Introduction
In a world where understanding autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is more critical than ever, the prevalence rates and their implications for families demand attention. With estimates indicating that as many as 1 in 100 children are affected globally, and even more alarming figures in certain regions, the landscape of autism is complex and ever-evolving.
Variations in diagnosis rates highlight the pressing need for awareness and support, particularly as parents grapple with the long-term implications for their children. From genetic and environmental influences to disparities in healthcare access, a myriad of factors shape the experiences of families navigating autism.
As the discourse around autism expands, so too does the urgency for advocacy, education, and community support. This article delves into the current state of autism prevalence, the factors influencing these rates, and the vital role of advocacy in ensuring that families receive the resources and support they need to thrive.
Current Global Prevalence Rates of Autism
Recent estimates suggest that the worldwide occurrence of ASD is around 1 in 100 youngsters, although this number varies greatly across various areas. Significantly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports a diagnosis rate of 1 in 44 children in the United States, highlighting a troubling upward trend in cases of the disorder. This increase can largely be attributed to heightened awareness, refined diagnostic criteria, and more rigorous screening practices.
For example, Andorra has a rate of 547.02 cases per 100,000, demonstrating the global differences in incidence rates. Globally, the percentage of autism in the world fluctuates between 0.1% and over 2%, with certain countries exhibiting higher rates, which may reflect their healthcare systems' enhanced abilities to detect and diagnose the condition effectively. As one expert suggests, this trend may indicate that the country's healthcare system is better at detecting and diagnosing this condition than are the healthcare systems of other countries.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider the long-term implications of the condition, as roughly 75% of adults diagnosed with it in the US experience underemployment or unemployment. This context emphasizes the essential need for ongoing advocacy and assistance, particularly as parents voice legitimate worries regarding their offspring's future and the requirement for sufficient planning as they grow older. Additionally, the increase in peer-reviewed articles on the condition from 800 in 2003 to 3,400 in 2013 signifies a rise in education and awareness, yet parents remain worried about the future care of their children with the condition, emphasizing the need for better planning support.
Factors Influencing Autism Prevalence Worldwide
The percentage of autism in the world varies significantly, as the occurrence of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Recent findings from the ADDM Network emphasize the significance of comprehending these variations, as they aggregate data from various locations to identify trends in the percentage of autism in the world over the years. Genetic studies reveal compelling statistics: the SNP-heritability of the condition can range from as high as 65% in multiplex families to only 12% in recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS).
This variability highlights the significance of genetic predisposition, especially in families with a history of the condition. The case study titled 'Common Genetic Variation in Autism' further illustrates this point, showing how the SNP-heritability of the condition varies and highlighting the need for improved methodologies in genetic research. Environmental factors also play a crucial role; exposure to toxins during pregnancy, maternal health conditions, and the quality of prenatal care are key contributors to rates of this condition.
Cultural perceptions can complicate the landscape—many communities may stigmatize this condition or misunderstand its manifestations, leading to significant underreporting and misdiagnosis. This underreporting can obstruct precise diagnosis and assistance for individuals with developmental disorders. Additionally, disparities in healthcare access and educational resources can further obstruct the identification and support of affected children.
It is crucial for parent advocates to raise awareness and encourage training within various communities, ensuring that all families possess the essential resources to manage the challenges related to developmental disorders. V. Warrier emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to understanding these factors, advocating for comprehensive strategies that encompass both genetic insights and environmental considerations.
Disparities in Diagnosis and Awareness of Autism
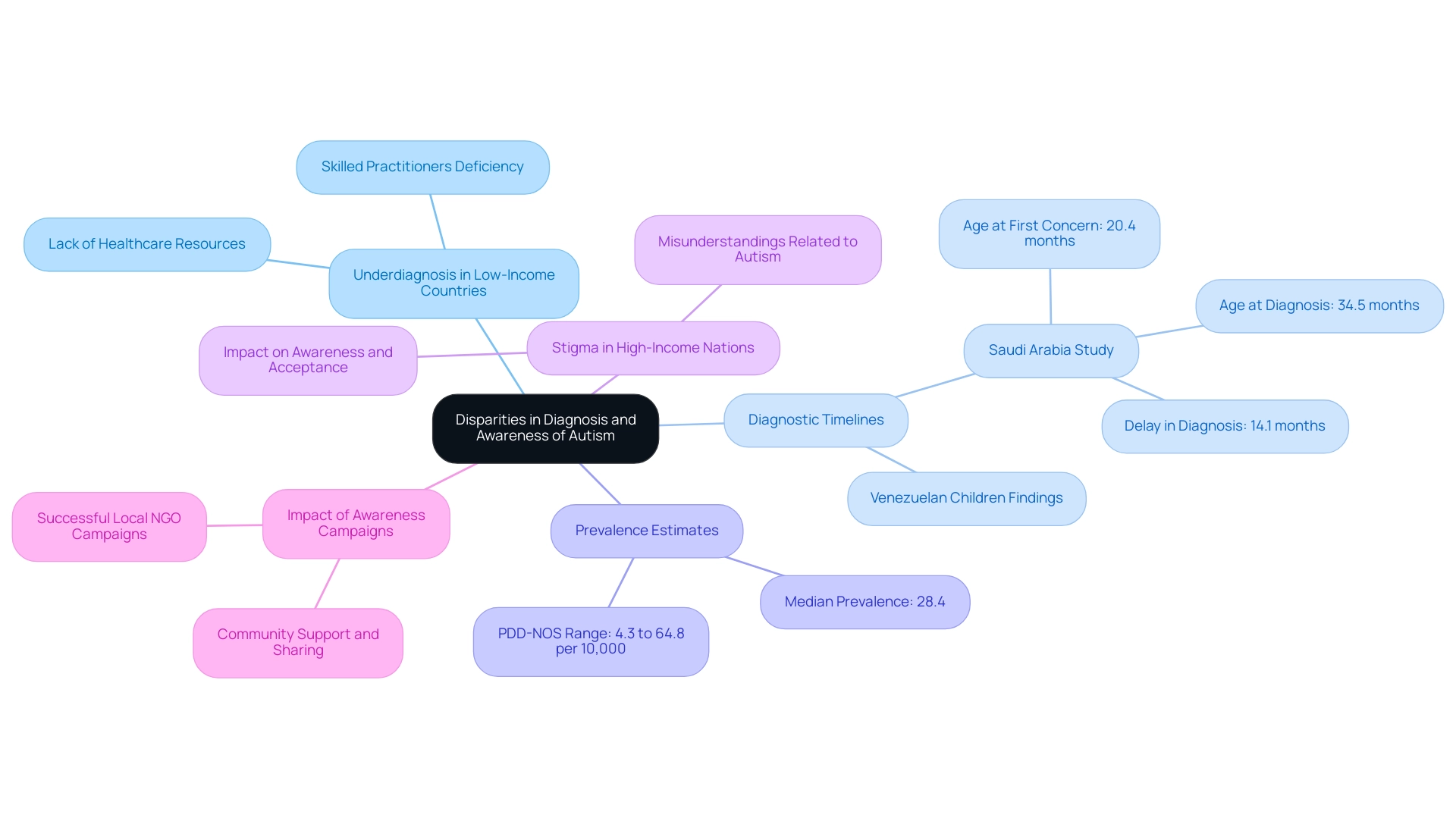
The landscape of developmental disorder diagnosis and awareness is marked by significant disparities across different countries and communities. In numerous low- and middle-income countries, a deficiency of available healthcare resources and skilled practitioners leads to significant underdiagnosis of the condition. For instance, a study conducted by Alotaibi et al. (2021) in Saudi Arabia revealed that the average age at which parents first expressed concern was 20.4 months, while the age at diagnosis was 34.5 months, resulting in a delay of 14.1 months. This highlights the variability in diagnostic timelines and the need for timely intervention. Statistics indicate that the prevalence estimates for PDD-NOS, which contribute to the percentage of autism in the world, range from 4.3 to 64.8 per 10,000, with a median of 28.4, underscoring the varying levels of awareness and diagnosis across different regions.
Additionally, Montiel-Nava et al. reported significant findings regarding the age of diagnosis of spectrum disorder in Venezuelan children, emphasizing the need for a global perspective on these disparities. Conversely, high-income nations, despite possessing more resources, struggle with stigma and misunderstandings related to the condition, which can impede awareness and acceptance.
As noted by Brighter Strides ABA, changes in diagnostic criteria have played a significant role in the observed trends in prevalence of the condition. Successful awareness campaigns, like those conducted by local NGOs, have proven effective in enhancing diagnosis and acceptance in various communities, demonstrating the power of education in transforming perceptions. Furthermore, establishing a supportive community where parents can share experiences and resources is essential, empowering families to navigate the complexities related to the condition effectively.
The Importance of Advocacy and Support for Families
Advocacy and assistance are crucial for families navigating the complexities of autism spectrum disorder. Parents are at the forefront of this journey, playing an essential role in advocating for their offspring's unique needs—be it through securing appropriate therapies, educational accommodations, or essential community resources. Research indicates that peer advocacy significantly influences systemic advocacy, with a total effect of 0.554 (p < 0.001), underscoring the power of collaborative efforts.
By engaging with local assistance groups and organizations, families can access invaluable information and emotional guidance tailored to their circumstances. Moreover, various methods in [Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, including:
- Discrete Trial Training
- Natural Language Acquisition
can be tailored to address unique requirements, showcasing the significant effect of personalized interventions on individuals with developmental disorders. Participating in advocacy at both community and policy levels not only increases awareness but also improves resource availability for individuals with developmental disabilities.
As stated by Burke et al. (2022), empowering parents through knowledge is indicative of more effective advocacy programs, particularly when they are tailored to specific types of advocacy, such as legislative advocacy. By fostering a culture of empowerment and support, we can cultivate a more inclusive environment for children with autism, ensuring they receive the care and opportunities they truly deserve.
Conclusion
Understanding autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is essential for families facing its challenges. With global prevalence rates indicating that about 1 in 100 children are affected, and figures like 1 in 44 in the United States, the need for advocacy and support is more pressing than ever. This rise in diagnoses, attributed to improved awareness and diagnostic criteria, underscores the importance of addressing the long-term implications for individuals with autism, many of whom face significant barriers to employment as adults.
The factors influencing autism prevalence are complex, involving genetic and environmental elements, as well as cultural perceptions that can hinder accurate diagnosis and support. Parent advocates are crucial in fostering awareness and ensuring families have the resources they need to navigate these challenges effectively.
Disparities in diagnosis and awareness further highlight the urgency for timely interventions. Families in lower-income regions often experience delays in receiving diagnoses, while those in higher-income areas may confront stigma and misunderstandings. Successful awareness initiatives demonstrate that education can transform perceptions and foster acceptance, creating a supportive environment for families.
Ultimately, advocacy is vital for securing the necessary resources and support for children with autism. By collaborating with local organizations and advocating for policy changes, families can help build a more inclusive society. As the dialogue around autism continues to grow, the concerted efforts of parent advocates will be instrumental in ensuring that children with autism receive the understanding, care, and opportunities they deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the estimated occurrence of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) worldwide?
Recent estimates suggest that the worldwide occurrence of ASD is around 1 in 100 youngsters, although this number varies greatly across different regions.
What is the diagnosis rate of ASD in the United States?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports a diagnosis rate of 1 in 44 children in the United States, indicating a troubling upward trend in cases of the disorder.
What factors contribute to the increasing rates of ASD diagnoses?
The increase in ASD diagnoses can largely be attributed to heightened awareness, refined diagnostic criteria, and more rigorous screening practices.
How does the incidence of ASD vary by country?
For example, Andorra has a rate of 547.02 cases per 100,000, demonstrating significant global differences in incidence rates. Globally, the percentage of autism fluctuates between 0.1% and over 2%, with some countries showing higher rates due to better healthcare systems that can detect and diagnose the condition effectively.
What are the long-term implications for adults diagnosed with ASD in the United States?
Approximately 75% of adults diagnosed with ASD in the US experience underemployment or unemployment, highlighting the need for ongoing advocacy and assistance.
What concerns do parents have regarding their children with ASD?
Parents express legitimate worries about their offspring's future and the necessity for sufficient planning as they grow older, particularly regarding care and support.
How has awareness and education about ASD changed over the years?
The number of peer-reviewed articles on the condition increased from 800 in 2003 to 3,400 in 2013, signifying a rise in education and awareness about ASD. However, parents still remain concerned about future care for their children, emphasizing the need for better planning support.




