Overview
This article delves into the important topic of toddler stimming, shedding light on its various types, triggers, and effective management strategies. Understanding that stimming behaviors play a vital role in helping toddlers self-soothe and regulate sensory input is crucial for their emotional well-being and development. By providing insights on how caregivers can foster these behaviors within a nurturing environment and through appropriate interventions, we aim to support both children and their families.
As parents, it’s natural to seek ways to understand and assist your little ones during their stimming episodes. These behaviors not only serve as a coping mechanism but also as a means for toddlers to navigate their sensory experiences. We encourage you to explore the strategies shared in this article, as they can help create a supportive atmosphere for your child.
By engaging with this content, you’ll discover practical tips and heartfelt advice that resonate with your experiences. We invite you to reflect on your own journey and share your thoughts or questions in the comments. Together, we can build a community that understands and embraces the unique needs of our children.
Introduction
In the realm of child development, stimming—short for self-stimulatory behavior—plays a pivotal role in how toddlers interact with their environment and manage their emotions. This repetitive behavior, which can manifest as hand-flapping, rocking, or vocalizations, serves as a crucial coping mechanism for many children, particularly those on the autism spectrum. Understanding the intricacies of stimming is essential for caregivers, as it not only aids in emotional regulation but also enhances sensory processing.
As the prevalence of autism continues to rise, recognizing stimming behaviors can foster a more supportive atmosphere that nurtures children's growth and well-being. This article delves into the purpose and importance of stimming, identifies common behaviors in toddlers, explores the triggers that prompt these actions, and offers effective strategies for caregivers to manage and support their children’s sensory needs. Together, we can create an environment that embraces these behaviors and promotes understanding and compassion.
Define Stimming: Understanding Its Purpose and Importance
Stimming, often referred to as toddler stimming, encompasses self-stimulatory behaviors that include the repetitive movements or sounds toddlers use to self-soothe or manage sensory input. Common examples of these behaviors are hand-flapping, rocking, and vocalizations. Understanding toddler stimming is crucial, as it serves various important functions: it aids children in managing intense emotions, provides necessary sensory input, and can even enhance concentration during activities. Research shows that while most children receive an autism diagnosis after age four, reliable assessments can occur as early as age two. This underscores the importance of recognizing toddler stimming behaviors at an early stage.
Promoting non-autistic sensory behaviors can lead to self-discovery and emotional regulation, contributing positively to overall well-being. As Steven Zauderer notes, "These actions may appear repetitive or atypical to observers, but they are frequently a method of self-regulation and stimulation for non-autistic individuals." By viewing self-soothing as a natural action, caregivers can engage with it empathetically rather than with frustration, fostering a supportive environment that encourages the child's growth.
Experts emphasize that toddler stimming actions, although sometimes perceived as atypical, are often vital for self-regulation and sensory stimulation. This highlights the significance of understanding such practices within the broader context of child development. Furthermore, recognizing toddler stimming behaviors is especially relevant, given that typical indicators of autism include difficulties with social interaction and sensory processing. Additionally, acknowledging the genetic factors associated with autism—where up to 90% of the risk is linked to genetics—can aid in early identification and support for families at risk.
This comprehensive perspective highlights the importance of toddler stimming within the larger framework of autism, emphasizing the benefits of these behaviors, especially for children with autism. By embracing these actions, we can nurture our children’s emotional and sensory needs, paving the way for their growth and well-being.
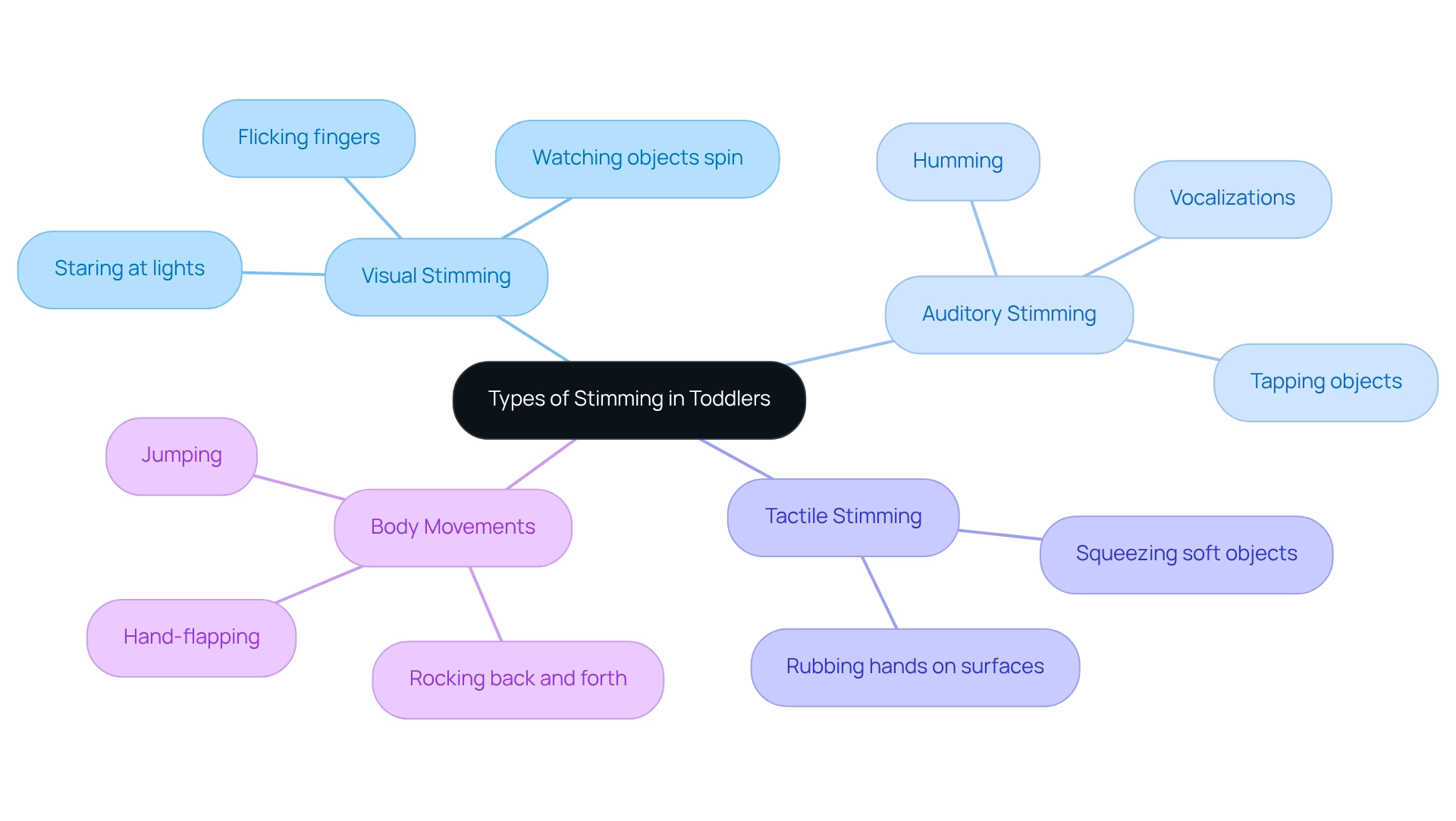
Identify Types of Stimming: Common Behaviors in Toddlers
Common types of stimming behaviors in toddlers encompass a variety of sensory-seeking actions that can be categorized into four main types:
- Visual Stimming: This includes behaviors such as staring at lights, watching objects spin, or flicking fingers in front of the eyes. These actions often provide visual stimulation and can be calming for the young one.
- Auditory Stimming: Toddlers may engage in repetitive sounds, such as humming, vocalizations, or even tapping objects. These auditory behaviors can help them self-regulate and find comfort in familiar sounds.
- Tactile Stimming: Engaging with different textures is common, with children rubbing their hands on various surfaces or squeezing soft objects. This tactile exploration is essential for processing stimuli and can be soothing.
- Body Movements: Actions like rocking back and forth, hand-flapping, or jumping are also prevalent. These movements can assist toddlers in managing their feelings and overwhelming stimuli.
Identifying toddler stimming behaviors is crucial for caregivers, as it helps them understand when a young one is seeking input or emotional support. By responding appropriately, caregivers can support their child's needs and promote a more inclusive environment. Education about self-regulating behaviors is vital to foster understanding and compassion among caregivers and the community.
As Steven Zauderer pointed out, "These actions may appear repetitive or strange to observers, but they are frequently a method of self-regulation and stimulation for non-autistic individuals." This perspective highlights the significance of acknowledging self-stimulatory behavior as a natural component of sensory experiences.
Additionally, with April 2 recognized as World Autism Awareness Day, it is crucial to acknowledge that autism is a complex and multifaceted disorder affecting millions worldwide. Understanding the statistics associated with autism can help promote awareness and encourage early intervention. Moreover, the recent case study on racial disparities in autism diagnosis emphasizes the necessity for fair practices in identifying and tackling sensory activities across various demographics.
Explore Triggers: Situations That Prompt Stimming in Toddlers
Understanding toddler stimming actions can be crucial for parents seeking to support their little ones. These behaviors often arise from various stimuli, indicating a child's need for sensory equilibrium. Consider these key situations:
- Sensory Overload: Environments that are excessively loud, bright, or chaotic can overwhelm toddlers. In such cases, they may engage in stimming as a coping mechanism. Research indicates that sensory overload is a significant factor, with many children displaying these responses in reaction to overstimulating environments. Notably, 55% of a sample met the criteria for an ADHD diagnosis, highlighting how common self-stimulatory actions can be in these contexts.
- Emotional Responses: Intense emotions like excitement, anxiety, or frustration can lead to increased stimming. Experts suggest that understanding these emotional triggers is essential for comprehending a young child's actions. Stimming often serves as a self-soothing technique during overwhelming moments. As one specialist noted, "Some youngsters partake in actions that seek sensory input, like rocking, spinning, or repetitive movements, to activate their sensory systems."
- Boredom or Under-stimulation: When toddlers lack sufficient engagement, they may resort to self-soothing behaviors to seek out sensory input. This conduct can signal that your child requires more engaging activities or interactions to sustain their focus and interest.
- Physical Discomfort: Factors such as tight clothing or uncomfortable seating can also provoke repetitive actions. It’s vital for caregivers to recognize these physical discomforts to create a more comfortable environment.
By recognizing these triggers, caregivers can make informed modifications to their child's surroundings and routines, ultimately fostering a supportive atmosphere that caters to their needs. Moreover, current studies, including the case analysis titled "Limitations and Future Directions in SPD Research," underscore the necessity for further investigation into sensory processing and its connection to self-stimulating actions, particularly in various clinical environments.
As you reflect on your child's behaviors, consider sharing your experiences in the comments or through newsletters. Together, we can create a community that understands and supports each other in this journey.
Implement Strategies: Effective Approaches to Manage Stimming
To effectively manage stimming behaviors in toddlers, caregivers can implement several key strategies that nurture and support their little ones:
- Create a Calming Environment: Reducing sensory overload is crucial. By minimizing noise and visual distractions, children can feel more secure and focused. When self-stimulatory actions increase, it often indicates that the child is experiencing heightened stress or anxiety, making a soothing atmosphere even more essential.
- Introduce Sensory Tools: Fidget toys, stress balls, and textured items can provide alternative outlets for sensory needs, helping to redirect repetitive actions into more manageable forms.
- Establish Routines: Consistent daily schedules foster a sense of security, significantly reducing anxiety and, consequently, the occurrence of repetitive behaviors. Research shows that predictable environments contribute to emotional stability in children.
- Teach Replacement Behaviors: Encouraging toddlers to adopt alternative coping strategies, such as deep breathing or using a stress ball, empowers them to manage their urges to stim effectively.
Recognizing the variety of self-stimulatory behaviors—such as visual, auditory, tactile, and movement-based stims—enables caregivers to tailor their approaches. For example, the case study titled "Are There Different Types of Stims?" highlights various sensory-motor activities, aiding in the understanding and support of individuals with autism. Creating a soothing atmosphere has been shown to decrease toddler stimming behaviors, enhancing their overall well-being. As Ruben Kesherim wisely states, "Recognizing this can lead to a more empathetic understanding of toddler stimming behaviors and contribute to better support strategies for those who experience them." By implementing these strategies, caregivers can help children navigate their sensory needs while fostering a nurturing and understanding environment.
Conclusion
Understanding stimming behaviors is essential for fostering the emotional and sensory well-being of toddlers, particularly those on the autism spectrum. Stimming serves various purposes, including self-soothing and sensory regulation, making it a vital aspect of child development. By recognizing the different types of stimming—visual, auditory, tactile, and body movements—caregivers can respond effectively to their child's needs, creating a supportive environment.
Identifying the triggers that prompt stimming behaviors, such as sensory overload, emotional responses, boredom, or physical discomfort, empowers caregivers to make informed adjustments in their child’s surroundings. Implementing strategies such as creating calming environments, introducing sensory tools, establishing routines, and teaching replacement behaviors can help children navigate their sensory experiences more effectively.
Ultimately, embracing and understanding stimming behaviors not only promotes a compassionate atmosphere for children but also encourages their growth and development. By fostering awareness and empathy, caregivers can play a crucial role in supporting children as they engage with the world around them. This holistic approach paves the way for healthier emotional regulation and sensory integration. Every child deserves the tools they need to thrive, reinforcing the importance of understanding and accepting stimming as a natural part of their development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is toddler stimming?
Toddler stimming refers to self-stimulatory behaviors that include repetitive movements or sounds toddlers use to self-soothe or manage sensory input, such as hand-flapping, rocking, and vocalizations.
Why is understanding toddler stimming important?
Understanding toddler stimming is crucial as it serves important functions like helping children manage intense emotions, providing necessary sensory input, and enhancing concentration during activities.
At what age can reliable assessments for autism occur?
Reliable assessments for autism can occur as early as age two, although most children receive an autism diagnosis after age four.
How can promoting non-autistic sensory behaviors benefit toddlers?
Promoting non-autistic sensory behaviors can lead to self-discovery and emotional regulation, contributing positively to a child's overall well-being.
How should caregivers view self-soothing behaviors in toddlers?
Caregivers should view self-soothing behaviors as natural actions and engage with them empathetically, fostering a supportive environment that encourages the child's growth.
What role do toddler stimming actions play in child development?
Toddler stimming actions are vital for self-regulation and sensory stimulation, highlighting their significance within the broader context of child development.
What are typical indicators of autism related to toddler stimming?
Typical indicators of autism include difficulties with social interaction and sensory processing, making it important to recognize toddler stimming behaviors.
How are genetic factors associated with autism relevant to toddler stimming?
Up to 90% of the risk for autism is linked to genetics, which can aid in early identification and support for families at risk, making the recognition of toddler stimming behaviors especially relevant.
What benefits do toddler stimming behaviors provide for children with autism?
Embracing toddler stimming behaviors can nurture children's emotional and sensory needs, paving the way for their growth and well-being.




