Overview
Understanding the signs of autism in 5-year-olds is crucial for every caregiver. Early recognition can pave the way for effective intervention, making a significant difference in a child's developmental journey. Are you aware of the subtle indicators to watch for? Limited eye contact, social withdrawal, and repetitive behaviors are key signs that may warrant further attention.
As parents, it’s natural to feel concerned about your child’s development. Recognizing these signs early can enhance not just developmental outcomes but also overall well-being. Imagine the relief of knowing that timely support can lead to a brighter future for your child.
If you notice these behaviors, don’t hesitate to seek guidance. Early diagnosis opens doors to resources and interventions that can truly make a difference. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Many parents share similar concerns and experiences. Consider reaching out to your pediatrician or local support groups to explore the next steps.
Your vigilance and care can change the trajectory of your child's life. Together, let’s ensure that every child receives the understanding and support they deserve.
Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects millions of children around the world, yet it often remains shrouded in misunderstanding and stigma.
As caregivers navigate the intricate landscape of autism, recognizing its early signs and understanding its implications becomes crucial for fostering positive outcomes.
This article explores essential aspects of ASD, including:
- Identifying key behavioral indicators in young children
- Understanding sensory sensitivities that can significantly impact daily life
By equipping caregivers with effective strategies and insights, we aim to illuminate the path toward meaningful support and intervention, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for both children and their families.
1. What is Autism Spectrum Disorder and Why It Matters
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition, presenting various challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. Each individual experiences autism uniquely, highlighting the importance for caregivers to be vigilant in recognizing its signs. Understanding the signs of autism in 5-year-olds is crucial for early intervention, which can significantly enhance a young person's developmental trajectory and overall well-being.
Research shows that timely diagnosis and intervention can lead to markedly improved outcomes. Individuals who receive early support are more likely to thrive in educational settings and beyond. Alarmingly, statistics reveal that approximately 1 in 6 (17%) individuals aged 3–17 years were diagnosed with a developmental disability during 2009–2017. Furthermore, around 8% of autistic students do not complete high school, compared to only 5% of their peers. This gap underscores the essential need for guardians to quickly recognize signs of developmental disorders and pursue suitable resources, ensuring that every young person has the opportunity to reach their full potential.
As the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes, "The CDC prevalence estimates for developmental disorders are for 8-year-old children across 11 monitoring sites in the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network in 2020." Additionally, the evolution of symbols in advocacy reflects changing perceptions within the community, emphasizing the significance of support and inclusion for caregivers. Together, we can foster an environment where every child is understood and supported on their unique journey.
2. Recognizing Early Signs of Autism in 5-Year-Olds
Caregivers play a crucial role in recognizing early signs of developmental disorders in their 5-year-olds. By being aware of several key indicators, they can make a significant difference in their child's development:
- Limited Eye Contact: Noticeable avoidance of eye contact or indifference during social interactions can be an early sign. Research indicates that around 50% of children with developmental disorders exhibit restricted eye contact, which can hinder their social growth. Delayed speech development is also a potential indicator of autism in 5-year-olds, as many individuals on the spectrum may experience postponed speech compared to their peers. This may present as reduced verbal communication or atypical speech patterns, such as echolalia, where they repeat words or phrases.
- Social Withdrawal: A preference for solitary play, disinterest in engaging with peers, or difficulty in responding to social cues can signal underlying challenges. Children may seem withdrawn or detached from their surroundings, making it essential for caregivers to observe these behaviors.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Common repetitive actions might include hand-flapping, rocking, or organizing toys in a specific order. These behaviors often provide comfort to young ones and can be key in identifying autism.
It's important to recognize that boys are diagnosed with autism 4.2 times more often than girls, highlighting a significant gender disparity in autism diagnosis. This disparity may partly arise from girls masking their symptoms more effectively, leading to delayed or missed diagnoses. Additionally, caregivers should be aware that epilepsy affects up to 30% of autistic youth, which can complicate their developmental journey.
By being vigilant and recognizing the signs of autism in 5-year-olds early, caregivers can seek timely evaluations and support. This proactive approach ultimately paves the way for successful interventions and improved outcomes for their children. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; reach out for support and share your experiences with others who understand.
3. Key Behavioral Indicators of Autism in Young Children
Key behavioral indicators of the condition in young individuals encompass several critical areas that caregivers should be attentive to:
- Difficulty with Social Interactions: Youngsters may struggle to engage in conversations or participate in interactive play with peers, often leading to feelings of isolation. These challenges, which can be considered signs of autism in 5-year-olds, are common. Many young individuals face difficulties in both verbal and nonverbal communication, understanding social cues, and forming friendships.
- Inflexibility: A pronounced preference for established routines and significant distress when these routines are disrupted can be indicative of a developmental disorder. This inflexibility is prevalent among young individuals with autism and can impact their daily functioning.
- Unusual Interests: Many individuals with autism display an intense focus on specific subjects or objects, frequently at the expense of other activities. This hyper-fixation can serve as both a strength and a barrier to social engagement.
- Lack of Response to Name: Some young individuals may not react when their name is called or may appear oblivious to their surroundings, which can affect their ability to connect with others.
Recognizing signs of autism in 5-year-olds is crucial for caregivers. It allows them to effectively communicate their observations to healthcare providers, facilitating timely assessments and interventions. As noted by Matthew J. Maenner from the CDC, "These data indicate that ASD is common across all groups of youth and underscore the considerable need for equitable and accessible screening, services, and supports for all youth." Furthermore, the median age of identification for individuals with ASD has not changed significantly over the years, highlighting the urgency of recognizing these indicators early on.
Additionally, case studies have shown that music therapy interventions can improve cognitive and emotional processing skills, which are crucial for social skills development in individuals with ASD. This illustrates practical interventions that can support social skills development, providing hope and direction for caregivers seeking to foster their child's growth.
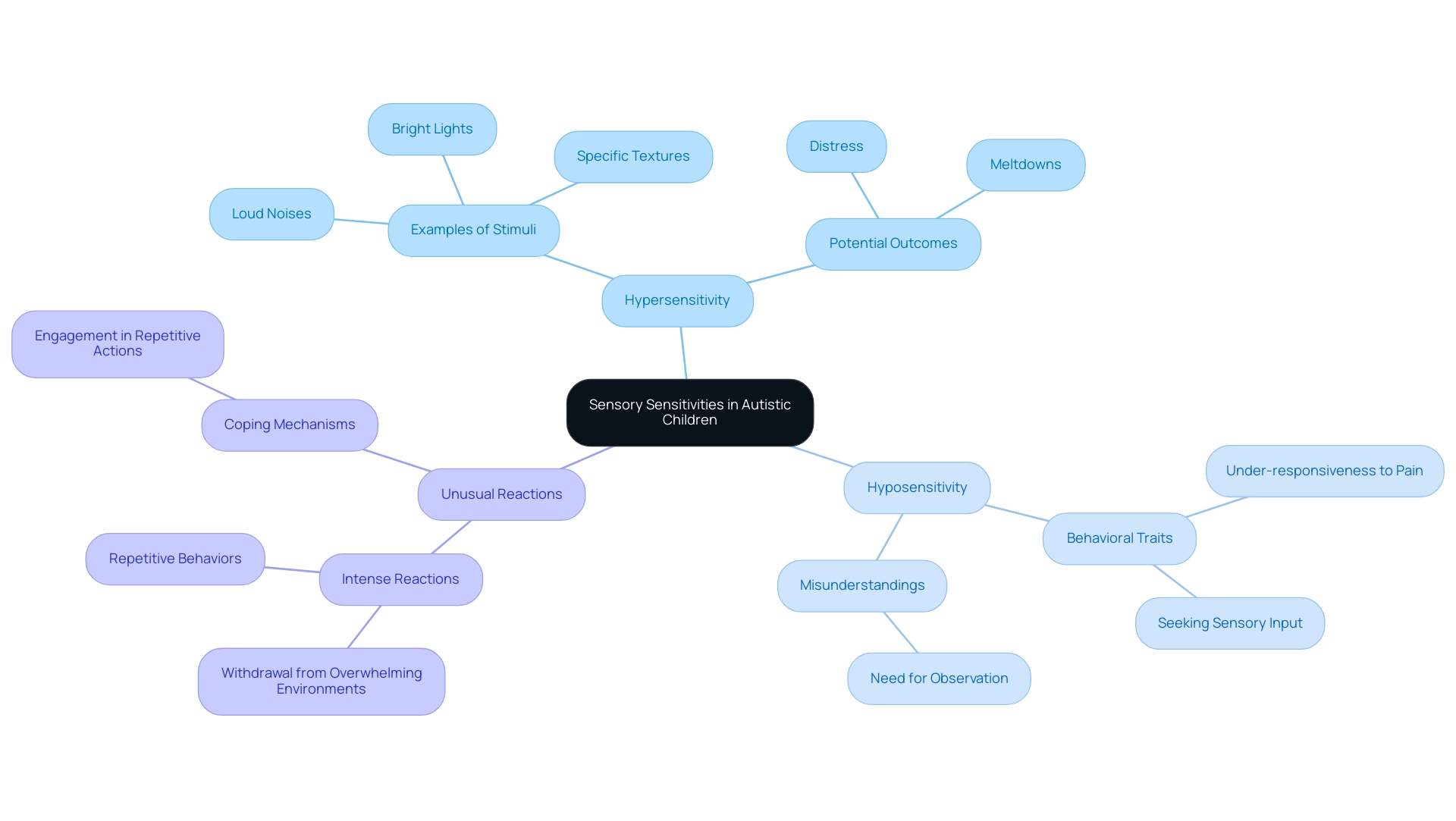
4. Understanding Sensory Sensitivities in Autistic Children
Understanding sensory sensitivities is a fundamental aspect of supporting caregivers of autistic individuals. Many individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) experience these sensitivities in various ways:
- Hypersensitivity: This condition involves an over-responsiveness to sensory stimuli, which can manifest as distress in response to loud noises, bright lights, or specific textures. Such sensitivities can lead to significant discomfort and result in meltdowns if not properly managed.
- Hyposensitivity: Conversely, some individuals may exhibit under-responsiveness, where they do not react to pain as expected or actively seek out sensory input in atypical ways. This behavior can often be misunderstood and may require careful observation to address effectively.
- Unusual Reactions: Autistic individuals may display intense reactions to sensory experiences, which can include withdrawal from overwhelming environments or, alternatively, engaging in repetitive behaviors as a coping mechanism. Identifying these patterns is essential for providers to foresee and alleviate stressors.
Recent demographic insights suggest that comprehending these sensory sensitivities is crucial for customizing support programs and health policies to effectively address the needs of autistic youth. For instance, a study involving 41 subjects with ADHD and 43 normal subjects highlights the prevalence of sensory sensitivities in these populations, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions.
Moreover, research has shown that autistic individuals can live well into their 70s, with life expectancy varying based on the severity of symptoms and quality of life. This underscores the significance of offering effective assistance for those who nurture, as addressing a young one's sensory needs can greatly influence their overall quality of life in the long run.
By understanding these sensory sensitivities, supporters can foster a more accommodating environment. This proactive strategy not only lessens potential stressors but also improves overall comfort and well-being for kids with developmental differences. Let's work together to create a nurturing space for our children, ensuring they feel understood and supported.
5. Supporting Your Child: Strategies for Caregivers of Autistic Children
To effectively support their autistic children, caregivers can implement a variety of strategies tailored to meet individual needs:
- Establish a Routine: Consistent daily schedules are crucial, as they help children with autism feel secure and better manage small changes in their environment. Research indicates that maintaining a routine significantly enhances adaptability, with studies showing that individuals with autism can adapt more easily to changes when routines are established.
- Use Visual Supports: Incorporating visual aids such as charts, schedules, or pictorial instructions can greatly improve communication and comprehension, providing clarity in various situations. This approach is supported by the case study titled "How ABA Therapy Supports the Development of Positive Behavioral Skills," which illustrates how visual supports can lead to positive behavioral outcomes.
- Encourage Social Interaction: Actively promoting opportunities for playdates and group activities fosters the development of social skills, enabling youngsters to practice interactions in a supportive setting.
- Practice Patience and Empathy: Acknowledging that each individual may respond differently is essential. By fostering an atmosphere of understanding and compassion, supporters can create a nurturing environment that accommodates the individual's unique responses.
As Lisa V. Ibañez, Lead Author, mentions, while some writers may have a financial conflict of interest, the strategies discussed here are grounded in empirical evidence that underscores their effectiveness in overcoming challenges encountered by youth with ASD. Implementing these strategies not only cultivates a positive atmosphere but also empowers caregivers to address the diverse needs of their autistic children effectively. As highlighted in recent studies, these approaches can lead to significant improvements in parent-child interactions and overall developmental outcomes.
Conclusion
Recognizing and understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is vital for caregivers who aspire to support their children effectively. This article highlights the importance of identifying early signs of autism, such as:
- Limited eye contact
- Delayed speech
- Social withdrawal
These indicators can pave the way for timely interventions. By being aware of these behavioral signs, caregivers can facilitate early diagnosis and access to essential resources, ultimately enhancing their child’s developmental journey.
Moreover, understanding the sensory sensitivities that many autistic children experience is crucial. Whether hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity, these sensory challenges can significantly impact daily life. By equipping caregivers with strategies to manage these sensitivities, the overall quality of life for both children and their families can improve immensely.
In conclusion, creating a nurturing and supportive environment is essential for children with autism. Implementing structured routines, utilizing visual supports, and encouraging social interactions are practical strategies that can foster positive outcomes. By remaining vigilant and informed, caregivers can help their children navigate the complexities of autism, ensuring they receive the support and opportunities necessary to thrive. Ultimately, empowering caregivers with knowledge and strategies not only benefits the children but also enriches family life as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social communication, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors. Each individual with autism experiences it uniquely.
Why is it important to recognize the signs of autism in 5-year-olds?
Recognizing the signs of autism in 5-year-olds is crucial for early intervention, which can significantly enhance a child's developmental trajectory and overall well-being.
What impact does early diagnosis and intervention have on individuals with autism?
Research indicates that timely diagnosis and intervention can lead to markedly improved outcomes, with individuals receiving early support more likely to thrive in educational settings and beyond.
What are some statistics regarding developmental disabilities in children?
Approximately 1 in 6 (17%) individuals aged 3–17 years were diagnosed with a developmental disability during 2009–2017. Additionally, around 8% of autistic students do not complete high school, compared to only 5% of their peers.
What key signs should caregivers look for in 5-year-olds that may indicate autism?
Caregivers should look for signs such as: Limited eye contact or avoidance during social interactions; Delayed speech development, including reduced verbal communication or atypical speech patterns; Social withdrawal, such as a preference for solitary play or difficulty responding to social cues; Repetitive behaviors, like hand-flapping or organizing toys in a specific order.
Is there a gender disparity in autism diagnosis?
Yes, boys are diagnosed with autism 4.2 times more often than girls. This disparity may be due to girls masking their symptoms more effectively, leading to delayed or missed diagnoses.
How prevalent is epilepsy among autistic youth?
Epilepsy affects up to 30% of autistic youth, which can complicate their developmental journey.
What should caregivers do if they recognize signs of autism in their child?
Caregivers should seek timely evaluations and support to ensure successful interventions and improved outcomes for their children. It is important to reach out for support and share experiences with others who understand.




