Introduction
Navigating the world of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be both challenging and rewarding for caregivers. With a spectrum that encompasses a wide range of symptoms and behaviors, understanding the intricacies of ASD is crucial for providing effective support.
From recognizing the unique social and communication hurdles faced by children with autism to exploring diverse treatment options, caregivers are positioned at the forefront of their child's advocacy and development.
Recent studies highlight alarming disparities in autism prevalence among different demographic groups, emphasizing the need for tailored approaches that cater to individual needs.
As the landscape of autism treatment continues to evolve with innovative therapies and research breakthroughs, caregivers are empowered to harness this knowledge, ensuring their children receive the best possible resources and support for a thriving future.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder: Key Concepts for Caregivers
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that manifests through a variety of symptoms impacting social communication, behavior, and sensory processing. Recognizing the nuances of this spectrum is vital; each individual presents unique challenges and strengths. Key concepts integral to understanding ASD include:
- Social Interaction Difficulties: Children with ASD often face challenges in interpreting social cues and establishing relationships.
Recent studies indicate that the prevalence of ASD is notably higher among minority groups, with rates 1.8 times greater among Hispanic youth and 1.6 times higher among non-Hispanic Black youth compared to their non-Hispanic White counterparts, whose prevalence is 2.43%.
- Communication Challenges: These can vary widely, from nonverbal communication to delays in speech development. As caregivers advocate for their young ones, effective communication strategies can play a crucial role in facilitating interactions and promoting understanding.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Many individuals with ASD engage in repetitive movements or adhere to specific routines, which can serve as coping mechanisms in response to sensory overload or anxiety.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Sensory processing issues are common, leading children to be either overly sensitive or under-responsive to sensory input, which can affect their daily experiences.
A recent study confirmed these disparities in that, compared with non-Hispanic White youth, ASD prevalence was 1.8 times as high among Hispanic and 1.6 times as high among non-Hispanic Black youth. Additionally, nations report varying rates of autism prevalence, with Qatar having the highest at 151.20 per 10,000 youths and France the lowest at 1 in 144, highlighting significant geographic disparities in autism diagnosis and reporting.
Understanding these aspects allows caregivers to better support their offspring and articulate their needs concerning the treatment of autism to healthcare professionals. With ongoing research and increasing awareness surrounding ASD, advocates can utilize this knowledge to foster acceptance and empower their offspring, ensuring they receive the appropriate resources and support necessary for the treatment of autism.
Exploring Treatment Options: From Established Therapies to Innovative Approaches
Caregivers are offered a diverse range of solutions for the treatment of autism that can significantly improve their offspring's development and well-being. Among these, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) stands out as a widely endorsed therapy, emphasizing the improvement of specific behaviors and skills through systematic reinforcement techniques. Research indicates that parental involvement in ABA exercises can lead to notable positive behavioral changes and skill generalization in everyday lives.
Expert insights highlight the numerous benefits of ABA, including improvements in IQ scores, enhanced communication skills, and advancements in adaptive behaviors. As noted, "This section will explore the specific benefits of ABA therapy, including improvement in IQ scores, enhancing communication skills, and its impact on adaptive behavior."
Additionally, it is crucial to note that 10% of people who died by suicide were likely to have undiagnosed autism, underscoring the importance of early intervention and treatment of autism options for ASD.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) serves as another vital approach, particularly advantageous for older youth and teenagers. This therapeutic method aids in managing anxiety and promoting emotional regulation, equipping young individuals with essential coping strategies. Success narratives are plentiful, highlighting the beneficial effects of CBT on young individuals with developmental disorders, further confirming its efficacy.
While there is currently no cure for autism, the treatment of autism with medications can play a crucial role in managing specific symptoms such as anxiety, ADHD, or depression. Parents are encouraged to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable medication options for their offspring.
Occupational Therapy is also key, focusing on enhancing daily living skills and improving sensory integration, which can be instrumental in fostering independence and confidence in individuals with ASD.
Additionally, innovative approaches are emerging, including social skills training, art therapy, and technology-assisted methods, which provide fresh avenues for support. These cutting-edge therapies demonstrate an increasing comprehension of ASD and provide caregivers a broader array of resources to support their kids.
A relevant case study, titled Liu et al. PECS Hospital Study, implemented PECS for one session a day, five days a week for six months in a hospital setting, demonstrating the effectiveness of structured interventions. Outcomes measured included C-PEP, providing concrete evidence of the benefits of such therapies.
Staying informed about the treatment of autism options is imperative for caregivers, as it empowers them to choose the most appropriate path tailored to their unique needs, ensuring they receive the best possible support for their growth.
Personalized Treatment Strategies: Tailoring Approaches to Individual Needs
Acknowledging that every individual with autism offers a distinct array of challenges and strengths, a customized intervention strategy becomes essential. Here’s how caregivers can effectively tailor strategies to meet individual needs:
- Assessment: Initiate comprehensive evaluations to pinpoint your child’s strengths, weaknesses, and specific requirements. This foundational step is crucial in crafting an effective treatment of autism plan.
- Collaboration: Partner closely with therapists to establish individualized goals that resonate with your student's interests and capabilities. This collaborative effort ensures that the strategies implemented are not only relevant but also engaging for your young one.
- Flexibility: Maintain an adaptable mindset; be prepared to modify strategies as your child matures and their needs change. This flexibility can significantly improve the effectiveness of therapies.
- Family Involvement: Actively engage family members in the care process. Their participation fosters a supportive environment, reinforcing the strategies in everyday situations. Research by Musetti et al. (2021) indicates that family engagement is linked to improved outcomes for children with autism, highlighting its vital role in the overall treatment success. Moreover, the systematic review highlights that parents’ quality of life enhances when they are actively engaged in programs.
- Early Diagnosis: Insights from the case study titled "How Early Autism Can Be Diagnosed" underscore the importance of early diagnosis and support. Identifying autism at an early stage can lead to timely support, which is crucial for the treatment of autism and better long-term outcomes.
As Georg Loss from F. Hoffmann‐La Roche Ltd. states, 'Personalized care strategies are essential in addressing the unique needs of each young individual, ensuring that actions are as effective as possible.' By concentrating on these personalized approaches, caregivers can not only enhance the effectiveness of interventions but also empower the individuals they support to thrive in their unique journeys.
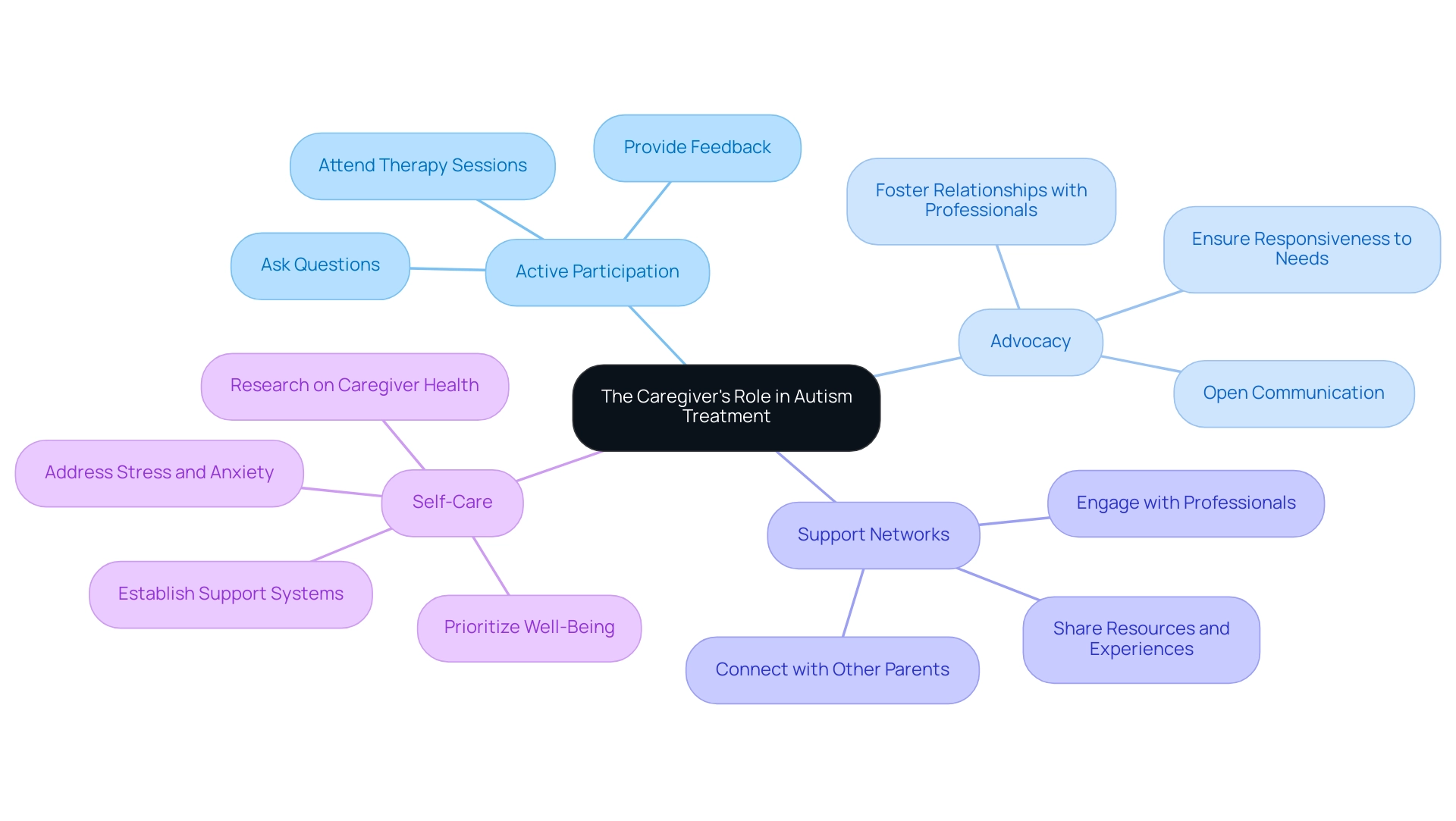
The Caregiver's Role: Supporting Treatment and Advocacy for Autism
As a caregiver, your participation is crucial to your offspring's care journey and can greatly impact their development. Here are several ways you can actively engage in the treatment of autism:
- Active Participation: Attend therapy sessions whenever possible, immersing yourself in the treatment of autism process. Ask questions and provide feedback to therapists and medical professionals to ensure that your loved one's needs are being met effectively.
- Advocacy: Take on the role of advocate for your loved one’s unique needs in educational and therapeutic environments. This means fostering open communication with teachers, therapists, and healthcare providers to ensure they are aware of and responsive to your needs.
- Support Networks: Establish connections with other parents and professionals. These relationships can provide invaluable resources and shared experiences that can enhance your advocacy efforts. Engaging with a community can help you feel less isolated and more empowered.
- Self-Care: Prioritize your own well-being. Caring for a person with autism can be stressful, so it’s vital to have your support systems in place. Research indicates that caregivers often experience high levels of stress, anxiety, and depression, highlighting the necessity of interventions aimed at improving their health. A systematic review published in J Phys Act Health (2021) indicated that informal carers in the UK have a prevalence of physical inactivity that can exacerbate these issues. When you look after yourself, you are in a better position to support your offspring effectively. Additionally, a mediation analysis examined the impact of caregiving on daily task completion, revealing that while caregiving poses challenges, it also emphasizes the importance of effective support systems. As Karli van Niekerk emphasized in her study, this research highlights the burden experienced by primary caregivers of individuals with ASD and is one of the few comprehensive studies on the treatment of autism in the context of South Africa. By embracing these roles, you not only improve your offspring's care experience but also contribute to better outcomes for their overall development.
Future Directions in Autism Treatment: Innovations and Research Advances
The treatment of autism is continually evolving, marked by promising new research and innovations that empower families and advocates alike.
- Emerging Therapies: Staying informed about innovative therapeutic approaches that leverage technology, such as virtual reality and teletherapy, can significantly enhance the learning experiences for children. These advancements cater to individual needs, ensuring that measures are tailored for effectiveness.
Various methods of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy can also be employed, enabling customized strategies that improve learning results.
- Research Advances: Current studies are exploring the neurobiology of developmental disorders, providing insights that could result in more effective treatments. For instance, the average age for a reliable diagnosis of the condition is around 2 years, yet intervention typically commences at an average age of 4.7 years, highlighting the critical need for timely action. The CDC reports that ASD prevalence is notably higher among Hispanic youth at 1.8 times and non-Hispanic Black youth at 1.6 times compared to their non-Hispanic White counterparts, underscoring the importance of equitable access to resources.
- Community Involvement: Engaging with community and advocacy groups provides families access to the latest resources, support, and collective knowledge, empowering them in their advocacy efforts. Recent studies recommend that social workers be trained to assist parents in planning, breaking the process into manageable steps, which can significantly alleviate the burden of navigating these complexities. Additionally, the puzzle piece has been a long-standing symbol of neurodiversity; however, many activists now reject it for being dehumanizing, advocating for alternative symbols like the rainbow infinity sign that promote inclusion and a more positive representation of the autistic experience.
- Holistic Approaches: There is a growing interest in integrating holistic methods, such as mindfulness practices and dietary considerations, into care plans. This multifaceted perspective on therapy acknowledges the varied experiences of individuals with autism, promoting a more inclusive approach to the treatment of autism. By remaining vigilant about these developments, caregivers can actively participate in their child’s treatment of autism journey and advocate for the most effective interventions, ensuring that every child receives the support they need to thrive.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires a deep understanding and commitment from caregivers. By recognizing the unique challenges that children with ASD face in social interactions, communication, behaviors, and sensory processing, caregivers can better support their children's needs. The disparities in autism prevalence among different demographic groups highlight the necessity for tailored approaches that ensure equitable access to resources and support.
A diverse array of treatment options, including:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Innovative therapies
empowers caregivers to choose the most effective interventions for their children. Personalizing treatment strategies through comprehensive assessments, collaboration with professionals, and active family involvement enhances the likelihood of successful outcomes.
The role of caregivers extends beyond treatment; they are vital advocates for their children, fostering open communication with educators and healthcare providers while building support networks. Prioritizing self-care is equally important, as it enables caregivers to maintain their well-being and effectively support their children.
As the landscape of autism treatment continues to evolve with ongoing research and emerging therapies, caregivers are encouraged to stay informed and engaged. This proactive approach not only enhances the support provided to children with ASD but also contributes to a more inclusive and understanding society. Empowered with knowledge and resources, caregivers can champion their children's needs, ensuring they have the opportunity to thrive and reach their fullest potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by a variety of symptoms that affect social communication, behavior, and sensory processing.
What are the common challenges faced by individuals with ASD?
Individuals with ASD often experience difficulties in social interaction, communication challenges, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities.
How do social interaction difficulties manifest in children with ASD?
Children with ASD may struggle to interpret social cues and establish relationships, making social interactions challenging.
What types of communication challenges do individuals with ASD face?
Communication challenges can range from nonverbal communication to delays in speech development, necessitating effective communication strategies from caregivers.
What are repetitive behaviors in individuals with ASD?
Many individuals with ASD engage in repetitive movements or follow specific routines, which can help them cope with sensory overload or anxiety.
What are sensory sensitivities in the context of ASD?
Sensory processing issues are common in ASD, leading individuals to be either overly sensitive or under-responsive to sensory input, affecting their daily experiences.
Is there a difference in the prevalence of ASD among different demographic groups?
Yes, studies show that the prevalence of ASD is higher among minority groups, with rates 1.8 times greater among Hispanic youth and 1.6 times higher among non-Hispanic Black youth compared to non-Hispanic White youth.
What are some treatment options available for individuals with ASD?
Treatment options include Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Occupational Therapy, and emerging therapies like social skills training and art therapy.
What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)?
ABA is a widely endorsed therapy that focuses on improving specific behaviors and skills through systematic reinforcement techniques, showing positive behavioral changes and skill generalization.
How does Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) benefit older youth with ASD?
CBT helps manage anxiety and promotes emotional regulation, providing essential coping strategies for young individuals with ASD.
Are there medications available for treating symptoms associated with ASD?
While there is no cure for autism, medications can help manage specific symptoms such as anxiety, ADHD, or depression. Parents are encouraged to consult healthcare professionals for suitable options.
What is the role of Occupational Therapy in treating ASD?
Occupational Therapy focuses on enhancing daily living skills and improving sensory integration, which can foster independence and confidence in individuals with ASD.
What is the significance of early intervention in ASD?
Early intervention is crucial as it can significantly impact the development and well-being of children with ASD, with studies indicating that a notable percentage of individuals who died by suicide may have had undiagnosed autism.
What innovative approaches are emerging for supporting individuals with ASD?
Innovative approaches include social skills training, art therapy, and technology-assisted methods, offering caregivers a broader range of resources to support their children.
How can caregivers stay informed about treatment options for ASD?
Staying informed about treatment options empowers caregivers to choose the most appropriate paths tailored to their children's unique needs, ensuring they receive the best possible support.




