Overview
The article focuses on understanding the rates of autism, highlighting the significant increase in diagnoses and the various factors influencing this trend. It provides statistical insights, such as the CDC's report indicating 1 in 36 children identified with autism, and discusses the emotional challenges faced by families, emphasizing the need for expanded healthcare services and tailored support systems to address the diverse needs of the autistic population.
Introduction
The landscape of autism is evolving rapidly, with current statistics revealing that approximately 1 in 36 children in the U.S. is diagnosed with autism, a significant increase that underscores the importance of awareness and support.
As parents navigate this complex journey, understanding the factors driving these rising diagnoses, the demographic variations, and the profound impact on families is essential.
This article delves into the multifaceted nature of autism, exploring the challenges faced by individuals and their families, while also highlighting the importance of building supportive communities.
With a focus on innovative research and treatment options, it empowers parent advocates to champion for the resources and services necessary to ensure the well-being of their children in an ever-changing world.
Current Statistics on Autism Prevalence
Recent statistics from the CDC indicate that roughly 1 in 36 youngsters in the United States is identified with a spectrum disorder, representing an astounding 312% rise in diagnoses since the year 2000. This remarkable rise underscores a heightened awareness and recognition of autism spectrum disorders, which is crucial for both parents and professionals navigating these challenges. Additionally, a concerning statistic from Changsha, China, shows that 67.1% of mothers of autistic kids reported experiencing both depression and anxiety symptoms, highlighting the emotional challenges faced by many parents.
Furthermore, 18.6% of parents of autistic individuals meet the criteria for a provisional diagnosis of PTSD, emphasizing the psychological impact on families. The implications of such statistics extend beyond mere numbers; Grosvenor's group emphasizes that
the population of autistic adults in the U.S. will continue to grow, underscoring a need for expanded health care services.
In light of these statistics, the case study titled 'Independence for Autistic Individuals' suggests that parents should teach basic living skills to their autistic offspring, as they should not be left home alone before the age of 12 or 13, depending on maturity.
Comprehending the present condition of developmental disorder assessments not only guides the strategy for assistance but also enables parent advocates to advocate for the resources and services their offspring require in a changing environment.
Factors Driving the Increase in Autism Diagnoses
The increasing rates of diagnoses can be linked to several key factors that illustrate our developing comprehension of this condition:
- Increased Awareness: There is now a heightened public awareness surrounding this disorder, which has prompted more parents to seek evaluations for their offspring. This proactive method is essential in guaranteeing that more people obtain the support and services they require.
- Changes in Diagnostic Criteria: Over time, the criteria for diagnosing this condition have undergone significant changes, allowing for a broader spectrum of individuals to be identified. These adjustments have made it easier for those who might have gone undiagnosed in the past to receive proper recognition and care.
- Improved Data Collection Methods: Advances in tracking and reporting methods have led to more accurate prevalence rates. A report from the CDC's Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network indicated that about 1 in 6 (17%) children aged 3–17 years were diagnosed with a developmental disability during the period from 2009 to 2017. This improved data gathering is vital for comprehending and meeting the needs of the community affected by developmental disorders.
As we observe these changing elements, it is important to acknowledge their influence on molding our communities' perception of such conditions. A recent 2023 UK study revealed that autistic men without learning disabilities have an average life expectancy of 74.6 years, a stark contrast to those with learning disabilities, who average 71.7 years. For women, the figures are similarly revealing.
Such statistics highlight the significance of awareness and customized assistance systems. Moreover, the rates of autism indicate that autistic individuals are three times more likely to die from a preventable injury than the general population, highlighting the urgent need for increased awareness and support. Furthermore, case studies emphasizing the need for inclusive services for the diverse ASD population underscore the urgency of bridging gaps in healthcare access and ensuring culturally-informed care. The demand for enhancement in this area is increasingly urgent as we aim for a society that fully assists individuals with developmental disorders throughout their lives.
Additionally, symbols of advocacy for individuals on the spectrum, such as the butterfly with puzzle-piece wings and the 'rainbow circle,' play an important role in promoting awareness and unity within the community.
Demographic Variations in Autism Prevalence
Grasping the demographic differences in the prevalence of the condition is crucial for parent advocates aiming to assist their offspring effectively. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 1 in every 100 youths has a developmental disorder, highlighting the significance of this issue. Autism is diagnosed significantly more often in males than females, with estimates indicating a ratio of approximately 4:1.
This disparity raises questions about the underlying factors influencing diagnosis rates, particularly as ongoing research uncovers new insights into gender differences in autism.
Age plays a crucial role in diagnosis trends, as younger children are increasingly recognized due to heightened awareness and screening efforts. Conversely, many older individuals may have been overlooked, reflecting a historical gap in identifying the condition. By addressing these age-related dynamics, advocates can better navigate the challenges faced by individuals who may have gone undiagnosed for years.
Socio-economic status also impacts the prevalence of developmental disorders, as families from diverse backgrounds experience varying access to diagnostic services and support systems. This discrepancy can lead to differences in the reported rates of autism, highlighting the necessity for tailored resources that address specific community needs. For instance, a survey revealed that 36.5% of caregivers of autistic individuals utilize ABA therapy, with many recommending it based on positive outcomes observed in their dependents.
As Luke Grosvenor from Kaiser Permanente's Division of Research highlights,
The population of autistic adults in the U.S. will continue to grow, underscoring a need for expanded health care services.
Furthermore, it's important to note that 8% of autistic students in the U.S. do not finish high school, compared to 5% of all students, which highlights the educational challenges faced by autistic individuals. Recognizing and addressing these demographic differences empowers parent advocates to push for comprehensive support, ensuring that all children receive the care they deserve.
The Impact of Autism on Individuals and Families
The influence of autism is deep and complex, affecting individuals and their households in significant ways.
Challenges for Individuals:
Autistic individuals often encounter difficulties in communication, social interactions, and sensory processing, which can lead to unique obstacles in their daily lives.
Relationship Dynamics:
The emotional toll on households is substantial.
Recent studies reveal that approximately 72.5% of mothers of autistic children experience symptoms of depression, highlighting the need for awareness and support. Furthermore, having a sibling with autism increases the risk for ASD, emphasizing the broader implications within households. Comprehending these complexities is essential for supplying the necessary resources that allow households to cope and thrive.
By fostering a supportive community, which is vital for addressing these challenges, we can empower households to seek the help they need. Significantly, 36.5% of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders report utilizing Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, with high satisfaction rates indicating its positive influence on household dynamics. The relationship between community assistance and caregiver satisfaction with ABA therapy highlights the significance of these resources in improving household well-being.
Additionally, case studies show that effective ABA data collection methods can lead to remarkable improvements in daily lives, community integration, and the prevention of repetitive behaviors. The journey of navigating this condition is undeniably challenging, but with the right support and resources, families can foster resilience and empowerment in their lives.
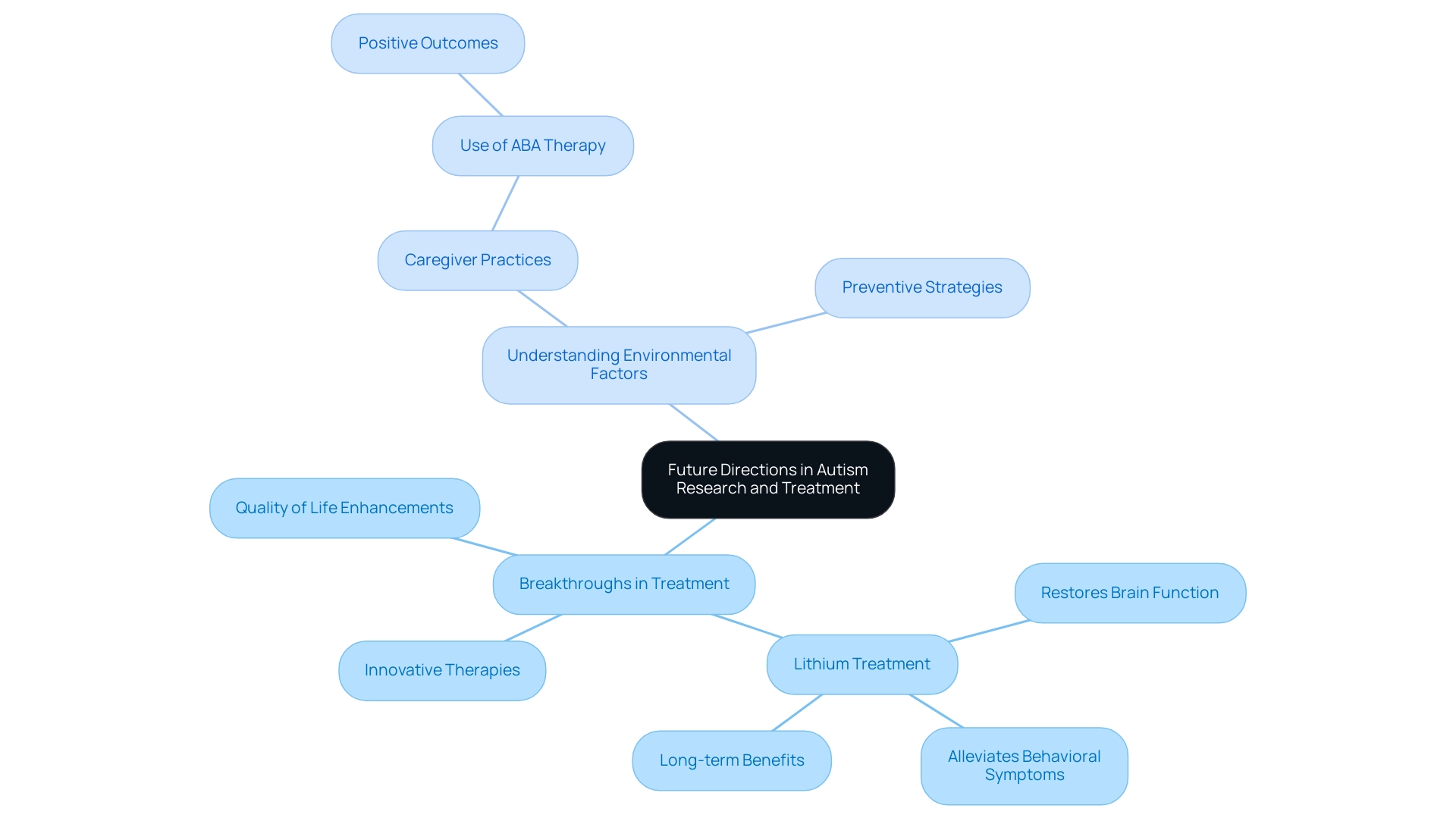
Future Directions in Autism Research and Treatment
As we look towards the future, several pivotal areas in autism research and treatment are gaining traction:
- Breakthroughs in Treatment: Ongoing investigations are delving into innovative therapies and interventions that hold the promise of significantly enhancing the quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum. For example, recent research has emphasized the potential of lithium, traditionally utilized for bipolar disorder, in restoring brain function and alleviating behavioral symptoms in individuals with developmental disorders. Research from the Institute for Basic Science demonstrated that lithium treatment could normalize brain size, improve excitatory neuron function, and enhance social interactions in juvenile models with developmental disorders caused by mutations in the Dyrk1a gene. These effects were shown to last into adulthood, suggesting long-term benefits that could translate into better outcomes for affected individuals. Additionally, Mina Makar emphasizes the significance of progressing innovative therapies, stating that "AstraZeneca's commitment to advancing heart failure research and innovative therapies addresses critical needs in cardiovascular health," which aligns with ongoing efforts in treating developmental disorders.
- Understanding Environmental Factors: Researchers are increasingly focused on how environmental influences may interact with genetic predispositions to shape the development of this condition. This exploration is crucial, as it opens avenues for preventive strategies and tailored interventions. A recent survey revealed that 36.5% of caregivers utilize Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy for their children, with many reporting positive outcomes. This highlights the significance of remaining knowledgeable about these developments, enabling parents and advocates to assist the unique needs of individuals with developmental disorders and to promote effective treatment options that improve their lives.
Building a Supportive Community for Autism
Creating a nurturing community for individuals affected by developmental disorders is essential for encouraging connection and empowerment. Begin by interacting with other families who have kids with developmental differences; exchanging experiences and resources can offer essential perspectives and emotional encouragement. With the World Health Organization reporting that 1 in every 100 individuals has autism, the rates of autism indicate a high likelihood of finding others on a similar journey.
Joining local or online assistance groups is equally important. These platforms allow parents to exchange strategies and insights, creating a network of shared knowledge and encouragement. Different types of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy cater to individual needs, ranging from structured lessons to play-based learning, providing families with tailored resources to support their children.
As Laura NG, MA BCBA Clinical Operations Manager, emphasizes,
Discover how individuals on the spectrum experience love, form relationships, & navigate romantic feelings in this article.
This perspective highlights the importance of understanding emotional experiences within the autism community. Recent research titled 'Hope, Growth, and Possibilities for Autistic Youth' indicates that most individuals with severe language delays eventually acquire language skills, with 78.8% of school-age autistic individuals doing well in at least one developmental area by age 10.
This study offers hope for parents, reinforcing the message that children can thrive even while meeting the criteria for ASD, especially in light of the increasing rates of autism. Advocacy plays a significant role to—work together with local organizations to advocate for improved resources, services, and policies that assist individuals with developmental disorders and their relatives. Efforts to enhance cultural competency in autism diagnosis and support services are essential as they help guarantee that all households, particularly those from diverse backgrounds, receive the assistance they require.
By fostering a strong community, families can feel less isolated, more informed, and empowered in their journey.
Conclusion
The increasing prevalence of autism, with approximately 1 in 36 children diagnosed in the U.S., highlights a critical need for heightened awareness and support. Understanding the factors contributing to this rise, including:
- Increased public awareness
- Changes in diagnostic criteria
- Improved data collection
Equips parent advocates with the knowledge necessary to navigate this evolving landscape. Recognizing demographic variations in autism prevalence further emphasizes the importance of tailored resources and inclusive services that meet the diverse needs of families.
The profound impact of autism on individuals and families cannot be overstated. Challenges in communication and social interactions often lead to significant emotional strain on caregivers, with many experiencing symptoms of depression and anxiety. However, with the right support systems in place, families can foster resilience and empowerment. Utilizing effective therapies such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) can enhance family dynamics and promote positive outcomes for autistic individuals.
Looking to the future, ongoing research into innovative treatments and environmental influences presents new opportunities for improving the quality of life for those on the autism spectrum. Building a supportive community is essential in this journey; by connecting with others, sharing resources, and advocating for enhanced services, families can create a robust network that champions the well-being of individuals with autism. Together, through awareness and collective action, a brighter and more inclusive future for autistic individuals and their families can be achieved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What recent statistics indicate about autism spectrum disorder diagnoses in the United States?
Recent statistics from the CDC show that approximately 1 in 36 children in the U.S. is identified with a spectrum disorder, reflecting a 312% increase in diagnoses since the year 2000.
What factors contribute to the rise in autism spectrum disorder diagnoses?
The rise can be attributed to increased public awareness, changes in diagnostic criteria, and improved data collection methods.
How does the rise in autism diagnoses affect parents emotionally?
A significant statistic from Changsha, China, indicates that 67.1% of mothers of autistic children experience symptoms of depression and anxiety, while 18.6% of parents meet the criteria for a provisional diagnosis of PTSD.
What are the implications of the increasing population of autistic individuals in the U.S.?
The growing population underscores the need for expanded healthcare services to support autistic individuals and their families.
What recommendations are made for parents of autistic individuals regarding independence?
The case study titled 'Independence for Autistic Individuals' suggests that parents should teach basic living skills to their autistic children, as they should not be left home alone before the age of 12 or 13, depending on their maturity.
Why is understanding the current state of developmental disorder assessments important for parents?
Understanding the current state helps guide strategies for assistance and empowers parent advocates to advocate for necessary resources and services for their children.
What does the 2023 UK study reveal about life expectancy for autistic individuals?
The study shows that autistic men without learning disabilities have an average life expectancy of 74.6 years, while those with learning disabilities average 71.7 years.
What are the risks associated with autism, according to the statistics?
Autistic individuals are three times more likely to die from a preventable injury compared to the general population, highlighting the urgent need for increased awareness and support.
How do symbols of advocacy contribute to the autism community?
Symbols like the butterfly with puzzle-piece wings and the 'rainbow circle' play an important role in promoting awareness and unity within the autism community.




