Overview
Understanding the causes of autism is vital for parents seeking clarity and support. Research indicates that a combination of genetic and environmental factors contributes to autism, with genetics accounting for an impressive 80-90% of cases. However, it's essential to recognize that environmental influences, such as prenatal exposure to toxins and maternal infections, also play a significant role.
This knowledge is not just academic; it has real implications for early detection and intervention. By understanding these factors, parents can take proactive steps that significantly improve outcomes for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Imagine the peace of mind that comes from knowing you can make a difference in your child's life.
We encourage you to explore resources and support systems available to you. Sharing experiences and insights can foster a nurturing community, where parents uplift one another. Together, we can navigate the complexities of autism with compassion and understanding.
Introduction
In the realm of neurodevelopmental conditions, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) captures our attention due to its intricate nature and the profound impact it has on individuals and families.
As we witness rising prevalence rates, it becomes increasingly important to understand the nuances of ASD—from its diverse symptoms to the critical significance of early diagnosis and intervention.
Misconceptions about its causes continue to circulate, highlighting the urgent need for accurate information to foster acceptance and support within our communities.
This article invites you to explore the intricacies of autism, delving into its:
- Definition
- Underlying factors
- Common myths
- Substantial benefits of timely intervention
Together, we can illuminate the path toward a more informed and compassionate approach to autism care.
Define Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that presents enduring challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. The term 'spectrum' reflects the diverse range of symptoms and severity that individuals with autism may experience. ASD can manifest in various ways, influencing how individuals connect with others, interpret information, and respond to sensory experiences.
Current statistics reveal a concerning trend: the prevalence of ASD continues to rise, with recent research indicating that 1 in 36 children in the United States is diagnosed with the disorder as of 2025. Particularly alarming is the fact that Black children face a higher proportion of co-occurring intellectual disability at 52.8%, highlighting significant disparities in how ASD impacts different demographics. This underscores the urgent need for parents, educators, and healthcare professionals to gain a thorough understanding of what causes a child to be autistic, as this knowledge is essential for developing effective support and assistance strategies. Many autistic individuals encounter difficulties in initiating and sustaining conversations, which can lead to feelings of social isolation. Experts emphasize that early detection and tailored interventions can dramatically improve outcomes for children with ASD, enabling them to thrive in various environments. In fact, 73.6% of autistic students in the US graduate high school with a diploma, showcasing the positive results that can stem from effective support.
Moreover, a 2022 report highlighted that 72.5% of mothers of autistic children in Chang Sha, China, experienced symptoms of depression, illustrating the broader implications of ASD on families and the pressing need for community support and resources. As the World Health Organization advocates for improved surveillance and support for individuals with this condition, the case study titled 'Global Actions on Mental Health and Autism' calls for addressing the gaps in early detection and care for mental and neurodevelopmental conditions. This emphasizes the importance of a collaborative approach to meet the needs of those affected by ASD.
Explore Causes of Autism: Genetic and Environmental Factors
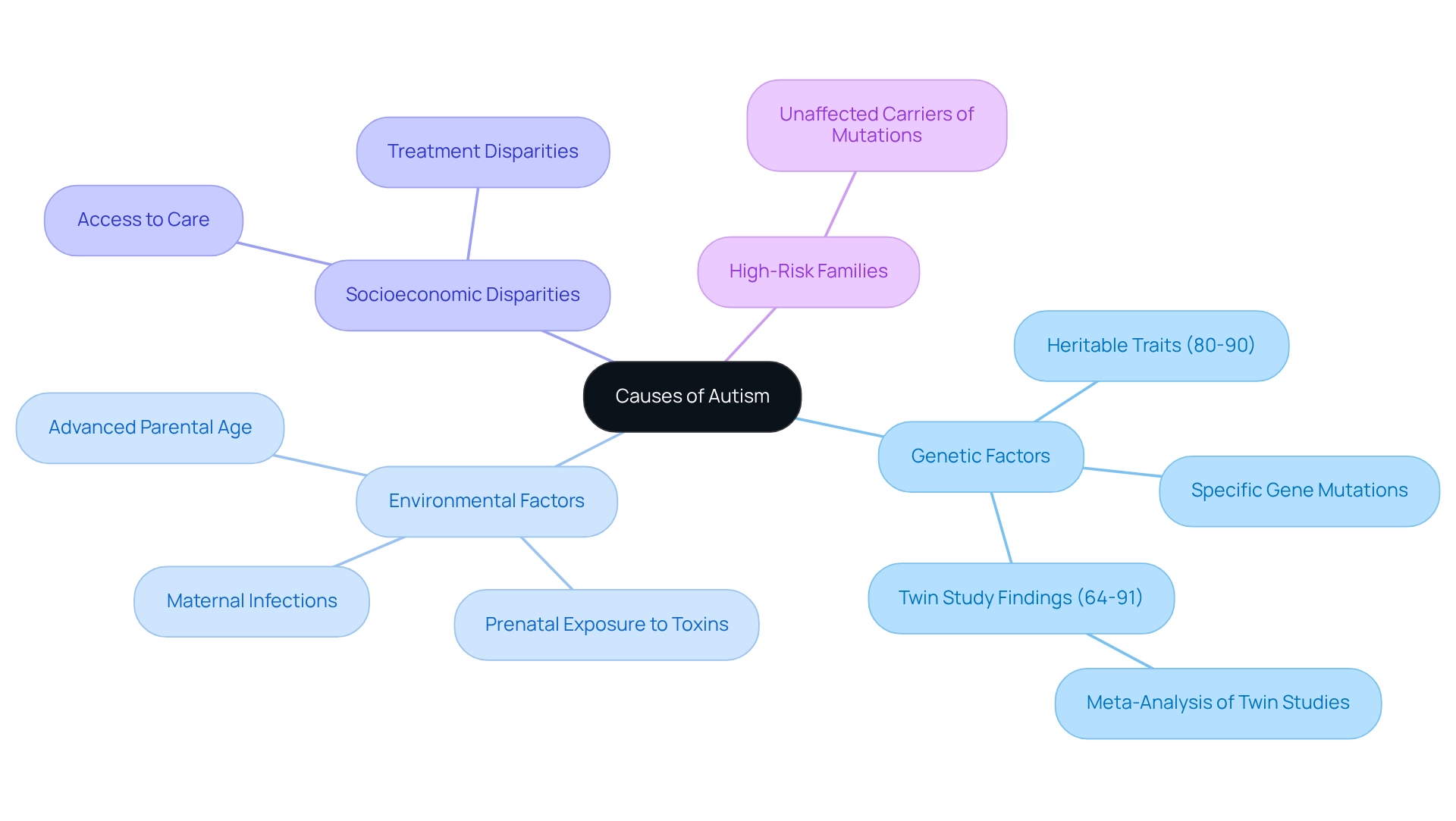
Understanding the complexities of this condition can be overwhelming for many parents. Research indicates that it emerges from a delicate interplay of genetic and environmental factors, which can feel daunting. Recent studies reveal that heritable traits account for about 80-90% of cases, with specific gene mutations identified as significant risk factors. A 2015 meta-analysis of twin studies reinforced this notion, estimating that genetics contribute between 64% and 91% to the development of the condition.
However, it's not just genetics at play. Environmental influences, such as:
- Prenatal exposure to toxins
- Maternal infections during pregnancy
- Advanced parental age
further complicate the landscape. For families facing these challenges, it is crucial to recognize that high-risk families often harbor unaffected carriers of causative mutations, highlighting the intricate relationship between genetics and environment.
As Daniel H. Geschwind, MD, PhD, poignantly notes, "There are also huge diagnostic and treatment disparities by socioeconomic status." This statement emphasizes the broader implications of these factors, which can affect access to care and support. Additionally, a 2022 study found that prior maternal depression did not predict child behavior problems later, adding another layer of complexity to our understanding of maternal influences.
Significantly, recent discoveries suggest that the twinning process itself is not a risk factor for the spectrum condition. Grasping these complex interactions is essential for thoroughly investigating what causes a child to be autistic. If you find yourself navigating these challenges, know that you are not alone. Seeking support and sharing experiences can make a world of difference.
Clarify Misconceptions: What Does Not Cause Autism?
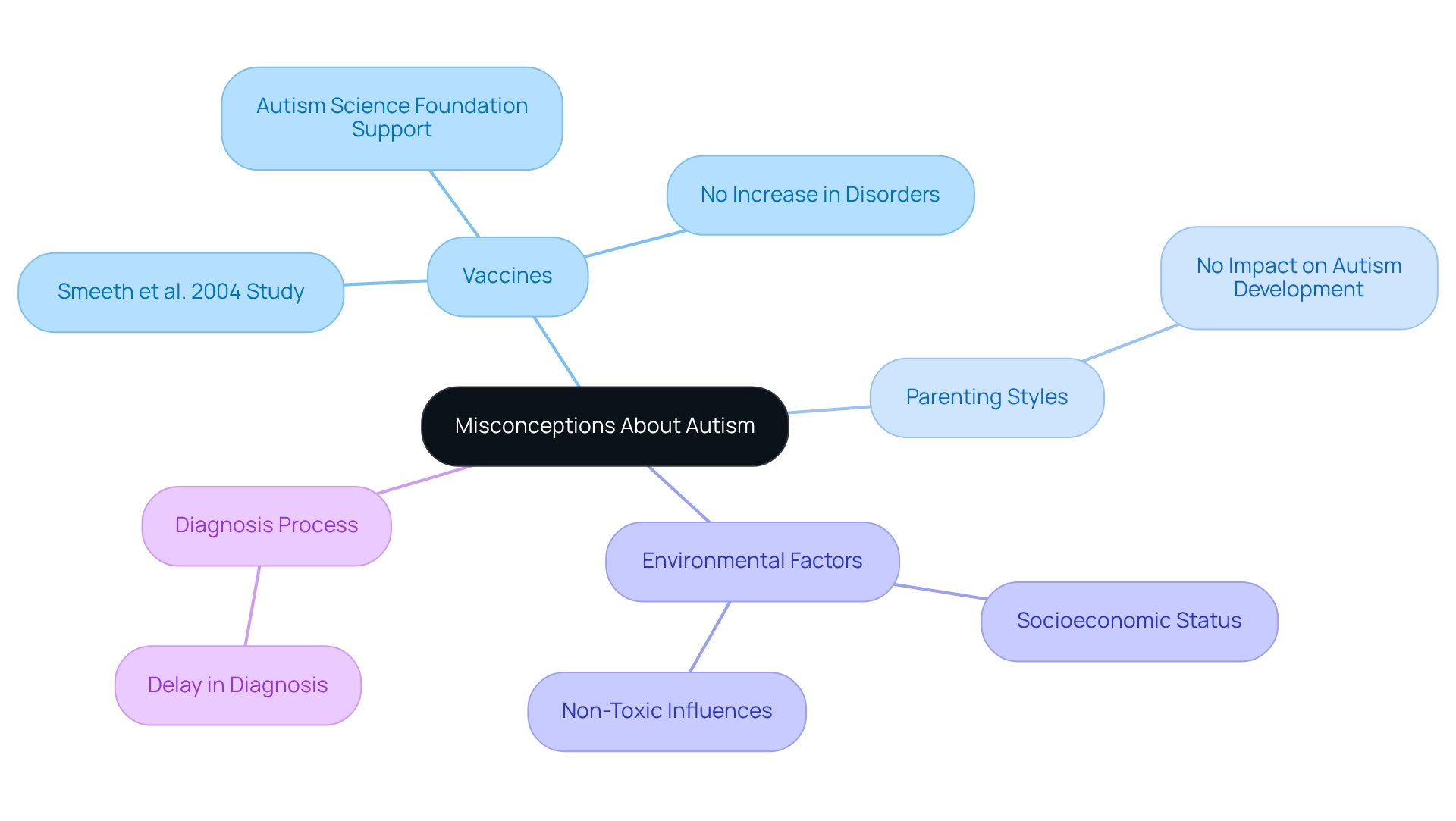
Misunderstandings about what causes a child to be autistic persist, making it essential to provide clear explanations regarding this topic. One significant myth is the belief that vaccines lead to developmental disorders. However, extensive research has thoroughly debunked this notion. For example, a notable study by Smeeth et al. in 2004, which examined a substantial UK database over 28 years, found no connection between the MMR vaccine and an increased risk of developmental disorders or other pervasive conditions. Moreover, researchers have consistently reported no sudden changes in the incidence of developmental disorders following the introduction of the MMR vaccine, reinforcing the absence of a causal link. Organizations like the Autism Science Foundation work diligently to ensure that research related to autism is scientifically sound, providing current information on its causes and further supporting these findings.
Beyond vaccine myths, misconceptions also extend to parenting styles and environmental factors. Research indicates that elements such as socioeconomic status and non-toxic environmental influences do not contribute to the development of autism. It's also important to recognize that the diagnosis process may experience a delay of several years between the detection of early signs and the final diagnosis, which can lead to misunderstandings. Understanding what does not lead to autism and what causes a child to be autistic is crucial for reducing stigma and promoting acceptance of individuals on the spectrum. By addressing these misconceptions and framing the narrative around vaccines in a way that resonates with parents, we can foster a more informed and supportive community for those affected by autism. Let's work together to create an environment where understanding prevails and support flourishes.
Highlight Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Recognizing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) early is vital for providing the right support, significantly influencing long-term outcomes. Research indicates that children diagnosed at a young age are more likely to benefit from tailored therapies, which can enhance their social, communication, and behavioral skills. For instance, timely intervention programs like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) have proven effective in improving developmental trajectories, helping children reach their full potential. Statistics show that children receiving prompt support experience considerable improvements in their skills compared to those who start therapy later.
Moreover, the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services in the U.S. is $175.44, highlighting the financial implications of acting swiftly—something parents should keep in mind. Experts stress that parents and caregivers should seek evaluations as soon as they notice signs of autism, as timely support can have a profound effect on a child's development.
A case study titled 'The Role of Health System Data in Understanding Autism Diagnosis' underscores the importance of early identification, demonstrating how targeted strategies can address disparities and allocate resources effectively. Additionally, Luke Grosvenor, PhD, points out that understanding variations in diagnosis rates among different age, gender, and racial groups can inform strategies and resource distribution, reinforcing the long-term benefits of early assistance.
As the landscape of autism care continues to evolve, the consensus among therapists is clear: early intervention is not merely beneficial; it is transformative, paving the way for improved outcomes and a brighter future for children with autism. If you suspect your child may be on the spectrum, don’t hesitate to reach out for support. Your timely action could make all the difference.
Conclusion
Exploring Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) reveals its multifaceted nature, highlighting the vital need to understand its definition, underlying causes, and the profound impact of early intervention. ASD presents a wide range of symptoms and challenges, especially in social communication, which can create significant disparities in outcomes among individuals. The alarming statistics regarding the rising prevalence of ASD underscore the urgency for informed support, particularly given the higher rates of co-occurring conditions in specific demographics.
Moreover, it’s essential to dispel common misconceptions about the causes of autism, notably the unfounded belief that vaccines are responsible for the disorder. Extensive research has consistently shown no causal link between vaccines and autism, emphasizing the importance of accurate information to combat stigma and foster acceptance. By understanding the genetic and environmental factors at play, families and professionals can navigate the complexities of this condition more effectively.
The critical role of early diagnosis and intervention cannot be overstated. Evidence indicates that timely support can lead to significantly improved outcomes for children with autism. Programs like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) have proven effective, illustrating that early intervention is not just beneficial but transformative. As the dialogue around autism continues to evolve, nurturing a compassionate and informed approach will pave the way for better support systems and resources, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for those on the spectrum and their families. Embracing this knowledge is vital for building a more inclusive and understanding society where individuals with autism can truly thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by enduring challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. The term 'spectrum' indicates the diverse range of symptoms and severity that individuals with autism may experience.
How prevalent is ASD in the United States?
As of 2025, recent research indicates that 1 in 36 children in the United States is diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Are there disparities in ASD diagnoses among different demographics?
Yes, particularly concerning is the higher proportion of co-occurring intellectual disability among Black children, which stands at 52.8%. This highlights significant disparities in how ASD impacts different demographics.
Why is understanding the causes of autism important?
A thorough understanding of what causes a child to be autistic is essential for parents, educators, and healthcare professionals to develop effective support and assistance strategies for individuals with ASD.
What challenges do autistic individuals face in social situations?
Many autistic individuals encounter difficulties in initiating and sustaining conversations, which can lead to feelings of social isolation.
How can early detection and interventions affect outcomes for children with ASD?
Early detection and tailored interventions can dramatically improve outcomes for children with ASD, enabling them to thrive in various environments.
What percentage of autistic students in the US graduate high school with a diploma?
Approximately 73.6% of autistic students in the US graduate high school with a diploma, showcasing the positive results that can stem from effective support.
What impact does ASD have on families, particularly mothers of autistic children?
A 2022 report indicated that 72.5% of mothers of autistic children in Chang Sha, China, experienced symptoms of depression, illustrating the broader implications of ASD on families and the need for community support and resources.
What does the World Health Organization advocate for regarding ASD?
The World Health Organization advocates for improved surveillance and support for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder, emphasizing the need to address gaps in early detection and care for mental and neurodevelopmental conditions.
What is the significance of the case study titled 'Global Actions on Mental Health and Autism'?
The case study calls for a collaborative approach to meet the needs of those affected by ASD, addressing the gaps in early detection and care for mental and neurodevelopmental conditions.




