Overview
Understanding self-stimulatory behavior, often referred to as stimming, is vital for parents and caregivers. These behaviors play significant roles, such as helping individuals with developmental disorders self-soothe and regulate their emotions. By recognizing and accepting these behaviors, you can provide better support for your child, enhancing their quality of life. This understanding fosters a more inclusive environment, allowing everyone to thrive.\n\nAs you navigate the challenges of parenting, remember that you are not alone. Many parents share similar experiences, and by connecting with others, you can gain valuable insights and support. Consider reaching out to local support groups or online forums where you can share your journey and learn from one another.\n\nUltimately, embracing and understanding stimming can lead to a more compassionate approach to caring for your child. Let’s work together to create a world where all children feel accepted and valued.
Introduction
In a world where understanding and acceptance of neurodiversity are becoming increasingly vital, self-stimulatory behavior, or "stimming," emerges as a significant aspect of the autistic experience. From hand-flapping to repetitive vocal sounds, stimming includes a variety of actions that serve essential functions, such as emotional regulation and sensory processing. Research shows that approximately 90% of children with autism engage in stimming, underscoring that these behaviors are not merely distractions but crucial expressions of communication and coping.
This article explores the multifaceted nature of stimming, delving into its various forms and purposes. It also highlights strategies caregivers can employ to foster a supportive environment. By promoting understanding and acceptance of stimming, we can empower individuals with autism, enhancing their quality of life and encouraging a more inclusive community. Together, let's embrace these expressions and support our loved ones on their unique journeys.
1. Name: What is Self-Stimulatory Behavior (Stimming)?
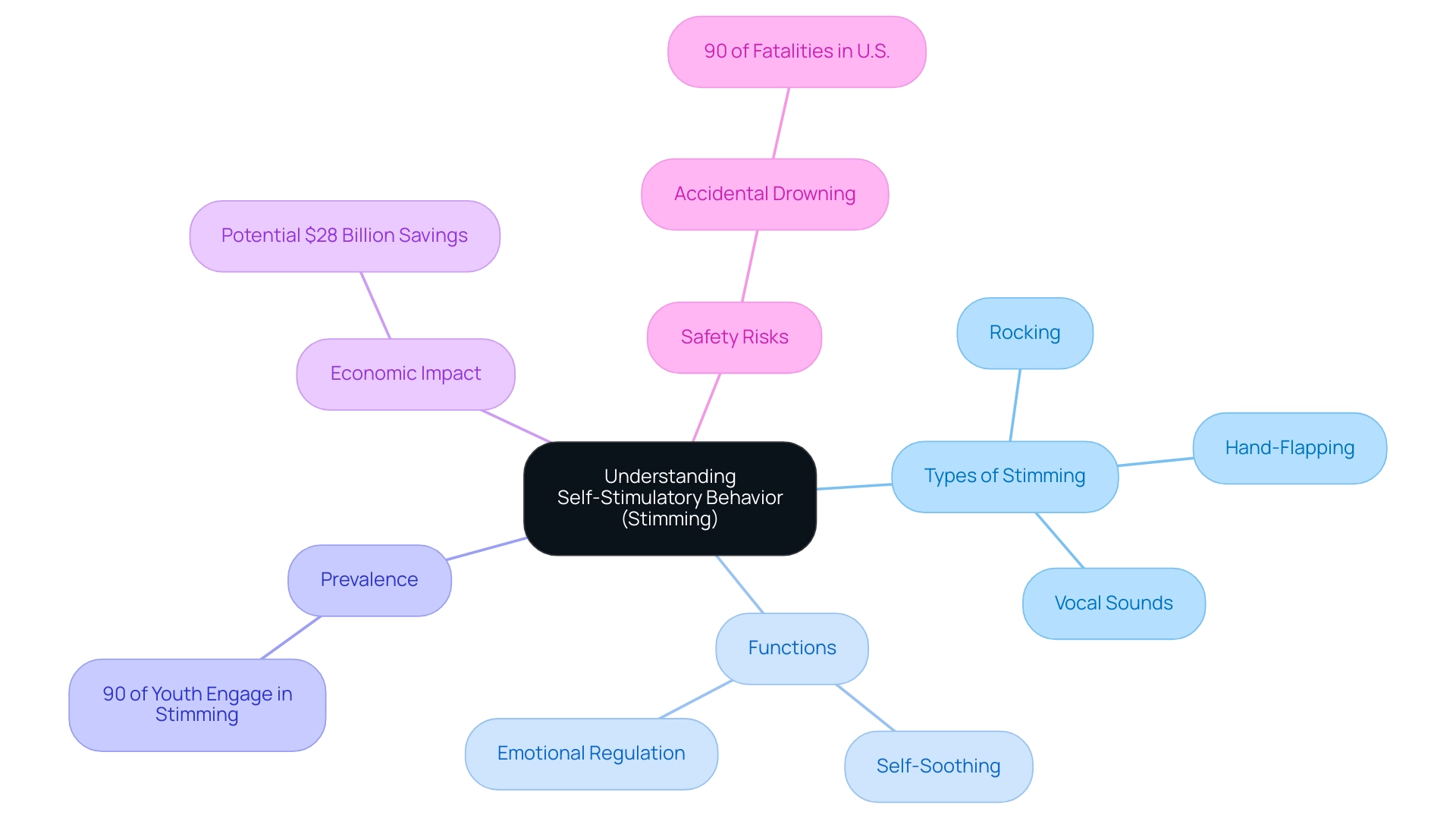
Self-stimulatory behavior, often referred to as 'stimming,' includes a variety of repetitive activities such as hand-flapping, rocking, or making vocal sounds. These behaviors are commonly observed in individuals with developmental disorders and serve important functions, including self-soothing and sensory regulation. Understanding self-stimulatory behavior is essential for parents and caregivers, as it provides valuable insight into their children's needs and responses to various stimuli.
Did you know that studies show around 90% of youth with developmental disorders engage in some form of stimming? This statistic highlights how prevalent and significant these behaviors are in their everyday lives.
Stimming can express excitement or act as a coping mechanism during overwhelming moments, playing a vital role in emotional regulation. The National Autism Association emphasizes that recognizing these behaviors can lead to better support and interventions, ultimately improving the quality of life for children with these conditions. Furthermore, ongoing research underscores the importance of including personal experiences in studies, guiding the development of more effective interventions tailored to the unique needs of autistic individuals.
This understanding is particularly crucial, as acknowledging profound developmental disorders can enhance access to vital supports and services.
As we look ahead to 2025, our understanding of self-stimulatory behavior continues to evolve. New studies are focusing on its functions and implications for emotional well-being. Remarkably, if spending on behavioral strategies for youth with developmental disorders helps reduce costs for young adults in 2025, the financial burden of these conditions could decrease by approximately $28 billion. This underscores the economic importance of successful behavioral approaches. This growing body of research highlights the need for parents and caregivers to embrace self-stimulatory behavior as a natural and essential aspect of neurodiversity, fostering a more inclusive environment that supports their children's growth.
It is also vital to remain aware of the risks associated with this condition; accidental drowning remains a leading cause of death for children affected by developmental disorders, accounting for roughly 90 percent of fatalities reported in this group in the U.S. Therefore, recognizing stimming actions is crucial, not only for providing emotional support but also for ensuring safety.
2. Name: Understanding the Purpose of Stimming in Autism
Stimming actions are vital in the lives of individuals with autism, serving multiple essential functions. These actions primarily act as coping mechanisms for anxiety, offering relief from overwhelming emotions or sensory overload. For many autistic individuals, self-stimulatory behavior becomes a form of communication, expressing feelings ranging from joy and excitement to distress.
Recognizing that these repetitive actions are not just distractions allows caregivers to better support their children in expressing their needs and emotions through these instinctive movements. This understanding fosters a nurturing environment where children can thrive.
Moreover, engaging in self-stimulatory behavior can enhance focus and create a sense of comfort, especially in unfamiliar or stressful settings. As Laura NG, a Clinical Operations Manager, highlights, grasping the nuances of such behaviors is crucial for promoting effective communication and emotional expression. Some children with autism may also benefit from medication to manage co-occurring conditions like ADHD or anxiety, which can complicate their experiences with repetitive behaviors.
Incorporating professional guidance through Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy can help individuals develop alternative strategies for harmful behaviors while honoring their need for self-regulation. A case study titled 'Seeking Professional Guidance for Stimming Management' illustrates how ABA therapy can effectively assist individuals in managing sensory behaviors, ensuring they have healthy coping mechanisms while respecting their self-regulation needs. By embracing stimming as a natural part of their child's experience, caregivers can cultivate an environment that respects and nurtures their unique ways of interacting with the world. This approach not only supports their children's well-being but also fosters a deeper understanding of their experiences.
3. Name: Exploring the Different Types of Stimming Behaviors
Self-stimulatory behavior manifests in various forms, primarily categorized into visual, auditory, tactile, and motor stims. Understanding these categories is crucial for caregivers, as it enables them to identify and support their children's unique needs. For instance, visual stimming may involve:
- Staring at moving objects
- Flickering lights
- Observing repetitive patterns
This provides sensory input and comfort. Similarly, auditory stimming can include:
- Making sounds like humming
- Clapping
- Repeating phrases
This serves as a self-soothing mechanism. Tactile stimming allows individuals to explore their sensory environment through engaging with various textures, such as:
- Rubbing fabrics
- Squeezing stress balls
Lastly, motor stimming encompasses repetitive movements like:
- Hand-flapping
- Spinning
- Rocking back and forth
This helps to regulate emotions and provide stability.
Recognizing these different types of stimming actions is essential for caregivers, as it empowers them to identify which behaviors are most prevalent in their children. This understanding fosters tailored support and promotes a more inclusive environment, ultimately reducing stigma associated with these actions. Recent findings reveal that:
- 12% of individuals with developmental autism (DA)
- 21% with social autism (SA)
- 2% of non-autistic (NA) participants
reported using painful stims, highlighting the importance of addressing these actions with empathy and understanding.
Furthermore, inhibiting self-stimulatory behavior can lead to adverse cognitive impacts, such as a lack of focus and disorientation. As illustrated in the case study titled 'Impact of Social Acceptability on Repetitive Actions,' many individuals felt pressured to hide their repetitive actions due to social norms, resulting in anxiety and frustration. One parent poignantly expressed, "I don't know what to do or how to act," underscoring the need for guidance and resources in navigating these challenges.
By recognizing and affirming sensory-seeking actions, caregivers can help children feel more accepted and understood. It's vital to embrace these behaviors and seek support, fostering a nurturing environment where every child can thrive.
4. Name: Effective Strategies for Managing Stimming Behaviors
To effectively manage stimming behaviors, caregivers can implement the following strategies:
- Identify Triggers: As caregivers, it's important to closely observe when and where your child engages in self-soothing actions. This helps to pinpoint potential triggers or stressors. Understanding these patterns is crucial, as it allows for proactive management of self-stimulatory behavior in their environment.
- Provide Alternatives: Introducing safe and acceptable alternatives, such as fidget toys, can fulfill sensory needs without causing disruption. These tools not only assist in self-regulation but also promote independence. Recent advancements in pediatric occupational therapy highlight the significance of such strategies in enhancing treatment plans and patient outcomes, fostering development and independence in young individuals.
- Create a Calm Environment: Reducing overwhelming sensory input is vital. Crafting a tranquil environment where your child feels safe can significantly decrease the occurrence of self-soothing behaviors. This approach aligns with findings suggesting that a supportive sensory environment can positively influence self-stimulatory behavior in autism.
- Schedule Sensory Breaks: Designating specific times for sensory activities throughout the day can help maintain focus during other tasks. This organized method enables young individuals to engage in self-calming actions while enhancing productivity in their daily routines.
- Positive Reinforcement: Encouraging and praising your child when they utilize alternative self-soothing actions or effectively manage their impulses fosters a sense of achievement. This reinforcement not only builds confidence but also promotes the adoption of healthier coping mechanisms.
These strategies strike a balance between permitting natural self-stimulatory behavior and ensuring safety and comfort in various settings. As specialists emphasize, self-stimulatory behavior is often viewed as a self-regulatory mechanism that assists individuals in coping with intense sensations or emotions. Therefore, it's crucial to approach these practices with understanding and support. Collaborating with ABA therapists can also be invaluable for effectively implementing these strategies, as they provide tailored guidance and support.
Innovations in autism therapy, as discussed in the case study, demonstrate how groundbreaking advancements can transform the lives of individuals with autism, offering new hope and progress in their treatment.
5. Name: Promoting Acceptance of Stimming in Society
Encouraging acceptance of self-regulating actions is essential for fostering a supportive atmosphere for autistic individuals. This acceptance not only nurtures their well-being but also cultivates a sense of belonging within the community. To promote understanding, consider these effective strategies:
- Education: Share information about stimming with teachers, peers, and community members. By doing so, we can significantly reduce stigma and misconceptions surrounding these actions. Research indicates that approximately 75% of diagnosed and suspected autistic participants, and 35% of non-autistic participants, do not always exhibit self-stimulatory behavior in their preferred manner. This highlights the urgent need for awareness and understanding.
- Advocacy: Actively support initiatives that promote neurodiversity and acceptance in educational institutions and workplaces. Recent advocacy efforts show that when schools adopt inclusive practices, they create environments where all students can flourish. This leads to enhanced social acceptance and a deeper comprehension of repetitive actions.
- Normalize Self-Stimulatory Behavior: Encourage a viewpoint that sees self-stimulatory behavior as a natural and healthy action rather than something to be suppressed or concealed. Shifting this mindset can help mitigate social acceptance issues, allowing individuals to express themselves freely and authentically.
- Encourage Empathy: Share personal stories from individuals who engage in self-soothing behaviors, emphasizing the benefits and significance of these actions. As one participant noted, "I get flustered. I don’t concentrate," illustrating the cognitive effects that can arise from suppressing repetitive movements, such as lack of concentration and confusion.
By promoting acceptance, we can empower individuals with autism to feel more comfortable expressing themselves. This ultimately leads to enhanced self-esteem and greater integration within the community, fostering a better understanding of self-stimulatory behavior. Furthermore, research methodologies, such as those outlined in the case study titled "Research Methodology for Stimming Study," provide valuable insights into the experiences of stimming behaviors, reinforcing the importance of understanding and acceptance. Together, we can create a more inclusive society.
Conclusion
Understanding and accepting stimming behaviors is essential in fostering a supportive environment for individuals with autism. Stimming, which encompasses a variety of self-stimulatory actions, serves crucial functions such as emotional regulation, communication, and sensory processing. Recognizing that approximately 90% of children with autism engage in these behaviors highlights their significance and the need for caregivers to embrace them as natural expressions of their child's needs.
Through effective strategies, such as identifying triggers, providing alternatives, and promoting a calm environment, caregivers can support their children while respecting their unique ways of interacting with the world. Imagine a child who finds comfort in repetitive movements or sounds; these actions are not just behaviors, but vital tools for navigating their experiences. Additionally, fostering societal acceptance through education and advocacy can significantly reduce stigma and enhance understanding of stimming behaviors. By normalizing these actions and encouraging empathy, society can empower autistic individuals, allowing them to feel more comfortable expressing themselves and improving their overall quality of life.
Ultimately, the journey towards understanding and accepting stimming is a collective effort that requires ongoing education and advocacy. By embracing these behaviors, caregivers and communities can create inclusive environments that not only support the emotional and sensory needs of individuals with autism but also celebrate their unique identities. A commitment to acceptance and understanding can lead to a richer, more inclusive society for everyone. Let us work together, share our stories, and advocate for a world where every individual feels valued and understood.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is self-stimulatory behavior, or stimming?
Self-stimulatory behavior, commonly referred to as stimming, includes repetitive activities such as hand-flapping, rocking, or making vocal sounds. These behaviors are often observed in individuals with developmental disorders and serve important functions like self-soothing and sensory regulation.
How prevalent is stimming among youth with developmental disorders?
Studies indicate that around 90% of youth with developmental disorders engage in some form of stimming, highlighting its significance in their daily lives.
What functions does stimming serve for individuals with autism?
Stimming serves multiple essential functions, including acting as a coping mechanism for anxiety, expressing emotions, enhancing focus, and providing comfort in overwhelming situations.
Why is it important for parents and caregivers to understand stimming?
Understanding stimming provides valuable insight into children's needs and responses to stimuli, allowing caregivers to better support their emotional expression and create a nurturing environment.
How can stimming impact emotional regulation?
Stimming can express excitement or act as a coping mechanism during overwhelming moments, playing a vital role in emotional regulation for individuals with developmental disorders.
What role does research play in understanding stimming?
Ongoing research emphasizes the importance of including personal experiences in studies, which helps guide the development of effective interventions tailored to the unique needs of autistic individuals.
What are the economic implications of effective behavioral strategies for youth with developmental disorders?
If spending on behavioral strategies helps reduce costs for young adults with developmental disorders by 2025, the financial burden of these conditions could decrease by approximately $28 billion.
What safety risks are associated with stimming in children with developmental disorders?
Accidental drowning is a leading cause of death for children with developmental disorders, accounting for roughly 90% of fatalities reported in this group in the U.S. Recognizing stimming actions is crucial for ensuring safety.
How can caregivers support children who engage in stimming?
Caregivers can support children by recognizing stimming as a natural behavior, promoting effective communication, and considering professional guidance like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy to manage harmful behaviors while respecting self-regulation needs.




