Overview
Understanding the stages of autism is essential for caregivers. These stages include:
- Early Childhood (0-5 years)
- Middle Childhood (6-12 years)
- Adolescence and Adulthood (13+ years)
Each stage presents unique developmental challenges and support needs that can significantly impact the lives of those with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
As caregivers, recognizing these phases allows for tailored interventions that can enhance communication skills and improve overall quality of life. Imagine the difference it can make when you provide the right support at the right time. By learning about these stages, you empower yourself to make informed decisions that nurture growth and development.
We encourage you to reflect on your experiences and consider how understanding these stages can help you and your loved ones. Share your thoughts and stories with us; your insights could inspire others on this journey. Together, we can create a supportive community that fosters understanding and compassion for individuals with ASD.
Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) presents a complex array of challenges that affects not only individuals but also families and communities at large. Understanding ASD is crucial for developing effective interventions that cater to each person's unique needs, especially given its diverse symptoms and varying degrees of severity. As the prevalence of autism continues to rise, the importance of early diagnosis and tailored support becomes increasingly evident.
This article delves into the nuances of ASD, exploring its significance and the developmental stages individuals experience. It highlights the varying levels of support required and the profound impact that early intervention can have on enhancing quality of life. By shedding light on these critical aspects, we aim to empower caregivers and professionals alike to foster a more supportive environment for those on the spectrum. Together, we can create a community that understands and uplifts every individual touched by autism.
Define Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Significance
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition that presents enduring challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. The term 'spectrum' highlights the varied range of symptoms and severity levels that individuals may experience. For parents and professionals alike, understanding what are the stages of autism is crucial, as it directly influences the tailored strategies and support needed to address each person's unique requirements. This figure is notably lower than that of the 8-year-old group, underscoring the significance of age-related identification in developing effective support strategies. Moreover, grasping the traits of ASD can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected, as early identification facilitates prompt and efficient assistance.
Specialists emphasize the profound impact of early support, with research indicating that children who receive appropriate aid are more likely to develop essential social communication skills. Additionally, the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services in the U.S. is $175.44, highlighting the financial challenges parents face when seeking support.
Alarmingly, 8% of autistic students in the U.S. do not complete high school, compared to 5% of all students. This statistic illustrates the long-term implications of ASD and the critical necessity for early intervention. The prevalence of autism among white children stands at 24.3 cases per 1,000, indicating demographic differences that are vital for understanding the condition's impact across various communities.
This understanding not only empowers parents and specialists but also fosters a collaborative environment that can lead to improved outcomes for individuals with ASD. Furthermore, reports suggest that communities should actively monitor ASD trends and service needs to better allocate resources and support for those affected. Together, we can create a more supportive landscape for individuals with ASD and their families.
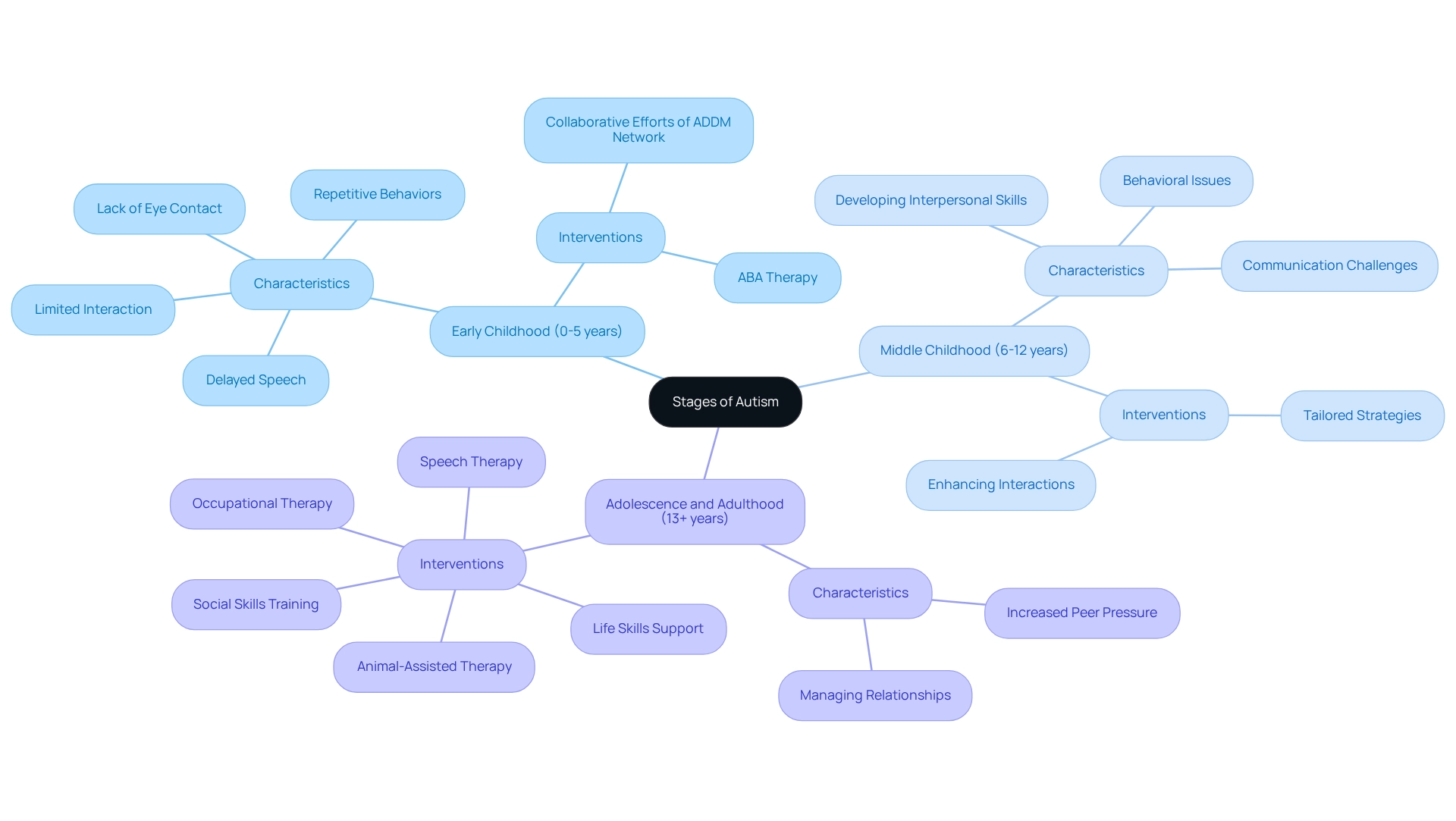
Explore the Three Stages of Autism: Characteristics and Implications
Understanding what are the stages of autism can be invaluable for caregivers seeking to support their loved ones.
- Early Childhood (0-5 years): This crucial developmental stage often reveals signs such as limited interaction with others, delayed speech, and repetitive behaviors. Parents may notice a lack of eye contact or challenges in responding to social cues. It's heartening to know that about 36.5% of caregivers choose ABA therapy during this time, emphasizing its importance in fostering communication and social skills. The collaborative efforts of ADDM Network Sites across the U.S. provide a broader context for understanding early childhood autism characteristics. As highlighted by Maenner MJ in the MMWR Surveillance Summary, recognizing the prevalence and traits of autism in 8-year-olds underscores the critical role of early intervention.
- Middle Childhood (6-12 years): As children transition into middle childhood, they may begin to develop some interpersonal skills, yet communication and understanding social norms can still be challenging. Behavioral issues might become more noticeable, calling for tailored interventions. Educators stress the importance of strategies that enhance interactions and communication, which are vital for improving daily living skills and peer relationships.
- Adolescence and Adulthood (13+ years): In this stage, individuals face increased pressures and expectations from peers. Support typically centers around life skills, fostering independence, and managing relationships. For caregivers, understanding what are the stages of autism is crucial, as it enables them to provide appropriate support and strategies that adapt to their loved one's evolving needs. Case studies reveal that therapies such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training significantly enhance communication and social interactions for children on the spectrum. These therapies not only improve personal outcomes but also positively impact family dynamics and coping strategies, illustrating the long-term benefits of early intervention.
By recognizing these stages, caregivers can better navigate the journey of autism, ensuring that their loved ones receive the support they need to thrive.
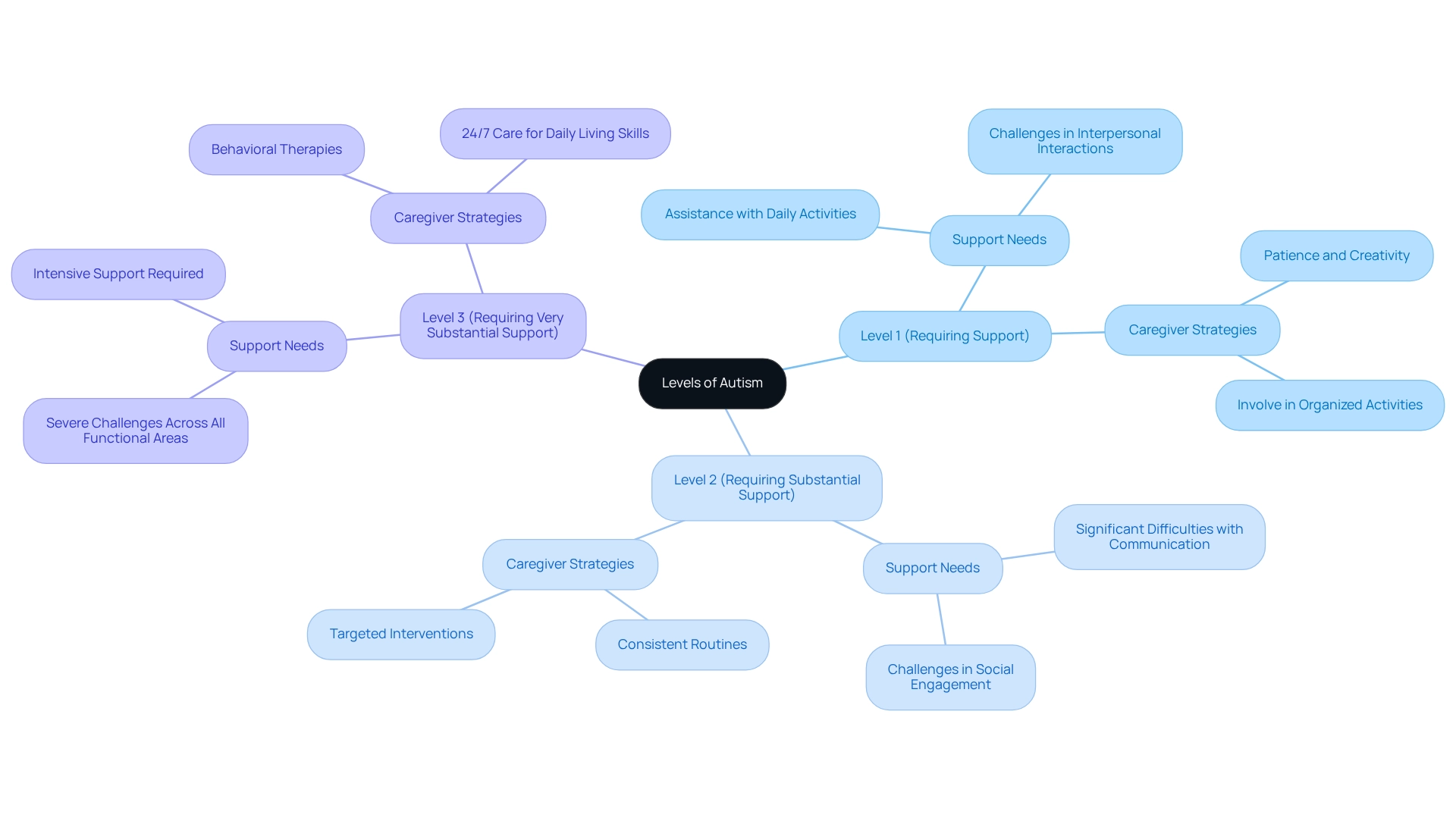
Identify Levels of Autism: Support Needs and Strategies for Caregivers
The DSM-5 categorizes autism, outlining what are the stages of autism into three distinct levels, each reflecting the degree of support an individual requires.
- Level 1 (Requiring Support): Individuals at this level may experience challenges in interpersonal interactions and require assistance with daily activities. Caregivers can enhance interpersonal skills by involving them in organized activities that encourage interaction and communication. As many caregivers have shared, patience and creativity are essential in supporting these individuals, and they often highlight strategies that have worked for them.
- Level 2 (Requiring Substantial Support): Those classified under Level 2 often face more significant difficulties with communication and social engagement. Consistent routines and targeted interventions can be immensely helpful in managing behaviors and enhancing communication abilities. Statistics indicate that the prevalence of Level 2 autism assistance requirements is notable, underscoring the need for tailored strategies in this category.
- Level 3 (Requiring Very Substantial Support): Individuals in this category encounter severe challenges across all functional areas. Caregivers must provide intensive support, which may include behavioral therapies and, in some cases, 24/7 care to assist with daily living skills and ensure safety. Understanding what are the stages of autism is crucial for effectively tailoring support strategies. For example, people with Level 1 autism often benefit from interpersonal skills training, while those at Level 2 may thrive in more organized settings. Real-world instances demonstrate that strategies such as speech therapy and social narratives can significantly enhance outcomes for individuals at all levels. As O. Ivar Lovaas wisely stated, 'If they can't learn the way we teach, we teach the way they learn,' which highlights the necessity for adaptable teaching methods.
Additionally, the case study titled 'Do Seed Oils Cause Autism?' addresses parental concerns and misconceptions, providing valuable context that can guide assistance strategies. As Haley Moss aptly notes, while milestones may be reached at different times, each achievement is a significant victory in its own right. We encourage caregivers to share their experiences and insights, fostering a supportive community where everyone can learn and grow together.
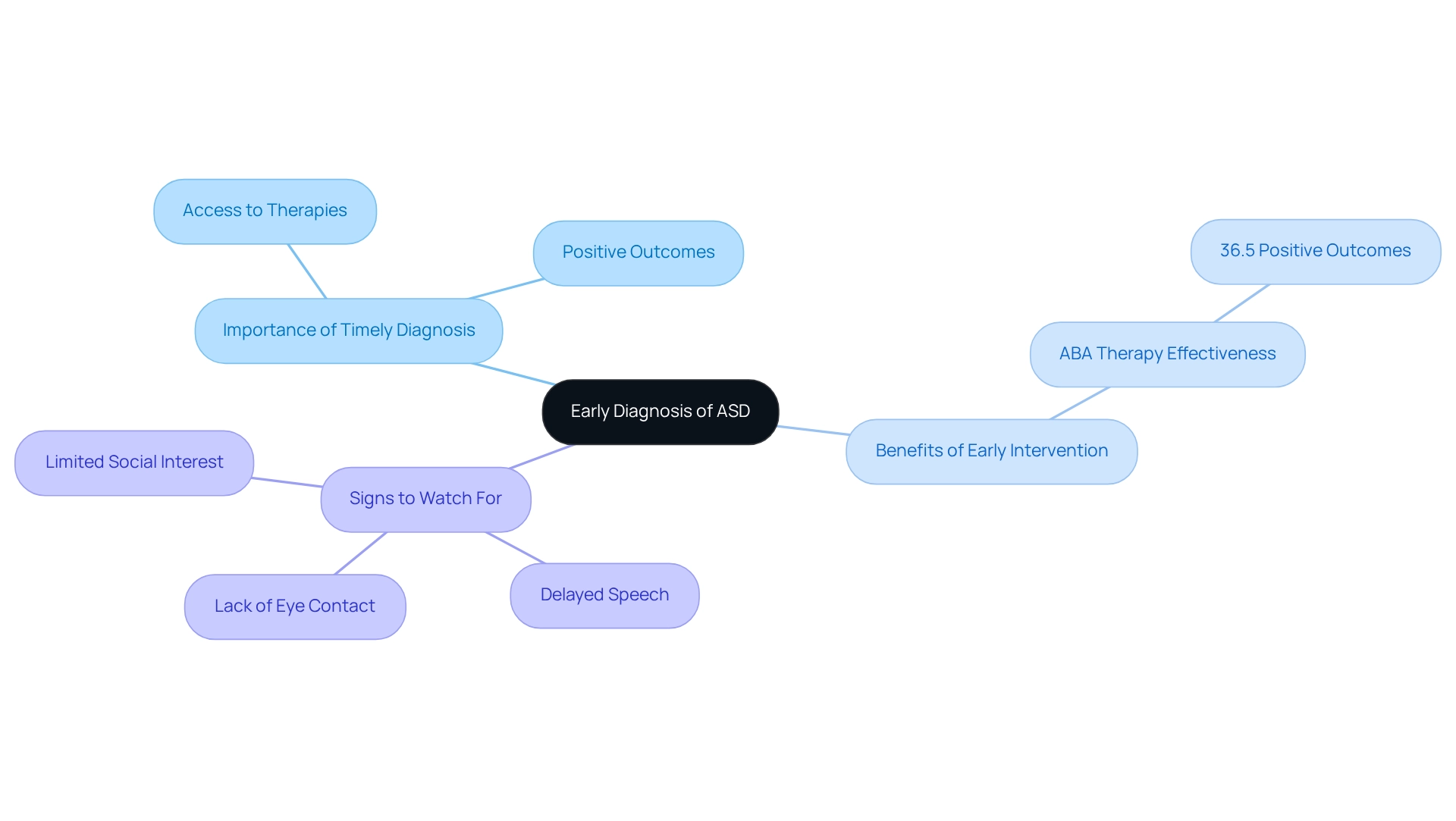
Emphasize Early Diagnosis: Impact on Support and Development
Recognizing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in a timely manner is essential for providing effective assistance and support. Research indicates that children diagnosed before the age of three are notably more likely to benefit from therapies designed to enhance their social, communication, and behavioral skills. Early support can lead to significant improvements in developmental outcomes, empowering children to reach their fullest potential. For example, studies show that early access to Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy can bring about measurable enhancements in daily life for children with autism. A case study titled "Benefits of ABA Therapy" reveals that 36.5% of caregivers report positive outcomes from such interventions, underscoring the effectiveness of early therapy.
Caregivers are encouraged to stay alert for early signs of autism, including:
- Delayed speech
- Lack of eye contact
- Limited interest in social interactions
When concerns arise, seeking professional evaluations promptly can make a significant difference. The impact of early diagnosis goes beyond personal development; it nurtures a supportive environment that equips children with the vital skills they need to thrive. Recent findings highlight the importance of collaboration among professionals, families, and communities in delivering comprehensive support for individuals with ASD. By prioritizing early diagnosis and intervention, families can profoundly influence their child's developmental trajectory, paving the way for a brighter future.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is fundamental for creating effective support systems that cater to the unique needs of individuals and their families. The exploration of ASD reveals its multifaceted nature, characterized by diverse symptoms and varying levels of severity. Recognizing the importance of early diagnosis is crucial, as it can lead to timely interventions that significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected. The statistics concerning prevalence and educational outcomes underscore the urgency of this understanding, particularly the alarming rates of high school completion among autistic students.
The developmental stages of autism highlight the evolving challenges individuals face from early childhood through adolescence and adulthood. Each stage presents distinct characteristics that require tailored interventions, ensuring that individuals receive the appropriate support as they grow. The emphasis on different levels of autism illustrates the necessity for caregivers to adapt their strategies according to the specific needs of the individual, reinforcing the idea that a one-size-fits-all approach is ineffective.
Ultimately, fostering a community that understands and supports individuals with ASD is essential for improving their outcomes. Empowering caregivers and professionals with knowledge about early intervention, developmental stages, and levels of support can create an environment where individuals on the spectrum can thrive. By working together, it is possible to build a more inclusive society that recognizes the potential of every individual touched by autism, ensuring that they are not only supported but also celebrated for their unique contributions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition characterized by enduring challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. The term "spectrum" indicates the varied range of symptoms and severity levels experienced by individuals.
Why is understanding the stages of autism important?
Understanding the stages of autism is crucial for parents and professionals as it directly influences the tailored strategies and support needed to address each person's unique requirements.
How does early identification of ASD impact support strategies?
Early identification of ASD significantly enhances the quality of life for those affected, as it facilitates prompt and efficient assistance, leading to better outcomes.
What is the impact of early support on children with ASD?
Research indicates that children who receive appropriate early support are more likely to develop essential social communication skills.
What are the financial challenges parents face when seeking support for ASD?
The average cost of therapeutic behavioral services in the U.S. is $175.44, highlighting the financial challenges that parents encounter when seeking support for their children.
What is the high school completion rate for autistic students in the U.S.?
Alarmingly, 8% of autistic students do not complete high school, compared to 5% of all students, illustrating the long-term implications of ASD and the necessity for early intervention.
What is the prevalence of autism among white children?
The prevalence of autism among white children is 24.3 cases per 1,000, indicating demographic differences that are important for understanding the condition's impact across various communities.
How can communities support individuals with ASD?
Communities should actively monitor ASD trends and service needs to better allocate resources and support for those affected, fostering a collaborative environment that leads to improved outcomes.




