furthermore, ongoing initiatives are underway to secure affordable and comprehensive insurance coverage for autism therapy, which is vital for families seeking assistance. By subscribing to their newsletter, users can access the latest insights and strategies related to sensory activities and ABA therapy, ensuring they remain informed about advancements in the field, including the most recent studies on sensory activities in autism for 2025. This commitment to education and community support positions ASD Media as an invaluable resource for those looking to deepen their understanding of sensory behaviors in autism.
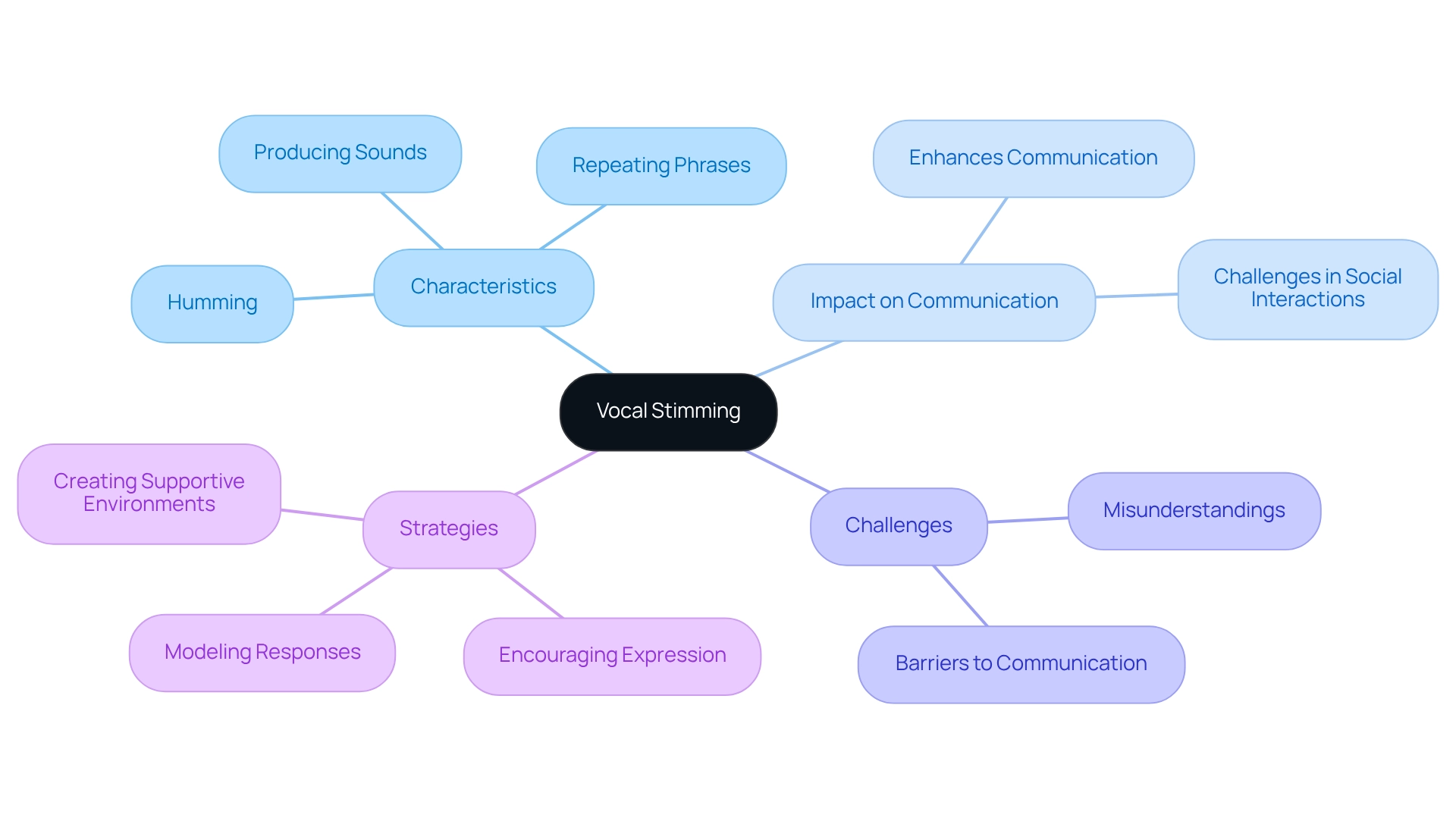
Vocal Stimming: Characteristics and Impact on Communication
Vocal self-soothing can take many forms, such as humming, repeating phrases, or producing various sounds. These vocalizations serve as both self-soothing mechanisms and emotional expressions. For many children with autism, research shows that vocal stimming, as a type of stimming, can significantly enhance communication, helping them connect in specific situations. However, this can also pose challenges in social interactions. Take echolalia, for instance—where individuals repeat words or phrases they’ve previously heard. This behavior can sometimes be misunderstood by peers and adults, creating potential barriers to communication.
Recent studies highlight the need to view echolalia as a complex phenomenon rather than simply a deficit. It plays a vital role in language development and social engagement. Understanding this perspective is crucial, as it aligns with findings suggesting that clinical training programs should incorporate insights from individuals with lived experiences, including various types of stimming. This helps deepen our understanding of these behaviors.
Moreover, the mirror neuron theory, despite facing criticism for its lack of empirical support, sheds light on the intricate communication challenges in autism, especially regarding echolalia. By grasping these behaviors, caregivers can implement effective communication strategies that honor each individual's unique needs, fostering positive interactions.
Strategies may include:
- Modeling appropriate responses
- Encouraging alternative forms of expression
- Creating supportive environments that nurture understanding and patience
Establishing effective therapeutic settings is essential for achieving better outcomes in autism treatment. It ensures that children who engage in vocal repetition receive the necessary support for their development, paving the way for meaningful connections and growth.
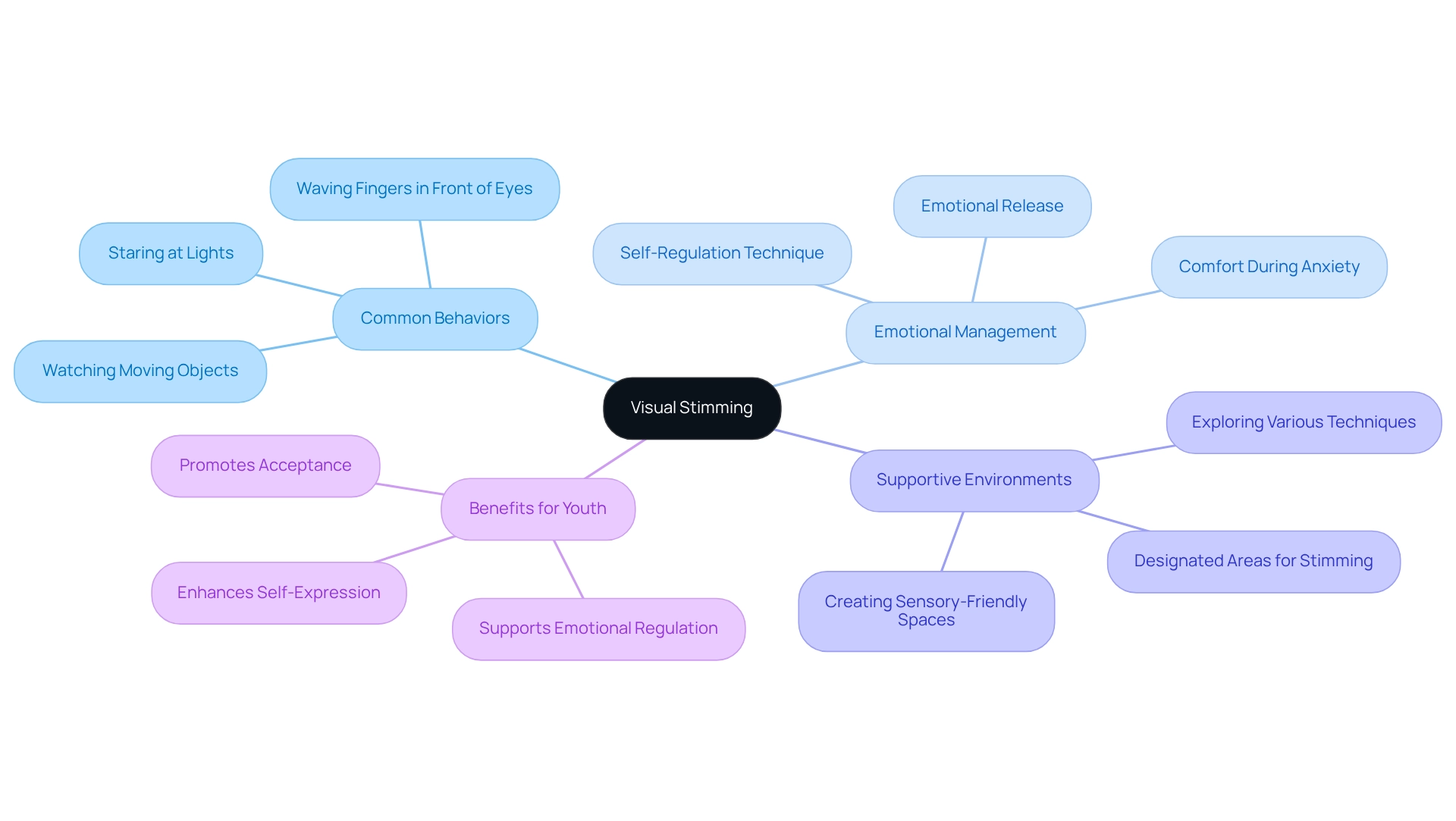
Visual Stimming: Understanding Its Role in Self-Regulation
Visual self-stimulation is a type of stimming that includes repetitive visual actions, such as gazing at rotating items or waving fingers in front of the eyes. Common behaviors include staring at lights and watching moving objects. These actions serve as essential tools for individuals to navigate sensory overload, providing comfort during overwhelming moments. For instance, a young person may engage in visual self-soothing during times of anxiety, utilizing it as a self-regulation technique. Research indicates that such actions can significantly aid in emotional management, with many young individuals finding solace in these repetitive practices.
Creating sensory-friendly spaces that nurture visual stimulation is crucial for fostering an inclusive environment. Designated areas where young individuals can safely engage in these behaviors can enhance self-expression and overall well-being. Case studies, such as 'Incorporating Visual Stimulation Positively,' have shown that embracing visual stimulation can positively impact emotional release and comfort, empowering individuals to manage their perceptual experiences more effectively.
Recognizing the benefits of visual self-soothing, which is a type of stimming, not only promotes acceptance but also aids in anxiety management for youth with autism. Valuing the diversity of perceptual experiences encourages understanding and acceptance of individuals who engage in visual self-soothing. By grasping the significance of these actions, parents and professionals can better support youngsters in their journey toward emotional regulation and processing stimuli. As Sonny Jane, a lived-experience educator, beautifully expresses, "Stimming can occur to communicate joy or excitement, serving as an extension of one's emotions.
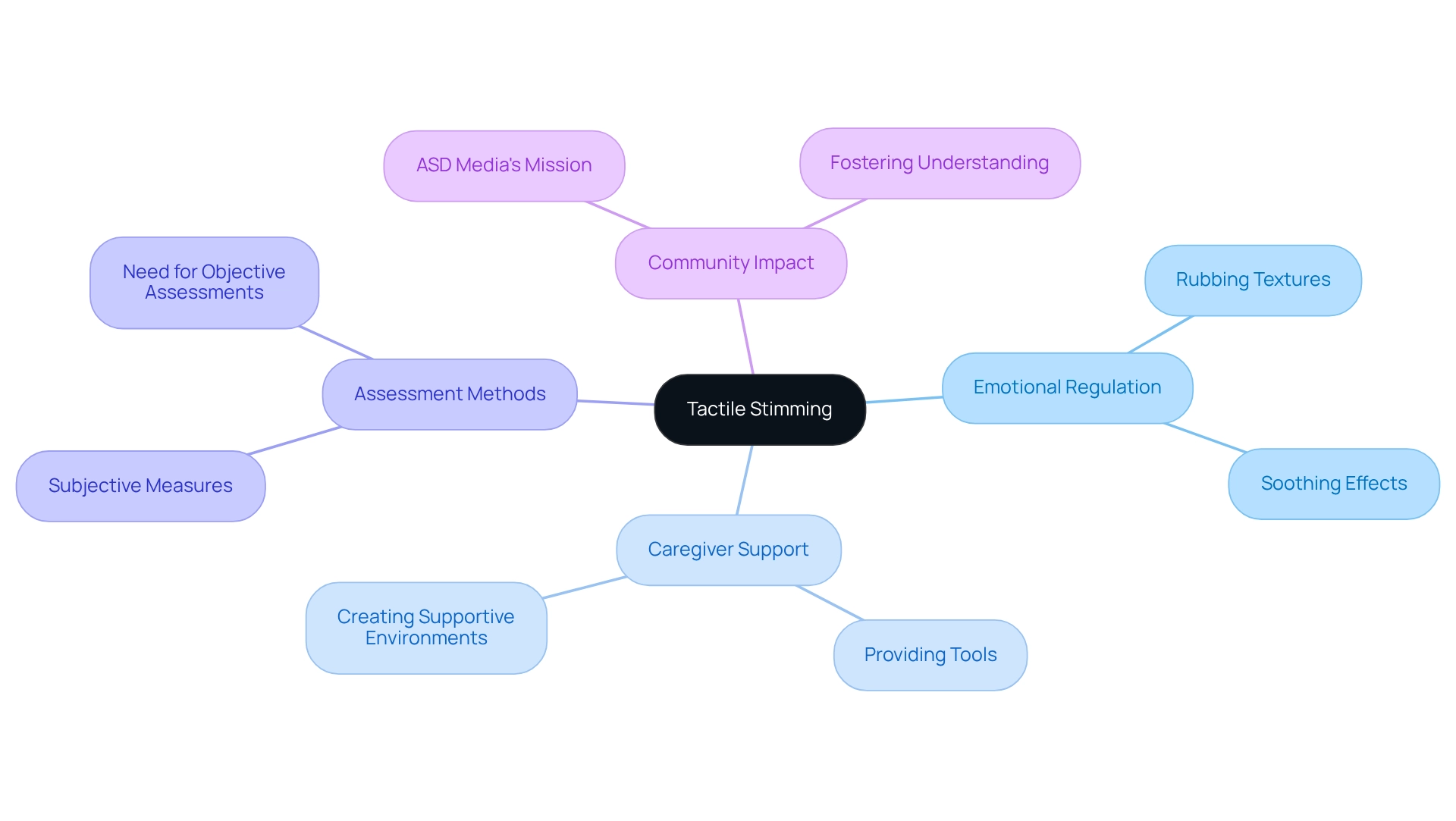
Tactile Stimming: Exploring Sensory Input and Self-Soothing
Tactile stimming is a type of stimming that includes actions such as rubbing, scratching, or exploring various textures, which serve as essential inputs for emotional regulation and anxiety management in children with autism. Research shows that perceptual deficits can be detected as early as six months in infants later diagnosed with autism, underscoring the early emergence of these behaviors. For instance, a child may rub a soft fabric to find comfort during stressful moments, demonstrating the soothing effects of tactile engagement, a specific type of stimming. Understanding the role of this type of stimming empowers caregivers to provide appropriate tools and activities that promote comfort and self-soothing. Sensory integration therapists highlight the significance of these behaviors, which can be considered a type of stimming, noting their potential to greatly influence emotional regulation and alleviate anxiety. As Sam Bankman Fried mentioned, while it remains unconfirmed whether he has autism, discussions around his neurodivergent traits shed light on the varied experiences of individuals on the spectrum.
Additionally, parent-reported measures have traditionally been used to assess symptoms related to perception in young individuals with ASD. However, these subjective evaluations may not fully capture the complexities of processing. This points to the need for more objective methods to accurately assess and understand processing challenges in ASD.
By integrating tactile stimuli tools, caregivers can cultivate nurturing environments that enhance emotional well-being and foster positive coping strategies for young individuals with autism. The mission of ASD Media—to improve the lives of youth with ASD and their families through home and community-based ABA therapy—aligns with the importance of recognizing and supporting a type of stimming, which includes tactile self-stimulatory behaviors. Together, we can create a more understanding and supportive community.
Auditory Stimming: The Influence of Sound on Behavior
Auditory self-stimulation encompasses repetitive sounds, such as humming, tapping, or vocalizations, which serve as vital tools for individuals navigating sensory overload and expressing their emotions. Imagine a child humming a beloved tune, seeking comfort amid chaos. As Vicky, a therapist, insightfully remarked, "Vicky knew what it would mean to him to have his song recorded," underscoring the profound emotional significance of sound in the lives of individuals with autism. Understanding the impact of auditory stimulation is crucial for caregivers, enabling them to craft effective strategies that assist individuals in managing their sensory experiences. By fostering an environment that acknowledges these behaviors, caregivers can enhance communication and emotional regulation, ultimately nurturing a sense of security and well-being.
Research indicates that auditory stimming is a type of stimming that can greatly influence actions and communication, providing a valuable channel for emotional expression. Implementing tailored strategies—like creating quiet spaces or integrating calming sounds—can effectively manage sensory overload and encourage positive interactions. Experts in the field emphasize that recognizing and affirming these auditory patterns is essential for cultivating a supportive environment that promotes growth and connection.
Moreover, the case study titled 'Family Support in Alan's Rehabilitation' illustrates how family involvement plays a crucial role in aiding individuals with auditory sensitivities, highlighting the importance of emotional support throughout their recovery journey. By embracing these insights and strategies, caregivers can make a meaningful difference in the lives of those they support.
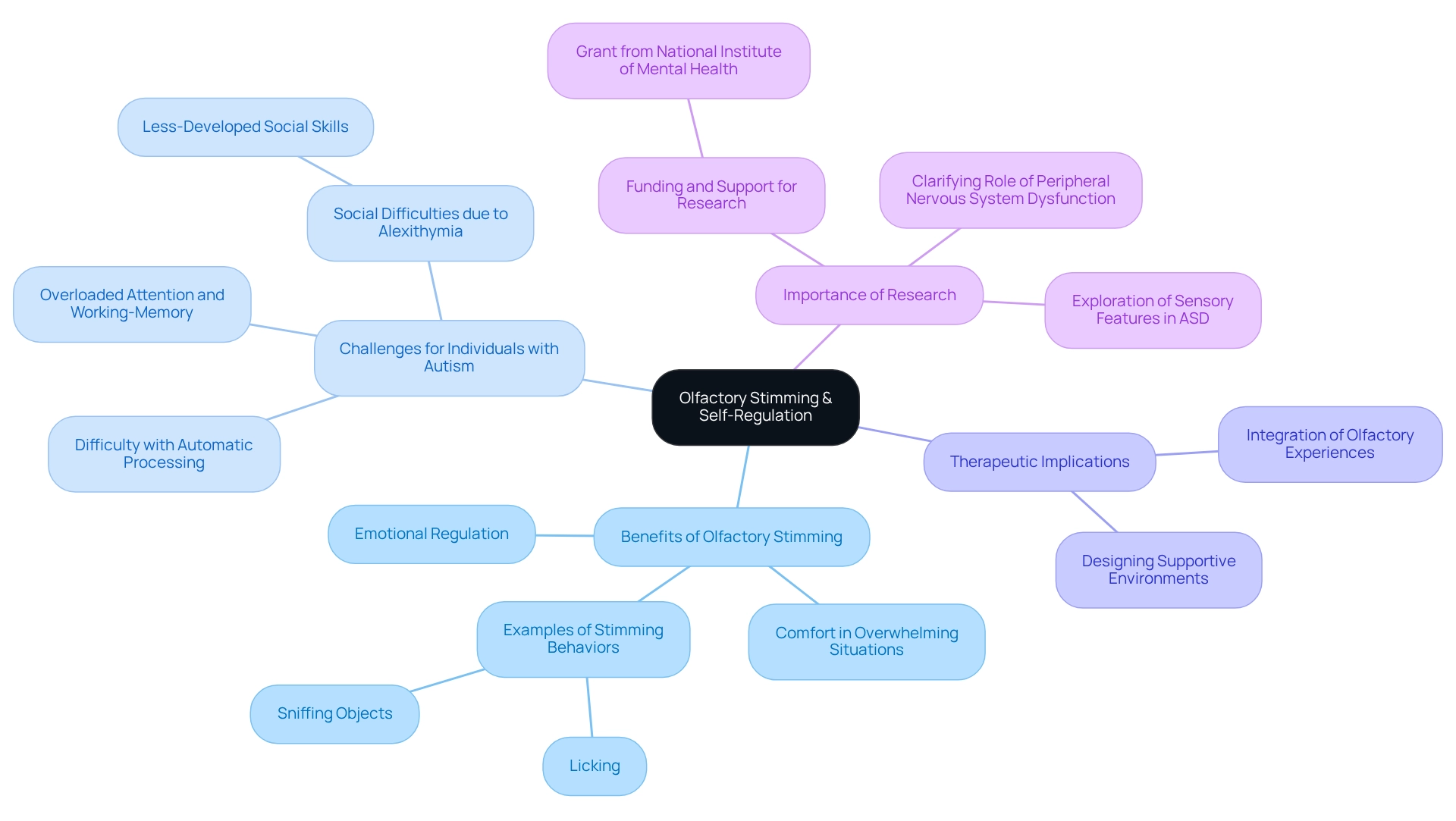
Olfactory Stimming: The Role of Scent in Self-Regulation
Olfactory stimming is a type of stimming that involves behaviors linked to the sense of smell, like sniffing objects or licking, which can be essential self-regulation tools for individuals with autism. These comforting actions help children navigate overwhelming situations. For example, a child might repeatedly sniff a favorite scent to find solace during stressful times.
Research indicates that children with autism may struggle to process information automatically, relying more on already taxed attention and working-memory networks. This makes sensory-related behaviors, such as olfactory self-soothing, a type of stimming that is particularly vital for emotional regulation. Recognizing the significance of this type of stimming through olfactory stimulation allows caregivers to create environments that cater to these needs, ultimately fostering emotional well-being. By designing spaces that support olfactory experiences, we not only enhance comfort but also promote positive emotional outcomes. This underlines the importance of ongoing exploration of sensory characteristics in autism research.
Experts stress that scent can play a pivotal role in self-regulation, highlighting the necessity of integrating olfactory experiences into therapeutic practices.
Furthermore, research by Scheerer et al. reveals that autistic individuals with alexithymia face additional social challenges, emphasizing the broader implications of processing difficulties. Continued funding and support for research in these areas are crucial for deepening our understanding and developing effective interventions. As we learn more, we can better support our loved ones, ensuring they have the tools they need for emotional and social success.
Movement-Based Stimming: Managing Sensory Overload Through Motion
Movement-based stimming is a type of stimming that includes behaviors like rocking, spinning, and jumping, which are essential for individuals to cope with sensory overload and seek comfort. For instance, a young person might rock back and forth during anxious moments, using this motion as a self-soothing mechanism. As Dorsey (R.) wisely notes, 'Using a neurodiversity-affirming model, we should never withhold a child’s special interest to gain compliance.' Recognizing the significance of these actions enables caregivers to create secure environments that foster movement-based self-soothing, ultimately enhancing emotional regulation and comfort.
Moreover, studies indicate that teaching deep breathing techniques can further assist individuals in managing their experiences and redirecting focus from vocal self-soothing. This underscores how various strategies can complement each other in navigating sensory overload. Insights from physical therapists also highlight the advantages of movement in autism therapy, suggesting that physical activity can play a crucial role in improving emotional regulation.
A compelling case study on Access to Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) reveals the necessity of providing robust communication systems for non-speaking students. Such systems empower them to express their needs effectively, without impeding their spoken language development. This aligns with the broader mission of fostering acceptance and inclusivity, ultimately leading to a more supportive society for individuals with autism, especially concerning the type of stimming that aids in managing sensory overload as we move into 2025. It emphasizes the need to integrate physical activity into therapeutic practices for children with autism. Additionally, the recent publication 'Transforming Lives: The Impact of ABA in Managing Self-Injury' highlights ongoing advancements in ABA therapy, further affirming the significance of these practices.
Social Stimming: Navigating Interactions Through Repetitive Behaviors
Social stimming is a type of stimming that includes repetitive actions, such as hand-flapping or bouncing, often observed during social interactions. These behaviors can be vital expressions of excitement or essential mechanisms for managing anxiety in social contexts. For instance, a child may flap their hands when joyfully reuniting with friends. Recognizing the significance of these social behaviors, particularly the type of stimming, is crucial for caregivers, as it enables them to foster positive interactions while honoring the individual's need for self-expression.
Research indicates that sensory overload can trigger these repetitive actions, often caused by loud sounds, intense smells, bright lights, or specific textures. This underscores the importance of creating supportive environments. As Level Ahead ABA emphasizes, "Arrange a consultation today and allow Level Ahead ABA to assist your young one in flourishing and achieving their utmost potential," highlighting the value of expert guidance in addressing these behaviors.
Moreover, a study titled 'Individual Variability in Stimming Responses' revealed that the type of stimming is a highly personalized response, shaped by individual history and context. By grasping the nuances of social behaviors, caregivers can better facilitate interactions that promote comfort and connection, ultimately enhancing the social skills development of children with autism. Level Ahead ABA also offers specialized programs tailored to meet the unique needs of autistic individuals, including a type of stimming, providing valuable resources for parents and caregivers.
Echolalia: Distinguishing Between Repetition and Stimming
Echolalia, the repetition of words or phrases previously heard, often occurs without full comprehension. This behavior can serve as both a means of communication and a self-soothing mechanism. For example, a young person might echo a line from a favorite television show when feeling anxious or overwhelmed. Recognizing echolalia as a type of stimming is crucial for caregivers, as it paves the way for personalized communication approaches that honor the individual’s unique needs.
Research shows that echolalia can significantly influence communication strategies in individuals with autism. The NIDCD suggests a standardized method for assessing language abilities in individuals with ASD, highlighting the importance of understanding echolalia within the context of communication development. Echolalia acts as a bridge for expressing thoughts and emotions, even when direct language skills are still maturing. By grasping the nuances of echolalia, caregivers can nurture more effective interactions.
Consider a case study on positive prompting, which illustrates how this approach can enhance emotional regulation in youth with autism. By using familiar expressions or cues, caregivers can help young individuals manage their emotions, leading to improved behavior and emotional resilience. This case study underscores the significance of echolalia in emotional regulation, providing a means for young people to articulate their feelings.
Moreover, insights from communication specialists stress the value of patience and adaptability when engaging with echolalic speech. Carrie, a speech-language pathologist, notes, "Sometimes, in order to progress with a young learner who doesn’t seem to be 'getting' language, we have to let go of our ideas of what language development should resemble." Caregivers should pay attention to the context in which echolalia occurs, as it can reveal important clues about the individual’s emotional state and communicative intent.
Ultimately, distinguishing echolalia from other types of stimming allows for a more nuanced understanding of a young person's behavior. This understanding fosters more effective communication strategies and enhances social interactions. Furthermore, ongoing advancements, such as software designed to assist individuals with ASD in articulating complex ideas, highlight the evolving resources available to improve communication in youth with autism.
Understanding the Spectrum of Stimming: Implications for Support and Intervention
Self-soothing behaviors in children with autism encompass a diverse range of expressions, including various types of stimming such as:
- Vocal
- Visual
- Tactile
- Auditory
- Movement-based
- Social forms
Each type of stimming serves distinct functions, including self-regulation, perception, or emotional expression. Visual self-soothing can involve repetitive movements or patterns that offer calming tactile feedback, while vocal self-soothing may include humming or repeating sounds that assist with emotional regulation.
Understanding the range of self-soothing actions, including different types of stimming, is essential for caregivers and experts. This knowledge enables them to offer customized assistance that honors each person's unique needs. Research shows that establishing a sensory-friendly environment—characterized by dim lighting and reduced loud sounds—not only improves the effectiveness of interventions but also directly supports the sensory preferences of individuals engaged in self-soothing activities. This connection highlights the importance of such environments as a strategy for enhancing overall support.
Expert insights emphasize that a type of stimming is not inherently harmful; rather, it is a valid means of self-expression and self-regulation. As one ABA therapist pointed out, "Stimming actions should be respected and understood as part of the individual's communication and coping strategies." This perspective reinforces the necessity for interventions that honor this type of stimming while providing appropriate assistance.
Case studies illustrate that applying focused strategies for different types of stimming can lead to enhanced communication skills and developmental progress. For instance, the case study 'Empowering Communication: Strategies to Support Children with Speech Delays' highlights early intervention techniques that can also be utilized for repetitive actions, showcasing a comprehensive approach to assistance that addresses both communication and perceptual needs.
By nurturing a welcoming atmosphere that recognizes the range of self-stimulatory behaviors, caregivers can empower individuals with autism to thrive and effectively manage their sensory experiences, including their type of stimming. It is crucial to acknowledge the challenges associated with visual stimming, as addressing both the benefits and challenges provides a more balanced view and aligns with the need for comprehensive support strategies. Ultimately, this approach enhances the overall quality of life for individuals with autism.
Conclusion
Understanding and supporting stimming behaviors in individuals with autism is essential for fostering emotional well-being and promoting positive interactions. By recognizing these behaviors as valid expressions rather than deficits, caregivers and professionals can create supportive environments that cater to individual sensory needs. The various forms of stimming—vocal, visual, tactile, auditory, movement-based, social, and olfactory—each serve distinct functions that aid in self-regulation and sensory processing.
Tailored interventions play a critical role in addressing the unique challenges associated with stimming. Implementing strategies that respect and honor these behaviors can enhance communication abilities and improve overall quality of life. Creating sensory-friendly spaces is particularly important, as these environments can significantly reduce anxiety and sensory overload, allowing individuals to thrive.
Ultimately, fostering a deeper understanding of stimming behaviors empowers caregivers to support individuals on the autism spectrum effectively. By embracing the spectrum of stimming and integrating insights from research and lived experiences, we can promote acceptance and inclusivity. Together, we can ensure that individuals with autism have the tools they need to navigate their sensory experiences and enhance their emotional regulation. Through collaboration and informed support, a brighter future awaits those on the autism spectrum.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stimming and why is it important for children with autism?
Stimming, or self-stimulatory actions, is common among children with autism and serves crucial functions like self-regulation and sensory processing. It is important as it helps children manage their sensory experiences and emotions.
How does ASD Media support understanding of stimming behaviors?
ASD Media provides essential resources, including articles, guides, and community support, to help parents and professionals understand stimming behaviors and manage sensory activities effectively.
What role does ABA therapy play in managing stimming behaviors?
ABA therapy can uncover functional alternatives to repetitive behaviors by recognizing individual sensory needs and crafting tailored intervention strategies, which enhance communication skills and reduce reliance on self-stimulatory activities.
What is the significance of personalized therapeutic approaches in autism therapy?
Personalized therapeutic approaches focus on the specific needs of the individual with autism, promoting progress and addressing specific goals rather than just the diagnostic label.
What initiatives are being undertaken regarding insurance coverage for autism therapy?
Ongoing initiatives are underway to secure affordable and comprehensive insurance coverage for autism therapy, which is vital for families seeking assistance.
How can individuals stay informed about advancements in sensory activities and ABA therapy?
Individuals can subscribe to ASD Media's newsletter to access the latest insights and strategies related to sensory activities and ABA therapy, including recent studies on sensory activities in autism.
What are vocal self-soothing behaviors, and how do they relate to communication in autism?
Vocal self-soothing behaviors include humming, repeating phrases, or producing various sounds. They can enhance communication but may also pose challenges in social interactions, such as echolalia, where individuals repeat words or phrases they've heard.
Why is it essential to understand echolalia in the context of autism?
Understanding echolalia as a complex phenomenon rather than a deficit is crucial because it plays a vital role in language development and social engagement.
What strategies can caregivers implement to support communication in children with vocal stimming?
Strategies include modeling appropriate responses, encouraging alternative forms of expression, and creating supportive environments that nurture understanding and patience.
What is visual self-stimulation and its significance for individuals with autism?
Visual self-stimulation involves repetitive visual actions, such as gazing at rotating items or watching moving objects, which serve as self-regulation techniques during overwhelming moments and can aid in emotional management.
How can sensory-friendly spaces benefit children engaging in visual self-soothing?
Creating sensory-friendly spaces allows young individuals to safely engage in visual self-soothing behaviors, enhancing self-expression and overall well-being.
What is the broader impact of recognizing the benefits of visual self-soothing?
Recognizing the benefits promotes acceptance and aids in anxiety management for youth with autism, encouraging understanding of their diverse perceptual experiences.




