Overview
This article highlights effective strategies for enhancing social skills in children with autism, a concern many parents share. Understanding the challenges faced by these young individuals is crucial, and structured interventions can make a significant difference. Techniques such as role-playing, peer interactions, and the use of visual supports not only improve interpersonal abilities but also enhance the overall quality of life for these children.
Imagine your child engaging confidently with peers, sharing laughter, and building friendships. These interventions have been shown to foster such connections, creating a nurturing environment where children can thrive. By incorporating these strategies into daily routines, parents can help their children navigate social situations more effectively.
As you explore these approaches, consider reaching out to local support groups or professionals who specialize in autism. They can provide valuable resources and guidance tailored to your child's unique needs. Together, we can create a supportive community that empowers children with autism to shine in their social interactions.
Introduction
In the journey of nurturing children with autism, social skills training shines as a beacon of hope, guiding them toward meaningful interactions and deeper connections. This structured approach encompasses a variety of techniques, from role-playing to visual supports, all designed to empower children as they navigate the complexities of social environments.
Research underscores the profound impact of tailored interventions, highlighting the crucial role of parents and caregivers in this developmental process. By fostering an inclusive atmosphere and leveraging evidence-based strategies, families can significantly enhance their children's social competence, ultimately enriching their quality of life.
As training methods continue to evolve, equipping children with the necessary tools for social success becomes increasingly critical, paving the way for a more connected and understanding society.
Understanding Social Skills Training for Autism
Interpersonal skills training for young individuals with developmental disorders is a vital resource, providing structured interventions that help them engage appropriately in social settings. Techniques such as role-playing, modeling, and narrative stories are commonly used to enhance learning. The primary goal is to empower children with autism to develop social skills that enable them to navigate their environments, interpret social cues, and build meaningful relationships with both peers and adults.
Recent statistics highlight the effectiveness of these structured interventions. For instance, behavioral interventions have demonstrated a significantly longer duration, averaging 362.42 hours, compared to just 20.11 hours for cognitive interventions. This extended engagement is crucial, allowing for deeper learning and practice of interpersonal skills.
Case studies further illustrate the impact of interpersonal skills training. One notable study examined changes in Vineland socialization scores, revealing that while Cluster 1 participants showed only slight improvements, Cluster 2 displayed considerable variability, with some individuals even experiencing declines as they aged. This underscores the necessity for tailored strategies that consider personal differences in the development of interpersonal abilities.
As Fatemeh Abadi wisely noted, "Data gathering and data analysis" are essential for understanding these outcomes and refining intervention strategies.
The importance of training in autism social skills cannot be overstated. It not only nurtures the development of essential skills but also significantly enhances the overall quality of life for young individuals with autism. Successful interventions lead to improved outcomes in these social skills, making it imperative for parents and professionals to prioritize these strategies.
Looking ahead to 2025, advancements in social skills training are continuously evolving, focusing on integrating diverse assessment tools and exploring the mechanisms behind transfer patterns. Current best practices emphasize the need for structured, evidence-based approaches that adapt to the unique needs of each individual, ensuring they receive the support necessary to thrive socially. Importantly, the downward trend in socialization scores for Cluster 2 at follow-up highlights ongoing challenges that must be addressed through innovative and responsive training methods.
The Importance of Social Skills in Autism
Interpersonal abilities are vital for individuals on the autism spectrum, serving as the cornerstone for developing essential social skills. These skills pave the way for effective communication, the formation of friendships, and an overall enhancement of quality of life. Research indicates that young people who nurture strong interpersonal abilities are more likely to engage in meaningful exchanges, significantly improving their emotional regulation and alleviating feelings of loneliness. In 2025, the importance of these skills is underscored by findings that children with developmental disorders who actively participate in group activities report a higher quality of life, with studies showing that such interactions can lead to better mental health outcomes.
Interestingly, a recent survey revealed that 31.3% of participants began using CBD products during the COVID-19 pandemic, reflecting evolving support strategies for autism.
The development of interpersonal abilities not only benefits individuals; it fosters a supportive environment that encourages peer connections and community engagement. For example, the CDC report presents a comparative analysis of autism prevalence among various ethnic groups in the US, highlighting the differing impacts of autism across demographics. This underscores the need for tailored, culturally aware approaches to interpersonal training.
Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in this developmental journey by prioritizing interpersonal growth. By creating opportunities for their children to practice these skills in safe and nurturing environments, they can build confidence and enhance their ability to navigate social situations. Engaging in organized activities, such as group play or community events, can provide valuable experiences that improve interpersonal competence.
As Yolande Loftus notes, CDC data estimates a male-to-female ratio of 4:1 in individuals with developmental disorders, while other studies suggest a ratio closer to 3:1. This discrepancy highlights the need for focused strategies in interpersonal development.
Moreover, the recognition of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) as an effective treatment for individuals with developmental challenges, endorsed by the American Psychological Association, reinforces the importance of structured interventions in fostering interpersonal skills. Community workers also play a vital role in supporting parents, breaking down the process into manageable steps and ensuring families receive the assistance they need.
In summary, investing in interpersonal development is essential for young people to enhance their autism social skills. This investment not only enriches their personal experiences but also contributes to a more inclusive society. By focusing on these skills, families can empower their children to thrive socially and emotionally, ultimately leading to a more fulfilling life.
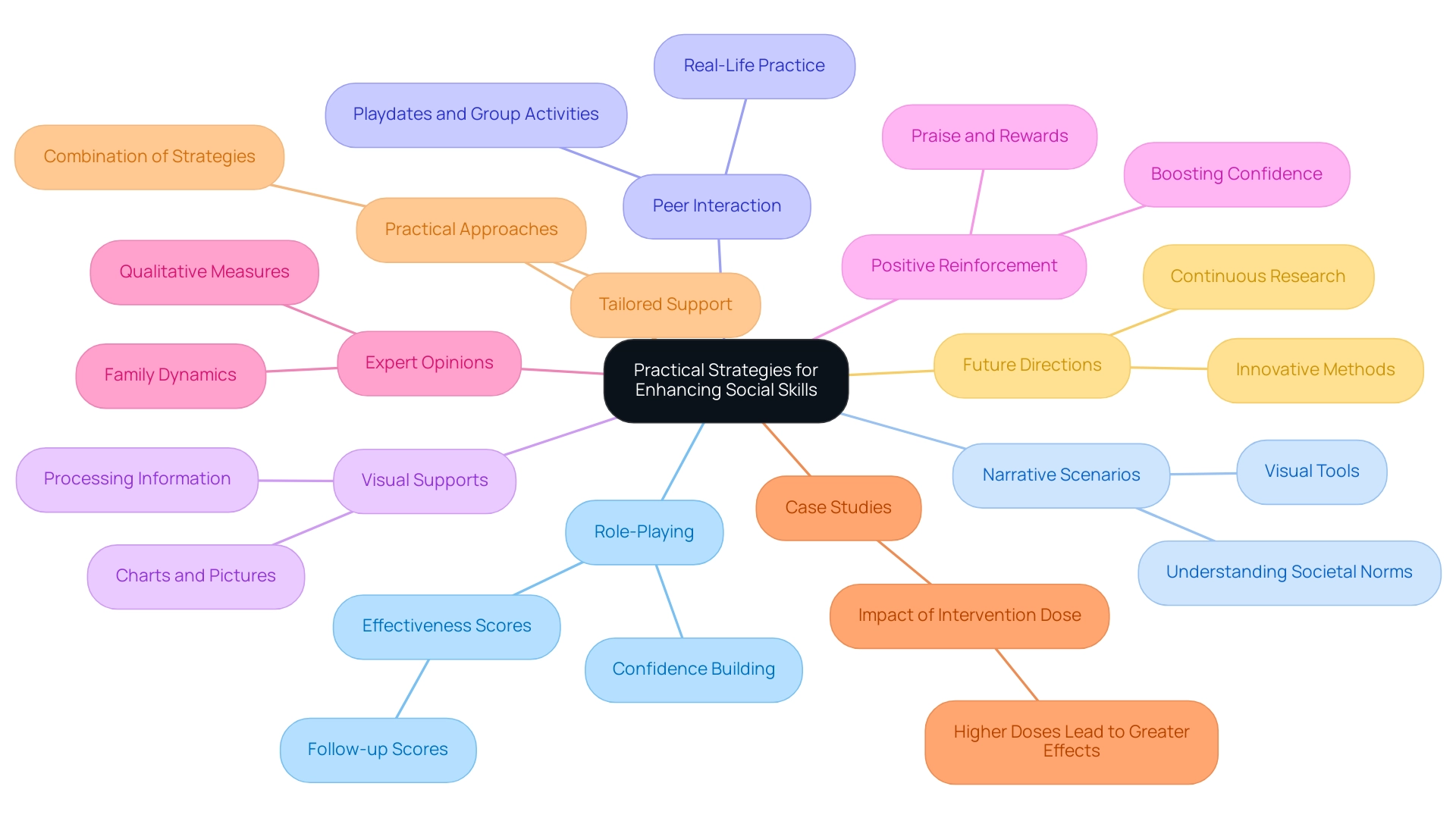
Practical Strategies for Enhancing Social Skills
Participating in role-playing scenarios offers children a valuable opportunity to practice autism social skills within a nurturing and supportive environment. This technique not only helps them grasp various community contexts but also allows them to explore different responses, fostering confidence in real-life situations. Research shows that structured role-playing can significantly enhance socialization scores, with participants demonstrating a range from 20 to 90 in follow-up assessments.
Utilizing narrative scenarios serves as an effective method for illustrating interpersonal situations and appropriate responses. These stories act as visual tools that help young individuals comprehend societal norms and expectations. By presenting relatable situations, narratives can enhance understanding and retention of interpersonal abilities, making them a vital resource in autism therapy.
- Peer Interaction: Facilitating playdates or group activities with peers provides essential real-life practice opportunities. These interactions are crucial for developing autism social skills, as they allow children to apply what they have learned in role-playing and narrative scenarios within real-life contexts, reinforcing their learning through experience.
- Visual Supports: Implementing visual aids, such as charts or pictures, can greatly enhance understanding of interpersonal concepts and cues. Visual aids assist children in developing autism social skills by helping them process information more efficiently, simplifying their understanding of complex interpersonal interactions and expectations.
- Positive Reinforcement: Using praise and rewards to strengthen successful interactions encourages children to repeat those behaviors. Positive reinforcement not only boosts their confidence but also solidifies their learning, making it more likely that they will engage in desired interactions in the future.
- Expert Opinions: Specialists emphasize the importance of incorporating qualitative metrics and creative methods, like media-based interventions, to improve the effectiveness of interpersonal training programs. M.Z. notes that future research should integrate these elements to enhance outcomes. This perspective highlights the need for ongoing research and adaptation of strategies to meet the evolving needs of individuals with autism.
- Case Studies: Various case studies illustrate the impact of intervention intensity on the development of interpersonal abilities. For example, one study found that higher doses of intervention led to greater transfer effects across all domains, underscoring the importance of tailored approaches based on age and intervention type. These findings stress the significance of intervention intensity in achieving better outcomes for individuals with ASD.
Recent statistics on effectiveness indicate that structured role-playing techniques can lead to measurable improvements in autism social skills among youth. A systematic review published on December 30, 2024, supports the idea that targeted interventions yield positive outcomes, reinforcing the value of these strategies in therapy.
- Practical Approaches: To effectively improve interpersonal abilities, practitioners should consider a combination of role-playing, narratives, and peer interactions. This multifaceted approach ensures that children receive comprehensive support tailored to their unique needs.
- Future Directions: As the field progresses, continuous research will be crucial in identifying deficiencies and areas for enhancement in interpersonal training. By exploring innovative methods and incorporating family dynamics, practitioners can further improve the effectiveness of their programs. Additionally, addressing the identified gaps in the literature on game design for interpersonal development will be essential for future advancements.
The Role of Parents and Caregivers in Skill Development
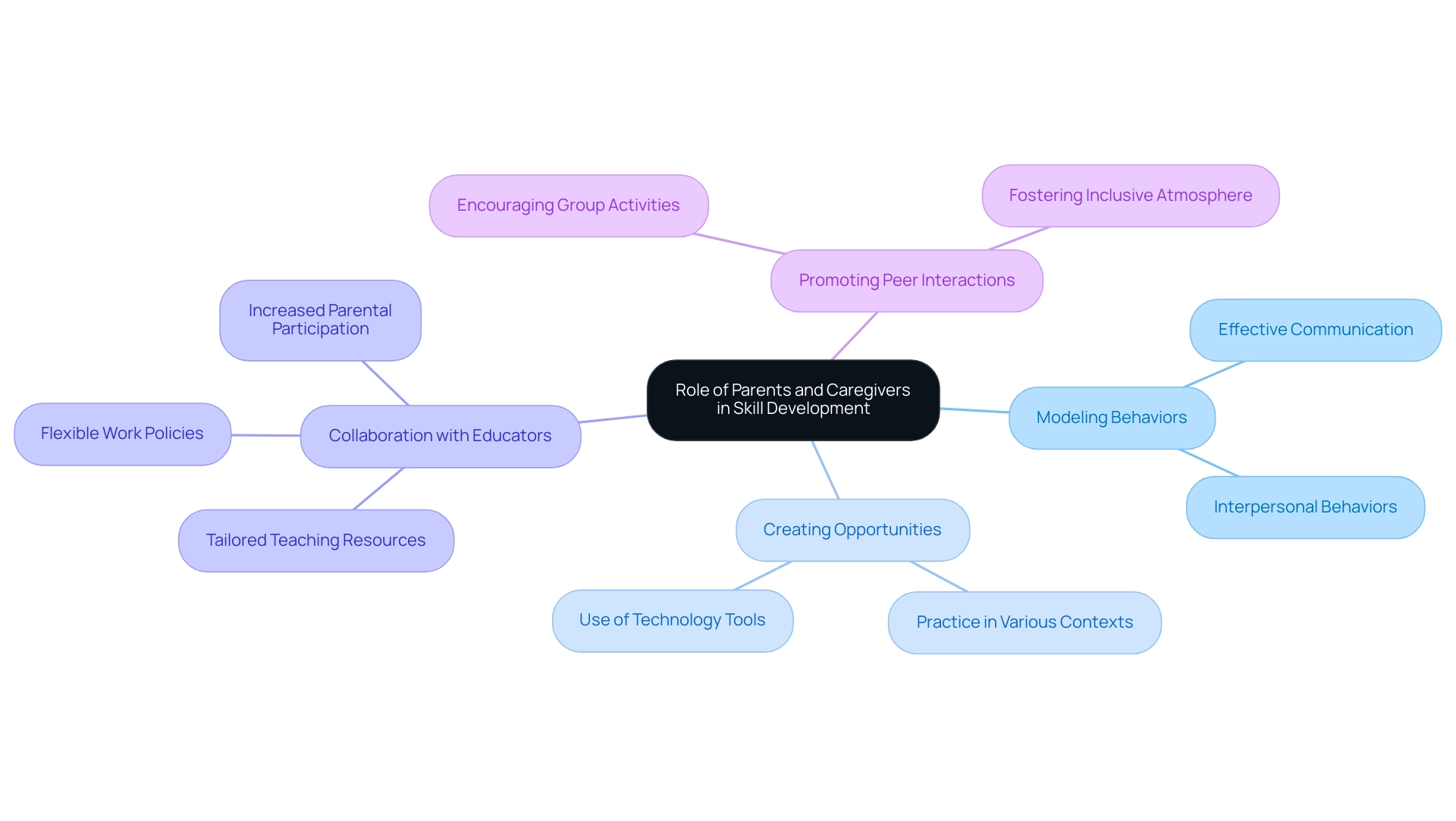
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in nurturing the development of autism social skills in young individuals. Their active participation can significantly enhance learning outcomes by modeling appropriate interpersonal behaviors, creating opportunities for practice, and reinforcing positive interactions. Research indicates that parental involvement in training autism social skills correlates with better results; in 2025, data revealed that children whose parents actively engaged in their autism social skills development showed increased confidence and competence in social interactions.
Caregiver modeling is essential in this journey. By demonstrating effective communication and interpersonal behaviors, parents provide a framework for their children to emulate. This alignment between home and community environments is crucial, as it helps young individuals generalize their skills across various contexts.
For example, a recent case study illustrated how integrating technology tools used at home into classroom settings led to noticeable improvements in a student's concentration and participation. This underscores the importance of consistency in learning environments. As one educator shared, "We introduced technology tools that he used at home into the classroom as well, and we saw a noticeable improvement in his concentration and participation. I think this alignment between home and school really helped create a more effective and comfortable learning environment for him."
Expert insights highlight that social workers and educators must collaborate with parents to create manageable steps for planning their children's futures. This partnership can involve developing tailored teaching resources and encouraging flexible work policies that enable parents to balance their responsibilities while actively participating in their children's education. Suggestions also include increasing parental involvement in school activities, which can further strengthen the support network for youth.
Moreover, the role of parents extends beyond direct instruction; they can facilitate the development of autism social skills by promoting peer interactions and encouraging participation in group activities. By fostering an inclusive atmosphere, parents can help their children navigate interpersonal situations more effectively.
In conclusion, the engaged involvement of parents and guardians is crucial in enhancing autism social skills for youth with developmental disorders. By modeling behaviors, providing practice opportunities, and collaborating with educators, they can create a supportive framework that empowers youth to thrive socially.
Evidence-Based Techniques for Effective Social Skills Training
Effective interpersonal skills training for youngsters with autism relies on a variety of evidence-based techniques that have been shown to yield positive outcomes. These methods can truly make a difference in the lives of children and their families. Here are some of the most impactful approaches:
- Modeling: This technique involves demonstrating suitable interpersonal interactions, allowing young individuals to observe and imitate desired behaviors. By watching these interactions unfold, children can better comprehend cues and responses, creating a foundation for their own social skills.
- Video Modeling: Utilizing video examples to illustrate interpersonal scenarios is a powerful tool in training. Research suggests that video modeling can greatly improve interpersonal abilities by offering clear visual representations of suitable actions. In 2025, studies emphasized its effectiveness, demonstrating that youngsters who interacted with video modeling displayed enhanced interactions compared to those who did not. Imagine the confidence they can gain from seeing themselves succeed in these scenarios!
- Peer-Mediated Interventions: Involving typically developing peers in interpersonal training can create a supportive environment for children with autism. These peers facilitate interpersonal interactions and provide helpful feedback, fostering more natural and effective communication abilities. What a wonderful way to build friendships!
- Naturalistic Teaching: This approach incorporates interpersonal abilities training into daily activities and routines, encouraging the application of acquired competencies. By embedding training within familiar contexts, young individuals are more likely to use their skills in real-life situations, enhancing their interpersonal competence. Think of how much easier it will be for them to connect with others in everyday settings.
- Cognitive Behavioral Techniques: Teaching young individuals to identify and manage their feelings in interpersonal situations is essential. These techniques empower children to navigate social interactions more effectively, fostering resilience and adaptability.
Recent findings indicate that while some participants showed only marginal improvements in socialization scores, others demonstrated significant variability, underscoring the importance of tailored interventions. A statistic revealed that 1.92% of participants exhibited weak ability in evaluating transferability, highlighting the challenges in assessing the effectiveness of interpersonal training. A study titled "Future Research Directions in Transferability of Social Training" emphasized the need for diverse assessment tools and consideration of various influential factors to enhance the effectiveness of these interventions.
Furthermore, Leonardo Zoccante observed that this study provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of the Skills, Autonomy, and Awareness Module for individuals with level 1 ASD. It emphasizes how age and interpersonal experience shape distinct adaptive profiles. By utilizing these evidence-based methods, parents and professionals can establish a strong foundation for cultivating interpersonal abilities in youngsters with autism. This ultimately promotes significant relationships and improves their overall quality of life. Together, we can make a meaningful impact on their journey.
Practicing and Generalizing Social Skills
To ensure that autism social skills are effectively learned and applied, it is crucial to practice these interpersonal abilities across various environments. This multifaceted approach can be achieved through several strategies.
- Organized Playdates: Arranging playdates with friends provides youngsters with the opportunity to develop interpersonal skills in a natural setting. These interactions can significantly enhance their ability to generalize learned behaviors, fostering meaningful connections with others. One mother shared how her son excels in therapy games at a local group, where he can ask 'why' certain interaction skills are important in a safe and supportive space.
- Community Activities: Involving youngsters in community events or group activities offers valuable chances for interaction. Engagement in such activities not only boosts confidence but also helps young individuals navigate societal norms across various contexts.
- Role-Playing Different Scenarios: Practicing various interpersonal situations through role-play prepares children for real-life interactions. This method allows them to explore different responses and understand the nuances of interpersonal exchanges, making them more adept in actual situations.
- Feedback and Reflection: Providing constructive feedback after interactions is essential. This process helps youngsters understand what was successful and identify areas for enhancement, thereby strengthening their learning and promoting growth.
Studies show that organized playdates can significantly influence the development of autism social skills in youngsters with developmental disorders. In 2025, research indicates that youngsters involved in these playdates demonstrate enhanced communication and interaction abilities, leading to deeper connections with peers. Additionally, ongoing research and customized approaches are vital to ensure the effectiveness of interpersonal training for youth with developmental disorders, as emphasized in numerous studies.
By applying these methods, caregivers and experts can foster enriching experiences that encourage interaction development, ultimately enabling youth with developmental disorders to enhance their autism social skills and navigate social environments with confidence. The challenges faced by families are considerable, with parental lost income from caring for a young individual with developmental challenges exceeding $18,000 annually. This underscores the necessity of effective interpersonal training.
Utilizing Visual Supports and Social Stories
Visual supports and social stories are invaluable tools for teaching social skills to individuals with autism, significantly enhancing their ability to navigate social interactions. These strategies include:
- Picture Schedules: These visual aids assist young learners in understanding the order of daily activities and establishing clear expectations, thus minimizing anxiety and confusion. Research indicates that implementing picture schedules can lead to a marked decrease in frustration, as they simplify complex instructions and enhance understanding.
- Emotion Cards: These cards help young individuals recognize and express their emotions, fostering emotional intelligence and enhancing their ability to communicate feelings effectively.
- Community Stories: These narratives provide detailed descriptions of interpersonal situations and appropriate responses, allowing children to visualize and comprehend societal norms. The effectiveness of narrative techniques in autism education has been well documented, with studies demonstrating that they can significantly enhance autism social skills and comprehension. As noted by Sofia M. Borron, "Four different research articles that have been peer-reviewed and are academic journals assess the effectiveness of visual prompts for students with ASD," underscoring the importance of these tools.
Integrating these tools into everyday practices not only supports the growth of interpersonal abilities but also encourages a deeper comprehension of interactions. For instance, a case study titled "[Unveiling the Lifelong Impact of Supportive Care ABA" highlights the long-term benefits of supportive care in ABA therapy, demonstrating that such interventions contribute to sustained improvements in behavior and overall family well-being. This case study illustrates how visual aids and narratives can lead to significant improvements in youngsters' interpersonal abilities and family interactions.
NASET offers a platform for sharing literature reviews and research on developmental disorders and special education, making it a valuable resource for parents and professionals seeking to deepen their understanding of these strategies.
As we progress through 2025, the incorporation of visual aids and narrative techniques remains vital in training for individuals on the spectrum, enabling youth to participate more fully in their communities and strengthening their interpersonal relationships.
Encouraging Peer Interaction and Modeling
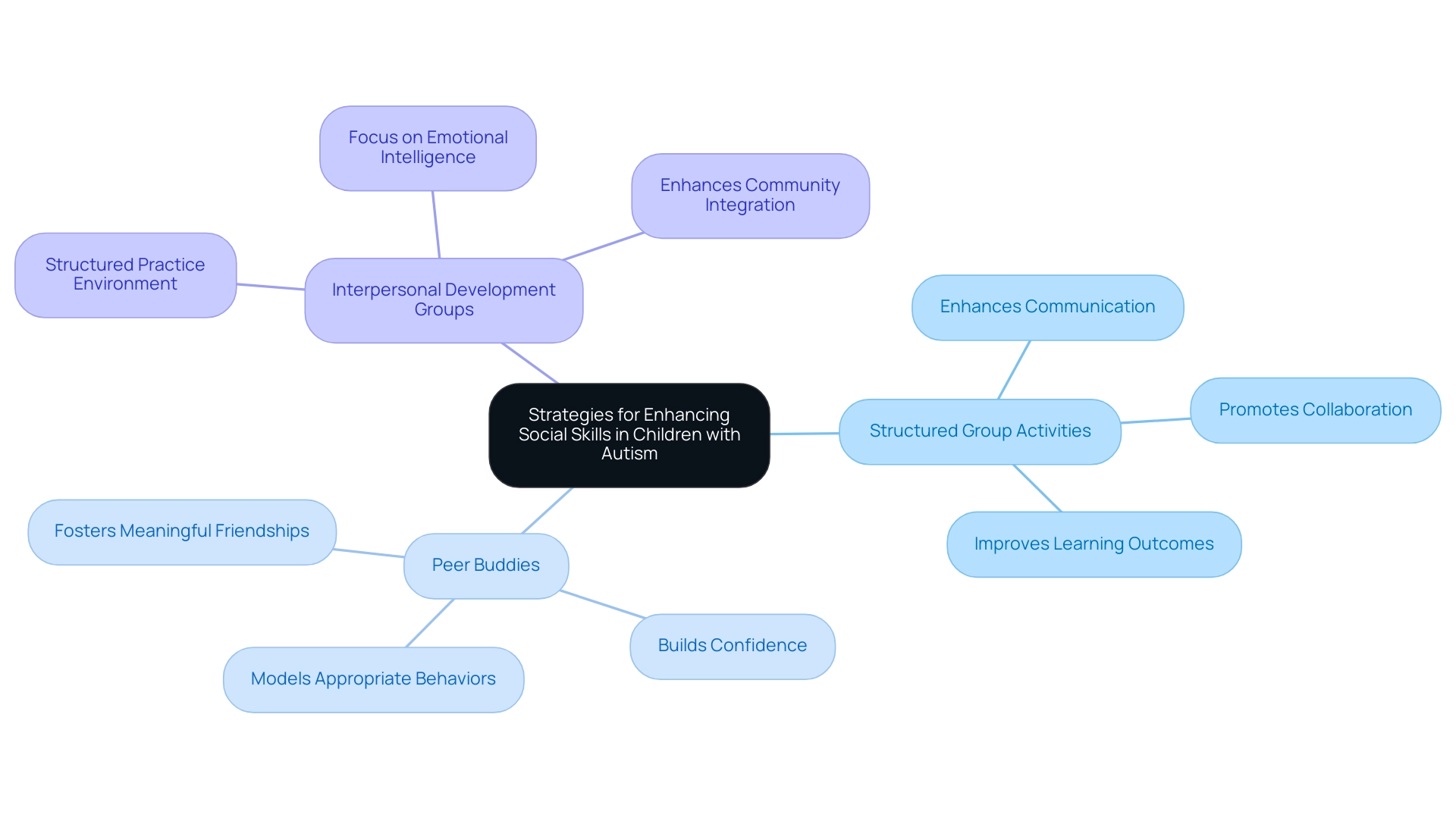
Peer interactions play a vital role in enhancing social skills among children with autism. By implementing effective strategies to encourage peer engagement, we can significantly foster their interpersonal development. Here are some key approaches that can make a difference:
- Structured Group Activities: Creating opportunities for young individuals to engage in group games or collaborative projects is essential. These organized environments not only enhance communication but also promote collaboration, allowing children to develop their social skills in a nurturing atmosphere. Research shows that structured settings can lead to significant improvements in learning outcomes for individuals with autism, ultimately advancing their interpersonal skills.
- Peer Buddies: Pairing children with companions who can model appropriate interpersonal behaviors is an effective strategy. Peer buddies provide crucial support and guidance, helping children navigate social situations with greater confidence. This approach not only aids in skill acquisition but also fosters meaningful friendships, which are vital for emotional well-being.
As Situmorang observed, enhancing the interpersonal communication and social skills training of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) through peer interactions can improve their integration into community life.
- Interpersonal Development Groups: Enrolling children in specialized interpersonal development groups offers a structured setting for practicing interactions. These groups focus on enhancing social skills, interpersonal communication, and emotional intelligence, contributing to better integration into the community.
A systematic review of the PEERS intervention method, designed for adolescents and young adults with ASD, revealed significant improvements in six outcome indicators related to social skills, such as interpersonal knowledge and emotional intelligence. The results highlight the effectiveness of organized group activities in fostering social skill development, with positive impacts noted on brain function.
Encouraging peer interaction is not just beneficial; it is essential for the overall growth of individuals in developing social skills. By implementing these strategies, caregivers and professionals can create enriching experiences that empower young individuals to thrive both socially and emotionally. Let's work together to support these vital connections and help our children flourish.
Fostering Emotional Recognition and Expression
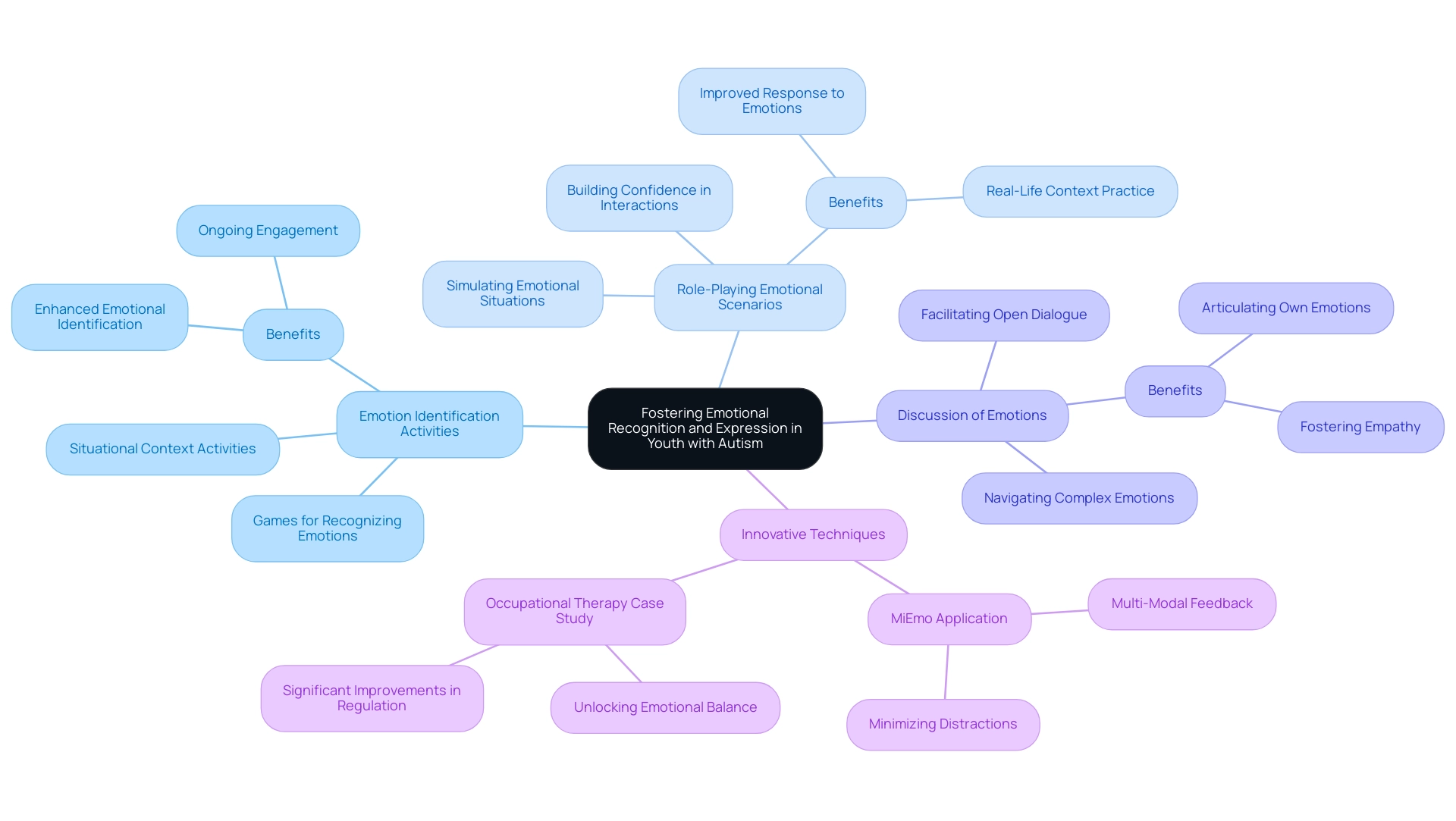
Emotional recognition and expression are vital in nurturing social skills for youth with autism. By fostering these skills, we can help young individuals thrive. Here are several compassionate techniques that can be employed:
- Emotion Identification Activities: Engaging youngsters in games or activities that focus on recognizing various emotions through facial expressions or situational contexts can significantly enhance their ability to identify feelings. Research shows that consistent practice leads to greater improvements across all domains, highlighting the importance of ongoing engagement in their emotional development.
- Role-Playing Emotional Scenarios: This technique allows young individuals to simulate emotional situations and practice appropriate responses. Role-playing not only helps them learn how to react in real-life contexts but also builds their confidence in interpersonal interactions, essential for developing social skills. Recent case studies reveal that this approach can lead to significant improvements, especially in understanding and responding to the emotions of others.
- Discussion of Emotions: Facilitating open discussions about feelings encourages youngsters to articulate their own emotions and fosters empathy for others. By creating a safe space for dialogue, young individuals can learn to navigate complex emotional landscapes, which is crucial for building meaningful connections and enhancing their social skills.
Looking ahead to 2025, promoting emotional awareness in young individuals with developmental disorders remains a priority. Innovative methods like MiEmo are emerging, employing advanced multi-modal feedback—incorporating music and colors linked to emotions—to enhance engagement during socio-emotional training activities. This user-friendly application minimizes distractions and sensory overload, which is essential for effective learning. The growing demand for effective emotional recognition training has surged by over 5,852% from 2010 to 2021, underscoring its increasing importance in therapeutic settings.
Additionally, the case study titled 'Unlocking Emotional Balance: The Transformative Power of Occupational Therapy' illustrates how emotional regulation can be enhanced in youth, reinforcing the effectiveness of these techniques. By applying these approaches, ASD Media aims to empower parents and professionals, nurturing a supportive community that enhances the social skills of youth with developmental disorders. Together, we can make a difference in their lives.
Ensuring Ongoing Support and Reinforcement
To foster the continuous growth of social skills in children with autism, it's essential to provide steady support and reinforcement strategies. Here are several effective approaches:
- Regular Check-Ins: Engaging in regular discussions with young individuals about their interactions and the challenges they face can significantly enhance their self-awareness and problem-solving skills. These conversations not only shed light on their experiences but also create a safe space for them to share their feelings and concerns.
- Positive Reinforcement: Consistently acknowledging and rewarding positive social behaviors is crucial. This can be accomplished through verbal praise, small rewards, or special privileges, motivating children to engage in and repeat these behaviors. Research indicates that positive reinforcement can lead to a marked improvement in social skills, making it a foundational element of effective training.
- Parent and Caregiver Training: Equipping parents and caregivers with the knowledge and resources to support their children's social development at home is vital. Training programs can offer tailored strategies, ensuring caregivers can reinforce skills learned in therapy sessions. This ongoing learning cultivates a supportive environment where children can practice and apply their social skills in real-life situations.
- Employing Task Analysis: Breaking down social skills into manageable steps through task analysis can transform learning experiences. This method allows children to master each component of an interaction before attempting the entire process, fostering independence and confidence in social settings. As highlighted in recent news, task analysis in ABA therapy is revolutionizing how autistic individuals acquire social skills, making these abilities more attainable.
- Community Engagement: Encouraging participation in community activities offers children opportunities to practice their social skills in varied environments. Interacting with peers in organized settings, such as clubs or sports, can enhance their social skills and ability to navigate interpersonal situations effectively.
- Support Networks: Building a support network among families can be invaluable. Sharing experiences and strategies empowers parents and caregivers, fostering a collaborative environment that benefits everyone involved. Given that parental lost earnings due to caring for a child with developmental challenges exceed $18,000 annually, nurturing such networks can alleviate some financial pressures families face.
- Monitoring Progress: Regularly assessing a child's social skills through observations and feedback can help identify areas needing extra attention. This continuous evaluation ensures that strategies remain effective and relevant to the individual's evolving needs.
By implementing these strategies, parents and caregivers can create a nurturing environment that promotes the growth of social skills in children with autism, ultimately enhancing their ability to connect with others and thrive in various social contexts. As Tova Leibowitz, BCBA, Clinical Director, emphasizes, discovering how to make an ABA session enjoyable and engaging for autistic children is key to their success.
Conclusion
Enhancing social skills in children with autism is a journey filled with opportunities for growth, collaboration, and unwavering dedication. This article has highlighted various evidence-based strategies, such as role-playing, social stories, and peer interactions, which are essential in equipping children with the skills they need for meaningful social engagement. Research supports the effectiveness of these interventions, showing that tailored approaches can lead to significant improvements in social competence and overall quality of life.
The involvement of parents and caregivers is crucial in this developmental process. By modeling appropriate behaviors and fostering supportive environments, families can reinforce the skills learned in structured settings. Engaging in community activities and facilitating peer interactions enrich the learning experience, allowing children to practice their skills in real-world contexts. The importance of continuous support and positive reinforcement is paramount, as these elements are vital for sustaining progress and nurturing confidence in social situations.
As we look to the future of social skills training, integrating new techniques and adapting existing strategies will be essential. Ongoing research and collaboration among educators, parents, and professionals are critical to refining these approaches to meet the unique needs of each child. By prioritizing social skills development, we can work together toward a more inclusive and understanding environment, where children with autism can thrive and build meaningful connections with those around them. Let us continue this important journey, supporting one another and our children every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of interpersonal skills training for young individuals with developmental disorders?
The purpose of interpersonal skills training is to provide structured interventions that help young individuals, particularly those with autism, engage appropriately in social settings, develop social skills, interpret social cues, and build meaningful relationships.
What techniques are commonly used in interpersonal skills training?
Common techniques include role-playing, modeling, and narrative stories, which enhance learning and help individuals practice social interactions.
How effective are structured interventions compared to cognitive interventions?
Behavioral interventions have shown to be significantly more effective, averaging 362.42 hours of engagement compared to just 20.11 hours for cognitive interventions, allowing for deeper learning and practice of interpersonal skills.
What do recent case studies reveal about the impact of interpersonal skills training?
Case studies indicate variability in outcomes; while some participants show improvements in socialization scores, others may experience declines, highlighting the need for tailored strategies based on individual differences.
Why is training in autism social skills important?
Training in social skills enhances the overall quality of life for young individuals with autism, enabling them to develop essential skills that lead to improved social interactions and emotional regulation.
What advancements are expected in social skills training by 2025?
Advancements are focusing on integrating diverse assessment tools and exploring mechanisms behind transfer patterns, with an emphasis on structured, evidence-based approaches tailored to individual needs.
How can parents and caregivers support the development of interpersonal skills in children with autism?
Parents and caregivers can create opportunities for practice in safe environments, engage children in organized activities, and prioritize interpersonal growth to build confidence and enhance social navigation.
What role do community workers play in supporting interpersonal skills training?
Community workers assist parents by breaking down the process into manageable steps and ensuring families receive the necessary support for their children’s development.
What is the significance of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) in interpersonal skills training?
ABA is recognized as an effective treatment for individuals with developmental challenges, reinforcing the importance of structured interventions in fostering interpersonal skills.
What are some practical approaches to improving interpersonal abilities in children with autism?
Effective approaches include a combination of role-playing, narrative scenarios, peer interactions, visual supports, and positive reinforcement to provide comprehensive support tailored to individual needs.




