Overview
The percentage of people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is currently diagnosed in approximately 2.7% of youths in the United States, translating to about 1 in 37 youths, with global estimates ranging from 1 in 100 to 1 in 150 individuals. This information is supported by the article's discussion of recent CDC statistics and the factors contributing to the rising prevalence, including improved awareness and diagnostic practices, which highlight the need for enhanced advocacy and support systems for individuals with autism.
Introduction
The rising prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) has become a pivotal topic in today’s society, impacting families, educators, and healthcare systems alike. With approximately 1 in 36 children now diagnosed with autism, the urgency for understanding the complexities of this condition has never been greater.
This article delves into the multifaceted nature of autism, exploring its characteristics, current prevalence rates, and the demographic variations that shape its understanding. It also highlights historical trends in diagnosis and the societal implications of increasing autism rates.
By equipping parents and advocates with essential insights and resources, the aim is to foster a supportive environment that celebrates the unique strengths of individuals with autism while addressing the challenges they face.
Understanding Autism: Definition and Characteristics
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition that presents unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. The term 'spectrum' aptly describes the diverse range of abilities and challenges individuals on the spectrum may experience. Key characteristics of ASD often include:
- Significant challenges in interpreting social cues
- Varying levels of language development
- A propensity for repetitive behaviors or [focused interests
Recent statistics](https://cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/data) reveal that the growing recognition of the condition's prevalence is reflected in the percentage of people with autism, with a total identification of 6,245 individuals with ASD across multiple sites. This statistic is particularly relevant in Wisconsin, where 54.8% of the population aged 8 years is White, potentially influencing the demographic understanding of ASD prevalence. Comprehending these traits is essential for caregivers and specialists, particularly as recent studies in 2024 keep revealing the complexities of the condition.
Furthermore, it’s essential for parents to be aware that those raising autistic individuals often face higher levels of stress compared to their neurotypical counterparts, influenced by various factors. As Matthew J. Maenner from the CDC states, 'Understanding the complexities of ASD is crucial for effective support and intervention.' The limitations identified in studies, such as reliance on the quality of existing records, potential misclassification of cognitive abilities, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on data collection, emphasize the importance of cautious interpretation of findings regarding the percentage of people with autism.
By grasping these complexities, advocates can better support individuals with developmental differences and foster an environment that nurtures their unique strengths and challenges.
Current Prevalence Rates of Autism Worldwide
Recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reveals that the percentage of people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is now diagnosed in approximately 2.7% of youths in the United States, or about 1 in 37 youths, marking a significant increase over the past few decades. This rise is attributed not only to actual increases in cases but also to heightened awareness and advancements in diagnostic practices. Autism is a complex neurological condition that does not have a cure, but early therapy and intervention can help manage behaviors and improve quality of life.
Globally, the estimates for the percentage of people with autism vary considerably, ranging from 1 in 100 to 1 in 150 individuals, influenced by regional differences and varying diagnostic criteria. Such statistics are crucial for parents and professionals alike, as they underscore the necessity for enhanced advocacy for resources and support systems. As Natalie Schad, a specialist in early intervention, emphasizes,
Joyfully assisting individuals reach their full potential since 2014 using an individualized and natural approach.
This sentiment is echoed by many caregivers, with a survey revealing that 36.5% utilize Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, reporting substantial improvements in their children's behavior and communication skills. The high satisfaction rates among caregivers regarding ABA therapy reinforce the importance of understanding these trends in developmental diagnosis, highlighting the need for inclusion and support while empowering advocates to promote acceptance and celebrate the strengths of neurodivergence.
Demographic Variations in Autism Prevalence
Recent studies indicate that this condition is identified more often in boys than in girls, with the actual male-to-female ratio being nearer to 3:1 instead of the frequently mentioned 4:1. This disparity can be attributed to both biological factors and the different ways the condition manifests in each gender. Notably, girls with autism tend to exhibit more genetic mutations, indicating that they may require a greater genetic burden to develop the condition.
Furthermore, age is a significant factor in diagnosis, as younger individuals are increasingly identified earlier due to improved awareness and screening practices. As Tom Flis, Clinical Director of the Center for Autism at Sheppard Pratt, notes,
If the prevalence is inaccurate with regard to females, then many of these assessments are normed more towards the male presentation of ASD.
Recent findings also reveal that females with ASD have significantly higher camouflaging scores than males, and this camouflaging correlates negatively with emotional expressivity, indicating potential gender differences in symptom expression.
Additionally, there are inconsistencies in ASD symptom presentation between genders, which can complicate the diagnostic process. For parent advocates, understanding these demographic variations is crucial, as they can significantly influence the support and resources available for their children. Real-world examples further illustrate that the presentation of symptoms associated with the condition can vary widely between boys and girls, underscoring the need for tailored approaches in assessment and intervention.
Ultimately, it is crucial to consider the influence of sexism and patriarchy on research related to this condition, as highlighted by individuals like Al, who emphasize the need for a more inclusive understanding across genders.
Historical Trends in Autism Diagnosis and Prevalence
Historically, this condition has encountered considerable difficulties in acknowledgment and assessment, especially for its milder forms, which were frequently overlooked or misidentified. The introduction of the DSM-III in the 1980s was a pivotal moment, as it formally acknowledged the condition as a distinct classification, leading to a dramatic shift in awareness and understanding. Since then, the criteria for diagnosing this condition have evolved further, notably with the DSM-5's expansion of the spectrum.
This change has enabled a larger percentage of people with autism to obtain suitable evaluations, reflecting not only a genuine rise in cases but also a significant shift in societal views of the condition. Recent studies suggest that the prevalence of neurodevelopmental disorders, including the percentage of people with autism, in California keeps increasing, a trend that is not significantly influenced by the low domestic out-migration rate of about 1.4% per year among youth aged 0–10. As emphasized in the case study titled 'Impact of Migration on Autism Incidence Rates,' the analysis assumed that out-migration rates among youths were independent of the disorder, confirming that overall trends in prevalence were largely unaffected by migration patterns.
As Irva Hertz-Picciotto, a notable researcher in public health, explains,
We also identify faulty assumptions... in a simulation study that attempted to assess the contributions to time trends in developmental disorders from artifacts such as changes in definition, age at identification, and ascertainment.
This historical viewpoint is invaluable for parents who are navigating the complexities of developmental disorders today, empowering them to advocate for their offspring and understand the nuances of diagnosis and prevalence.

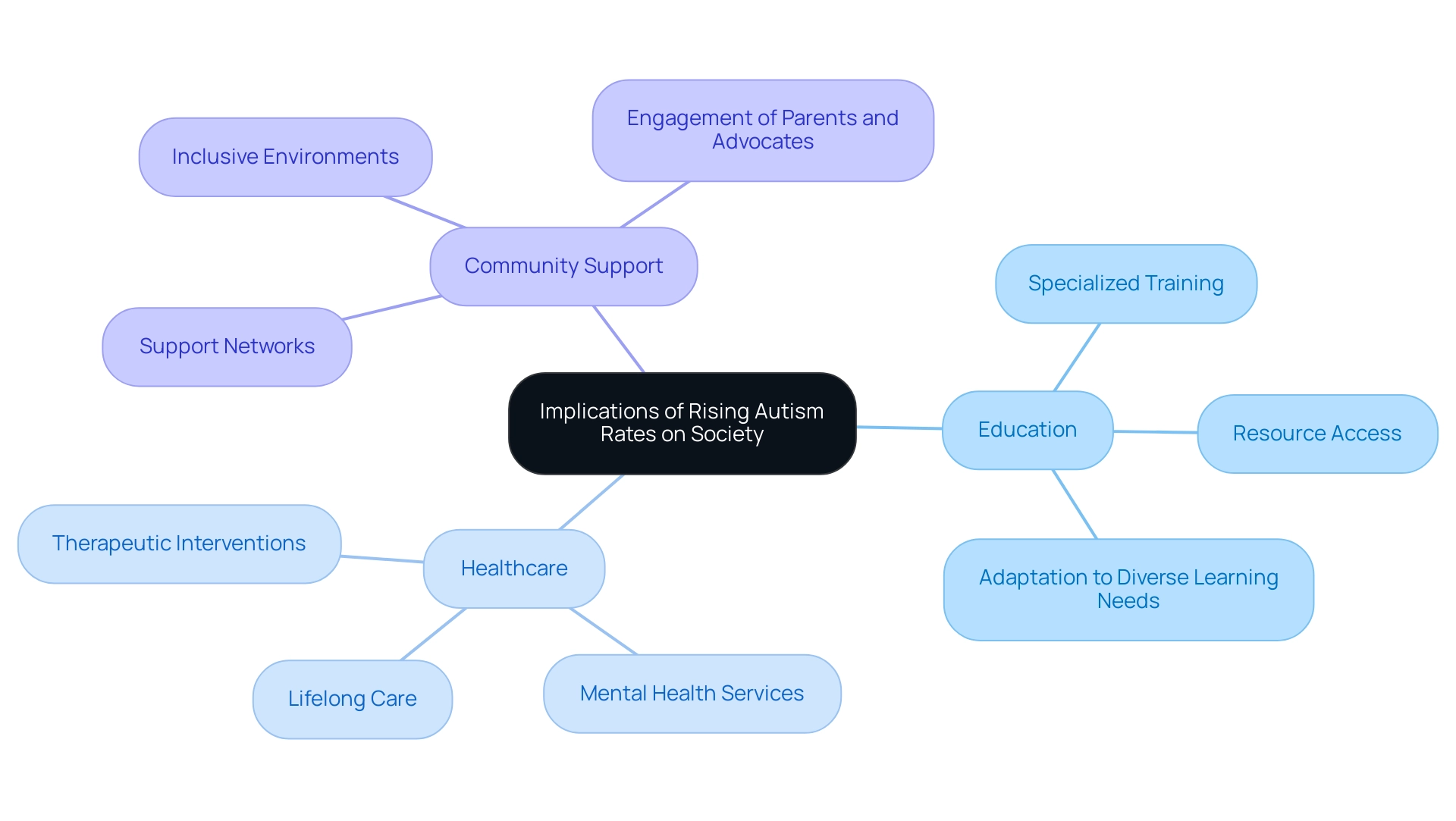
Implications of Rising Autism Rates on Society
The rising occurrence of spectrum disorder (ASD) carries significant implications for society, particularly in education, healthcare, and community support systems. Recent statistics indicate that 1 in 36 children are now recognized with a developmental disorder, highlighting an urgent need for schools to adapt to the diverse learning requirements of these students. Additionally, the National Survey of Children's Health (NSCH) data suggests a correlation between state-level educational rewards and increased ASD diagnosis, emphasizing the need for systemic changes to enhance ASD detection.
Educators are called to receive specialized training and access additional resources to ensure effective accommodations. According to Spectrum SPARK,
The term 'profound condition' refers to individuals with symptoms so severe they’ll likely need lifelong 24/7 care.
This classification has sparked controversy, particularly regarding its implications for divisions within the neurodiverse community, affecting girls and minority groups.
Notably, the percentage of people with autism who are classified as autistic 8-year-olds with profound developmental disorder is 26.7%, indicating a demand for lifelong care. Healthcare systems must also evolve, providing comprehensive support that includes mental health services and therapeutic interventions tailored to individual needs. Community organizations are vital in creating inclusive environments and establishing support networks for families, helping to bridge the gaps in services.
As awareness expands, it becomes imperative for parents and advocates to actively engage with these systems, ensuring that individuals with autism are equipped with the necessary resources to flourish in their communities.
Conclusion
The complexities surrounding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) reveal a pressing need for awareness and understanding. With approximately 1 in 36 children now diagnosed with autism, recognizing its defining characteristics—including challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior—is essential for both parents and professionals. As the prevalence of ASD continues to rise, driven by improved diagnostic practices and heightened awareness, it becomes increasingly important for advocates to support individuals with autism and celebrate their unique strengths.
Demographic variations in autism prevalence highlight significant factors that influence diagnosis and support. Understanding the disparities in diagnosis between genders and recognizing the diverse manifestations of autism can empower advocates to tailor their approaches effectively. Historical trends in autism diagnosis remind us of the importance of ongoing education and advocacy, as societal perceptions shift and evolve. This historical insight equips parents with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of autism today.
As society grapples with the implications of rising autism rates, the call for systemic change in education, healthcare, and community support systems becomes undeniable. The need for specialized training for educators, comprehensive healthcare support, and inclusive community environments is paramount. By actively engaging with these systems, parents and advocates can ensure that individuals with autism have the resources and support necessary to thrive. Ultimately, fostering a culture of understanding and acceptance not only benefits those with autism but enriches society as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition characterized by unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. It encompasses a diverse range of abilities and challenges that individuals may experience.
What are the key characteristics of ASD?
Key characteristics of ASD often include significant challenges in interpreting social cues, varying levels of language development, and a propensity for repetitive behaviors or focused interests.
What are the recent statistics regarding the prevalence of ASD?
Recent statistics indicate that approximately 2.7% of youths in the United States are diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder, which translates to about 1 in 37 youths. This marks a significant increase over the past few decades, attributed to both actual increases in cases and heightened awareness.
How does the demographic makeup influence the understanding of ASD prevalence?
In Wisconsin, for example, 54.8% of the population aged 8 years is White, which may influence the demographic understanding of ASD prevalence and the statistics reported.
What challenges do parents of autistic individuals face?
Parents raising autistic individuals often experience higher levels of stress compared to those with neurotypical children, influenced by various factors related to the complexities of ASD.
What are the limitations in current studies on ASD?
Limitations in studies include reliance on the quality of existing records, potential misclassification of cognitive abilities, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on data collection, which necessitates cautious interpretation of findings regarding autism prevalence.
What is the significance of early therapy and intervention for individuals with ASD?
While there is no cure for autism, early therapy and intervention can help manage behaviors and improve the quality of life for individuals with ASD.
What percentage of caregivers report improvements in their children’s behavior through Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy?
A survey revealed that 36.5% of caregivers utilize ABA therapy, reporting substantial improvements in their children's behavior and communication skills.
Why is understanding the complexities of ASD important for advocacy?
Grasping the complexities of ASD is essential for advocates to better support individuals with developmental differences and to foster an environment that nurtures their unique strengths and challenges.




