Introduction
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential for fostering a supportive environment for individuals navigating its complexities. As a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition, autism presents a spectrum of symptoms that vary widely among individuals, influencing their social interactions, communication abilities, and behaviors.
With prevalence rates showing significant disparities across demographics, it's crucial for advocates to recognize the unique challenges faced by those on the spectrum, including adults who may go undiagnosed. This article delves into the intricacies of autism, from identifying key signs in adults to navigating the diagnostic process and accessing vital resources.
By equipping themselves with knowledge and strategies, advocates can empower individuals with autism to thrive and embrace their unique identities within a diverse community.
Defining Autism: Understanding the Spectrum
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition that presents a diverse array of symptoms impacting social interaction, communication, and behavior. The term 'spectrum' reflects the varying degrees of support individuals may require, ranging from those who need substantial assistance to those who can navigate life independently. This understanding is essential, particularly as recent studies have indicated that the occurrence of this condition is not uniform; for example, Egypt reports a prevalence of 89.40 per 10,000 children.
Furthermore, historical context reveals that diagnoses related to developmental disorders were historically more common among white children, but improved access to diagnostic services has helped bridge this gap. As we explore the characteristics of ASD, it becomes evident that there is no singular 'type' of the condition. Key traits commonly associated with the disorder include:
- Challenges in social communication
- A tendency towards restricted interests
- Repetitive behaviors
Furthermore, based on findings from the CDC, disparities exist in diagnoses, with prevalence rates being:
- 1.8 times higher among Hispanic children
- 1.6 times higher among non-Hispanic Black children compared to their non-Hispanic White counterparts
This emphasizes the significance of understanding the spectrum and recognizing the potential signs of undiagnosed autism in adults. By understanding these foundational concepts, parent advocates can better support individuals navigating the complexities of the condition, fostering an inclusive environment that acknowledges and celebrates diversity within the spectrum.
Identifying Key Signs of Autism in Adults
Adults often exhibit unique indicators, such as signs of undiagnosed autism in adults, which are crucial to identify, particularly in relation to communication difficulties. These include:
-
Interpersonal Communication Challenges: Individuals may struggle with understanding cues, maintaining conversations, or making eye contact.
Research indicates that signs of undiagnosed autism in adults lead to significant difficulties in these areas, as shown in a study by Johnson et al. noting that infants born late or moderately preterm were 1.3 times more likely to be identified with delayed interpersonal skills compared to peers born at term. This statistic underscores the importance of recognizing signs of undiagnosed autism in adults, which can lead to social communication difficulties that impede interactions in various social settings.
-
Many adults with autism show signs of undiagnosed autism in adults through either heightened or diminished responses to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, or textures. This sensitivity can lead to discomfort or distress in environments that may seem ordinary to others.
-
Repetitive Behaviors: Engaging in consistent routines or repetitive movements often provides individuals with a sense of comfort and structure, and these can be considered signs of undiagnosed autism in adults. These behaviors can serve as a coping mechanism that helps manage anxiety in interpersonal situations.
-
A profound focus on specific topics or hobbies, which is a common sign of undiagnosed autism in adults, often results in an extensive knowledge base in those areas. This intense interest can serve as both a strength and a challenge in social contexts.
To effectively assist those on the spectrum, the case study titled 'Understanding and Supporting Autistic People' illustrates practical strategies that parents and advocates can utilize. Identifying signs of undiagnosed autism in adults is an essential initial action for parents and advocates, directing them toward seeking the necessary assistance and resources to better help individuals with developmental differences in navigating the world.
Understanding Undiagnosed Autism in Women: Unique Challenges and Signs
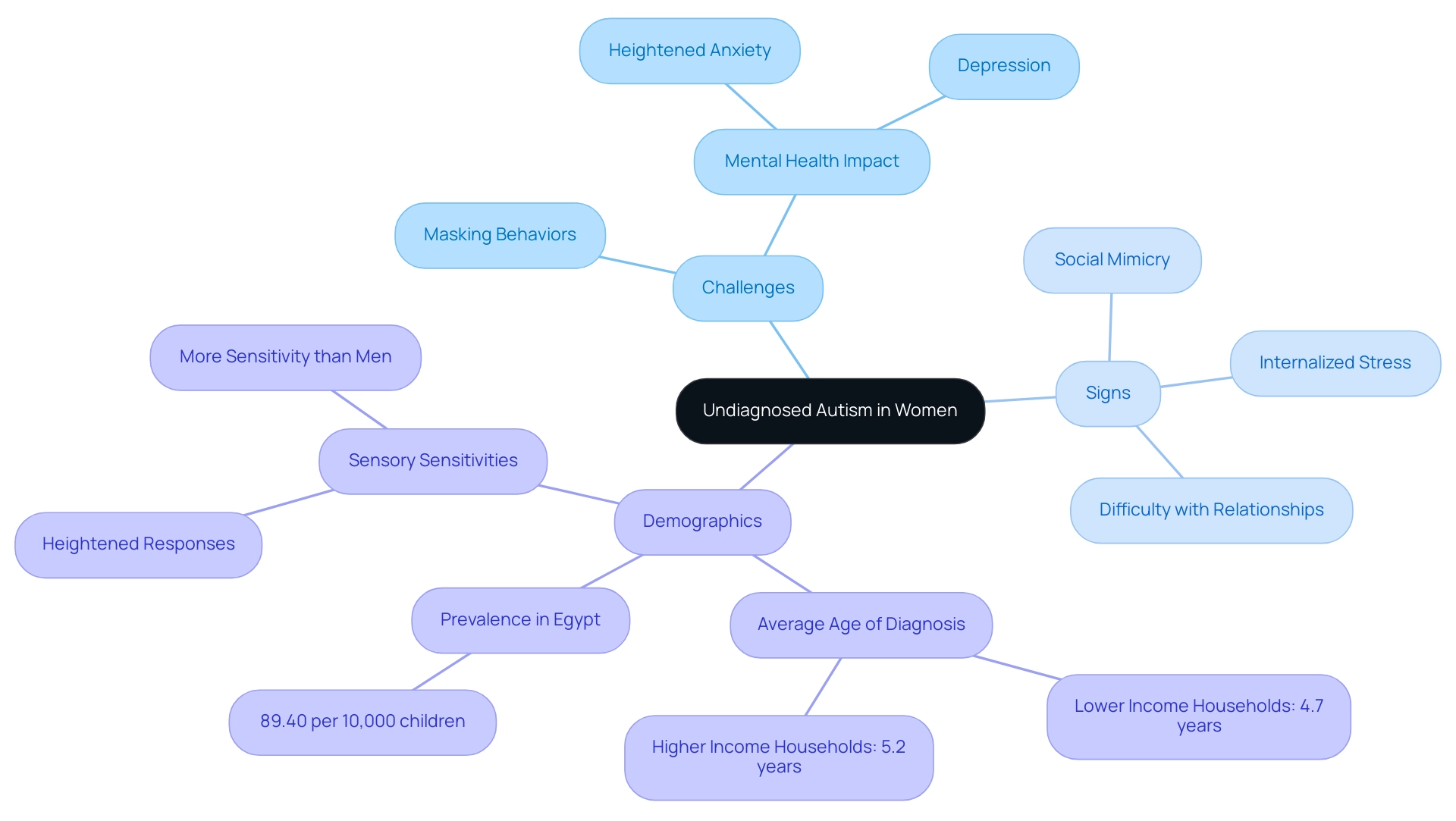
Women with developmental disorders often navigate a complex landscape of challenges that can obscure their symptoms, leading to underdiagnosis. Frequently, these women adopt masking behaviors, consciously altering their actions to align with societal expectations. As a result, they may experience heightened anxiety and depression, struggling to meet the demands placed upon them.
Identifying the signs of undiagnosed autism in adults is essential for advocacy and support. Key indicators include:
- Social Mimicry: Many women may imitate peers' behaviors to blend in, often at the cost of their own authenticity.
- Internalized Stress: The pressure to conform can manifest as significant anxiety, impacting overall well-being.
- Difficulty with Relationships: Despite a strong desire for meaningful connections, many women face challenges in forming deep relationships, often feeling isolated.
Additionally, studies reveal that the average age of diagnosis for children in lower-income households is 4.7 years, compared to 5.2 years in higher-income households, highlighting disparities in diagnosis. Furthermore, with a prevalence of 89.40 per 10,000 children reported in Egypt, it is essential to consider the broader context of this condition across different demographics.
Notably, many girls and women with developmental disorders recognize their sensory sensitivities, which can lead to heightened responses to various stimuli, indicating that they tend to be more sensitive to sensory issues than men. By understanding the signs of undiagnosed autism in adults, we empower ourselves to better support women who may remain undiagnosed, fostering a more inclusive environment for all.
Navigating the Diagnosis Process: Steps and Benefits
The diagnostic process for adults seeking assessment for developmental disorders typically unfolds in several key steps:
- Self-Assessment: Start by reflecting on your behaviors, social interactions, and any signs of undiagnosed autism in adults that may present as challenges in your daily life. This personal insight is crucial for understanding the signs of undiagnosed autism in adults within your unique experiences.
- Gathering Information: Collect relevant documents, such as your medical history, and seek input from family or friends who can provide additional context about the signs of undiagnosed autism in adults. This information will be valuable during the evaluation of signs of undiagnosed autism in adults.
- Professional Evaluation: Schedule an appointment with a qualified professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist with expertise in spectrum disorders. Their experience will guide you through the complexities of the diagnostic process.
- Diagnosis and Recommendations: Following the evaluation, the professional will provide a diagnosis, if applicable, and recommend resources or therapies tailored to your needs. Comprehending the signs of undiagnosed autism in adults can provide various advantages, including improved self-awareness, access to crucial assistance services, and effective methods for handling daily challenges. Based on recent discoveries, people diagnosed with a developmental disorder can see considerable enhancements in their quality of life when they obtain suitable assistance. It's important to note that Severity Level 3 requires 'very substantial support' for social communication and restricted/repetitive behaviors, highlighting the varying levels of support needed across the autism spectrum. Furthermore, therapy should be pursued if warranted, regardless of whether a person meets the criteria for ASD, as this can provide valuable assistance. In a relevant case study titled 'Comparative Analysis of Co-occurring Somatic Disorders in ASD,' researchers examined the complexities of the diagnostic process and the importance of understanding co-occurring conditions, which can significantly impact a person's experience. As noted by De Benedictis CA,
Autism Spectrum Disorders: Diagnosis and Treatment,
the process not only clarifies a person's experiences but also opens doors to a network of resources designed to help manage challenges effectively. Participating in this process enables people to advocate for their needs and seek the assistance they deserve.
Support and Resources for Adults Living with Autism
Adults with developmental disorders have access to a variety of assistance systems aimed at improving their well-being and independence. Key resources include:
-
Therapy Options: Engaging in therapies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) can provide people with valuable coping strategies tailored to their unique needs.
Recent statistics show that effective therapy can lead to significant improvements in managing depression and anxiety symptoms, with assessments often conducted using tools like the PHQ-9 and GAD-7. Significantly, there are presently 59,976 board-certified behavior analysts (BCBAs) in the U.S., offering specialized assistance for people on the spectrum.
-
Peer Support Groups: These groups serve as a vital lifeline, connecting individuals who share similar experiences. The sense of community fostered within these groups not only alleviates feelings of isolation but also provides opportunities for shared learning and encouragement.
-
Online Resources: Platforms such as the Autism Self Advocacy Network (ASAN) and the National Autistic Society provide a wealth of information and forums, enabling adults with developmental differences to access resources and connect with others in the community.
-
Skill-Building Workshops: Participating in workshops that focus on social skills, job readiness, and daily living skills can significantly enhance independence and self-confidence.
It is crucial to note that the average age for a dependable diagnosis of developmental disorders is around 2 years, with intervention typically starting at an average age of 4.7 years. Timely identification and action can be life-saving; a study shows that 10% of individuals who died by suicide were likely to have undetected developmental disorders. By actively engaging with these support systems, adults can better recognize the signs of undiagnosed autism in adults and cultivate a robust network that empowers them to navigate their unique challenges effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is vital for creating an inclusive environment that recognizes and addresses the diverse needs of individuals on the spectrum. This article has explored the multifaceted nature of autism, highlighting the importance of recognizing its signs in adults, particularly those who may be undiagnosed. Key traits such as:
- Social communication challenges
- Sensory sensitivities
- Restricted interests
have been identified as essential for parent advocates to understand, enabling them to provide better support.
The unique challenges faced by women with autism further emphasize the need for awareness and advocacy. By recognizing the signs of undiagnosed autism, advocates can help alleviate the struggles many women endure while navigating societal expectations. Additionally, the diagnostic process serves as a crucial step for adults seeking to understand their experiences, with significant benefits including:
- Enhanced self-awareness
- Improved access to resources
Finally, the array of support systems available, from therapy to peer support groups and skill-building workshops, underscores the potential for individuals with autism to thrive. By actively engaging with these resources, adults on the spectrum can build meaningful connections and foster their independence. Empowering individuals with autism through knowledge and support not only enriches their lives but also strengthens the fabric of a diverse and inclusive community.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by a diverse range of symptoms that affect social interaction, communication, and behavior. The term "spectrum" indicates the varying degrees of support individuals may need, from substantial assistance to independent functioning.
What are the common characteristics of ASD?
Key traits associated with ASD include challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors.
Are there disparities in the prevalence of ASD among different demographics?
Yes, studies indicate disparities in diagnosis rates, with prevalence being 1.8 times higher among Hispanic children and 1.6 times higher among non-Hispanic Black children compared to non-Hispanic White children.
What are some signs of undiagnosed autism in adults?
Signs of undiagnosed autism in adults may include interpersonal communication challenges, heightened or diminished responses to sensory stimuli, repetitive behaviors, and intense focus on specific topics or hobbies.
How do women with developmental disorders experience ASD differently?
Women may exhibit masking behaviors to conform to societal expectations, leading to underdiagnosis. They may experience internalized stress, difficulties in forming relationships, and heightened sensory sensitivities.
What steps are involved in the diagnostic process for adults seeking assessment for developmental disorders?
The diagnostic process typically includes self-assessment, gathering information, professional evaluation, and receiving a diagnosis with tailored recommendations.
What resources are available for adults with developmental disorders?
Key resources include therapy options (like CBT and DBT), peer support groups, online resources (such as ASAN and the National Autistic Society), and skill-building workshops.
Why is timely identification of developmental disorders important?
Timely identification can significantly improve quality of life and access to essential support services. Studies show that a significant percentage of individuals who died by suicide may have had undetected developmental disorders.