Introduction
Understanding autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is crucial for parents and caregivers who strive to support their children's development and well-being. The DSM-5 provides a comprehensive framework for diagnosing ASD, outlining specific criteria that highlight the importance of early identification and intervention. This article delves into the key diagnostic criteria, the significance of timely evaluations, and the resources available to families navigating this journey.
By empowering themselves with knowledge about ASD, parents can advocate effectively for their children, ensuring they receive the necessary support to thrive. With insights from recent research and expert opinions, this exploration aims to equip families with the tools they need to foster a nurturing environment that promotes growth and resilience.
Understanding the DSM-5 Criteria for Autism Diagnosis
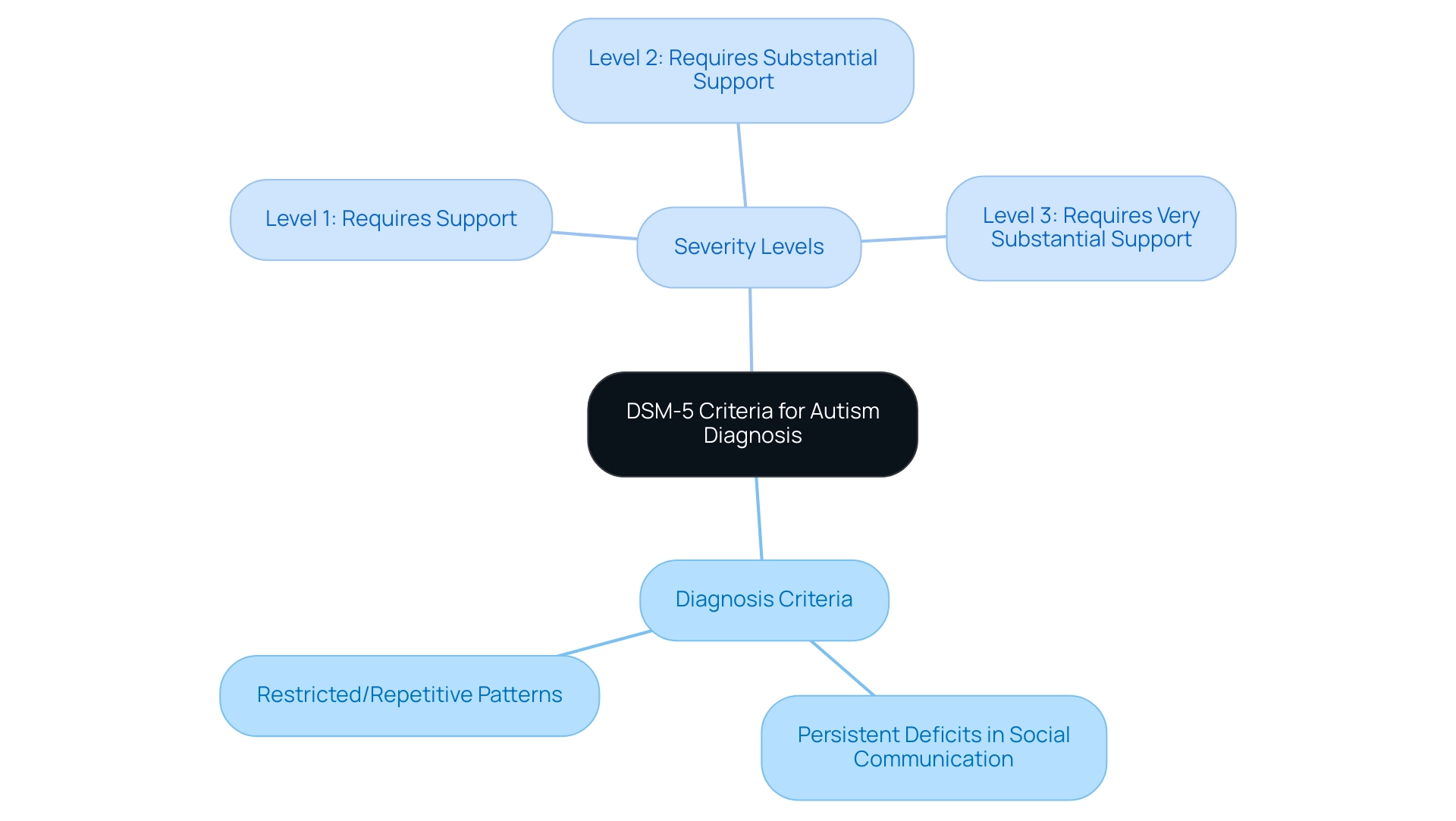
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), provides an essential framework for diagnosing spectrum disorder (ASD) through well-defined criteria for autism. Specifically, the diagnosis hinges on two fundamental areas:
- Persistent deficits in social communication and interaction
- Restricted or repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities
These criteria for autism enable clinicians to evaluate an individual's behavior and communication skills across various contexts, which facilitates an accurate diagnosis.
For parents and caregivers, understanding the criteria for autism is vital, as it equips them with the knowledge to recognize developmental milestones and behavioral indicators that may warrant further evaluation. As remarked by Sara Jane Webb from Seattle children’s Hospital, this understanding enables parents to advocate effectively for their children, ensuring they receive the essential assistance and interventions early on. Notably, the American Psychiatric Association released the DSM-5-TR in 2022, providing updated insights into the diagnosis of developmental disorders.
Additionally, the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network has highlighted significant data on ASD prevalence, revealing that the average age of diagnosis can vary significantly across states, which underscores the importance of timely intervention. Furthermore, the severity of spectrum disorder is categorized into three levels according to the DSM-5:
- Level 3 requires very substantial support
- Level 2 requires substantial support
- Level 1 requires support
This information is not merely academic; it has real-world implications for parents aiming to ensure their offspring receive appropriate care.
Key Diagnostic Criteria: Social Communication and Behavioral Patterns
The DSM-5 outlines critical criteria for autism spectrum disorder (ASD), prominently featuring significant difficulties in social communication and interaction. Children with ASD often struggle to understand and respond to social cues, find it challenging to form relationships, and may exhibit limited use of nonverbal communication. Furthermore, many individuals display restricted interests or repetitive behaviors, such as a strong insistence on sameness, engaging in repetitive movements, or developing an intense focus on specific topics.
For instance, many young individuals might become captivated by a particular subject, which can serve as a motivating factor for learning. However, if these interests become all-consuming or diverge from their peers' interests, they may hinder the individual's ability to engage in reciprocal conversations and form social connections. A case study titled 'Intense Interests' illustrates this point, showing that while these interests can motivate learning, they may also limit social interactions if not aligned with peers.
In Wisconsin, the prevalence of ASD among males is notably high, at 28.1 per 1,000 youths aged 8 years. As noted by Williams AR in the MMWR Surveillance Summary, understanding the criteria for autism and its prevalence and characteristics is crucial for early identification. This statistic underscores the importance of recognizing these behaviors early.
By recognizing possible issues, parents and caregivers can pursue timely intervention and assistance, establishing the foundation for their offspring's social and emotional growth. Additionally, music therapy interventions can be effectively combined with evidence-based strategies to address the diverse needs of youth with different levels of ASD, offering further avenues for support.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Its Impact on Functioning
The early diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is crucial, as it helps to identify the criteria for autism, which opens the door to timely interventions that can profoundly improve a young person's development and overall quality of life. Statistics reveal a concerning trend: a higher cumulative incidence of ASD identification occurs by age 48 months among youth compared to those identified by age 8, highlighting the critical window for effective intervention. Research shows that children who receive early support tend to exhibit improved outcomes in communication, social skills, and overall functioning.
As the University of Cambridge poignantly states,
Early diagnosis, intervention, and treatment can be lifesaving.
Alarmingly, studies indicate that 10% of individuals who died by suicide were likely to have undiagnosed autism, emphasizing the urgency of timely evaluations based on the criteria for autism. Parents who recognize the signs and pursue assessments promptly play a pivotal role in addressing the criteria for autism to facilitate access to therapies and resources that foster growth and learning.
By doing so, they empower their offspring to better navigate social environments and achieve key developmental milestones. The ongoing research by the ADDM Network aims to increase access to additional data sources to identify inequities in ASD services, addressing barriers to early identification and intervention. This is particularly relevant in light of the long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on ASD identification, ensuring that every child has the opportunity to thrive.
For further reading, the relevant research can be found under PMCID PMC10491411 and PMID 37692637.
Critiques and Controversies of the DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria
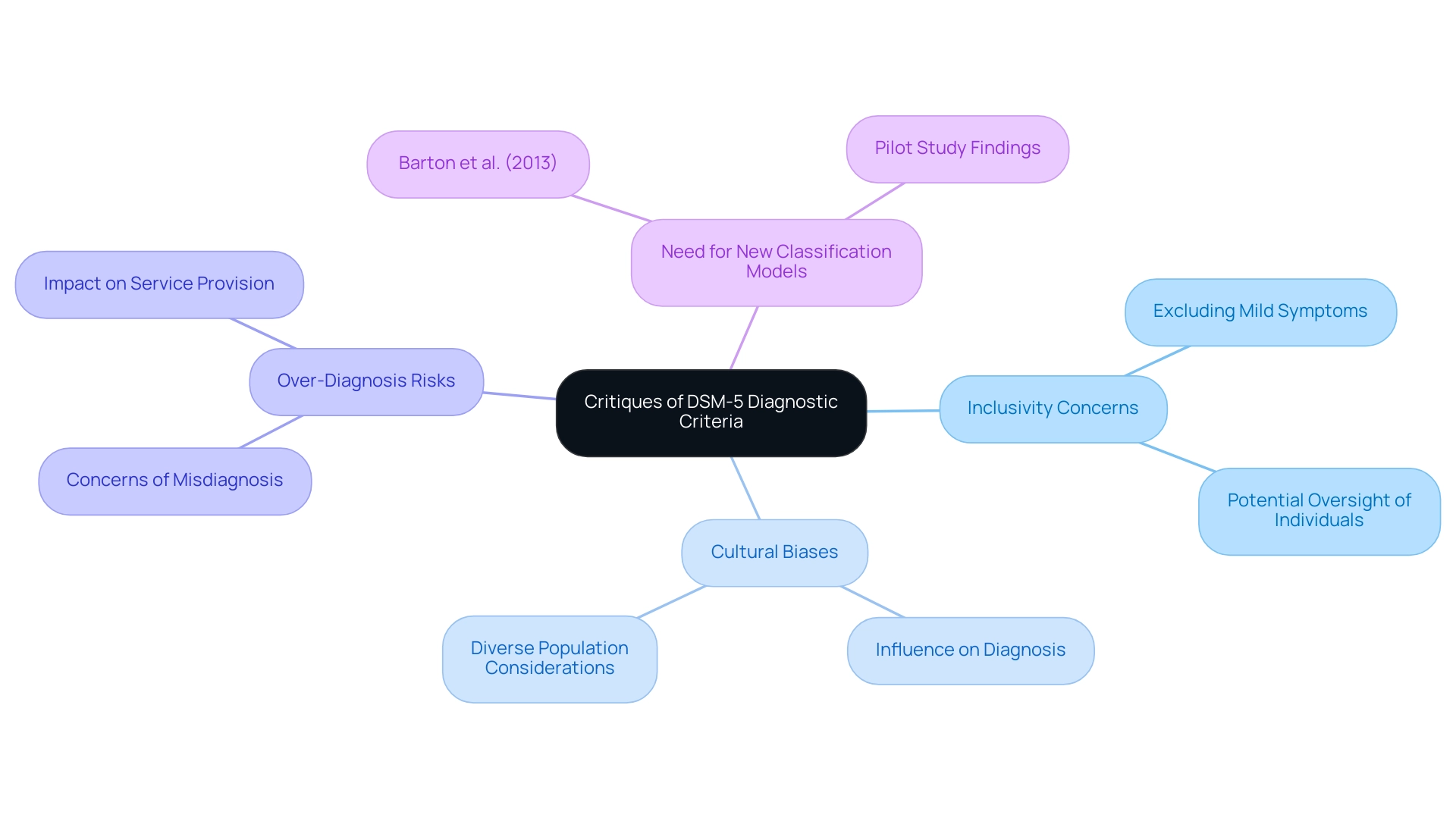
The criteria for autism in the DSM-5 diagnostic guidelines for spectrum disorder (ASD) have come under scrutiny for their inclusivity and the potential oversight of individuals who may not fit neatly into the specified categories. Critics emphasize that the criteria for autism could inadvertently exclude those with milder symptoms who need assistance. The American Psychiatric Association points out that
the DSM-5 text and criteria represent a significant departure from the previous construct of a spectrum of discrete entities separable by symptom or symptom severity.
This evolution raises concerns about the criteria for autism, as it risks over-diagnosis for some individuals while simultaneously neglecting others who genuinely need assistance. Furthermore, ongoing discussions reveal the presence of cultural biases that may influence the acknowledgment of this condition in diverse populations, which is crucial for parents and professionals to consider. A study by Barton et al. (2013) emphasizes the need for a new classification model for ASD to achieve accurate diagnoses, supporting the argument for a more inclusive approach.
Furthermore, the case study 'Conclusion on DSM-5 Changes' emphasizes that the modifications to the criteria for autism and other developmental disorders have garnered mixed feedback, with worries about possibly overlooking youngsters requiring services and assistance. A recent pilot study demonstrated the significance of using a classification guide to assess records of youth with spectrum disorders or related diagnoses, achieving high reliability in classifying ASD case status.
Comprehending these critiques and the broader implications encourages a more nuanced approach to diagnosis, empowering parents to advocate for more inclusive practices that ensure every child receives the assistance they require.
Resources and Support for Individuals with Autism
Navigating the intricacies of the condition can be challenging, but there is a strong network of resources and assistance systems available to families. Organizations such as the Autism Society and numerous local support groups provide essential information, advocacy, and opportunities for community engagement. For parents seeking professional assistance, services like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy are specifically designed to cater to the diverse needs of individuals on the spectrum.
These therapeutic interventions, which average $175.44 per session, have demonstrated significant positive effects on developmental outcomes, empowering families to nurture their child's growth. Furthermore, online platforms and forums serve as invaluable spaces for parents to connect, share experiences, and gain insights from others who understand their journey. The ADDM Network plays a crucial role in tracking ASD characteristics across communities, which highlights the importance of the criteria for autism in accurate diagnosis and assessment to understand the prevalence of this condition.
The importance of early diagnosis, especially concerning the criteria for autism, cannot be exaggerated; research from the University of Cambridge highlights that early identification, intervention, and treatment can be lifesaving. A striking study from the United Kingdom revealed that 10% of individuals who died by suicide likely had undiagnosed autism, underscoring the critical need for prompt assistance. Findings from ASD prevalence studies can inform local and national initiatives, policies, and research to better support youth and families affected by ASD.
By effectively leveraging these resources, families can cultivate a nurturing environment that promotes growth, resilience, and well-being for their children.
Conclusion
Understanding autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is imperative for parents and caregivers who are dedicated to supporting their children’s development. The DSM-5 outlines essential criteria that facilitate early diagnosis and intervention, emphasizing the importance of recognizing social communication deficits and repetitive behavioral patterns. By familiarizing themselves with these diagnostic criteria, parents can more effectively identify potential challenges and advocate for timely evaluations, ensuring their children receive the necessary support.
The significance of early diagnosis cannot be overstated. Research indicates that interventions provided at a young age can lead to improved outcomes in communication and social skills, ultimately enhancing overall functioning. Parents play a crucial role in this process by being vigilant and proactive in seeking assessments, which can open the door to vital resources and therapies that promote growth and resilience.
While the DSM-5 provides a foundational framework, ongoing discussions about its inclusivity highlight the need for a more nuanced understanding of ASD. Recognizing the potential for cultural biases and the risk of overlooking individuals with milder symptoms is essential for fostering an equitable approach to diagnosis and support.
Fortunately, a wealth of resources is available to assist families in navigating the complexities of autism. From local support groups to professional therapies designed to cater to diverse needs, families can find the tools they need to create a nurturing environment. By leveraging these resources and advocating for their children, parents can make a profound difference in their children’s lives, ensuring they have the opportunity to thrive and reach their full potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the DSM-5 and its role in diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
The DSM-5, or the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, provides a framework for diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) through well-defined criteria, focusing on persistent deficits in social communication and interaction, as well as restricted or repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.
What are the key criteria for diagnosing autism according to the DSM-5?
The key criteria for diagnosing autism include: 1. Persistent deficits in social communication and interaction. 2. Restricted or repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.
Why is it important for parents and caregivers to understand the criteria for autism?
Understanding the criteria for autism helps parents and caregivers recognize developmental milestones and behavioral indicators that may require further evaluation, enabling them to advocate effectively for their children and ensure they receive necessary interventions early on.
How does the severity of autism spectrum disorder vary according to the DSM-5?
The severity of autism spectrum disorder is categorized into three levels according to the DSM-5: 1. Level 3 requires very substantial support. 2. Level 2 requires substantial support. 3. Level 1 requires support.
What is the significance of the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network's findings?
The Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network highlights significant data on ASD prevalence, revealing variations in the average age of diagnosis across states, which emphasizes the importance of timely intervention for effective care.
What are common challenges faced by children with autism spectrum disorder?
Children with ASD often struggle with understanding and responding to social cues, forming relationships, and may exhibit limited nonverbal communication. They may also have restricted interests or repetitive behaviors that can impede social interactions.
How can intense interests of children with ASD affect their social interactions?
While intense interests can motivate learning, if these interests become all-consuming or differ from their peers' interests, they may hinder the individual's ability to engage in reciprocal conversations and form social connections.
What is the prevalence of ASD among males in Wisconsin?
In Wisconsin, the prevalence of ASD among males is notably high, at 28.1 per 1,000 youths aged 8 years.
How can music therapy be utilized for children with ASD?
Music therapy interventions can be effectively combined with evidence-based strategies to address the diverse needs of youth with different levels of ASD, providing additional support avenues.




