Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) affects individuals in unique ways, encompassing a wide range of neurodevelopmental conditions that impact social skills, communication, and behavior. With the prevalence of autism on the rise, it is vital to recognize the signs and seek proper diagnosis and support.
In this article, we will explore the diagnosis process, symptoms, characteristics, and the impact of ASD on individuals and their families. We will also provide tips and resources for parents and caregivers to empower them in their journey of advocating for their children's well-being. Join us as we delve into the world of autism and discover how understanding and support can create a more inclusive and accommodating society.
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) encompasses a range of neurodevelopmental conditions that can profoundly affect social skills, communication, and behavior. Each individual experiences ASD in unique ways, resulting in a diverse spectrum of needs and abilities.
A recent recognition reveals that as many as 1 in 45 adults in the U.S are diagnosed with ASD. Enhanced public health campaigns and better screening are helping to unearth the prevalence of autism in our society.
However, it's quite concerning that many grown-ups may be living with undiagnosed autism or could have been inaccurately labeled with other conditions in the past. For individuals who might have navigated life puzzled by certain tendencies and challenges — recognizing key behaviors can light the path to better understanding themselves or a loved one. Adults with autism often encounter persistent hurdles in social communication and may exhibit repetitive patterns of behavior. Such self-awareness and diagnosis can unlock the door to tailored support, ultimately leading to a more accommodating and aware society.
Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
The process of identifying Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is multifaceted, involving a constellation of assessments by various specialists such as psychologists, pediatricians, and speech therapists. These evaluations delve into the nuances of an individual's communication abilities, social interaction patterns, behavioral traits, and personal developmental trajectory.
Diagnosis adheres to stringent criteria detailed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Additionally, the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD), especially ICD-11 which came into effect in January 2022, offers a standardized approach for recording and analyzing health data, ensuring consistency in disease statistics and semantic interoperability across different health care uses. Despite the structured frameworks in place, the community acknowledges the complexity of ASD diagnosis, wherein self-identification as neurodivergent or autistic is respected among peers, particularly when formal diagnosis yields inconclusive outcomes or bears no significant influence on the support needed by the individual.
Symptoms and Characteristics of ASD
Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder may exhibit a range of symptoms and characteristics. These can include challenges in social communication, difficulty with nonverbal cues, repetitive movements or behaviors, intense interests in specific topics, sensory sensitivities, and difficulties with changes in routine. It's important to remember that every person with ASD is unique, and the way these symptoms manifest can vary greatly.
Understanding the Autism Spectrum
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is indeed a colorful tapestry of cognitive function, marked by a plethora of abilities, challenges, and social nuances. This diversity, often likened to a spectrum, is rooted in the Neurodiversity movement's philosophy that every brain is wired uniquely.
Affirming this, some propose melding the scientific and social definitions of neurotypes to gain a richer understanding. Such an approach underscores that while some individuals may require substantial support, others might showcase exceptional intellectual capabilities or have distinct communication styles.
Emphasizing the individuality within ASD, it's posited that neurotypical, or NT, wiring, previously assumed to be the 'norm' and most coveted, may not be representative of most individuals. The Neurodiversity advocates challenge this preconception, suggesting that each neurotype, including those on the autism spectrum, embodies a version of healthy brain function with its own set of strengths and challenges. Recognizing each person as a unique mosaic of capabilities, the movement calls for a shift in perspective, advocating for acceptance and support rather than merely categorization.
Impact of Autism on Individuals and Families
Autism can have a significant impact on individuals and their families. It may present challenges in daily living, social interactions, education, and employment.
The emotional well-being of both individuals with ASD and their family members can also be affected. However, it's important to recognize that with the right support and interventions, individuals with ASD can thrive and lead fulfilling lives.
Related Conditions and Comorbidities
Autism Spectrum Disorder is often associated with other conditions and comorbidities. These can include intellectual disabilities, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and sleep disorders. It's essential to consider these co-occurring conditions when developing a comprehensive treatment plan for individuals with ASD, as they may require additional support and interventions.
Tips for Parents and Caregivers
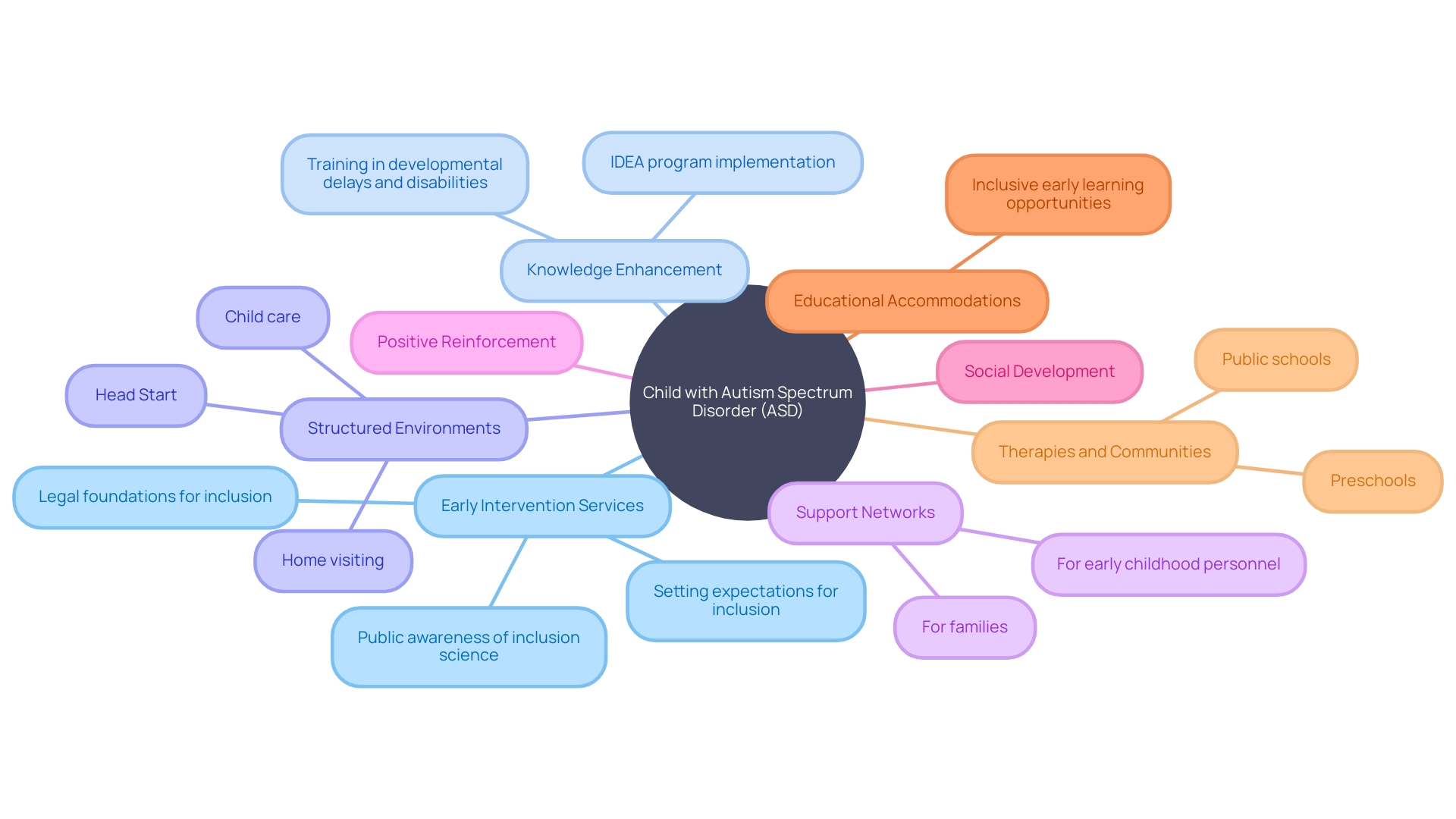
Being a proactive force in the life of a child with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is transformational. It is essential to recognize the significance of early intervention services, which can make a world of difference for your child by starting therapy promptly. Enhancing your knowledge about ASD is not just empowering; it equips you with insights to fully grasp your child's world and the spectrum of resources at your disposal.
Structured environments and predictable routines act as anchors, providing the stability and order that children with ASD often rely on. Building a support network is also fundamental. Connecting with autism advocacy groups and fellow parents provides a shared space for experiences, wisdom, and strength.
It's important to uphold patience, empathy, and consistent positive reinforcement in daily interactions. These approaches foster a nurturing atmosphere for your child to thrive. Celebrate every milestone and strength, as each victory shines a light on their distinct talents.
To assist children with ASD in social development, encourage their social endeavors, as these experiences are key to honing their interpersonal skills. Ensuring that your child's educational journey accommodates their unique needs is another act of advocacy that can greatly impact their success. It's a powerful reminder that while the prevalence of ASD is evident—with statistics showing 1 in 45 adults in the U.S. diagnosed—many adults might have gone through life undiagnosed or misdiagnosed.
Understanding signs of autism, such as struggles with social communication and repetitive behaviors, provides clarity for adults questioning whether they could be on the spectrum. Above all, remember that you are not navigating these waters alone. A web of therapies, guides, and supportive communities stands ready to join you in enriching the life of a child with ASD.
Conclusion
To conclude, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex condition that affects individuals uniquely. Proper diagnosis and support are vital, with assessments and self-identification as valid approaches.
ASD manifests in various challenges, emphasizing the importance of recognizing individuality. The Neurodiversity movement promotes acceptance by acknowledging the strengths and challenges within the autism spectrum.
A more inclusive society can be achieved through understanding and accommodating diversity. ASD has a significant impact on individuals and families, but with adequate support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
Considering related conditions and comorbidities is crucial in developing comprehensive treatment plans. For parents and caregivers, early intervention and knowledge about ASD are key.
Creating structured environments, building support networks, and practicing patience and empathy are vital in nurturing development. Awareness of potential undiagnosed or misdiagnosed cases is essential, encouraging individuals to seek understanding and clarity. Recognizing signs is a powerful step towards self-awareness and support. Parents and caregivers are not alone in their journey. An array of therapies, guides, and supportive communities are available to enrich the lives of individuals with ASD. Together, we can foster a more inclusive and supportive society for those on the autism spectrum.




