Introduction
The journey of navigating Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) treatment can be both daunting and empowering for parents. With a spectrum of therapies and medications available, understanding the diverse options is crucial for making informed choices that cater to a child's unique needs.
From the well-established benefits of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) to the supportive role of medication, each approach plays a vital part in enhancing communication, social skills, and overall well-being. By exploring these treatment modalities, parents can unlock pathways to progress, enabling their children to thrive in a world that often feels overwhelming.
This article delves into the various treatment options available, highlighting:
- The importance of early intervention
- The integration of behavioral therapies with medication
- The invaluable resources that can guide families along this transformative journey.
Exploring Treatment Options for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition, presenting a wide array of manifestations and severity levels. The therapeutic landscape for autism is equally diverse, leading to the inquiry of what is the best medicine for autism, as it offers a variety of therapies and medications tailored to address specific symptoms and challenges. Understanding these options empowers parents to make informed decisions for their children.
Key treatment modalities include:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Widely recognized for its efficacy, ABA focuses on enhancing specific behaviors and skills through reinforcement techniques. This approach has shown considerable success in teaching vital communication, social skills, and daily living techniques. Interestingly, approximately 36.5% of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders report using ABA therapy, highlighting its prevalence and acceptance among families. Moreover, the types of ABA therapy differ, with various methods making a considerable impact for individuals on the spectrum.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This therapeutic approach is especially helpful for young individuals with developmental disorders who experience anxiety. CBT encourages identifying negative thought patterns and developing positive coping strategies, empowering individuals to navigate their emotions effectively.
- Speech and Language Therapy: Considering that numerous youngsters with developmental conditions encounter communication difficulties, speech therapy is essential in improving verbal abilities and social interaction. This therapy facilitates better interactions with peers and family, fostering social inclusion.
- While no medication can cure autism, certain prescriptions can alleviate symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and attention deficits, leading to the inquiry of what is the best medicine for autism. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and stimulants are commonly prescribed, tailored to meet individual needs.
- Occupational Therapy: Focused on improving daily living skills and sensory integration, occupational therapy equips individuals to function more effectively in their environments, enhancing their overall quality of life.
Recent advancements in ABA therapy have underscored the importance of tailored approaches that can significantly impact children's learning and behavioral outcomes. As the field evolves, the presence of nearly 59,976 board-certified behavior analysts (BCBAs) in the U.S. ensures that families have access to qualified professionals equipped to guide them through these treatment options. Additionally, it is essential to recognize that genetic-environmental interactions highlight the complexity of ASD development, where genetic susceptibilities may be activated by environmental triggers.
Judy Singer once stated, "A rainbow infinity sign is another widely used symbol for individuals on the spectrum," reflecting the diversity and acceptance within the community. By investigating these varied therapies, caregivers can attain a clearer insight into the complex nature of care, enabling them to determine the most appropriate methods for their offspring's distinct requirements.
Integrating Behavioral Therapies with Medication for Effective Autism Management
A comprehensive method for autism management understands that no individual solution can address the varied requirements of every youth. By combining behavioral therapies with medication, parents can address what is the best medicine for autism while creating a more comprehensive care plan customized to their offspring's unique needs. This integrated approach encompasses several key elements:
-
Behavioral Interventions: Techniques such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) are effective in teaching essential skills and mitigating challenging behaviors.
Research has shown that when behavioral interventions are combined with medication, it can help determine what is the best medicine for autism, leading to significantly improved outcomes. Notably, the Vineland ABC Change ≥2.5 at 24 months indicates significant improvement for individuals in the Low adaptive level, underscoring the benefits of combined therapies.
-
Regular Monitoring and Adjustments: Ongoing collaboration with healthcare professionals is essential. Regular assessments facilitate the evaluation of medication and therapy effectiveness, enabling timely modifications to optimize each individual's care plan.
-
Family Involvement: Active participation from family members in the care process cultivates a supportive environment. Caregivers can acquire strategies to reinforce positive behaviors at home, ensuring consistency and stability across various settings, which is vital for the young one's development.
-
Support Networks: Establishing connections with other guardians and professionals can yield invaluable insights and encouragement. Support groups play an essential role in sharing experiences and uncovering new strategies and resources that can improve the healing journey.
Embracing a holistic approach to developmental support empowers parents and enhances the lives of their offspring, ensuring they receive the thorough care necessary for their growth and well-being. This is emphasized by the fact that only 15% of covered youth referred for ABA-based behavioral health care receive the recommended hours, highlighting the need for greater awareness and proactive management in therapies. Additionally, as noted by FAIR Health Inc., exploring the average costs of services for individuals with developmental disorders can inform families about the financial aspects they may need to navigate.
Ultimately, by concentrating on a cooperative and diverse approach, parents can foster significant progress in their offspring's lives.
The Role of Early Intervention in Autism Treatment
Research consistently underscores that early intervention is a game-changer in enhancing development and quality of life for individuals with autism. Engaging in treatment as early as possible leads to significant improvements in communication, social skills, and adaptive behaviors, setting a strong foundation for future growth. For instance, research shows that individuals with communication challenges do best when introduced to augmentative and alternative communication as early as 12 months.
Key elements of effective early intervention include:
- Individualized Treatment Plans: Crafting personalized approaches that reflect each individual's unique strengths and challenges is essential. Such customized plans guarantee that therapies are not only relevant but also effective, aligning with the individual's specific needs.
- Guardian Training and Support: Actively involving caregivers in the intervention process equips them with valuable strategies to promote their offspring's development at home. This training frequently includes techniques for reinforcing skills acquired during therapy sessions, enabling parents to be effective advocates for their children.
- Multidisciplinary Teams: Collaboration among professionals—including speech therapists, occupational therapists, and behavioral analysts—creates a comprehensive approach. This teamwork addresses all facets of a young person's development, ensuring comprehensive support.
- Monitoring Progress: Regular assessments are crucial for tracking an individual's progress and adjusting interventions as necessary. Continuous assessment is essential to sustain the effectiveness of the treatment strategy and adjust to the individual's changing requirements.
Josephine Shenouda, DrPH, MS, highlights the necessity of increased support, stating,
With prevalence estimates of the condition nearing 7% in certain communities, enhanced assistance for EIPs and better access to clinical and educational services will be crucial to tackle the rising number of affected youth and to diminish socioeconomic and racial disparities in identification and care.
A real-world example of the impact of early intervention is seen in Ethan, who participated in group activities at preschool by age four, demonstrating the potential unlocked through early support. Additionally, the case study titled 'Giving Thanks' illustrates how an autistic adult expresses gratitude towards family, friends, and therapy for their positive life experiences, highlighting the role of support systems in enhancing the quality of life for individuals with developmental differences.
By emphasizing early support, caregivers can greatly influence their offspring's capacity to manage the intricacies of developmental challenges, unlocking their complete potential and nurturing a more promising future.
Understanding Medication Options for Autism Management
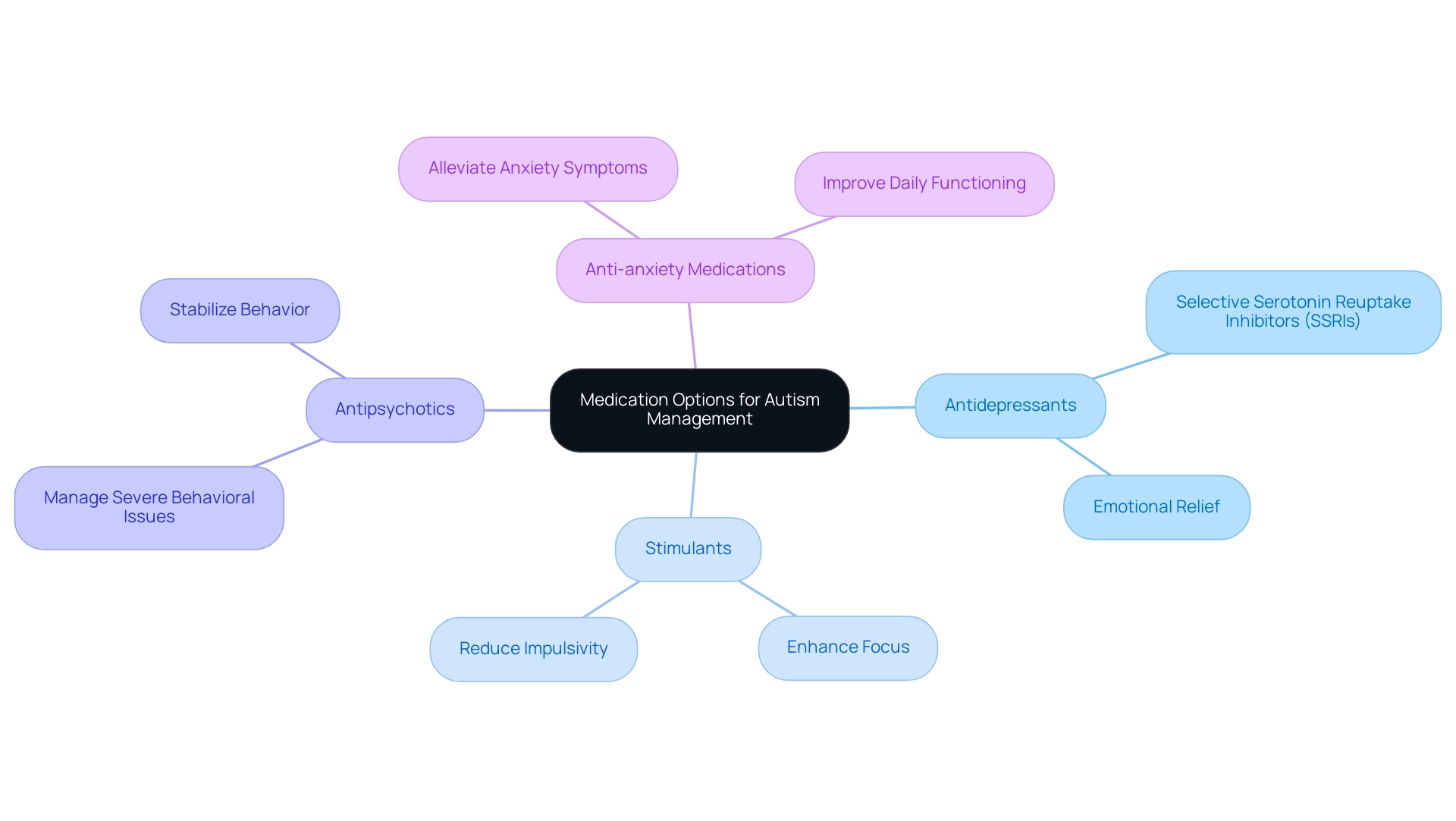
Navigating the landscape of medication for managing developmental disorders is a crucial step for parents who are often left wondering what is the best medicine for autism to achieve the best outcomes for their offspring. Understanding what is the best medicine for autism and the various medication options available, along with their benefits and side effects, can empower caregivers to make informed decisions. The primary categories of medications include:
- Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly used to address anxiety and depression in youth with autism. These medications can provide significant relief for emotional challenges, leading to improved overall well-being.
- Stimulants: Typically prescribed for attention-related difficulties, stimulants can enhance focus and reduce impulsivity, enabling young individuals to engage more fully in educational and social settings.
- Antipsychotics: For managing severe behavioral issues such as aggression or self-injury, antipsychotics may be prescribed. These medications can provide essential support in stabilizing behavior, fostering a safer environment for young individuals and their families.
- Anti-anxiety Medications: These medications can effectively alleviate anxiety symptoms that may hinder a young person's daily functioning, allowing for a more enjoyable and productive life.
Collaboration with healthcare providers is vital to determine what is the best medicine for autism and make necessary adjustments to medication effectiveness. Open communication regarding any side effects or concerns is crucial for optimizing results. As emphasized in a recent survey, 36.5% of caregivers reported using ABA therapy to assist their offspring in overcoming the challenges of ASD, highlighting the significance of a multifaceted approach to managing this condition.
Additionally, sodium valproate was prescribed in 16% of cases, illustrating the variety of medication options available. The findings suggest a need for further studies across different regions and settings in South Africa to better understand pharmacotherapy in ASD management. By remaining knowledgeable and proactive, guardians can guarantee that their child's care plan is customized to their specific requirements.
Empowering Parents through Resources and Support
Navigating the journey of autism care can indeed feel overwhelming for caregivers, but it’s important to know that a wealth of resources is available to guide them along the way.
- Support Groups: Engaging with other caregivers can be immensely beneficial, offering both emotional support and practical advice. With 41.3 percent of respondents belonging to autism-specific support groups, it’s clear that these communities play a vital role in sharing experiences and strategies that can ease the journey.
However, it's important for guardians to be aware that reliance on these support groups may lead to an increased use of alternative treatments, which can detract from proven methods.
- Educational Resources: A plethora of websites, books, and webinars are accessible, equipping guardians with crucial information on treatment options, behavioral strategies, and advocacy. These resources enable guardians to make informed choices for their offspring's care. Furthermore, professional advice and information on typical challenges encountered by parents can be accessed through seminars, offering timely and pertinent insights.
- Professional Guidance: Working together with specialists in fields like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy and speech therapy can greatly improve a young person's development. Customized treatment strategies developed with the advice of specialists guarantee that each individual's distinct requirements are addressed efficiently.
- Advocacy Organizations: Many organizations are dedicated to assisting families impacted by developmental disorders, offering resources, workshops, and essential information regarding rights and accessible services. This support is essential for navigating the complexities of autism care. The average age of diagnosis for young individuals in lower-income households is 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years in higher-income households, highlighting the impact of socioeconomic factors on early intervention.
By tapping into these resources, parents can cultivate confidence in their ability to support their offspring and advocate for their needs. Remarkably, research indicates that by middle childhood, 78.8% of school-age autistic children are thriving in at least one developmental area by age 10, with many excelling across the board. This reinforces the notion that with the right support and interventions, success is not only possible but achievable.
Conclusion
The exploration of treatment options for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) reveals a landscape rich with possibilities for enhancing the lives of children and their families. By understanding the diverse therapies available—ranging from Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) to medication—parents are empowered to make informed choices that best suit their child's unique needs. Early intervention stands out as a crucial element, laying the groundwork for improved communication, social skills, and overall development.
Integrating behavioral therapies with medication further underscores the importance of a holistic approach to autism management. This combination not only enhances the effectiveness of treatments but also fosters a supportive environment where children can thrive. Regular monitoring and family involvement are essential components of this strategy, ensuring that treatment plans are adaptable and responsive to each child's evolving requirements.
Moreover, the wealth of resources available—from support groups to educational materials—serves as a vital lifeline for parents navigating this journey. By leveraging these tools, families can cultivate confidence and advocacy skills that are instrumental in securing the best outcomes for their children. The path may be challenging, but with the right knowledge and support, meaningful progress is not just a possibility; it is a reality. Embracing these strategies opens doors to a brighter future for children with autism, empowering them to reach their full potential in a world that is both complex and rewarding.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition characterized by a wide range of manifestations and severity levels.
What are some key treatment modalities for autism?
Key treatment modalities for autism include Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Speech and Language Therapy, Occupational Therapy, and medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and stimulants.
How does Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) work?
ABA focuses on enhancing specific behaviors and skills through reinforcement techniques, helping individuals improve communication, social skills, and daily living techniques.
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) used for in autism treatment?
CBT is particularly helpful for young individuals with developmental disorders who experience anxiety, as it encourages the identification of negative thought patterns and the development of positive coping strategies.
Why is Speech and Language Therapy important for those with autism?
Speech and Language Therapy is essential for improving verbal abilities and social interaction, which helps individuals better communicate with peers and family, fostering social inclusion.
Can medication cure autism?
No, there is no medication that can cure autism, but certain prescriptions can alleviate symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and attention deficits.
What role does Occupational Therapy play in autism treatment?
Occupational Therapy focuses on improving daily living skills and sensory integration, helping individuals function more effectively in their environments and enhancing their overall quality of life.
How can combining therapies and medications benefit individuals with autism?
Combining behavioral therapies like ABA with medication can lead to significantly improved outcomes, addressing the unique needs of each individual more effectively.
Why is regular monitoring and adjustments important in autism treatment?
Ongoing collaboration with healthcare professionals allows for regular assessments of medication and therapy effectiveness, enabling timely modifications to optimize care plans.
How can family involvement enhance autism treatment?
Active family participation in the care process cultivates a supportive environment, helping caregivers reinforce positive behaviors at home and ensuring consistency across different settings.
What is the importance of support networks for families of individuals with autism?
Establishing connections with other guardians and professionals can provide invaluable insights and encouragement, helping families share experiences and discover new strategies and resources.
What is the significance of a holistic approach to autism management?
A holistic approach empowers parents and enhances the lives of individuals with autism by ensuring they receive comprehensive care tailored to their growth and well-being.




