Overview
Asperger's Syndrome is a neurodevelopmental condition within the autism spectrum, characterized by difficulties in social interaction and repetitive behaviors, without significant delays in language development. The article elaborates on its historical evolution, diagnostic criteria, and the importance of tailored support strategies, highlighting the need for early recognition and intervention to improve the quality of life for individuals affected by the condition.
Introduction
The complexities of Asperger's Syndrome, nestled within the broader autism spectrum, reveal a rich tapestry of challenges and strengths that shape the lives of those affected.
Characterized by difficulties in social interaction and a penchant for focused interests, individuals with Asperger's often navigate a world that can feel overwhelming and isolating.
As awareness grows, so does the understanding of this condition, emphasizing the importance of tailored interventions and support strategies that can significantly enhance social skills and communication.
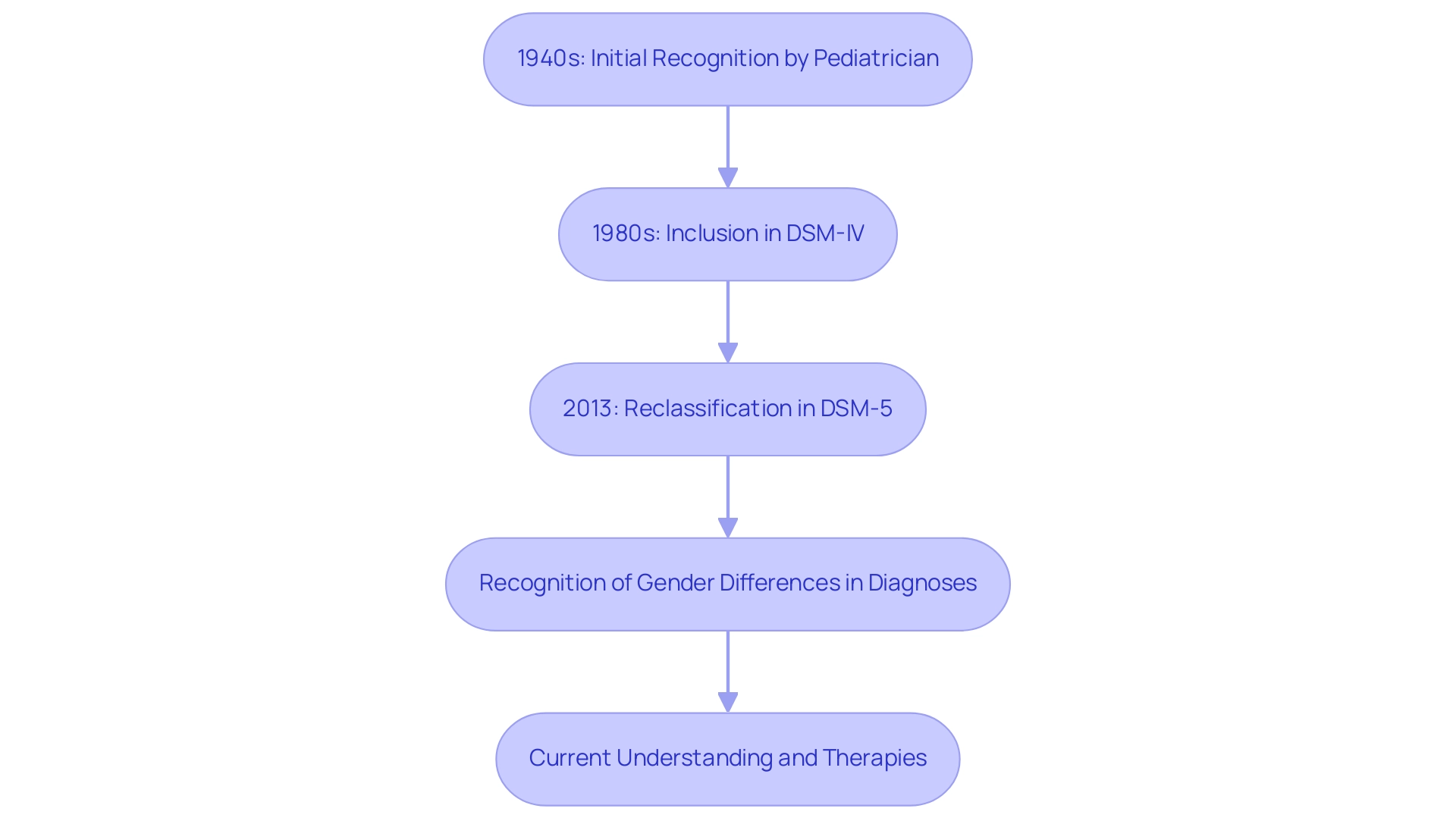
With a historical backdrop that traces back to the observations of Hans Asperger in the 1940s, the evolution of diagnostic criteria and the reclassification of Asperger's within the DSM-5 highlight the ongoing need for informed discussions and advocacy.
This article delves into the nuances of Asperger's Syndrome, exploring its symptoms, distinctions from other forms of autism, and the vital role of effective support systems in fostering a brighter future for individuals on this unique journey.
Defining Asperger's Syndrome: An Overview
What is Asperger's Syndrome? It is acknowledged as a neurodevelopmental condition that exists within the spectrum of developmental disorders, characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction, along with limited and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. Significantly, individuals on the autism spectrum typically do not exhibit considerable delays in language development, which sets them apart from other types of autism. This distinction is essential for comprehending the complexities of the syndrome, as it influences how people communicate, engage with others, and interpret their surroundings.
Recent studies indicate that effective interventions can significantly enhance social skills and communication for individuals on the autism spectrum. Additionally, awareness of the unique characteristics of this condition is vital for parents and professionals alike, enabling them to develop tailored strategies that foster support and understanding for individuals navigating the world with it. For example, current studies emphasize that having a sibling with a developmental disorder raises the chance of developing a similar condition, suggesting the genetic and environmental interaction at play.
The Cleveland Clinic notes that having a sibling with a developmental disorder increases the risk for ASD, emphasizing the importance of understanding familial factors. Furthermore, a case study on the co-occurrence of epilepsy and autism reveals that epilepsy affects up to 30% of children with autism, illustrating the complexities and additional challenges that may impact children with the condition. This nuanced understanding is essential for effectively addressing the needs of children with autism, particularly considering that 8% of autistic students in the U.S. do not complete high school, compared to 5% of all students.
Additionally, the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services is approximately $175.44, highlighting the financial implications of support for individuals on the autism spectrum.
The Historical Evolution of Asperger's Syndrome
What is Asperger's syndrome? It was initially recognized in the 1940s by an Austrian pediatrician, who meticulously documented a group of children exhibiting unique social and communication difficulties while retaining strong cognitive skills. His pioneering observations laid the groundwork for understanding this condition, which gained wider recognition in the 1980s when it was formally included in the DSM-IV as a distinct diagnosis. However, significant changes occurred in 2013 with the release of the DSM-5, which reclassified the condition, leading to discussions about what is Asperger's syndrome under the broader umbrella of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
This shift signifies not only an evolution in diagnostic criteria but also reflects a growing understanding of the spectrum nature of this condition and its diverse manifestations. Significantly, research shows that over four times as many boys are diagnosed with autism compared to girls, emphasizing the necessity for awareness of gender differences in autism presentations. Moreover, Hans contributions continue to impact contemporary diagnostic methods, highlighting the significance of detailed evaluations that consider diverse communication abilities.
While there is no cure for autism spectrum disorder, various therapies, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), communication skills training, and occupational therapy, can assist individuals in managing their symptoms and improving social interactions. Additionally, it is crucial to note that there is no evidence to support an association between ASD and immunization as an environmental risk factor, reinforcing the importance of informed discussions around the condition. As the field progresses, it is crucial to recognize the historical milestones that influence current understandings of what is Asperger's syndrome and autism collectively, paving the way for ongoing research and advocacy.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Asperger's Syndrome
What is Asperger's Syndrome, and how does it present a unique profile of symptoms characterized by notable difficulties in understanding interpersonal cues and forming friendships? Individuals often demonstrate a tendency toward repetitive behaviors and exhibit intense focus on specific interests. They typically prefer structured routines and may struggle with adapting to changes, significantly affecting their daily lives.
Despite possessing average or above-average intelligence, many people encounter challenges with pragmatic language skills, complicating their social interactions. Recent studies indicate that 1 in 100 children worldwide is estimated to have autism, underscoring the importance of recognizing these symptoms early. This early recognition can lead to timely interventions, which are critical, given that the prognosis for people with the condition can vary significantly based on factors such as IQ, language skills, and family support.
It is also essential to understand what is Asperger's syndrome, particularly the cognitive aspects, which include deficits in 'theory of mind,' 'central coherence,' and 'executive functions.' Furthermore, over 70% of people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) experience additional conditions, such as anxiety or ADHD, which can complicate their clinical management and overall functioning. The case study titled 'Co-occurring Conditions in ASD' illustrates how these additional conditions impact individuals, highlighting the importance of addressing them in treatment plans.
As PD Dr. Martin D Ohlmeier aptly notes, 'Not every case of this syndrome has disease status and requires treatment.' This highlights the necessity for a nuanced understanding of Autism Spectrum Disorder and the advocacy for tailored support strategies.
Asperger's Syndrome vs. Autism: Understanding the Differences
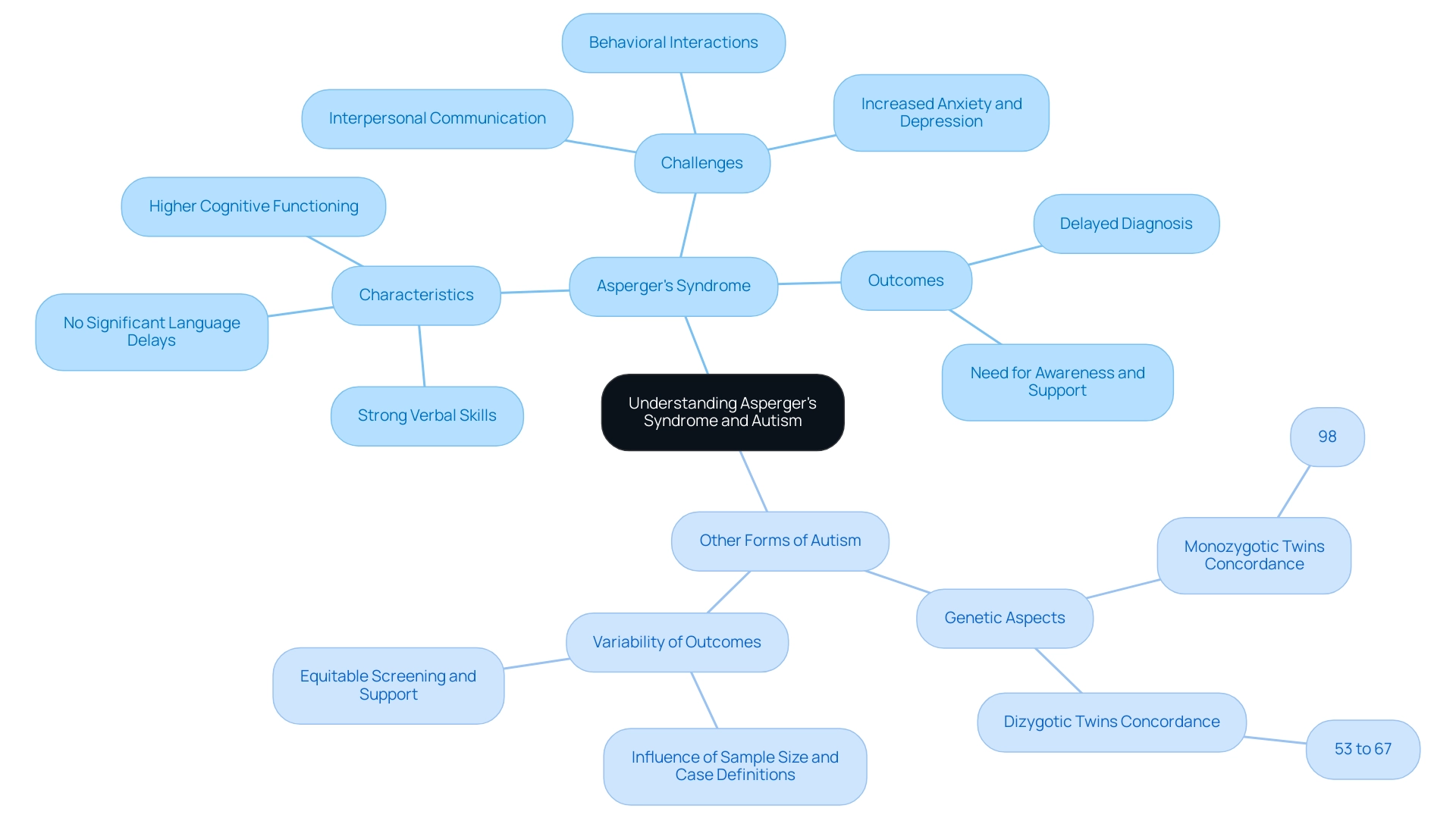
What is Asperger's syndrome is a condition that occupies a unique position within the autism spectrum, primarily characterized by the absence of significant language delays and a generally higher cognitive functioning compared to more severe forms of autism. Individuals diagnosed with Asperger's typically exhibit average to above-average intelligence and often possess strong verbal skills, setting them apart from others on the spectrum. However, despite these strengths, they encounter notable challenges in interpersonal communication and behavioral interactions.
Seyed Alireza Hosseini Mohammed Molla highlights that the outcomes for people with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can vary significantly based on numerous factors, including study sample sizes and case definitions. This variability underscores the necessity for equitable and accessible screening, services, and supports for all children, as the prevalence of ASD is consistent across diverse groups. The case study titled 'Transitioning to Adulthood with ASD' illustrates that many individuals diagnosed in adulthood have what is Asperger's syndrome, often due to their ability to conceal interaction difficulties.
As social demands increase, they may face challenges in maintaining adaptive functioning, leading to increased anxiety and depression. Furthermore, statistics reveal a 98% concordance rate for autism in monozygotic twins and 53% to 67% in dizygotic twins, highlighting the genetic aspects of ASD. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for parents and professionals alike, enabling the delivery of customized support and resources that meet the specific needs of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Current Diagnostic Criteria and Reclassification of Asperger's Syndrome
What is Asperger's Syndrome? It is now officially classified under the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) umbrella in the DSM-5, reflecting a significant shift in understanding this condition. Historically, the DSM-IV classified five separate diagnoses under 'Pervasive Development Disorders,' highlighting the evolution of diagnostic criteria over time. The updated criteria emphasize persistent deficits in social communication and interaction, combined with restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior.
This reclassification highlights the spectrum nature of the condition, recognizing that people may exhibit a wide array of symptoms and differing requirements for assistance. The American Psychiatric Association (APA) has highlighted this change, noting that in 2022, the DSM-5-TR clarified the autism diagnostic criteria, revising the language from 'manifested by the following' to 'as manifested by all of the following' to enhance clarity. This distinction is crucial for parents navigating assessments and interventions for their children.
Moreover, as the complexity of psychiatric disorders continues to evolve, the importance of family and community support becomes increasingly evident, significantly impacting the quality of life for adults with ASD. Studies have shown that strong support networks can improve outcomes, making it essential for parents to advocate for their children's needs and access appropriate resources. Grasping these criteria and the differing needs for support is crucial for parents, particularly as various interventions, including behavioral and educational strategies, are utilized to aid those with ASD.
Support Strategies and Interventions for Asperger's Syndrome
Effective support strategies for individuals with what is Asperger's syndrome encompass a range of interventions, including:
- Behavioral strategies
- Interpersonal skills training
- Parent training programs
Notably, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) techniques have proven particularly advantageous in managing challenging behaviors and improving communication skills. For instance, Liu et al.'s workplace training program demonstrated significant enhancements in workplace interpersonal behavior and emotional regulation over a rigorous six-month period, despite lacking a control group, which obscures the assessment of long-term effects. Furthermore, the effect size for self-report measures, excluding knowledge measures, was determined to be 0.20 based on six studies, emphasizing the quantitative impact of these behavioral interventions.
Furthermore, it is important to note that currently, no medications specifically target core ASD symptoms; however, risperidone and aripiprazole are FDA-approved for managing specific associated symptoms.
Creating structured environments, utilizing visual supports, and promoting peer interactions can significantly aid people in navigating social situations more adeptly. These strategies not only empower parents and caregivers to offer essential support but also foster the overall development and well-being of children by teaching them what is Asperger's syndrome.
The National Autistic Society emphasizes that interventions should be approached with caution, asserting that,
These should never be used by autistic people, of any age.
This perspective encourages a thoughtful consideration of effective interventions tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion
The exploration of Asperger's Syndrome reveals a complex interplay of challenges and strengths that individuals face within the autism spectrum. It is characterized by unique social interaction difficulties and a strong focus on specific interests without significant language delays, setting it apart from other autism forms. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for parents, educators, and healthcare professionals to develop tailored strategies that foster effective support and improve communication skills.
Historically, the evolution of Asperger's Syndrome from its identification in the 1940s to its reclassification under the Autism Spectrum Disorder in the DSM-5 underscores the importance of informed advocacy and awareness. This change reflects a deeper understanding of the spectrum nature of autism, recognizing that each individual presents a unique profile of symptoms and support needs. The necessity for equitable access to screening and services is paramount, particularly as the prevalence of autism remains consistent across various demographics.
As individuals with Asperger's navigate their unique journeys, the implementation of effective support strategies—including behavioral interventions and social skills training—can significantly enhance their quality of life. By fostering environments that promote understanding and acceptance, society can help individuals with Asperger's Syndrome thrive, ultimately paving the way for a brighter future. Recognizing the complexities of this condition and advocating for informed discussions and interventions is essential in supporting those on this journey, ensuring they are equipped to face the world with confidence and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Asperger's Syndrome?
Asperger's Syndrome is a neurodevelopmental condition within the spectrum of developmental disorders, characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and limited, repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. Individuals typically do not exhibit considerable delays in language development, distinguishing them from other types of autism.
How does Asperger's Syndrome differ from other types of autism?
Unlike other types of autism, individuals with Asperger's Syndrome generally do not experience significant delays in language development, which influences their communication and engagement with others.
What recent findings have been made regarding interventions for individuals with Asperger's Syndrome?
Recent studies indicate that effective interventions can significantly enhance social skills and communication for individuals on the autism spectrum, emphasizing the importance of tailored strategies for support and understanding.
What familial factors may increase the risk of developing Asperger's Syndrome?
Having a sibling with a developmental disorder raises the likelihood of developing a similar condition, highlighting the genetic and environmental interactions involved.
What percentage of children with autism also experience epilepsy?
Up to 30% of children with autism may also have epilepsy, indicating the complexities and additional challenges faced by these individuals.
What educational challenges do individuals with Asperger's Syndrome face?
Approximately 8% of autistic students in the U.S. do not complete high school, compared to 5% of all students, illustrating significant educational challenges.
What are the financial implications of support for individuals on the autism spectrum?
The average cost of therapeutic behavioral services for individuals on the autism spectrum is approximately $175.44, which can have financial implications for families seeking support.
Who first recognized Asperger's Syndrome and when?
Asperger's Syndrome was initially recognized in the 1940s by an Austrian pediatrician who documented a group of children with unique social and communication difficulties while retaining strong cognitive skills.
How has the classification of Asperger's Syndrome changed over time?
Asperger's Syndrome was formally included as a distinct diagnosis in the DSM-IV in the 1980s, but in 2013, the DSM-5 reclassified it under the broader category of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
What therapies are available for managing symptoms of Asperger's Syndrome?
Various therapies, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), communication skills training, and occupational therapy, can assist individuals in managing symptoms and improving social interactions.
Is there any evidence linking immunization to Asperger's Syndrome?
There is no evidence to support an association between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and immunization as an environmental risk factor.




