Overview
Understanding undiagnosed autism is crucial for parents and advocates. It empowers them to recognize signs, seek early intervention, and provide tailored support to individuals on the spectrum. Early diagnosis can significantly improve outcomes, making awareness of communication difficulties and social challenges essential. Unfortunately, these aspects are often overlooked due to traditional diagnostic criteria that may not fully account for variations in symptom presentation, especially in females. By fostering understanding and support, we can create a nurturing environment for those on the spectrum. Let's work together to ensure that every individual receives the care they deserve.
Introduction
In a world where understanding and acceptance of neurodiversity are increasingly vital, autism spectrum disorder (ASD) presents unique challenges that affect millions of individuals and their families. Navigating life with autism can be a complex journey, marked by social communication difficulties and sensory sensitivities. This article explores the core characteristics of autism, highlighting the critical importance of early diagnosis and intervention. It also addresses the far-reaching consequences of untreated conditions, offering insights that foster a deeper understanding.
By delving into the multifaceted aspects of autism, including its intersection with mental health and educational implications, we can begin to build robust support systems. This approach not only sheds light on the challenges faced but also emphasizes the necessity of community involvement. Together, we can create a clearer picture of how society can better support those on the spectrum.
Ultimately, fostering awareness and collaboration is essential. By sharing our experiences and advocating for those with autism, we can pave the way for improved outcomes and a more inclusive community. Let us come together to nurture understanding and acceptance, ensuring that every individual with autism feels valued and supported.
Defining Autism: Core Concepts and Characteristics
Autism, or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a multifaceted developmental condition that presents unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. Understanding its core characteristics is essential for parents and advocates, as it enables them to provide effective support and interventions.
- Social Communication Difficulties: Individuals with autism often face significant hurdles in interpreting social cues, engaging in conversations, and expressing their emotions. Recent research indicates that approximately 36.5% of caregivers utilize Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy to address these challenges. This statistic emphasizes the importance of effective communication strategies in assisting those on the spectrum.
- Repetitive Behaviors: This characteristic may manifest as repetitive movements, a strong preference for routines, or an intense focus on specific interests. These behaviors can serve as coping mechanisms for individuals navigating a world that may feel overwhelming.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Many individuals on the spectrum experience heightened or diminished sensitivity to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, or textures. Real-world examples illustrate how these sensitivities can impact daily life, making it crucial for caregivers to create supportive environments that accommodate these needs.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is actively working to provide essential data on ASD and develop resources for early identification, which is vital for improving outcomes. Furthermore, it is important to recognize that standard diagnostic criteria have historically been based on male behavioral patterns, which may contribute to misdiagnosis or underdiagnosis of autism in females. As noted by Kyle Coddington, "Standard diagnostic criteria were initially based on male behavioral patterns, potentially overlooking or misinterpreting signs in girls."
This oversight can result in a lack of appropriate support for those who may have undiagnosed autism and do not fit the traditional mold of developmental disorder presentation.
Additionally, understanding the financial implications of developmental disorder services is crucial. The average costs for common services related to developmental disorders in the U.S. vary significantly, with adaptive behavior services costing approximately $82.25 and emergency department visits averaging $1,397.22. Recognizing these financial burdens can help families and professionals seek appropriate resources and support.
Grasping these fundamental ideas not only equips parents and advocates but also nurtures a more inclusive community where individuals with developmental differences can flourish.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Prompt identification of undiagnosed autism is crucial, as it facilitates timely interventions that can greatly improve a young person's developmental path. Recent research highlights that individuals diagnosed before the age of 2.5 years exhibit markedly improved outcomes in communication and social skills. With the prevalence of autism now at 2.7% among youth in the U.S., the urgency for early identification and support cannot be overstated.
Effective early intervention strategies encompass a variety of therapeutic approaches, including:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): This structured method focuses on reinforcing positive behaviors while minimizing challenging ones, fostering essential skills for daily life.
- Speech Therapy: Aimed at enhancing communication abilities, this therapy is crucial for assisting young individuals in articulating their needs and engaging with others.
- Occupational Therapy: This therapy focuses on the enhancement of daily living skills and sensory integration, allowing individuals to navigate their environments more effectively.
Parents are strongly encouraged to pursue evaluations as soon as they observe developmental delays or atypical behaviors that could signal undiagnosed autism. The Safe Kids Worldwide campaign emphasizes that young individuals, including those with autism, should not be left home alone before the age of 12 or 13. This underscores the importance of teaching independence skills tailored to each person's needs. By equipping autistic children with basic living skills, parents can help them work towards greater independence in the future.
Current research continues to endorse the notion that early intervention not only improves immediate outcomes but also contributes to long-term success, especially for individuals with undiagnosed autism. Many autistic individuals can live into their 70s, depending on the severity of their symptoms. Families play a crucial role in this process, and they too require resources and support systems to manage the challenges of caregiving effectively. As Jane Miller notes, "Learn about the ABC data sheet, an essential tool in ABA. This guide covers how it helps track behaviors and aids in assessments of professionals in Texas." By fostering a collaborative environment, parents and professionals can unlock the potential of children with developmental challenges, ensuring they receive the best possible start in life.
Consequences of Untreated Autism: Social, Emotional, and Behavioral Impacts
Untreated conditions on the autism spectrum, such as undiagnosed autism, can lead to profound social, emotional, and behavioral challenges that significantly impact individuals and their families. These outcomes are complex and can manifest in various ways:
- Social Isolation: Many individuals with untreated conditions struggle to form and maintain friendships, which can lead to feelings of loneliness and exclusion. It's crucial to recognize that social isolation is prevalent among this population, with a significant percentage reporting a lack of meaningful social interactions.
- Emotional Distress: The emotional toll of untreated autism is considerable. Many individuals experience heightened levels of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem, often stemming from their difficulties in navigating social situations. A recent study revealed that 67.1% of mothers of autistic children reported symptoms of both depression and anxiety, underscoring the emotional burden on families. This statistic highlights the critical need for customized assistance strategies that address these individual emotional challenges.
- Behavioral Issues: Without appropriate help, individuals may exhibit increased aggression, self-injurious behaviors, or severe tantrums. These behavioral challenges can further alienate them from peers and family, creating a cycle of distress and isolation.
The importance of early intervention and tailored support strategies for those with undiagnosed autism cannot be overstated. A recent case study on supporting autistic youth with co-occurring mental health conditions emphasized that recognizing emotions, understanding triggers, and employing evidence-based treatments like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can significantly improve emotional regulation and overall well-being. This approach fosters open communication, promotes self-acceptance, and encourages peer interactions, which are crucial for enhancing social skills and reducing isolation.
Experts also stress that support strategies must be individualized, as not all methods work for every autistic person. Patricia Wright, PhD, MPH, and Katie Curran, MAAP, introduced Proof Positive - The Autism Well-being Alliance, highlighting the growing recognition of positive psychology's role in enhancing the well-being of autistic individuals. They emphasize that tailored and empathetic care is essential for effective assistance.
Recognizing these potential effects underscores the vital need for awareness, early diagnosis, and effective support systems to help individuals with undiagnosed autism thrive.
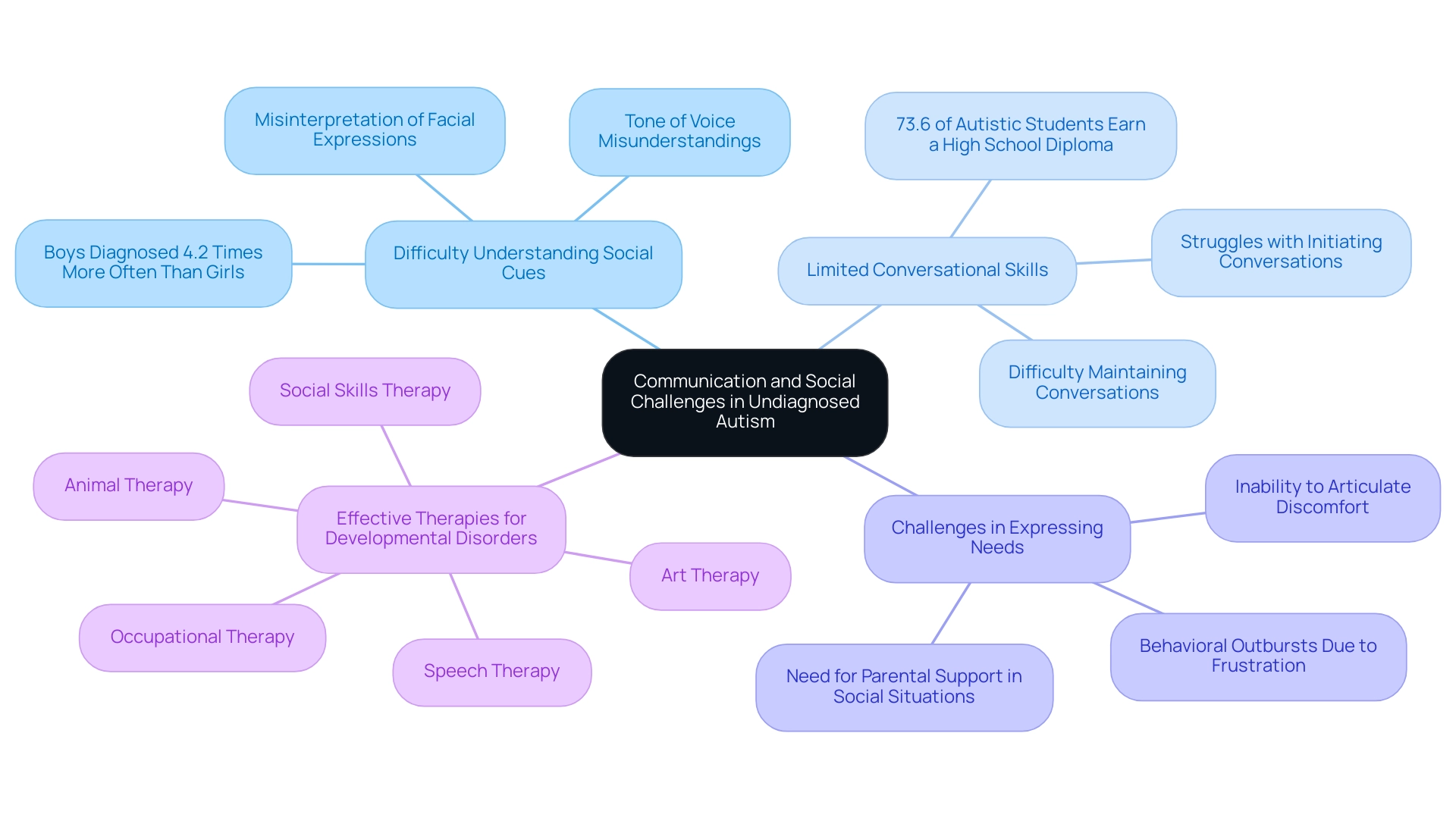
Communication and Social Challenges in Undiagnosed Autism
Individuals with undiagnosed autism often encounter unique communication and social challenges that significantly impact their daily interactions. Understanding these challenges is essential for parents and advocates, as it equips them to support youth with undiagnosed autism in navigating social environments.
- Difficulty Understanding Social Cues: Many individuals may misinterpret facial expressions, tone of voice, or body language. This can lead to misunderstandings in social situations. For instance, a child might not recognize when a peer is upset, resulting in unintentional social faux pas. It's important to note that boys are diagnosed with this condition 4.2 times more often than girls, often due to symptom masking in girls, which can result in overlooked signs of undiagnosed autism.
- Limited Conversational Skills: A common struggle for those with undiagnosed autism is initiating or maintaining conversations. This limitation can lead to social withdrawal, as they may feel overwhelmed or unsure of how to engage with others. Research indicates that effective communication is crucial for building relationships. Yet, many individuals with undiagnosed autism find themselves at a disadvantage. In fact, 73.6% of autistic students earn a high school diploma, highlighting the importance of addressing communication challenges for academic success.
- Challenges in Expressing Needs: The inability to communicate effectively can lead to frustration and behavioral outbursts. For example, a young person who cannot articulate their discomfort may resort to crying or acting out, which can be misinterpreted by caregivers and peers alike. Comprehending these communication obstacles is crucial for parents of children with undiagnosed autism, as it enables them to offer the required assistance in social situations. As Kyle Coddington noted, "Standard diagnostic criteria were initially based on male behavioral patterns, potentially overlooking or misinterpreting signs in girls," emphasizing the need for awareness in recognizing these challenges.
By fostering an understanding of these issues, caregivers can help create more inclusive and supportive experiences for individuals with undiagnosed developmental disorders. Moreover, investigating effective therapies for developmental disorders, such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills therapy, can offer parents valuable resources to help their children overcome communication difficulties. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by these challenges.
Educational Implications: Navigating School Systems with Undiagnosed Autism
Navigating the school system can be particularly challenging for individuals due to undiagnosed autism, leading to significant educational implications. One of the main problems is the absence of assistance; without an official diagnosis, young individuals with undiagnosed autism often miss out on crucial accommodations and aid services that could enhance their learning. This gap in support can result in behavioral issues, as those with undiagnosed autism may display behaviors that are misinterpreted as defiance or disinterest.
Such misunderstandings can lead to disciplinary actions rather than the necessary interventions that promote positive behavior and learning. Social integration poses another challenge. Children with undiagnosed autism may find it difficult to connect with their peers, which can severely impact their overall school experience and emotional well-being. A 2022 report highlighted that around 50% of mothers of autistic kids experience symptoms of depression, a statistic that underscores the emotional toll on families navigating these challenges.
Additionally, studies show that educational obstacles for students with undiagnosed autism are common, with many parents expressing challenges in obtaining suitable assistance within educational institutions. The CDC reports that the prevalence of developmental disorders varies among different ethnic groups, with 31.6 cases per 1,000 Hispanic youth, 29.3 per 1,000 Black youth, and 24.3 per 1,000 White youth, highlighting the broader implications of undiagnosed autism in diverse populations.
To tackle these issues, it is essential for parents to advocate for comprehensive assessments and support services. By actively engaging with educators and school administrators, parents can help ensure that their offspring receives the appropriate educational resources tailored to their unique needs. This advocacy is essential not only for the youth's academic success but also for cultivating a supportive environment that acknowledges and addresses the intricacies of undiagnosed autism.
Furthermore, with 36.5% of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders utilizing ABA therapy, seeking suitable therapies and support services is crucial for youth with developmental challenges. The standard diagnostic criteria for this condition, which were initially based on male behavioral patterns, may have overlooked signs in girls, further emphasizing the need for advocacy and comprehensive assessments. This holistic approach can significantly enhance the educational experiences and outcomes for children with undiagnosed autism.
Mental Health Considerations: The Overlap with Undiagnosed Autism
Undiagnosed conditions often intersect with various mental health challenges, significantly affecting people's overall well-being. It's important to recognize these intersections, as they can have profound implications for individuals and their families.
Anxiety Disorders: Many individuals on the autism spectrum experience heightened anxiety, often rooted in social challenges and communication difficulties. Recent studies reveal that anxiety disorders are common among those on the spectrum, with research indicating that about 40% of youth with this condition also face anxiety disorders. This overlap can intensify feelings of distress and impede social interactions, creating a cycle that can be hard to break.
Feelings of isolation and frustration are prevalent among those with depression, particularly in adolescents and adults with undiagnosed autism. Statistics show that around 50% of mothers of autistic individuals report symptoms of depression, underscoring the emotional toll these challenges can impose on families. The struggle to navigate social environments can lead to depressive symptoms, making it crucial for parents to remain vigilant about their child's mental health. As Brigid, the executive director of The Way We Move, poignantly states, "It is the same thing for me as a medication because often I will be having a lot of symptoms around anxiety or pain and start to feel worse until I remember I can take something for it."
Low Self-Esteem: The challenge of social integration can lead to a negative self-image among those on the spectrum. This low self-esteem can complicate their mental health further, creating a cycle of anxiety and depression. Real-world examples illustrate how adolescents with undiagnosed autism may internalize their struggles, resulting in a diminished sense of self-worth.
Recognizing these mental health concerns is vital for parents and advocates. Seeking appropriate assistance and interventions can create a substantial impact in the lives of those with undiagnosed conditions, fostering resilience and promoting a healthier emotional landscape. Recent discussions by experts such as Patricia Wright, PhD, and Katie Curran, MAAP, highlight the significance of understanding the interaction between developmental disorders and mental health. Initiatives like the Well-being Alliance focus on positive psychology's influence on well-being, providing valuable resources for families.
Additionally, Dr. Connor Kerns' case study on traumatic experiences in individuals with undiagnosed autism sheds light on the real-world challenges faced by this population, further illustrating the impact of undiagnosed conditions on mental health. It's essential for parents to engage with these insights and seek support, as they can make a meaningful difference in their child's life.
Building Support Systems: Resources for Families and Caregivers
Creating a strong assistance network is crucial for families navigating the challenges associated with autism. This journey can feel overwhelming, but there are key resources that can significantly enhance your support system:
- Support Groups: Connecting with other families can provide invaluable emotional encouragement and practical advice. Many parents find that involvement in peer groups leads to improved mental health outcomes, with numerous individuals reporting increased feelings of community and understanding. It's also important to recognize that the occurrence of autism varies by race and socioeconomic status, with higher rates among non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander youth compared to their non-Hispanic White counterparts.
- Professional Resources: Engaging with therapists, counselors, and educators who specialize in autism is essential for personalized support. Board-Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) play a vital role in helping families understand developmental disorders and create tailored therapy strategies that meet their child's unique needs. Remember, the average age of autism diagnosis is around 4 years, underscoring the importance of early intervention and support.
- Community Programs: Many communities offer programs and activities specifically designed for youth with autism, fostering social skills and promoting inclusion. A recent study highlighted that by middle childhood, approximately 78.8% of school-age autistic individuals are thriving in at least one developmental area, showcasing the positive impact of such community initiatives. Additionally, as Kyle Coddington pointed out, standard diagnostic criteria were originally based on male behavioral patterns, which may overlook or misinterpret indicators in girls. This highlights the need for customized assistance across various demographics.
As parents, you are encouraged to actively seek out these resources to cultivate a nurturing and supportive environment for your children. By utilizing these connections and programs, you can enhance your child's development and overall well-being.
Identifying Signs of Autism: A Guide for Parents and Advocates
Recognizing indicators of undiagnosed autism at an early stage is essential for enabling prompt intervention and assistance. As parents and advocates, being vigilant for specific signs can make a significant difference in a child's life.
- Delayed Speech or Language Skills: It's concerning when children do not speak single words by 16 months or form two-word phrases by age two—these are critical milestones in language development. Recent research highlights that around 30% of young individuals with developmental disorders exhibit significant delays in speech. This underscores the importance of closely monitoring these milestones.
- Limited Eye Contact: A tendency to avoid eye contact or a lack of response when their name is called can signal deeper issues. Research shows that children with autism often face challenges in social communication, making eye contact a crucial aspect to observe.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Engaging in repetitive actions or focusing intensely on certain objects may suggest the presence of autism. These behaviors can manifest as hand-flapping, rocking, or an intense focus on specific toys or topics. If you notice these signs, it’s vital to seek a professional evaluation. Early diagnosis can lead to effective interventions, which are crucial for improving outcomes. The American Psychological Association recognizes Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) as an evidence-based therapy with proven effectiveness, emphasizing the importance of professional assistance.
Additionally, understanding the financial burden of services for individuals with developmental disorders can help families navigate available resources. The average cost of adaptive behavior services is approximately $82.25. It's also important to consider the emotional impact on families; around 50% of mothers of autistic individuals experience symptoms of depression. Furthermore, environmental and genetic factors might protect girls from displaying ASD-related behaviors, indicating that signs of the condition can differ by gender.
By recognizing these signs and acting promptly, you can play a pivotal role in your child's development and well-being. Early intervention can significantly influence life expectancy and quality of life for those with undiagnosed autism. Together, we can create a supportive environment that fosters growth and understanding.
Fostering Community Support: Collaborating for Better Outcomes
Encouraging community assistance is crucial for improving outcomes for individuals with undiagnosed autism. Effective strategies can truly make a difference:
- Community Awareness Programs: These initiatives aim to educate the public about autism, fostering understanding and acceptance. By increasing awareness of undiagnosed autism, communities can reduce stigma and create a more inclusive environment.
- Collaborative Initiatives: Partnering with local organizations is vital for developing inclusive programs and resources. For instance, community centers can collaborate with schools and healthcare providers to offer workshops and support groups, ensuring families have access to essential resources.
- Advocacy Efforts: Encouraging families to engage in advocacy groups can lead to significant improvements in policies and resources for individuals with undiagnosed autism and other developmental disorders. Advocacy not only raises awareness but also drives legislative changes that benefit the community affected by undiagnosed autism.
Statistics reveal the pressing need for these efforts: while 74% of autistic students in the U.S. graduate with a diploma, this figure is notably lower than the 86% graduation rate for all students. Furthermore, 19% of autistic students receive a certificate of completion, and 8% do not finish high school, compared to just 5% of their peers. It is also significant that 36.5% of autism caregivers utilize Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, emphasizing the importance of community involvement in relation to therapy options.
These figures highlight the significance of targeted community assistance and advocacy to enhance educational outcomes for those with undiagnosed autism.
As Jane Miller aptly states, "Discover vital neurodiverse community support resources for people and families." By working collaboratively, communities can cultivate a more supportive environment for individuals with undiagnosed autism and their families, ultimately leading to better life outcomes and enhanced quality of life. This aligns with ASD Media's mission to empower parents and professionals in the ABA therapy field, fostering a community that shares experiences and resources.
Conclusion
Understanding autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is crucial for creating a supportive environment for individuals on the spectrum. It’s important to recognize the core characteristics of autism, such as social communication difficulties, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities. Early diagnosis and intervention can lead to significant improvements in communication and social skills, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for those affected.
The consequences of untreated autism extend beyond the individual, impacting families and communities. Social isolation, emotional distress, and behavioral challenges can emerge, highlighting the necessity for tailored support strategies. Recognizing the intersection of autism with mental health issues further underscores the importance of comprehensive care that addresses both the behavioral and emotional needs of individuals.
Building robust support systems is vital for families navigating the complexities of autism. Resources such as support groups, professional services, and community programs play a pivotal role in fostering resilience and promoting inclusion. Advocacy for early diagnosis and appropriate educational accommodations ensures that children receive the support they need to thrive academically and socially.
Ultimately, fostering community awareness and collaboration is essential for improving outcomes for individuals with autism. By working together, families, educators, and healthcare providers can cultivate a more inclusive society that values and supports neurodiversity. This collective effort not only enhances the lives of those with autism but also enriches the fabric of the community as a whole, paving the way for a future where every individual is recognized and celebrated for their unique contributions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted developmental condition characterized by unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior.
What are the core characteristics of autism?
The core characteristics of autism include social communication difficulties, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities.
How do social communication difficulties manifest in individuals with autism?
Individuals with autism often struggle to interpret social cues, engage in conversations, and express emotions, which can significantly hinder their social interactions.
What percentage of caregivers use Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy for autism?
Approximately 36.5% of caregivers utilize Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy to address social communication challenges in individuals with autism.
What are repetitive behaviors in autism?
Repetitive behaviors may include repetitive movements, a strong preference for routines, or an intense focus on specific interests, often serving as coping mechanisms.
How do sensory sensitivities affect individuals with autism?
Many individuals with autism experience heightened or diminished sensitivity to sensory stimuli, impacting their daily life and necessitating supportive environments from caregivers.
Why is early identification of autism important?
Early identification is crucial as it allows for timely interventions that can greatly improve developmental outcomes, particularly in communication and social skills.
What are some effective early intervention strategies for autism?
Effective early intervention strategies include Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, and occupational therapy.
What is the average cost of autism-related services in the U.S.?
The average costs for common services related to developmental disorders vary significantly, with adaptive behavior services costing approximately $82.25 and emergency department visits averaging $1,397.22.
What are the consequences of untreated autism?
Untreated autism can lead to social isolation, emotional distress, and behavioral issues, significantly impacting individuals and their families.
What emotional challenges do families of individuals with autism face?
Families often experience heightened levels of anxiety and depression, with 67.1% of mothers of autistic children reporting such symptoms.
How can tailored support strategies help individuals with autism?
Tailored support strategies, such as recognizing emotions and employing evidence-based treatments, can significantly improve emotional regulation and overall well-being for individuals with autism.
What role does positive psychology play in supporting individuals with autism?
Positive psychology is recognized as important for enhancing the well-being of autistic individuals, emphasizing the need for individualized and empathetic care.




