Overview
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a compassionate, scientific approach dedicated to understanding and transforming behaviors through systematic interventions. This method is particularly beneficial for individuals with autism and developmental disorders, offering hope and support to families navigating these challenges. The article emphasizes ABA's remarkable effectiveness in enhancing adaptive skills and lessening challenging behaviors. Research underscores the significant progress children experience in communication and social skills when they engage in sustained ABA therapy.
As parents, it’s natural to seek the best for your child. ABA not only provides tools for improvement but also fosters a nurturing environment where children can thrive. Imagine witnessing your child’s joyful communication and social interactions flourish—ABA can help make that a reality.
If you’re looking for ways to support your child, consider exploring ABA therapy further. There are numerous resources available to guide you on this journey, ensuring you’re not alone in this process. Together, we can create lasting positive changes for our children and families.
Introduction
In the world of behavioral therapy, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) emerges as a vital approach, especially for individuals with autism and developmental disorders. This method systematically analyzes and modifies behavior through evidence-based strategies, aiming not only to enhance essential life skills but also to address challenging behaviors that can impede personal growth.
Rooted in behaviorism, ABA has attracted significant attention from both researchers and practitioners, showcasing its transformative potential. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research and innovative practices are crucial to ensure that ABA remains effective and inclusive, meeting the diverse needs of individuals and families navigating the complexities of autism.
This article invites you to explore the core principles, techniques, benefits, and controversies surrounding ABA therapy, shedding light on its important role in fostering positive outcomes for those it serves.
Understanding the Basics: What Does ABA Stand For?
Applied Behavior Analysis, or ABA, is a compassionate scientific approach aimed at understanding and changing behaviors through systematic interventions. Rooted in the principles of behaviorism, ABA emphasizes the intricate relationship between actions and environmental factors. This method has proven especially beneficial for individuals with autism and other developmental disorders, focusing on enhancing socially significant behaviors while addressing challenging actions.
Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of ABA, revealing that children who engage in ABA for a minimum of 12 months show remarkable improvements in adaptive skills. For example, research utilizing the Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales-Second Edition found that many children achieved the Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) in their Adaptive Behavior Composite scores. This underscores the transformative potential of sustained ABA therapy in enhancing daily functioning for children with developmental disabilities. The main effect of mixed ANOVA on the dependent variable (targets mastered) across time was significant, F(2,160) = 32.893, p < 0.001.
Weihong Xu, a reviewer and editor of the manuscript, emphasizes the necessity of ongoing research in this field. She notes that future studies should encompass a wider age range and geographic diversity to improve the applicability of results.
The significance of ABA lies not only in its ability to modify behaviors but also in its capacity to foster skill acquisition. By utilizing evidence-based strategies, ABA practitioners can effectively nurture the development of vital life skills, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for individuals with autism. As the field continues to grow, ongoing research is essential to ensure that ABA practices are inclusive and relevant across various populations, broadening the reach and impact of this crucial therapeutic approach.
Core Principles of ABA: How It Works and Its Methodologies
The foundational principles of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) encompass reinforcement, punishment, and extinction, all of which are vital for modifying specific behaviors. Reinforcement can be understood in two ways:
- Positive reinforcement, which involves introducing a rewarding stimulus,
- Negative reinforcement, which entails removing an aversive stimulus.
Both strategies aim to encourage desired behaviors. It's important to note that research indicates most behaviors are reinforced when punishment is applied, highlighting the need for careful consideration when selecting treatment options.
Current methodologies in ABA, particularly Discrete Trial Training (DTT) and Natural Environment Training (NET), are instrumental in crafting effective intervention strategies. DTT breaks skills down into smaller, manageable components, allowing for focused teaching and practice. This structured approach is particularly beneficial for young individuals who thrive on clear, step-by-step guidance. On the other hand, NET underscores the significance of teaching skills within the context of everyday activities, creating natural learning opportunities that support the generalization of skills.
Involving consumer input in the treatment-selection process is essential. This ensures that interventions are not only effective but also practical for those working in early childhood care and education. As Glen Dunlap insightfully noted, "There is a necessity for intervention strategies that are both effective in diminishing challenging actions and practical for use by standard practitioners of early childhood care and education." Additionally, the case study titled 'Visual Analysis of Graphic Data' addresses the challenges of reproducibility in behavioral science, which is pertinent to understanding what ABA represents and the effectiveness of its methodologies.
As we advance our methods, the emphasis on tailoring interventions to meet the unique needs of each child remains crucial. This approach fosters effective learning and meaningful changes in behavior. Moreover, despite some concerns, a substantial body of research showcases the positive outcomes stemming from ABA interventions, encouraging ongoing dialogue and refinement of practices. Together, we can navigate these complexities and support our children in their growth journeys.
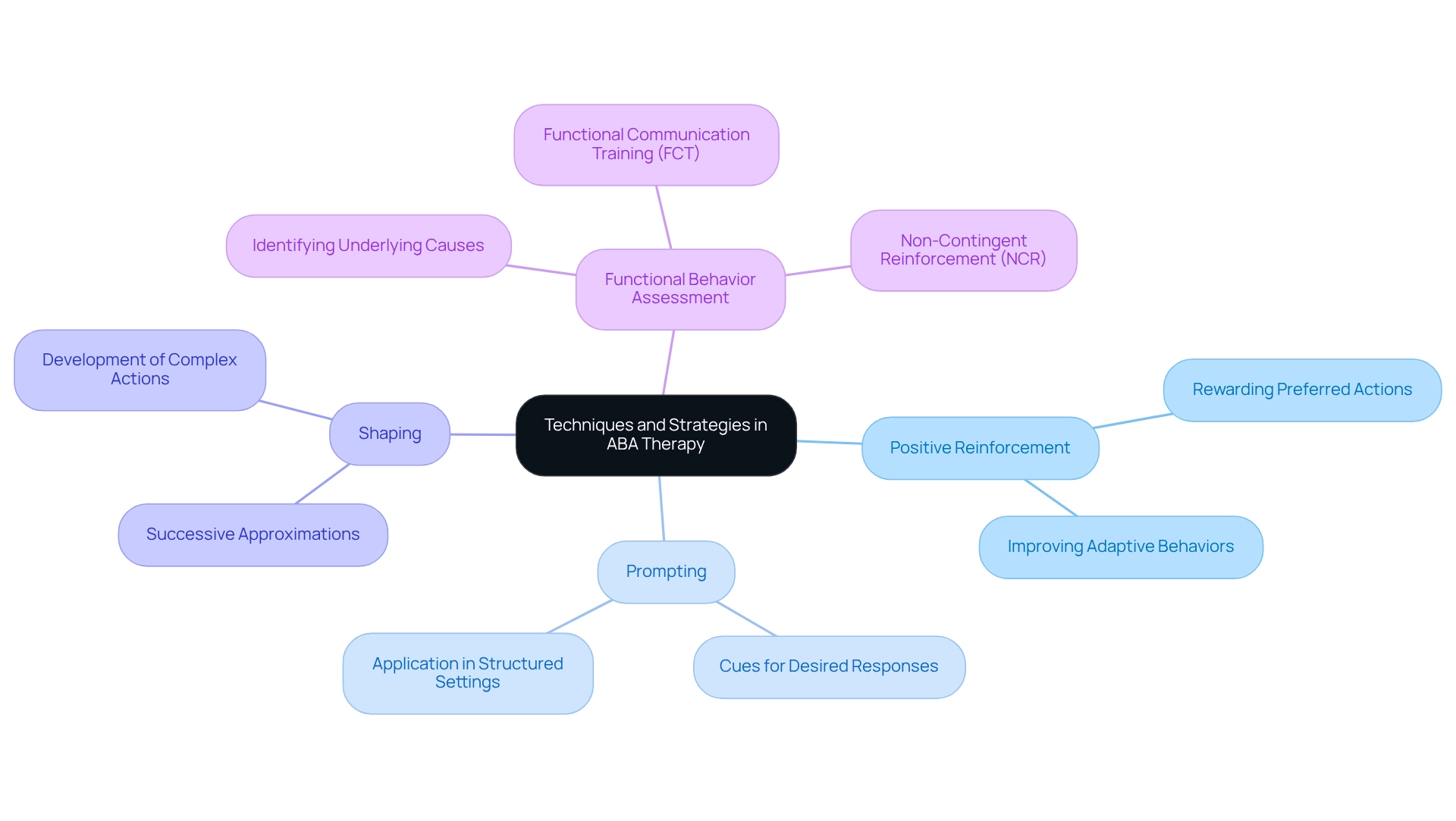
Techniques and Strategies in ABA Therapy: Practical Applications
ABA intervention employs a variety of methods designed to enhance learning and promote positive behavior changes effectively. One of the most widely recognized strategies is Positive Reinforcement, which involves rewarding preferred actions to encourage their repetition. This approach has been shown to significantly improve adaptive behaviors in young individuals, particularly those who have previously received ASD services. These children often benefit greatly from ongoing ABA support, highlighting its importance in their developmental journey.
Interestingly, children who have engaged with ASD services are more likely to continue in ABA therapy, underscoring the value of sustained support. Prompting is another vital technique in ABA, where cues are provided to encourage the desired response. This method can be especially advantageous in structured settings, such as clinics, as well as in natural environments, ensuring that skills are generalized across various situations.
Shaping is also a key strategy within ABA, where successive approximations of a target behavior are reinforced. This gradual process allows for the development of complex actions over time, helping individuals reach their goals.
Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) plays a crucial role in identifying the underlying causes of specific behaviors. By understanding these motivations, practitioners can tailor interventions more effectively, leading to improved behavioral outcomes. For example, in a case study involving two children, Jay and Betty, functional communication training (FCT) and non-contingent reinforcement (NCR) were explored.
The findings indicated that personalized interventions based on functional analysis could significantly reduce challenging behaviors and enhance communication skills. Jay's FCT and NCR sessions were compared to assess their effectiveness, while Betty's treatment focused on developing appropriate communication skills. However, it is essential to acknowledge that high rates of ABA discontinuation and low dosing can diminish the potential benefits of ABA, even with mandated insurance coverage. This reality highlights the challenges in ensuring consistent and effective treatment.
Recent strategies in ABA practices emphasize the importance of these methods in fostering positive behavioral changes. Experts, including Gregory P. Hanley, suggest that understanding the conditions under which the aversiveness of punishment is minimized is crucial. The effectiveness of Positive Reinforcement becomes particularly evident when it is integrated with other strategies, creating a holistic approach to behavior modification.
As research continues to evolve, incorporating these techniques into daily practice remains vital for maximizing the benefits of ABA. Parents and caregivers are encouraged to engage with these methods, ensuring that their loved ones receive the support they need to thrive.
The Benefits of ABA Therapy: Enhancing Skills and Reducing Challenges
[Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) intervention](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8702444) provides a wealth of benefits, especially for children diagnosed with autism and ADHD, showcasing the essence of what ABA truly represents. Recent studies indicate that ABA can lead to remarkable improvements in communication skills, social interactions, and daily living activities. For example, children undergoing ABA treatment often learn to express their needs more effectively, engage in socially appropriate behaviors, and develop essential life skills that promote their independence.
Moreover, ABA therapy has shown a significant reduction in challenging behaviors, such as aggression and self-harm, by teaching children alternative, more constructive actions. This structured approach not only nurtures behavioral improvements but also empowers children to succeed in educational settings, ultimately enhancing their overall quality of life.
The Surgeon General of the United States has acknowledged the efficacy of applied behavioral techniques in reducing inappropriate behaviors while improving communication, learning, and social skills. A noteworthy study revealed that after a 24-month period, 46% of participants remained engaged in ABA services, with 58% achieving the minimal clinically important difference in their behavior scores. This research was conducted within a unified healthcare system serving 4.7 million members, underscoring the effectiveness of ABA in fostering positive outcomes for youth.
Furthermore, expert opinions highlight the impact of applied behavioral techniques in enhancing communication and social skills, reinforcing the notion of what ABA stands for as a crucial component in therapeutic practices for individuals with autism. Real-world examples further demonstrate these benefits. Children who have participated in ABA treatment frequently exhibit significant progress in their ability to communicate and interact socially, showcasing the transformative nature of this therapeutic approach.
As research continues to evolve, it is vital to explore the long-term effects of ABA and its application across diverse groups, ensuring that the treatment remains adaptable and beneficial for all children in need. Future studies should also investigate the reasons behind service discontinuation and additional outcome measures beyond adaptive behavior, as highlighted in ongoing research. Additionally, the case study titled "Long-term Effects and Recommendations for ABA Implementation" suggests broadening the age range of participants and increasing session frequency to enhance the program's generalizability and impact.
Controversies and Criticisms: Understanding the Debate Around ABA
Despite its widespread acceptance, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) intervention has faced significant criticism, especially from neurodiversity advocates. Many detractors express concern that traditional ABA practices often prioritize compliance over the emotional well-being of individuals. This focus can lead to adverse experiences for some children, a concern underscored by the historical use of aversive techniques, such as electric shock, which have largely been abandoned in favor of more compassionate positive reinforcement strategies.
Rimland noted, "Like all modification programs, his [Lovaas] was 98% positive reinforcement, with only a trace of aversive control," highlighting a significant evolution in practice towards more humane approaches. This shift reflects a growing recognition of the importance of emotional well-being alongside behavioral compliance.
In recent discussions, the field has embraced ethical ABA practices that prioritize emotional health. Advocates of ABA emphasize its evidence-based efficacy, showcasing many favorable results when the approach is applied with compassion and an understanding of each individual’s unique needs. For instance, numerous children have benefited from customized ABA strategies that enhance social skills and reduce challenging behaviors without compromising their emotional well-being.
However, the conversation surrounding ABA treatment is further enriched by the perspectives of neurodiversity advocates, who call for a more inclusive understanding of autism that honors individual differences. While some experts critique ABA for its historical reliance on compliance, others recognize its potential when implemented ethically. It’s crucial to acknowledge that very few behavior analysts have engaged in conversion practices research or implementation, and such practices are universally condemned within the field of ABA today.
As this discussion evolves, it’s essential for parents and experts to navigate these complexities thoughtfully. By acknowledging both the criticisms and the positive impacts of ABA interventions, we can better support youth with autism. Engaging in open conversations and sharing experiences can foster understanding and promote the best outcomes for our children.
The Role of Parents and Caregivers in ABA Therapy: Collaboration for Success
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in the success of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA). Their active participation is essential for grasping what ABA truly means and for helping children generalize the skills they learn during therapy to real-life situations. By participating in therapy sessions and consistently reinforcing strategies at home, caregivers can significantly bolster their children's ability to practice and master new skills. Research has shown that when parents engage in the therapeutic process, young individuals often demonstrate improved communication, social skills, and behavior regulation.
Training programs designed for parents are crucial, equipping them with effective tools and techniques to support their children's development. These programs frequently highlight the importance of collaboration between therapists and families, fostering a supportive environment that maximizes the effectiveness of ABA interventions. A case study examining the standardization of parent training programs reveals variability in outcomes across different interventions, emphasizing the need for consistent approaches to enhance reliability and efficacy. This standardization is essential to ensure that all families receive the best possible support.
Moreover, professional insights suggest that ongoing collaboration among parents, therapists, and educators significantly increases the likelihood of individuals with autism thriving in treatment settings and beyond. As one specialist noted, "With ongoing cooperation among parents, counselors, and teachers, youngsters with autism have an increased chance to flourish both in treatment environments and outside of them." This collective effort not only enriches family interactions but also cultivates a community where experiences can be shared and support can be provided, ultimately leading to better outcomes for youth undergoing ABA treatment.
Additionally, the concept of parent-led ABA intervention presents a viable alternative to traditional clinical environments, while also underscoring the significance of ABA and the crucial role parents play in their children's therapeutic journey.
The Future of ABA Therapy: Trends, Research, and Innovations
Significant advancements in research and technology are increasingly shaping the future of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, which exemplifies what ABA stands for. These developments are not just technical; they represent a commitment to bettering the lives of those we serve. Key emerging trends include the integration of data-driven methodologies and innovative technologies, such as virtual reality, which are enhancing the delivery of therapeutic interventions. Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of these approaches, demonstrating that data-driven strategies can lead to improved outcomes for individuals with autism and ADHD.
For instance, a study conducted at the University of Southern California revealed how artificial intelligence and machine learning can engage young people more effectively. The research found that robots could sustain young people's attention and foster social interactions by utilizing video and audio data to monitor engagement levels. This highlights the potential of AI in transforming conventional therapeutic practices, making them more interactive and engaging.
Moreover, the focus on ethical practices within ABA interventions is gaining traction. There is an increasing acknowledgment of the importance of including the viewpoints of individuals with autism in treatment planning. This shift not only enhances the therapeutic experience but also ensures that interventions are tailored to meet the unique needs of each child. As we look toward 2025, the landscape of ABA practices, particularly in understanding what ABA stands for, is expected to evolve further. Ongoing research is expanding its applications beyond conventional autism treatment to include diverse populations and settings.
Statistics show that telehealth services are playing an essential role in offering reliable support, especially for families in rural or remote regions. This enhances access to quality ABA services, ensuring that families can access necessary resources and support, regardless of their geographical location. These advancements promise to improve the effectiveness and reach of ABA treatment, solidifying its position as an essential resource for families and professionals navigating the complexities of autism and related challenges.
As Dr. Michael Lee, a policy advisor, wisely notes, "The impact of policy changes on ABA therapy is significant, as they shape the resources and support available to families and practitioners alike." This is a call to action for all of us to stay informed and advocate for the necessary changes that can enhance the support available to our communities.
Conclusion
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a cornerstone in the therapeutic landscape for individuals with autism and developmental disorders. It profoundly enhances life skills and mitigates challenging behaviors. This article emphasizes the scientific foundation of ABA, showcasing its commitment to evidence-based practices that yield measurable improvements in adaptive behavior and communication skills. Techniques such as positive reinforcement, prompting, and functional behavior assessments are tailored to meet each child's unique needs, ultimately fostering independence and social engagement.
However, despite its successes, ABA is not without controversy. The ongoing debate regarding its ethical implications highlights the need for a balanced approach that prioritizes emotional well-being alongside behavioral compliance. As the field evolves, it is crucial for practitioners and caregivers to engage in open dialogues about best practices that respect individual differences while capitalizing on the therapeutic benefits of ABA.
Looking towards the future, the integration of technology and innovative methodologies promises to expand the reach and effectiveness of ABA therapy. With a growing emphasis on ethical practices and the inclusion of diverse perspectives, ABA is poised to adapt and thrive in an ever-changing landscape. As families and practitioners continue to collaborate, the potential for positive outcomes in the lives of individuals with autism remains promising. This reinforces the importance of this vital therapeutic approach. Together, let us continue to support one another and explore the best paths forward for our children.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a scientific approach designed to understand and change behaviors through systematic interventions, focusing on the relationship between actions and environmental factors. It is particularly beneficial for individuals with autism and other developmental disorders.
How effective is ABA for children with developmental disabilities?
Recent studies indicate that children who participate in ABA for at least 12 months show significant improvements in adaptive skills, with many achieving the Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) in their Adaptive Behavior Composite scores.
What are the foundational principles of ABA?
The foundational principles of ABA include reinforcement, punishment, and extinction, which are essential for modifying specific behaviors. Positive reinforcement introduces a rewarding stimulus, while negative reinforcement removes an aversive stimulus to encourage desired behaviors.
What methodologies are commonly used in ABA?
Common methodologies in ABA include Discrete Trial Training (DTT), which breaks skills into smaller components for focused teaching, and Natural Environment Training (NET), which teaches skills in the context of everyday activities to create natural learning opportunities.
Why is consumer input important in ABA treatment?
Involving consumer input in the treatment-selection process ensures that interventions are effective and practical for those working in early childhood care and education, making the strategies more applicable in real-world settings.
What is the significance of ongoing research in ABA?
Ongoing research is crucial for ensuring that ABA practices remain inclusive and relevant across various populations, helping to broaden the reach and impact of this therapeutic approach. Future studies should include a wider age range and geographic diversity.
How do ABA interventions impact the quality of life for individuals with autism?
ABA interventions foster skill acquisition and enhance the development of vital life skills, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals with autism and other developmental disabilities.




