Introduction
Asperger's Syndrome is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social interaction, communication, and behavior. Recognized as a milder form of autism, individuals with Asperger's often have average to above-average intelligence.
Understanding the unique characteristics of Asperger's Syndrome is crucial for providing appropriate support and intervention. This article explores the key characteristics, challenges in social interaction, communication patterns, repetitive behaviors, sensory sensitivity, emotional regulation, cognitive abilities, diagnosis, treatment strategies, and co-occurring conditions associated with Asperger's Syndrome. By gaining a deeper understanding of this condition, we can empower parents and advocates to navigate the challenges and ensure the well-being of their children.
What is Asperger’s Syndrome?
Asperger's Syndrome is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is characterized by difficulties in social interaction, communication, and a restricted range of interests and repetitive behaviors. It is considered to be on the milder end of the autism spectrum, with individuals typically having average or above-average intelligence.
This condition was first described by Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger in 1944, but it wasn't recognized as a separate diagnosis until much later. Understanding the unique characteristics of Asperger's Syndrome is essential to provide appropriate support and intervention for individuals with this condition.
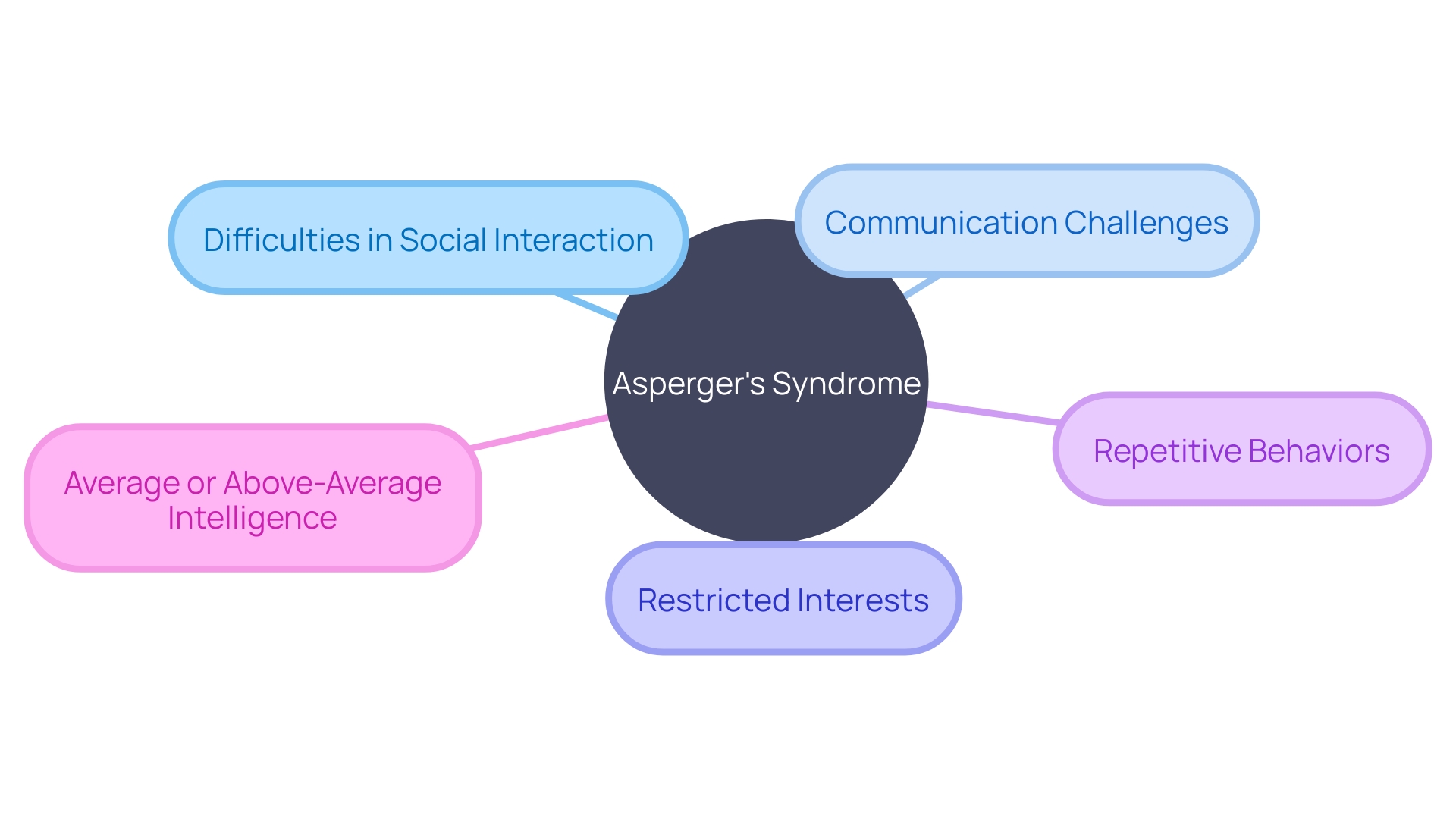
Key Characteristics of Asperger’s Syndrome
There are several key characteristics that are commonly associated with Asperger's Syndrome. These include difficulties in social interaction, such as challenges in understanding social cues, maintaining eye contact, and developing meaningful relationships.
Individuals with Asperger's Syndrome may also exhibit repetitive behaviors and a strong focus on specific interests. They may have difficulties with communication and language, such as literal understanding of language or a tendency to use formal and sophisticated vocabulary. Additionally, individuals with Asperger's Syndrome may struggle with sensory sensitivities and emotional regulation.
Social Challenges and Obsessive Interests
One of the hallmark features of Asperger's Syndrome is the presence of social challenges. Individuals with this condition may find it challenging to initiate and maintain conversations, interpret social cues, and understand non-verbal communication.
They may struggle with understanding sarcasm, irony, and humor. Additionally, individuals with Asperger's Syndrome often have intense and obsessive interests in specific topics, which can be a source of enjoyment and expertise for them. However, these interests may also limit their ability to engage in other activities and interact with peers.
Communication and Language Patterns
Communication and language patterns in individuals with Asperger's Syndrome can be unique. They may have difficulty understanding and using non-literal language, such as idioms and metaphors.
Some individuals may have a formal or stilted way of speaking, using complex vocabulary and speaking with a monotone voice. Others may struggle with initiating and maintaining conversations, often focusing on their own interests and difficulties with turn-taking. Speech delays or difficulties in early childhood may also be observed in some individuals.
Repetitive Behaviors and Sensory Sensitivity
Understanding the nuances of Asperger's Syndrome is crucial, especially when it comes to repetitive behaviors and sensory processing differences. Individuals may exhibit repetitive actions, such as hand-flapping or rocking, which are often mechanisms for self-regulation and comfort. Consistency in daily routines also plays a significant role in their lives, providing a sense of predictability and security.
Sensory experiences are uniquely intense for those with Asperger's, where ordinary sights, sounds, or textures can be overwhelming (hypersensitive) or barely noticeable (hyposensitive). Recognizing and respecting these sensory preferences is key to enhancing their environment for optimal comfort and well-being. With 1 in 45 adults in the U.S. diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder, a broader understanding of these signs is not only beneficial for those undiagnosed or misdiagnosed but also for society's acceptance and support of neurodiversity.
Emotional Regulation and Coping Mechanisms
Navigating the emotional landscape can be particularly challenging for individuals with Asperger's Syndrome. They often struggle with recognizing and expressing their own emotions, as well as interpreting the feelings of others. This disconnect can exacerbate stress, escalate frustration, and heighten anxiety.
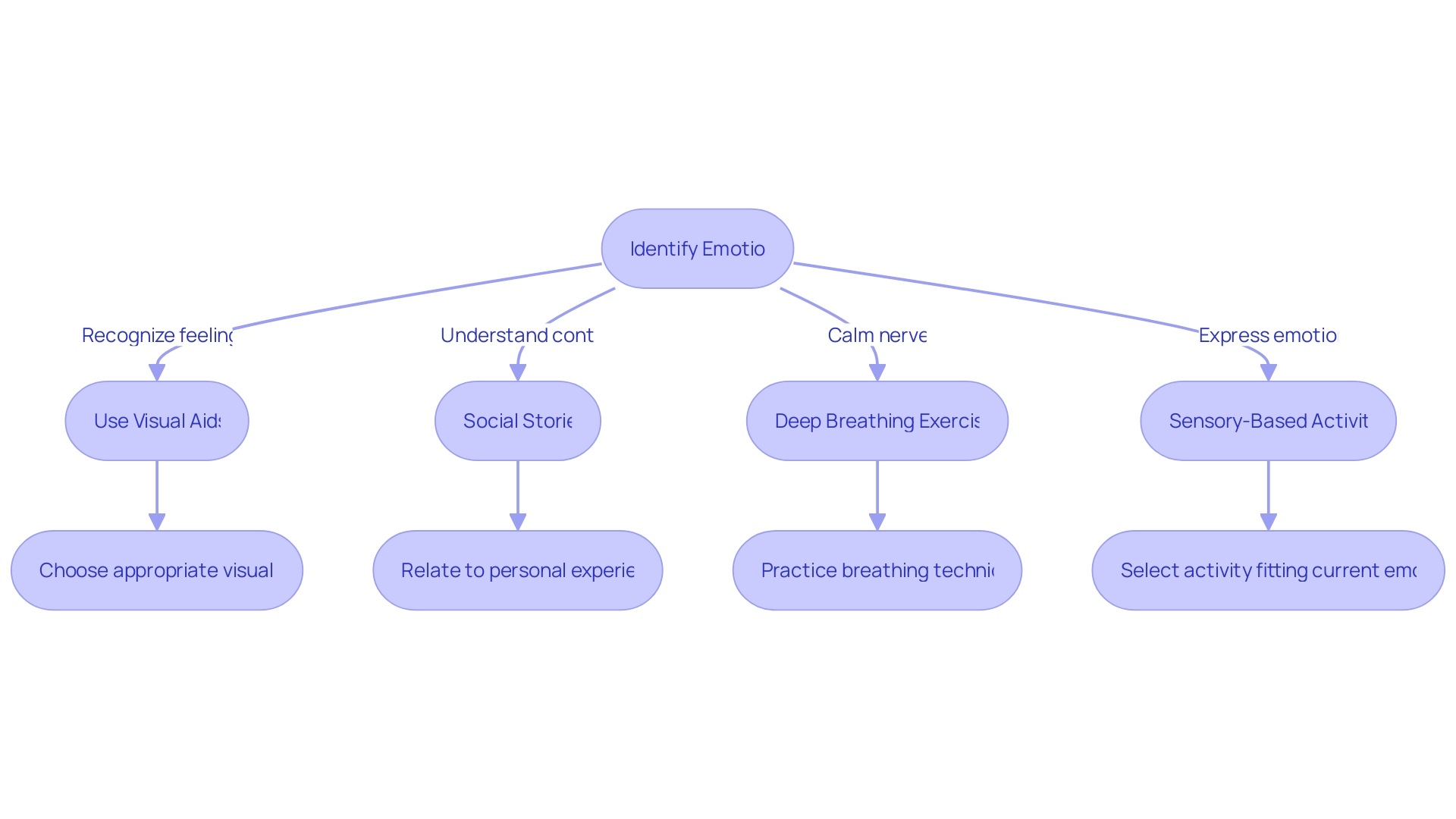
In the words of Aristotle over three millennia ago, the goal is to feel emotions 'at the right time, on the right occasion, towards the right people, for the right purpose, and in the right manner.' For those with Asperger's, achieving this balance is crucial yet daunting. To assist, there are tailored strategies that prove beneficial.
Visual aids can help in identifying emotions, while social stories provide context and structure for emotional responses. Practicing deep breathing exercises can calm the nervous system, and engaging in sensory-based activities can offer a constructive outlet for emotional expression. These tools are vital for individuals with Asperger's as they work towards emotional regulation and a harmonious interaction with the world around them.
Intellectual and Cognitive Abilities
While individuals with Asperger's Syndrome may face challenges in certain areas, they often demonstrate strengths in intellectual and cognitive abilities. Many individuals with this condition have above-average intelligence and possess a remarkable ability to focus on and retain information related to their specific interests.
They may excel in areas such as mathematics, technology, and logical reasoning. It is crucial to support and nurture these strengths to help individuals reach their full potential.
Diagnosis and Assessment of Asperger’s Syndrome
Identifying Asperger's Syndrome, a profile within the broader autism spectrum disorder (ASD), begins with a meticulous diagnostic process. A healthcare expert, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, undertakes this task, following a multi-faceted approach that includes examining the person's developmental history and observing their social and communicative behaviors.
The evaluation also delves into cognitive functioning. The significance of this process is underscored by the fact that, according to recent data, 1 in 45 adults in the U.S. are diagnosed with ASD, highlighting the critical need for precise and consistent diagnostic methods.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), provides a robust framework for these assessments, detailing specific criteria necessary for a diagnosis of Asperger's Syndrome. This rigorous approach ensures that individuals receive an accurate diagnosis, which is the first step towards understanding and support. Moreover, diagnoses are recorded using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), which standardizes data across healthcare systems and enables comprehensive research, furthering our understanding of Asperger's Syndrome on a global scale.
Treatment and Support Strategies
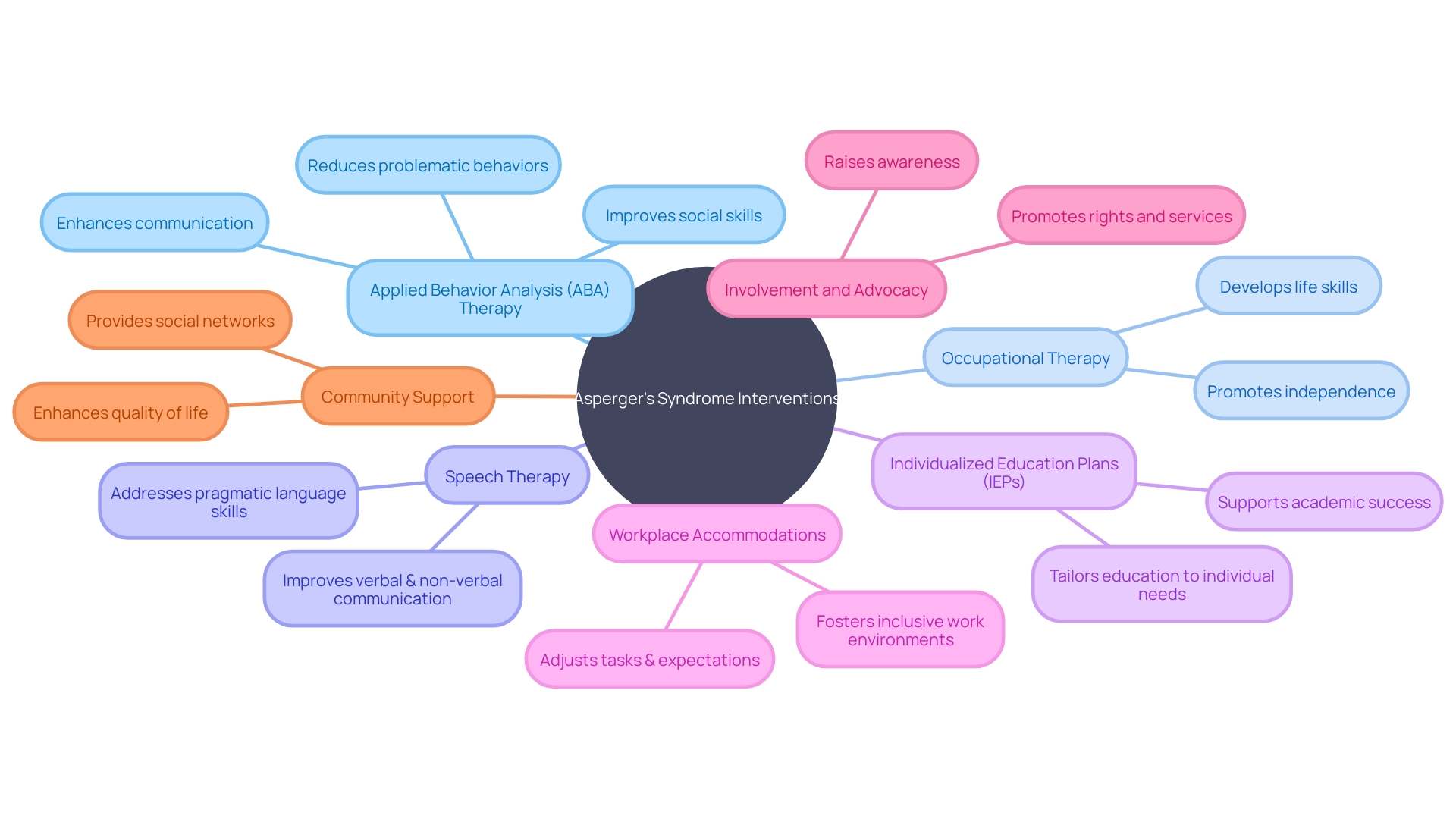
While Asperger's Syndrome remains a lifelong condition, proactive and tailored approaches can significantly enhance the lives of those affected. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is one such intervention that has shown promise in helping individuals hone their social and communicative abilities. By focusing on positive reinforcement, ABA therapy can lead to meaningful improvements in daily functioning.
Occupational therapy is another avenue that offers immense benefits, particularly in addressing sensory challenges and motor skill development, enabling individuals to better interact with their environment. Speech therapy also plays a crucial role by targeting the intricacies of language and communication, fostering clearer and more effective interpersonal interactions. Crucially, the implementation of individualized education plans (IEPs) and workplace accommodations are vital in ensuring that each person's unique requirements are met, thus facilitating a supportive learning and working environment.
The value of these interventions is immeasurable, as they empower individuals to navigate their challenges and unlock their full potential. As the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) underscores, involvement and advocacy are key to driving policy change and improving the lives of those with mental health conditions. Their advocacy actions demonstrate a commitment to ensuring that no one feels alone in their journey, highlighting the importance of community support and the impact of collective efforts on mental health.
Complications and Co-occurring Conditions
Navigating the complexities of Asperger's Syndrome extends beyond the core characteristics of the condition. Adults, who represent 1 in 45 diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in the U.S., often face a mosaic of additional challenges that intertwine with their primary diagnosis.
Anxiety disorders, depression, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) frequently accompany Asperger's, adding layers to the care and understanding required. Moreover, executive functioning difficulties can further complicate daily activities, calling for tailored strategies to manage these co-occurring conditions.
Acknowledging these concurrent issues is vital, as they can profoundly affect an individual's well-being. Proactive management of these conditions, in conjunction with Asperger's Syndrome, is essential to fostering a supportive environment that promotes overall health and life quality. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of ASD and its associated conditions is the first step toward achieving a comprehensive support system for those affected.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Asperger's Syndrome is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social interaction, communication, and behavior. Individuals with Asperger's struggle with social cues, have repetitive behaviors, and intense interests.
Communication patterns can be unique, with difficulties in understanding non-literal language. Understanding sensory preferences is crucial for their well-being.
Emotional regulation is challenging for individuals with Asperger's. Tailored strategies like visual aids and deep breathing exercises help them navigate their emotions.
Despite challenges, they often demonstrate strengths in intellectual abilities. Accurate diagnosis is essential to provide appropriate support. Treatment strategies include ABA therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, IEPs, workplace accommodations, advocacy actions, community support, and managing co-occurring conditions like anxiety and ADHD. By understanding the unique characteristics of Asperger's Syndrome and implementing appropriate support strategies, parents and advocates can ensure the well-being of their children.




