Overview
ABA therapy, or Applied Behavior Analysis, plays a vital role in nurturing positive behaviors, especially for individuals diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). This compassionate approach focuses on promoting constructive actions while addressing harmful behaviors through systematic interventions. By employing principles of learning theory and reinforcement strategies, ABA therapy has shown remarkable effectiveness in enhancing social skills, communication, and adaptive behaviors. Moreover, its applications extend beyond autism, offering support for various developmental disorders.
As parents, understanding how ABA therapy works can be both enlightening and reassuring. It’s not just about the techniques; it’s about the positive changes it fosters in your child's life. Imagine witnessing your child develop essential social skills and improved communication—this is the transformative power of ABA.
We encourage you to explore the resources available and consider how ABA therapy might support your family. Sharing your experiences can also be incredibly valuable; we invite you to connect with us in the comments or through our newsletters. Together, we can navigate this journey with compassion and understanding.
Introduction
In a world that is increasingly attuned to the diverse needs of individuals with developmental disorders, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy shines as a beacon of hope and progress. This scientifically validated approach not only seeks to enhance positive behaviors in those diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder but also addresses a wide array of behavioral challenges across various demographics.
As we embark on the journey of ABA therapy, we uncover a rich history rooted in behaviorism—a flexible methodology that has evolved to meet the unique needs of individuals. From its early pioneers to contemporary applications, ABA therapy continues to demonstrate its effectiveness in fostering essential skills and improving the quality of life for individuals and their families.
This exploration invites you to delve into the multifaceted aspects of ABA therapy, tracing its development, examining its techniques, and highlighting its broad applicability in various settings.
Define ABA Therapy and Its Purpose
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) treatment is a scientifically validated approach designed to improve specific behaviors in individuals, especially those diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and other developmental disorders. The primary goal of ABA is to promote positive behaviors while reducing harmful or undesired actions through systematic interventions. By leveraging principles of learning theory, ABA practices explore how behaviors are shaped by environmental factors and how they can be transformed through targeted reinforcement strategies. This approach illustrates the multifaceted purpose of ABA therapy, extending beyond merely diminishing negative behaviors to also focusing on teaching essential skills that significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals and their families.
Recent studies reveal how effective ABA therapy can be, showing that structured interventions lead to meaningful improvements in social skills, communication, and adaptive behaviors among children with developmental disorders. For instance, a thorough examination of implementation science in ABA practices underscores the necessity of effective strategies to translate research findings into real-world applications. It emphasizes ongoing evaluation and adaptation of service delivery models. As one expert noted, "to effectively translate research evidence on ASD interventions into wide-scale practice, an implementation framework is needed for states with mandates to address system, community, and family barriers and promote meaningful patient progress." This flexibility is crucial for meeting the unique needs of individuals on the spectrum, ensuring that support is both relevant and effective.
Moreover, ABA therapists often collaborate with other professionals, such as speech and occupational therapists, to create a holistic support system that addresses various aspects of a child's development. This interdisciplinary approach not only enhances the effectiveness of interventions but also fosters a more inclusive environment for learning and growth. The findings from the case study titled "Implementation Science in ABA Therapy" further highlight the importance of effective implementation strategies, demonstrating that ongoing evaluation and adaptation are essential for translating research findings into practice. Additionally, the diverse sample in recent research emphasizes the extensive applicability of ABA intervention across different demographics, reinforcing its effectiveness in improving outcomes for children with developmental disorders.
Trace the History and Development of ABA Therapy
The journey of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) treatment begins in the early 20th century, deeply rooted in behaviorism—a psychological framework that emphasizes observable actions over internal thoughts. Visionaries like John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner laid the groundwork for behavior modification techniques, which would later shape ABA practices. In the 1960s, Dr. Ole Ivar Lovaas emerged as a pioneer of ABA, systematically educating children with developmental disorders and demonstrating its effectiveness through rigorous research. This vital work not only established ABA as a structured intervention but also paved the way for its evolution in the years that followed.
As ABA interventions progressed, they embraced various techniques and methodologies to meet the unique needs of individuals with developmental disorders and related conditions. The endorsement of ABA by respected organizations, such as the American Psychiatric Association and the U.S. Surgeon General, has reinforced its status as a leading evidence-based intervention—underscoring its significance in the historical context of developmental disorders. Historical statistics reveal a marked increase in the adoption of ABA practices since the 1960s, reflecting its growing acceptance and application in therapeutic settings. Interestingly, the average age of African American/Black ABA therapists is 31 years, offering a demographic glimpse into the practitioners in this field.
Key individuals have played a crucial role in advancing ABA practices, ensuring that the approach remains adaptable to the evolving landscape of developmental disorder care. The formation of professional organizations and certification boards has been essential in standardizing practices and promoting high-quality interventions. As one expert noted, "Intervention over a small period has been touted as a method that isn’t effective, but workable depending on the child involved in it," highlighting the variability of ABA therapy's effectiveness based on individual circumstances.
Moreover, the case study titled "The Impact Of A Dedicated Family Care Team" sheds light on the importance of a committed family care team in providing tailored support for children with developmental disorders. The findings suggest that such a team not only empowers parents but also enhances the overall development of children facing these challenges. This ongoing development emphasizes what ABA therapy is used for, alongside other educational and therapeutic strategies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), in improving the lives of autistic individuals and their families.
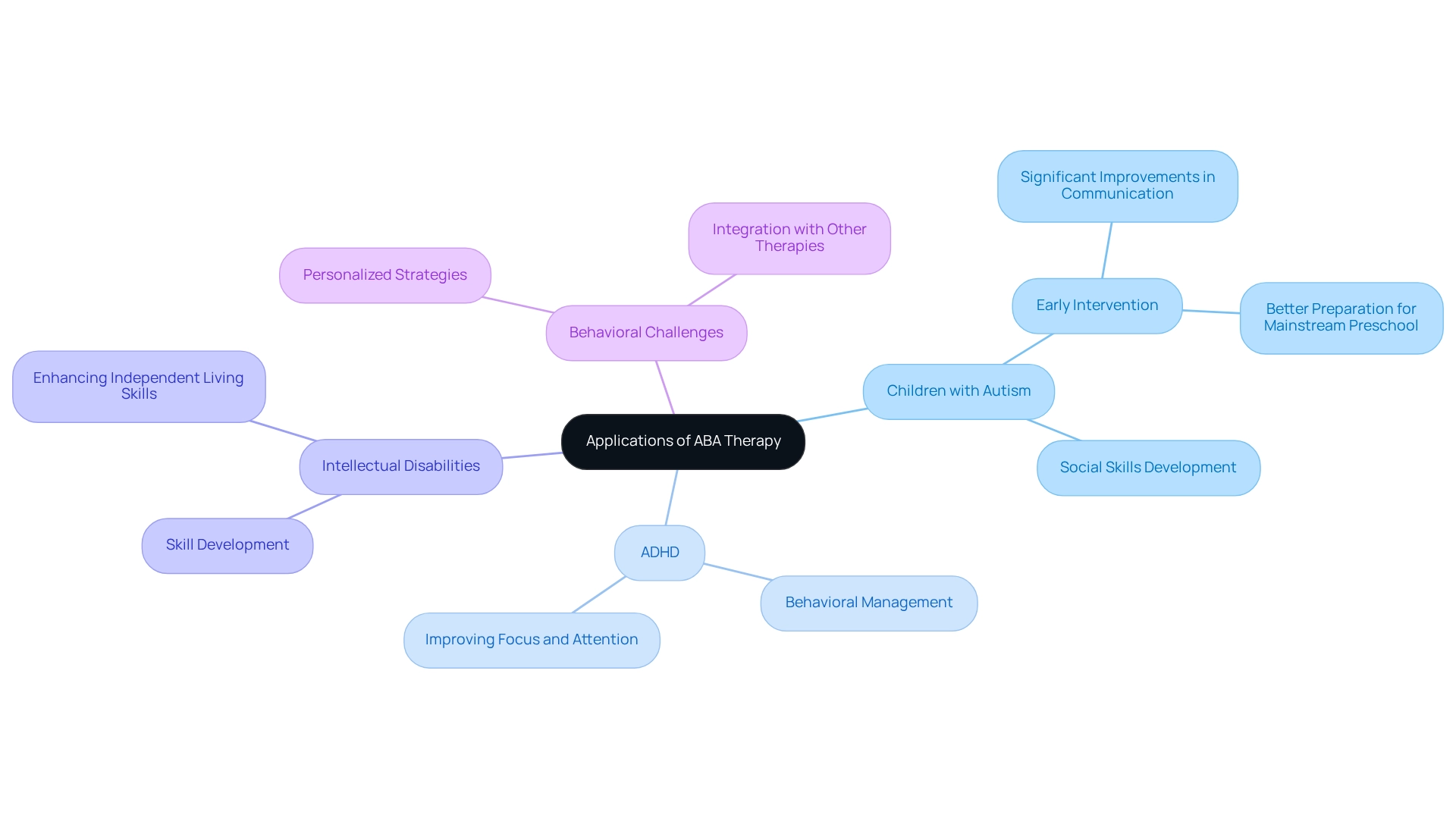
Examine the Applications of ABA Therapy Across Different Populations
While ABA intervention is widely acknowledged for its effectiveness in assisting children diagnosed with autism, it also raises an important question: what is ABA therapy used for beyond this demographic? Research shows that ABA therapy can be beneficial for individuals with:
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Intellectual disabilities
- Various behavioral challenges
In educational settings, it becomes crucial to explore what ABA therapy can do to improve learning outcomes and foster social skills among students with special needs. For instance, studies indicate that initiating ABA treatment before age two leads to significant enhancements in communication and social abilities, underscoring the importance of early intervention. This proactive approach prepares children for mainstream preschool and supports their ongoing skill development.
Moreover, ABA treatment is adaptable, allowing practitioners to tailor interventions according to the unique needs of each individual. This flexibility makes it a valuable resource not only for children but also for adults seeking to improve their independent living skills and workplace productivity. Practitioners emphasize that the core strength of ABA lies in its capacity to create personalized strategies that effectively address diverse populations. By integrating ABA with other therapeutic approaches and encouraging family involvement, parents can enhance the support their children receive, maximizing the potential for positive outcomes. As Stuart Duncan aptly states, 'Autism is my superpower,' highlighting the unique strengths that individuals with autism can possess.
Analyze Techniques and Methodologies in ABA Therapy
ABA interventions utilize a variety of techniques aimed at transforming behavior through reinforcement and organized learning. One of the most notable methodologies is Discrete Trial Training (DTT), which breaks down skills into manageable, teachable components. In contrast, Natural Environment Teaching (NET) emphasizes the acquisition of skills in real-world contexts, making learning more applicable and meaningful. Additionally, the Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS) offers vital support for non-verbal individuals, enhancing their ability to express their needs and desires.
Core techniques such as positive reinforcement, prompting, and shaping are fundamental in ABA. These methods empower therapists to encourage desired behaviors while minimizing maladaptive ones. Research underscores the effectiveness of these approaches, revealing significant improvements in social skills, communication, and overall functioning among participants in ABA. For example, studies have shown that DTT leads to remarkable learning outcomes, with many children exhibiting notable progress in skill acquisition. Furthermore, case studies illustrate the successful application of DTT in diverse educational settings, highlighting its role in fostering collaboration between educators and therapists. One such case study, titled "Understanding and Implementing Functional Behavior Assessments in Education," stresses the importance of teamwork in educational environments, demonstrating how effective implementation of FBAs can enhance collaboration between educators and therapists.
Ultimately, ABA therapy encompasses a range of methodologies grounded in evidence-based practices, yielding positive results for children with autism and ADHD. As Stuart Duncan beautifully expresses, "Autism is my superpower," reminding us of the incredible potential within neurodivergent individuals. Engaging in meaningful dialogue with knowledgeable individuals is essential for patients to acquire the wisdom necessary for progress in therapy. The interest in this subject is palpable, as evidenced by the 1,324 views on a related article, highlighting its significance and relevance for parent advocates.
Conclusion
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy serves as a vital lifeline for individuals with autism spectrum disorder and various developmental challenges. By emphasizing the enhancement of positive behaviors while reducing undesired actions through scientifically validated methods, ABA therapy not only improves individual outcomes but also enriches the lives of families. The journey of ABA, from its early behaviorist roots to its current interdisciplinary applications, showcases its remarkable adaptability and effectiveness across diverse populations.
The historical context of ABA therapy reveals a rigorous development process, driven by pioneers who established evidence-based practices recognized by leading organizations. This solid foundation has allowed ABA to extend its reach beyond autism, effectively supporting individuals with conditions such as ADHD and intellectual disabilities. The flexibility of ABA techniques ensures tailored interventions that meet the unique needs of each individual, highlighting the importance of early engagement and ongoing evaluation.
In summary, ABA therapy embodies a comprehensive approach that integrates various methodologies to foster skill development and positive behavioral change. As it continues to evolve, the emphasis on collaboration among professionals and the involvement of families remains crucial in enhancing the therapeutic experience. Ultimately, ABA therapy not only aims to change behaviors but also strives to empower individuals, shining a light on the strengths and potential within every person it serves. Together, we can continue to support and uplift those on this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) treatment?
ABA treatment is a scientifically validated approach aimed at improving specific behaviors in individuals, particularly those diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and other developmental disorders. Its primary goal is to promote positive behaviors while reducing harmful or undesired actions through systematic interventions.
How does ABA therapy work?
ABA therapy leverages principles of learning theory to explore how behaviors are shaped by environmental factors. It transforms behaviors through targeted reinforcement strategies, focusing not only on reducing negative behaviors but also on teaching essential skills that enhance the quality of life for individuals and their families.
What are the benefits of ABA therapy?
Recent studies show that ABA therapy leads to meaningful improvements in social skills, communication, and adaptive behaviors among children with developmental disorders. It emphasizes the importance of effective strategies to translate research findings into real-world applications.
Why is flexibility important in ABA therapy?
Flexibility is crucial in ABA therapy to meet the unique needs of individuals on the spectrum. It ensures that support is relevant and effective, allowing for ongoing evaluation and adaptation of service delivery models.
How do ABA therapists collaborate with other professionals?
ABA therapists often work with other professionals, such as speech and occupational therapists, to create a holistic support system that addresses various aspects of a child's development. This interdisciplinary approach enhances the effectiveness of interventions and fosters a more inclusive learning environment.
What does recent research indicate about ABA therapy?
Recent research emphasizes the extensive applicability of ABA interventions across different demographics and reinforces its effectiveness in improving outcomes for children with developmental disorders. It also highlights the importance of ongoing evaluation and adaptation of implementation strategies to translate research findings into practice.




