Introduction
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Therapy is a well-established method for assisting those with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), applying principles of behavior to foster meaningful, positive changes. However, this intensive approach has raised concerns among some autism advocates.
This article explores the challenges and benefits of ABA Therapy, strategies used in the therapy, the importance of collaboration with parents and caregivers, and the research and evidence supporting its effectiveness. It aims to provide guidance and resources to Parent Advocates navigating the complexities of ABA Therapy and ensuring the well-being of their children with ASD.
Understanding ABA Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Therapy, a well-established method for assisting those with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), applies principles of behavior to foster meaningful, positive changes. This therapy is grounded in the understanding that behavior is learned and can be reshaped through systematic interventions and reinforcements. As an early intervention, children spend significant time with an ABA-certified therapist, learning basic activities through repetition and reinforcement.
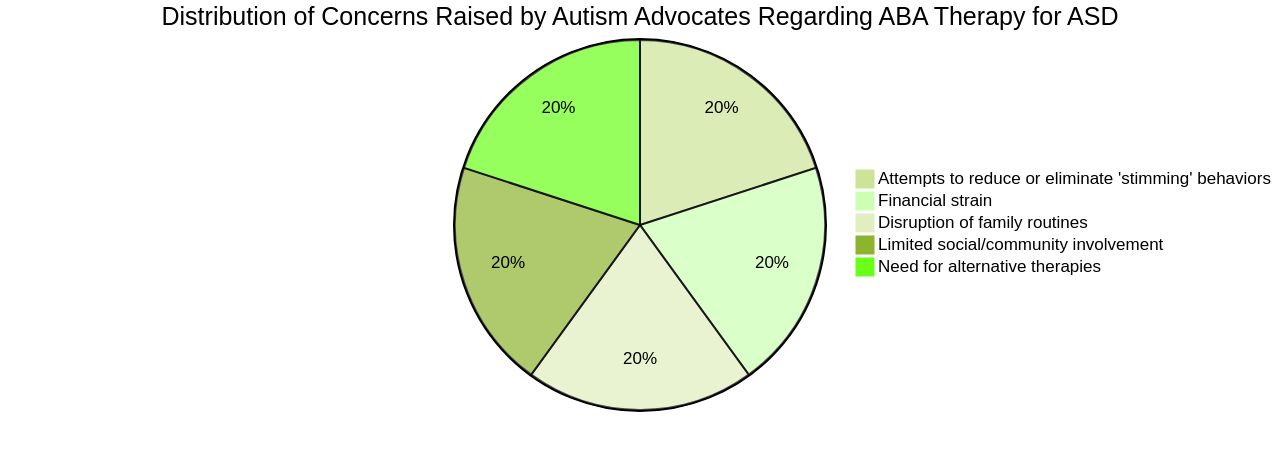
However, this intensive approach has raised concerns among some autism advocates. They argue that ABA sometimes attempts to reduce or eliminate behaviors like 'stimming' which help autistic children manage anxiety or sensory overload. ABA therapy is not a 'one size fits all' solution and can bring about various challenges for families.
Recommendations for extensive hours of therapy per week may lead to financial strain, disruption of family routines, and limited time for social/community involvement. The therapy-life balance is crucial for the child in treatment, their parents, and their siblings. Recent scientific studies have highlighted the need for alternative therapies for ASD, given the complexity of the disorder.
Research on the roles of dopamine and serotonin in development and their critical importance in neural circuit construction has opened new avenues for potential therapies. Preliminary studies on stem cell therapies also show promising results, indicating that this could be a viable alternative for managing ASD. Despite the challenges, comprehensive early intervention for toddlers with ASD has shown improvements in language, cognitive abilities, and adaptive behavior.
Brief behavioral interventions have been successful in enhancing social communication in young children with ASD. However, the effects on child outcome have been mixed when parents deliver these interventions. Despite the legal mandates for ABA, there is a shortage of trained personnel, and many young children with ASD are not receiving the necessary early intervention services.
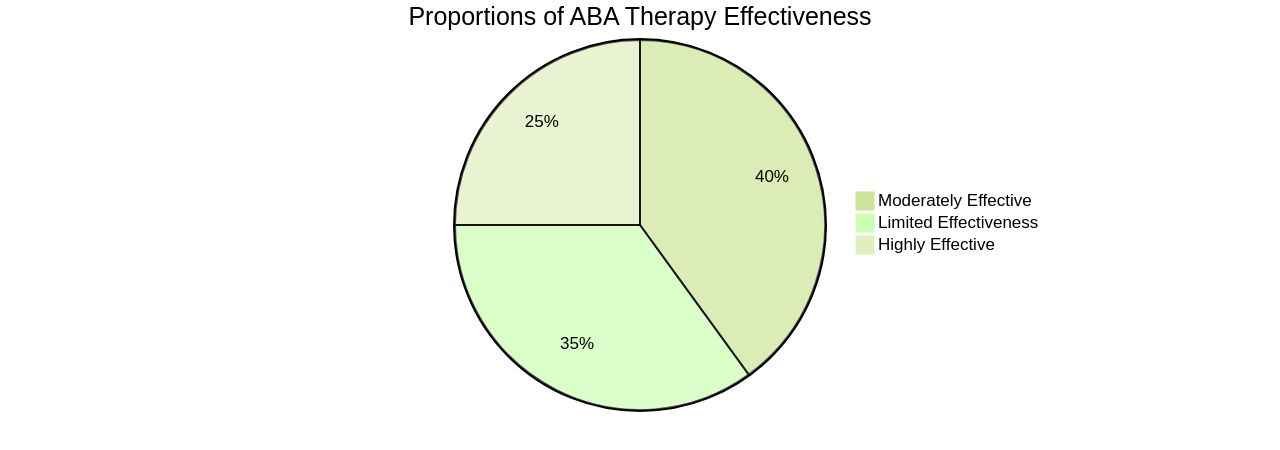
ABA therapy, like any other, should be carefully considered and tailored to the unique needs and abilities of each individual. The therapy's effectiveness should be measured objectively, with an understanding that each individual's journey with ASD is different. The ultimate goal should be to support the individual to lead a fulfilling and independent life, respecting their unique behaviors and abilities.
The Benefits of ABA Therapy
ABA Therapy is a multifaceted approach that assists individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) to enhance their functional skills. It focuses on nurturing essential life skills, including communication, social interaction, self-care, and academic abilities.
An anecdote hailing from a Florida practitioner, Kara, highlights the success of this independence therapy in enabling children to perform tasks on their own. The therapy is also designed to alleviate challenging behaviors such as tantrums, aggression, and self-injury, replacing them with appropriate behaviors, as emphasized in a study that noted behavioral improvements in young children with ASD.
However, the implementation of therapy should be individualized to suit the specific needs and circumstances of each child. It's critical to maintain a balance between therapy and life, considering the potential impact on family dynamics, privacy, and the child's social involvement.
An effective example is the case study of a single participant in a private clinic, where the treatment was segmented into several components, leading to a significant reduction in problem behavior and an increase in desirable behavior like functional communication, delay tolerance, and compliance. Despite these benefits, the effectiveness of ABA Therapy has been a topic of debate.
Some studies question its cost-benefit ratio and express concerns about the children's negative experiences of the therapy. It's essential to recognize that ABA is not a 'one size fits all' approach and its effectiveness may vary. Therefore, a commitment to scientific process and rigorous policy evaluation is crucial to ensure the therapy works for those who need it. In conclusion, ABA Therapy aims to improve the overall quality of life and enhance the independence of individuals with ASD. Its effectiveness, however, may vary, and it's imperative to tailor the therapy to the individual's unique needs and circumstances.
Strategies Used in ABA Therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Therapy is a dynamic therapeutic approach that is personalized to the unique capabilities and requirements of each individual. It employs discrete trial training (DTT), a method that simplifies skills into manageable, smaller steps to facilitate learning and practice.
Naturalistic teaching is another strategy that integrates learning opportunities into daily activities and natural environments. Positive reinforcement, including praise, rewards, and tokens, is a fundamental component of ABA Therapy that promotes and reinforces desired behaviors.
Additionally, visual supports, social stories, and visual schedules are utilized to enhance understanding and task execution. However, it's important to consider the balance between therapy and life.
The intensive nature of ABA, with recommendations often stretching to 30+ hours per week, can potentially strain family dynamics and finances, and infringe on privacy. Furthermore, the progress made in a clinical setting may not always translate to other environments. Therefore, it's crucial to consider a balanced, tailored approach that suits the individual's needs and the family's circumstances. ABA is not a 'one size fits all' solution; it's a tool that, when used appropriately, can enhance communication skills, social interactions, and independence, while also addressing sensory issues.
Collaboration with Parents and Caregivers
ABA Therapy is rooted in the understanding that parents and caregivers play a pivotal role in the intervention's success. It's not just about therapists working with the child, but also involves closely collaborating with parents to ensure they are equipped with the necessary guidance, support, and training.
This helps parents implement the intervention strategies consistently across different settings, thereby reinforcing the effectiveness of the therapy. In fact, a study conducted at the University of California highlighted the significance of parent involvement in ABA programs.
Parents reported noticeable improvements in their children's social skills and confidence after participating in the program. Moreover, they felt more positive and supported, gaining a deeper understanding of their child's development.
However, it's important to remember that ABA therapy is not a 'one size fits all' solution. A successful ABA program involves a thorough assessment by a Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA), setting specific, measurable goals for the child, and consistently monitoring progress.
Strategies are adjusted as necessary to ensure the child continues to benefit. While the therapy is undeniably beneficial, it's also essential to consider the potential impact on families. Recommendations of 30+ hours per week of therapy can lead to concerns about privacy, financial implications, and the balance between therapy and other aspects of life. Therefore, it's crucial to strike a balance between therapy and other social/community involvement, work, and family relationships. After all, the ultimate aim of ABA therapy is to empower parents to become active participants in their child's development and advocates for their well-being.
Research and Evidence for ABA Therapy
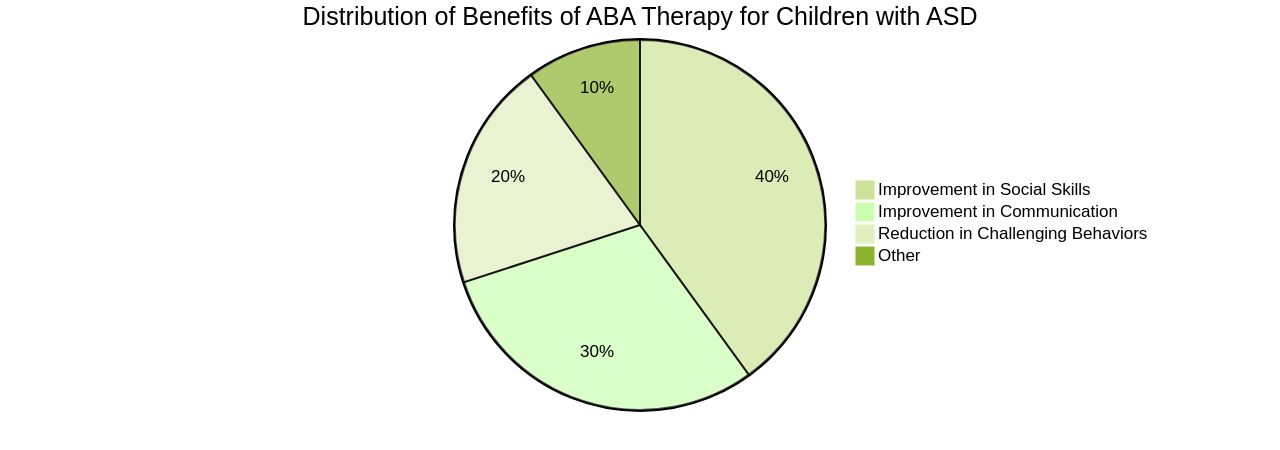
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Therapy, backed by a substantial body of research, has demonstrated significant improvements in children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). The therapy has been shown to enhance social skills, communication, and reduce challenging behaviors.
However, it's important to recognize that ABA Therapy is not a 'one-size-fits-all' solution. The therapy must be tailored to each child's unique needs and circumstances.
For instance, an intensive program, while effective for some, may not be the optimal solution for all. As such, it's crucial to maintain a balance between therapy and other aspects of life to prevent the potential strain on family dynamics and other relationships.
A key aspect of ABA Therapy's success is parent involvement, empowering parents with the knowledge and skills to support their children outside of therapy sessions. Studies have shown that parent-delivered interventions can lead to improvements in parent-child interactions. In one study, parents reported increased social skills and confidence in their children after participation in a group social skills program. However, it's also essential to consider the therapy's potential impact on the family, such as financial implications, privacy concerns, and time commitments. Lastly, it's important to note that the ultimate goal is to provide individuals with better options, fostering self-advocacy, and understanding of their unique abilities, enabling them to navigate the world more effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ABA Therapy is a well-established method for assisting individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by fostering positive changes. Despite its challenges, such as financial strain and disruption of routines, ABA Therapy has shown improvements in language, cognition, and adaptive behavior in children with ASD.
It is crucial to tailor the therapy to each individual's unique needs. ABA Therapy offers benefits in enhancing functional skills and replacing challenging behaviors.
However, its effectiveness may vary, and collaboration with parents is vital for success. They play a pivotal role in implementing strategies consistently.
The research supporting ABA Therapy is substantial, demonstrating improvements in social skills, communication, and reducing challenging behaviors. However, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Tailoring the therapy to each child's needs is essential. Overall, ABA Therapy aims to empower individuals with ASD to lead fulfilling lives while respecting their unique abilities. Parent Advocates can navigate the complexities of ABA Therapy to ensure their child's well-being by providing better options for self-advocacy and understanding their unique abilities.




