Introduction
The landscape of autism is evolving, marked by rising prevalence rates and a growing recognition of the diverse needs within the autism spectrum. Recent statistics reveal that approximately 1 in 100 children globally are diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), highlighting an urgent call for enhanced awareness and resources. In the United States, the prevalence has reached 1 in 44 children, underscoring the importance of timely support and informed advocacy.
As parents and advocates navigate these complex statistics, it becomes increasingly vital to address demographic variations and historical trends that influence diagnosis and support. This article delves into the current state of autism prevalence worldwide, the implications for public health and policy, and the critical role of community advocacy in ensuring that all autistic individuals receive the support they need to thrive.
Current Prevalence Rates of Autism Worldwide
Recent estimates from the World Health Organization (WHO) suggest that approximately 1 in 100 youth globally are diagnosed with spectrum disorder (ASD), which raises the question of what percent of people are autistic. This statistic not only underscores the increasing recognition of the condition but also highlights a critical need for enhanced awareness and resources worldwide. In France, the prevalence rate of the condition stands at 425.41 per 100,000 youth, exemplifying significant regional variation influenced by factors such as healthcare accessibility, diagnostic methodologies, and cultural attitudes towards disability.
In certain areas, rates can soar to 1 in 54 individuals, prompting the need to ask what percent of people are autistic, and highlighting the urgent necessity of understanding these disparities in a global context. Moreover, it is crucial to contemplate the long-term effects of individuals on the spectrum, as approximately 75% of adults identified with this condition in the US face underemployment or joblessness, highlighting the necessity for continuous assistance beyond childhood. As proponents for our youth, it is vital to acknowledge these statistics as a call to action, urging us to strive for enhanced frameworks and resources customized to the distinct requirements of autistic individuals and their families.
Moreover, the case study named 'Future Predictions' demonstrates the notable rise in autism education, research, and awareness, while also emphasizing parental worries regarding the future care of their autistic offspring, indicating a need for improved planning assistance.
Autism Statistics in the United States: Key Findings
Recent statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reveal what percent of people are autistic, showing that approximately 1 in 44 children in the United States is diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), which marks a notable increase in prevalence over the past few decades. This rising trend can be attributed to heightened awareness, refined diagnostic criteria, and improved access to healthcare services. Significantly, 50% of autistic youth in the U.S. who receive vocational rehabilitation (VR) start those services in high school, emphasizing the critical importance of timely assistance for families.
The CDC's revised statistics for 2024, derived from computed values, highlight this ongoing change, stressing the importance of strong support systems and resources for families impacted by developmental disorders. As highlighted in recent studies, there are significant racial disparities in autism prevalence, with non-Hispanic White children showing lower rates compared to their non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander counterparts. This disparity underscores the urgent need for targeted awareness and resources within diverse communities.
Moreover, conversations among parents indicate differing priorities, with mothers emphasizing the significance of professional qualities, respite, assistance groups, and counseling, while fathers concentrate more on social development aid and self-care. These differing priorities reflect the broader call for comprehensive community assistance systems. As we analyze these statistics and trends, it becomes increasingly clear that community advocacy and informed assistance are essential in addressing the needs of families, ensuring they have access to the resources necessary for their children's well-being.
The study’s findings also point to the importance of educating social workers to assist parents in planning effectively and managing the various stages of support.
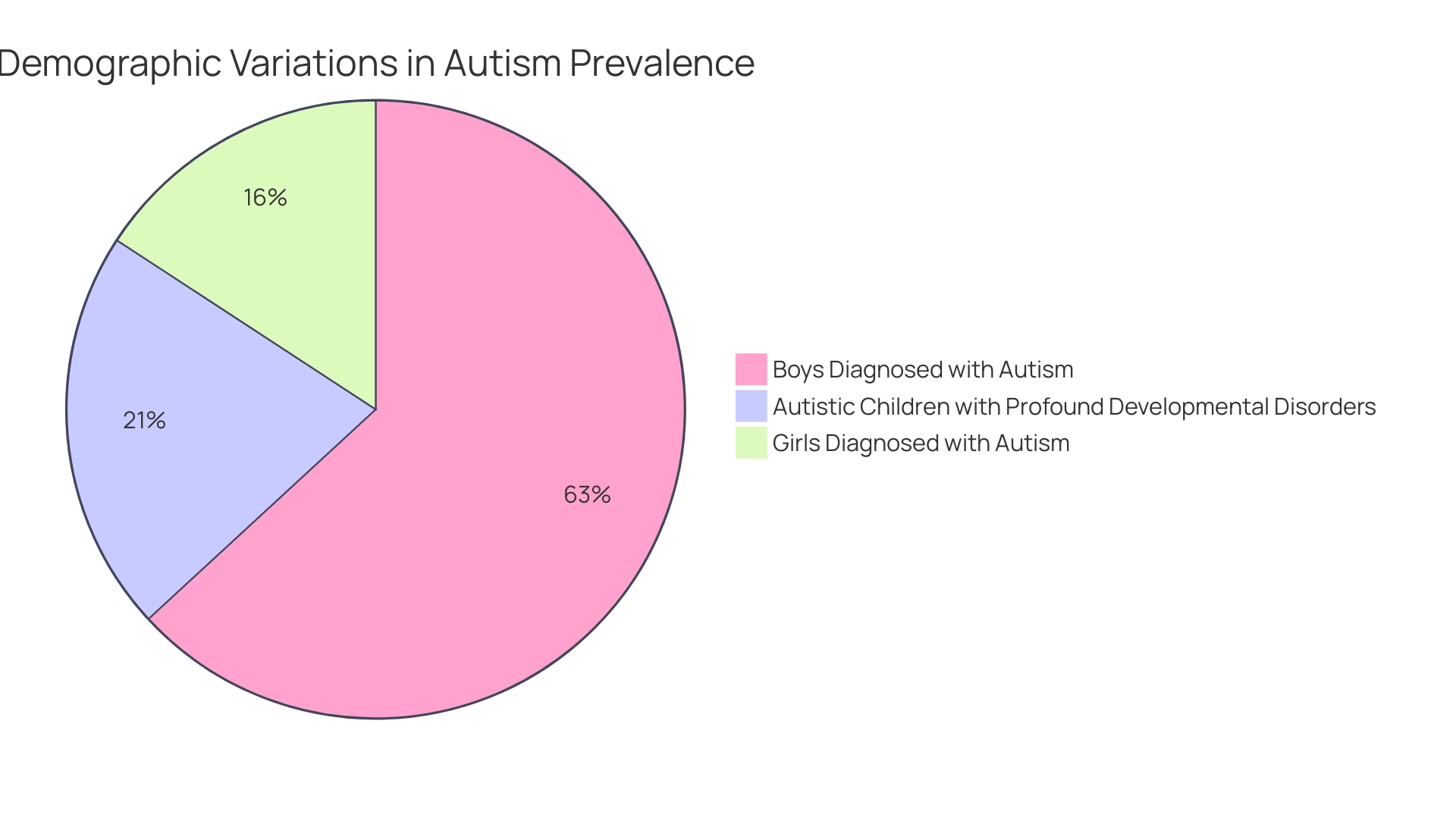
Demographic Variations in Autism Prevalence
Research highlights notable variations in prevalence of the condition across different demographics, raising the question of what percent of people are autistic and shedding light on critical factors that parent advocates should consider. Current statistics reveal that boys are diagnosed with this condition at a rate approximately four times higher than girls, prompting discussions about both biological and social influences that contribute to this disparity. In addition, 26.7% of autistic 8-year-olds in the US have profound developmental disorders, which underscores the need for tailored support, particularly in minority groups.
The combined prevalence of the condition in 2000 was 6.7 per 1,000 children, or approximately 1 in 150, which raises the question of what percent of people are autistic and provides historical context illustrating the increasing recognition of the disorder over the years. Furthermore, the landscape of autism diagnosis is not uniform across ethnic groups. Certain minority communities may experience higher rates of diagnosis, while others face underdiagnosis, often rooted in cultural stigma or limited access to healthcare resources.
Acknowledging these demographic differences is crucial for developing effective outreach initiatives and assistance systems that resonate with diverse populations. Recent studies emphasize the significance of customizing interventions to address the distinct requirements of diverse communities, ensuring that all children obtain the assistance they deserve. As one father noted, addressing unmet assistance needs is crucial, emphasizing the importance of including time for relaxation and self-care.
By promoting awareness and understanding of these variations, we can strive for a more inclusive approach to care and support.
Historical Trends in Autism Diagnosis and Prevalence
The landscape of developmental disorder diagnosis has transformed dramatically since its initial identification in the mid-20th century. As awareness and understanding have expanded, what was once considered a rare condition is now recognized as a significant public health concern, raising questions about what percent of people are autistic. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) initiated a more thorough monitoring of developmental disorder diagnoses in the early 2000s, revealing a notable rise in reported cases.
This increase can be attributed to a variety of factors:
- Refined diagnostic criteria
- Heightened awareness among healthcare professionals
- A broader public understanding of the spectrum nature of the condition
Statistics reveal that across different regions, prevalence rates can differ significantly, prompting an inquiry into what percent of people are autistic; for instance, in South Africa, autism affects approximately 1 in 160 individuals. Conversely, countries like India and China report lower rates, at 1 in 250 and 1 in 186 respectively.
These lower prevalence rates are often attributed to limited awareness, stigma, and a lack of resources, which hinder proper diagnosis and assistance. Furthermore, the average age of diagnosis for youngsters in lower-income households is 4.7 years compared to 5.2 years in higher-income households, emphasizing a significant disparity in access to diagnosis and assistance. Recent news has also highlighted emerging patterns in racial and ethnic differences in ASD identification among 8-year-olds, underscoring the necessity for customized approaches to address these disparities.
As we progress, it is essential to observe these trends and differences, ensuring that support systems are strong and responsive to the increasing number of individuals identified with the condition. Understanding these historical trends and the evolving nature of diagnostic criteria fosters a knowledgeable community, empowering parents to advocate for their offspring's needs effectively.
Implications of Autism Statistics for Public Health and Policy
The implications of autism statistics extend far beyond mere figures; they serve as critical indicators that inform public health initiatives and policy decisions with the potential to transform the lives of individuals on the autism spectrum. For instance, with a reported prevalence of 89.40 per 10,000 children in Egypt, the urgency for accessible services, educational resources, and strong assistance systems for families becomes starkly apparent. Policymakers are urged to take action, responsible for distributing funding and resources that effectively address these increasing demands within communities.
This responsibility is echoed in expert recommendations suggesting that social workers should be educated to assist parents in planning, breaking down the process into manageable steps while providing ongoing support throughout. Furthermore, Board-Certified Behavior Analysts at Prospera Healthcare play an essential role in assisting families comprehend the condition and create customized therapy plans, directly addressing the needs emphasized by the prevalence statistics. Moreover, these statistics empower parents and advocates to engage in meaningful discussions regarding policy changes that can cultivate a more inclusive society.
As advocates strive for progress, the cultural shift away from traditional symbols like the puzzle piece toward more inclusive representations, such as the rainbow infinity sign, illustrates a collective movement towards recognizing the diverse experiences within the spectrum. This shift not only reflects evolving perspectives but also underscores the essential role of advocacy in shaping a future where all individuals with autism can thrive.
Conclusion
The increasing prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) worldwide demands urgent attention and action from parents, advocates, and policymakers alike. With approximately 1 in 100 children globally diagnosed, and 1 in 44 in the United States, it is clear that the need for awareness, education, and resources has never been more critical. The disparities observed across different demographics and regions illustrate the complex landscape of autism, emphasizing the importance of tailored support systems and community advocacy to meet the unique needs of all individuals on the spectrum.
Understanding the historical trends and current statistics surrounding autism is essential for shaping effective public health initiatives and policies. As the landscape continues to evolve, it is imperative that advocates engage in dialogue, push for necessary changes, and work to dismantle barriers that hinder access to diagnosis and support. By fostering an inclusive environment that recognizes the diverse experiences within the autism community, stakeholders can ensure that every autistic individual receives the support they need to thrive.
In conclusion, the journey toward improved awareness and resources is a collective effort that requires the commitment of all involved. By standing together as advocates for change, families can create a brighter future for their children with autism, ensuring they have the tools, support, and opportunities to flourish in society. Now is the time to act, to harness the power of community, and to drive the change that will benefit all individuals on the autism spectrum.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the estimated prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) globally among youth?
Approximately 1 in 100 youth globally are diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), according to recent estimates from the World Health Organization (WHO).
How does the prevalence of autism vary by region?
In France, the prevalence rate of autism stands at 425.41 per 100,000 youth, indicating significant regional variation influenced by factors such as healthcare accessibility, diagnostic methodologies, and cultural attitudes towards disability.
What is the autism prevalence rate in the United States?
Recent statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicate that approximately 1 in 44 children in the United States is diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
What factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of autism diagnoses?
The rising trend in autism diagnoses can be attributed to heightened awareness, refined diagnostic criteria, and improved access to healthcare services.
What are the employment challenges faced by adults with autism in the US?
Approximately 75% of adults identified with autism in the US face underemployment or joblessness, highlighting the need for continuous support beyond childhood.
What disparities exist in autism prevalence among different racial groups?
Significant racial disparities have been observed, with non-Hispanic White children showing lower rates of autism compared to non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander children.
How do parents' priorities differ regarding support for their autistic children?
Mothers tend to emphasize the importance of professional qualities, respite, assistance groups, and counseling, while fathers focus more on social development aid and self-care.
What is the significance of timely assistance for autistic youth in the US?
It is critical as 50% of autistic youth in the U.S. who receive vocational rehabilitation (VR) start those services in high school, underscoring the need for strong support systems.
What role does community advocacy play in supporting families with autistic children?
Community advocacy is essential in addressing the needs of families, ensuring they have access to the necessary resources for their children's well-being.
Why is there a need for educating social workers regarding autism?
Educating social workers is important to assist parents in effectively planning and managing the various stages of support for their autistic children.




