Overview
Tactile stimming—self-soothing behaviors like rubbing or fidgeting—plays a vital role, especially for children with autism. These actions not only help in emotional regulation but also facilitate sensory exploration. For parents and caregivers, understanding these behaviors is essential. It empowers them to provide the right support and create nurturing environments that promote sensory interaction and emotional well-being.
As you navigate this journey, remember that you're not alone. Many parents share similar experiences and challenges. By recognizing the significance of tactile stimming, you can better appreciate your child's needs and foster a deeper connection. Consider reaching out to support groups or resources that can provide additional insights and encouragement.
Together, we can create spaces where our children feel safe and understood, allowing them to thrive emotionally and sensory-wise. Your commitment to understanding these behaviors is a powerful step toward nurturing their well-being.
Introduction
In the intricate journey of childhood development, tactile stimming stands out as a captivating yet often misunderstood behavior, especially in children with autism and ADHD. This behavior, characterized by repetitive actions that engage the sense of touch—like rubbing, squeezing, or fidgeting—plays a crucial role in self-soothing and sensory exploration.
As research increasingly underscores the significance of these actions in fostering emotional regulation and cognitive engagement, it becomes essential for parents and caregivers to understand their child's unique sensory needs.
This article invites you to explore the nuances of tactile stimming, highlighting its benefits, differentiating it from other forms of stimming, and providing practical strategies for support and management.
By embracing and acknowledging the importance of tactile stimming, families can create a nurturing environment that promotes emotional well-being and empowers children to navigate their sensory experiences with greater confidence.
What is Tactile Stimming?
Tactile stimming encompasses self-inducing actions that engage the sense of touch, manifesting in activities such as rubbing, scratching, or tapping surfaces, along with repetitive motions like squeezing or fidgeting with items. These behaviors, particularly tactile stimming, are notably prevalent among children with autism, serving various functions, including self-soothing and exploration of sensations. Understanding tactile stimulation is essential for parents and caregivers, as it empowers them to provide appropriate support and foster an environment conducive to sensory interaction.
Recent studies highlight the importance of tactile stimming in enhancing cognitive and social interactions. For instance, research advocates for the depathologization of self-stimulatory behaviors within educational settings, indicating that when integrated thoughtfully into learning activities, these actions can enhance engagement and facilitate communication among peers. A significant case study on embodied cognition and self-stimulatory behavior illustrates how cognitive processes are intricately connected to bodily actions, challenging traditional educational paradigms that often separate mind and body.
This perspective underscores the necessity for educational methods that recognize self-stimulatory behavior as a valid form of cognitive engagement, ultimately supporting diverse learners.
Statistics indicate that tactile stimming actions are not only common among youth with autism but also prevalent among individuals with ADHD. Tools such as fidget spinners, stress balls, chewable jewelry, and tactile mats serve as beneficial items that can help channel these actions positively. By acknowledging these behaviors, parents can gain a deeper understanding of their children's needs and provide effective strategies to address them.
Real-world examples demonstrate how tactile stimming can be positively redirected into tools that support exploration and emotional regulation.
Key characteristics of tactile stimming include their repetitive nature and the focus on tactile sensations, which can vary significantly among children. As Conn observes, "people are physically attuned to each other, act in synchronicity and enjoy each other’s presence, but carry out interaction in non-face-to-face and largely non-verbal ways." Recognizing these behaviors is vital for nurturing a supportive environment that encourages exploration and emotional well-being.
By embracing tactile self-soothing techniques, parents and caregivers can empower their children to navigate their experiences more effectively.
Why Do Individuals Engage in Tactile Stimming?
Children often engage in tactile stimming for various reasons, primarily to calm themselves during anxious or stressful moments, seek sensory experiences, or cope with overwhelming situations. These behaviors can serve as a comforting and predictable source, enabling young individuals to better manage their emotions and experiences. Research indicates that tactile stimming plays a significant role in anxiety control, allowing children to handle their sensory input and emotional reactions effectively.
For instance, occupational therapists highlight that tactile stimming can provide a soothing effect, helping children center themselves during distressing times. Moreover, the psychometric properties of the Screen for Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED) have yielded positive results in high-functioning youth with ASD, emphasizing the importance of effective anxiety management strategies. Cognitive behavioral therapy has also shown promise in reducing anxiety in youths with high-functioning autism, suggesting that a multifaceted approach may be beneficial.
Understanding triggers and utilizing tools that engage the senses are general tips for managing anxiety that can enhance tactile stimming. By recognizing these motivations and strategies, parents can create supportive environments tailored to their children's sensory needs, fostering a sense of safety and stability essential for emotional well-being. The complexities of gauging anxiety in youngsters with ASD, as discussed in the case study "Measurement Challenges in Assessing Anxiety in ASD," further underscore the necessity for ASD-specific anxiety assessments.
Additionally, as highlighted by Hallett, social anxiety was positively associated with IQ, while separation anxiety was negatively linked to IQ, providing a specialist perspective on the complexities of anxiety in young individuals. This comprehensive understanding can empower parents to better assist their children in managing anxiety through tactile stimming and other effective strategies.
Tactile Stimming vs. Other Types of Stimming
Tactile self-soothing is one of several unique sensory behaviors observed in children, alongside visual, auditory, and vestibular forms. It primarily engages the sense of touch, often manifesting through comforting actions like rubbing, squeezing, or fidgeting with objects. In contrast, visual self-stimulation may involve repetitive patterns, such as focusing on spinning objects or lights, providing soothing or energizing input.
Auditory self-stimulation encompasses sound-related actions, including humming, vocal expressions, or repeating phrases, serving as mechanisms for self-soothing or conveying excitement. Understanding these distinctions is vital for caregivers, as it empowers them to recognize and meet the unique sensory needs of their children effectively.
Research indicates that children with autism may exhibit a variety of self-stimulatory actions, with tactile stimming being particularly prevalent. For example, studies show that tactile stimulation can be more socially acceptable in certain contexts, especially when utilizing tools like fidget spinners or stress balls. These tools not only help manage self-stimulatory actions in public but also promote a deeper understanding of these behaviors among peers and adults.
By age 5, children are typically capable of singing or dancing, highlighting the importance of recognizing repetitive behaviors in the context of typical development. Experts note that while tactile stimming can provide immediate relief, it is essential to understand how it differs from visual and auditory forms. Tactile stimming often involves direct interaction with objects, offering a calming effect, whereas visual sensory activities may lead to increased focus on specific stimuli, which can sometimes be distracting.
Elena Cox, a senior data journalist at Stacker, emphasizes the importance of understanding processing differences. She asserts that creating an environment that supports these variations can significantly enhance the quality of life for youth with autism. Additionally, the case study titled "Promoting Understanding of Repetitive Behaviors" underscores the importance of social acceptance and strategies for managing these actions in public settings. By focusing on these aspects, caregivers can foster acceptance and understanding of their children's unique perceptual experiences, aligning with ASD Media's mission to encourage collaboration and development within the ABA therapy community.
Common Forms of Tactile Stimming Behaviors
Common types of tactile self-soothing actions in youngsters can be quite diverse and impactful. For instance, rubbing hands together or against various surfaces offers a calming sensation that helps regulate anxiety. Scratching or rubbing the skin often emerges as a reaction to discomfort or a quest for sensory input. Tapping fingers or objects repeatedly can serve as a self-calming mechanism during stressful moments, providing a sense of control. Additionally, squeezing stress balls or fidget toys has proven effective in helping children manage their needs; studies indicate that approximately 70% of kids with processing challenges use fidget toys regularly. This aligns with Dr. Vincent Carbone’s Three Buttons concept, where the Engagement Button (Green Button) highlights the importance of interacting with sensory tools to aid self-regulation. Playing with textured materials, such as fabrics or sensory toys, allows children to explore various sensations, which can be particularly beneficial for those with autism.
Recognizing these actions is vital for parents, as it deepens their understanding of their children's unique sensory preferences and requirements. Pediatric therapists often emphasize that tactile stimming serves as a crucial self-regulation tool, helping young individuals navigate their environments more comfortably. These stimming actions can also act as coping strategies for social anxiety or discomfort in social situations, underscoring their significance in a young person's daily life.
By observing and acknowledging these behaviors, caregivers can better support their children in developing effective coping strategies and enhancing their overall well-being. Consider the case of a two-year-old patient diagnosed with autism who engaged in head banging on hard and soft surfaces; this illustrates the potential seriousness of self-stimulatory actions and their impact on youth. Moreover, neurostimulation methods have shown promise in improving outcomes for individuals with severe autism symptoms, further emphasizing the need to address these behaviors in therapeutic settings.
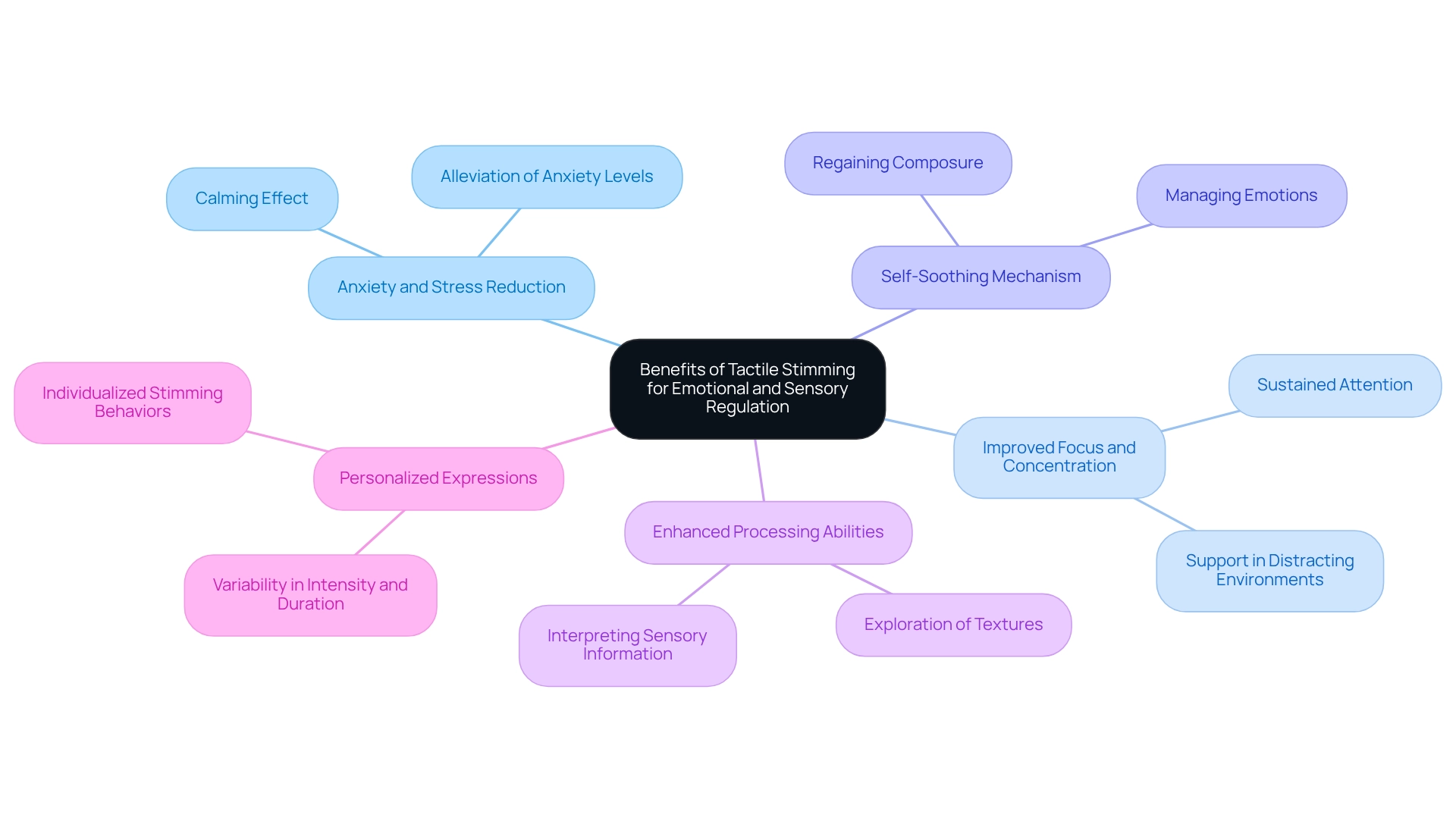
Benefits of Tactile Stimming for Emotional and Sensory Regulation
Tactile stimming offers a range of significant benefits for emotional and sensory regulation in children, and it’s important for parents to understand these advantages.
- Anxiety and Stress Reduction: Engaging in tactile stimming can provide a calming effect, helping to alleviate anxiety and stress. Studies suggest that such activities can lead to a significant decrease in anxiety levels, fostering a sense of calm. Imagine your child finding comfort in the simple act of squeezing a stress ball or running their fingers through soft fabric.
- Improved focus and concentration can also be achieved, as tactile stimming provides crucial input that helps individuals sustain their attention. This is particularly beneficial in environments that may otherwise be distracting or overwhelming. Think of how a child might thrive in a busy classroom when they have a small fidget toy to help them concentrate.
- Tactile stimming acts as a self-soothing mechanism during overwhelming situations, enabling youngsters to regain composure and manage their emotions effectively. When faced with sensory overload, these actions can be a lifeline, allowing them to navigate their feelings with greater ease.
- Enhanced processing abilities can be promoted through tactile stimming, as interacting with different textures encourages exploration. This exploration is essential for enhancing a young person's ability to interpret and respond to sensory information. Consider how a child might learn about the world around them by feeling different surfaces, from rough to smooth.
- It is crucial to acknowledge that the intensity, duration, and type of these actions can differ greatly from individual to individual, emphasizing the personalized aspect of such expressions. As Lorrie Henderson, Chief Clinical Officer, noted, "This study provides preliminary evidence of the effectiveness of SI interventions; more important, it provides information to guide the development of future high-level research studies." By comprehending these advantages, parents can foster an atmosphere that embraces and supports their child's inherent sensory-seeking behaviors.
- By nurturing acceptance and promoting healthy habits, families can aid in creating a more inclusive environment that acknowledges the functional role of repetitive behaviors in enhancing emotional well-being and sensory balance. Challenging negative views on self-stimulatory behaviors is essential for creating a supportive community that values neurodiversity. Together, let’s advocate for a world that recognizes and celebrates the unique ways our children engage with their surroundings.
How to Support and Manage Tactile Stimming
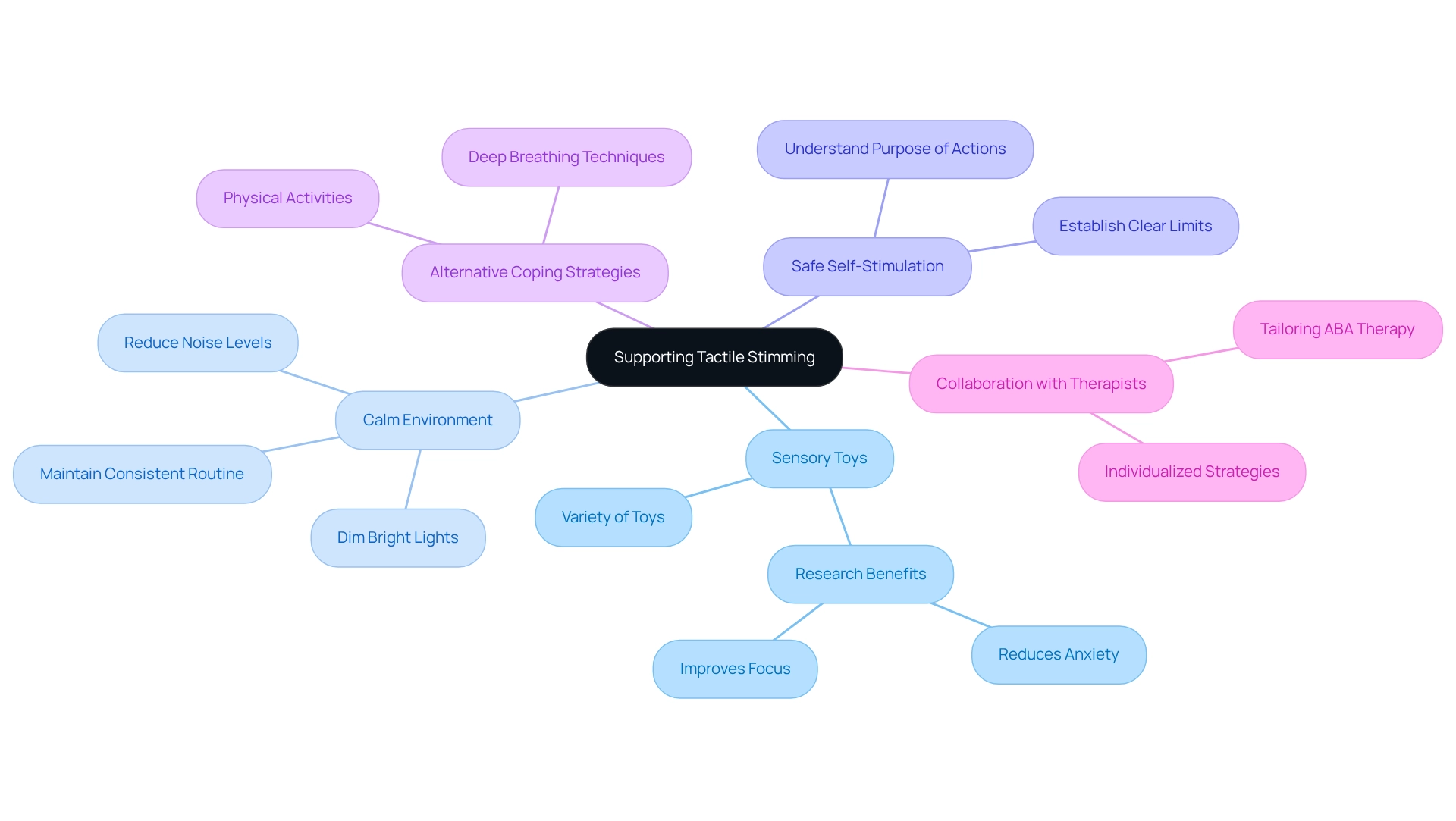
To effectively support and manage tactile stimming in children, parents can implement several key strategies that foster a nurturing environment.
- Provide a Variety of Sensory Toys: Offering an assortment of sensory toys and textured materials allows children to explore different sensations. This exploration can be particularly beneficial for those who engage in tactile stimming. Research indicates that sensory toys can significantly reduce anxiety and improve focus, making them a valuable resource. As noted in recent studies, rocking or spinning can provide a sense of comfort and help block out overwhelming stimuli like bright lights or loud noises.
- Create a Calm Environment: Establishing a calm and predictable environment is essential for minimizing anxiety triggers. This can include reducing noise levels, dimming bright lights, and maintaining a consistent routine, all of which contribute to a sensory-friendly space. Dr. Mary Barbera emphasizes that, in relation to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), tactile stimming can become more pronounced and frequent, highlighting the necessity for these strategies.
- Promote Safe Self-Stimulation: It is crucial to promote safe self-stimulation practices while establishing clear limits for actions that may be disruptive or harmful. Understanding the purpose of these actions can assist parents in supporting their children without undermining their innate coping strategies. A case study titled 'The Role of Repetitive Behaviors in Managing Sensory Input' illustrates how tactile stimming behaviors serve as a coping mechanism for individuals with autism, emphasizing the importance of understanding these actions.
- Teach Alternative Coping Strategies: When tactile stimming becomes excessive or leads to distress, teaching alternative coping strategies can be beneficial. This may involve incorporating soothing methods like deep breathing or engaging in physical activities that offer tactile stimulation.
- Collaborate with Therapists: Working closely with therapists to create individualized strategies that cater to each young person's distinct sensory preferences is essential. This partnership can result in customized strategies that improve the individual's capacity to manage their experiences effectively. Recent articles on tailoring ABA therapy to learning preferences and emotional regulation further support the relevance of these strategies.
These strategies not only help children feel understood and supported in their sensory experiences but also empower parents to foster a nurturing environment that promotes emotional regulation and well-being. By implementing these approaches, parents can create a supportive atmosphere that enhances their child's ability to thrive.
When to Be Concerned About Tactile Stimming
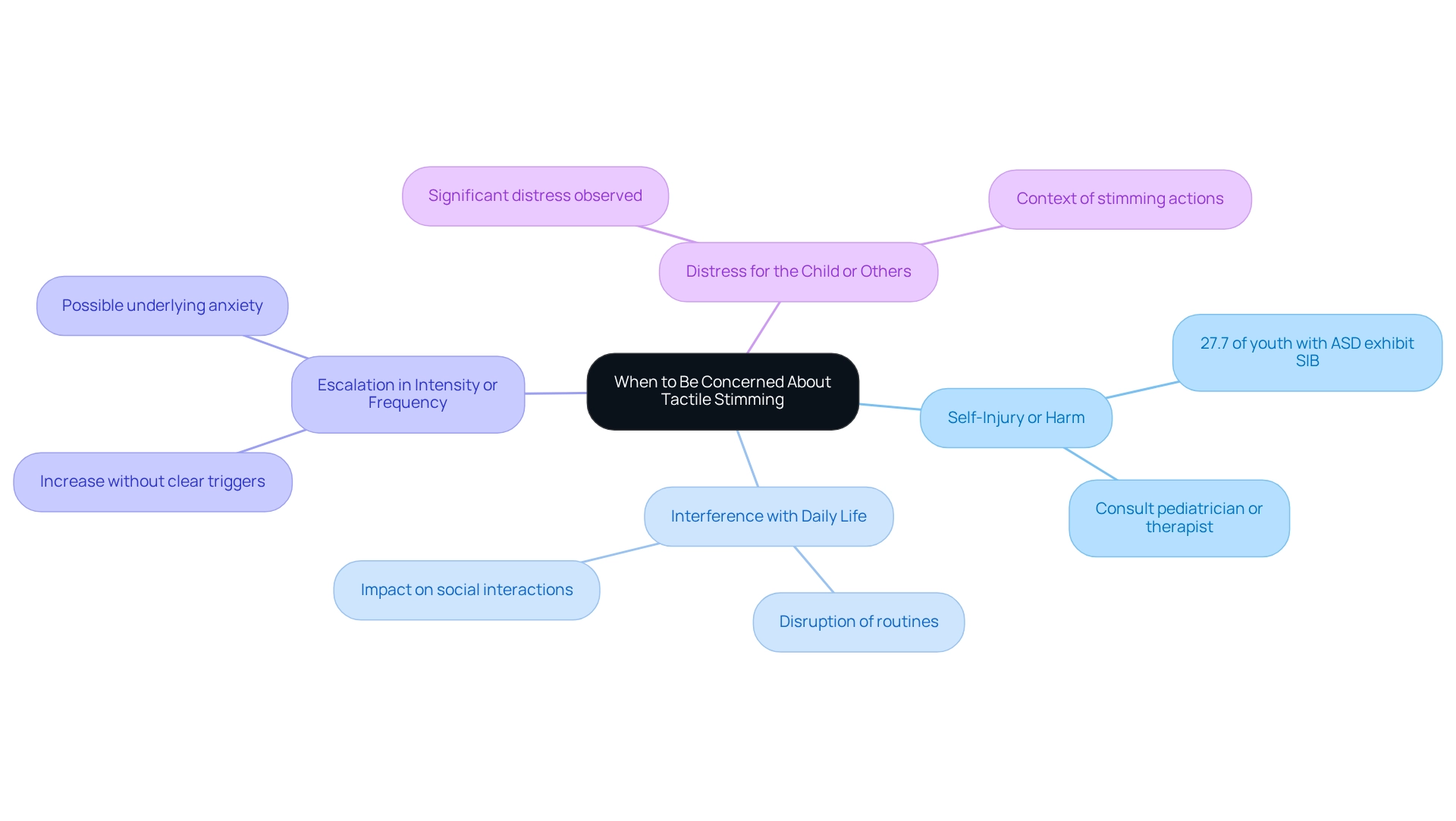
Tactile self-soothing can often be a harmless action, yet it may raise concerns in certain situations. As parents and caregivers, it’s essential to remain vigilant for signs that may indicate a need for professional intervention.
- Self-Injury or Harm: When tactile stimming leads to self-injurious behaviors (SIB), seeking help becomes crucial. Research shows that approximately 27.7% of youth with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) exhibit SIB, based on a study involving 8,065 individuals diagnosed with ASD. This statistic underscores the importance of closely observing these actions. As Eboni I. Lance M.D. advises, "Parents should contact their pediatrician, neurodevelopmental physician and/or behavioral therapist as soon as possible if their child starts exhibiting SIB."
- Interference with Daily Life: If self-soothing actions disrupt everyday activities or social interactions, it may signal a need for assistance. Children should be able to engage in their routines without excessive distraction or distress caused by self-stimulatory behavior.
- Escalation in Intensity or Frequency: An increase in the intensity or frequency of repetitive actions, especially without clear triggers, can be concerning. This escalation might suggest underlying anxiety or processing issues that require professional assessment.
- Distress for the Child or Others: If the repetitive actions cause significant distress for the child or those around them, it’s vital to address the situation. Mental health experts emphasize the importance of understanding the context of stimming actions, like tactile stimming, as they can sometimes mask deeper emotional or sensory difficulties.
In these situations, consulting with a healthcare professional or therapist can provide valuable guidance and strategies to manage these behaviors effectively. Prompt action is especially important, particularly given that a history of autistic regression can occur when children lose social, language, or behavioral skills between ages 1 to 2. By recognizing these signs and seeking help, parents can better support their children's development and well-being.
Key Takeaways and Ongoing Support for Parents
Key takeaways for parents and caregivers include:
- Tactile stimming is a natural behavior that plays a crucial role in sensory regulation and emotional expression. Understanding this can help caregivers appreciate its significance in their child's daily life.
- Recognizing the underlying reasons for tactile stimming allows caregivers to respond in supportive and affirming ways, fostering a positive environment for their children.
- By creating a nurturing space that acknowledges the benefits of tactile stimming, we can greatly enhance a young person's emotional health and overall development.
- It is also vital to monitor for any concerning behaviors that may arise, ensuring that both safety and emotional well-being are prioritized.
Ongoing support from experts and community resources is invaluable, empowering parents to effectively manage their child's sensory needs and challenges. For example, community programs, such as those implemented by City and Hackney CAMHS, have shown success in boosting parental confidence and satisfaction. In their project, 91% of participants reported satisfaction, and 82% felt more confident in managing their child's ASD, illustrating the impact of psychoeducation and peer support.
Engaging with local resources can connect parents with others facing similar challenges, creating a supportive network that fosters shared experiences and solutions. As noted by experts, "PPSG can be utilized to address stress and anxiety among parents of children with ASD or ADHD," highlighting the importance of community engagement. This connection not only provides practical support but also reassures parents that they are not alone on this journey.
Conclusion
Tactile stimming plays a vital role in childhood development, especially for children with autism and ADHD. This behavior, marked by repetitive tactile actions, serves essential functions like self-soothing, sensory exploration, and emotional regulation. By understanding these behaviors, parents and caregivers can create supportive environments that acknowledge and validate their child's unique sensory needs.
The article highlights the numerous benefits of tactile stimming, such as reducing anxiety, enhancing focus, and improving sensory processing skills. By providing suitable sensory tools and fostering calm environments, caregivers can empower children to navigate their sensory experiences more effectively. It's also important to distinguish tactile stimming from other stimming types, as this understanding can better address each child's specific needs.
However, it is equally important to recognize when tactile stimming may become concerning. Signs like self-injury, disruption of daily life, or increased intensity should prompt caregivers to seek professional guidance. Being aware of these indicators ensures that children receive the support necessary for their emotional and developmental well-being.
In summary, embracing tactile stimming as a natural behavior creates a nurturing atmosphere that enhances emotional health and overall development. Ongoing support from professionals and community resources can further empower parents, building a collaborative network that promotes understanding and acceptance of neurodiversity. By acknowledging and respecting tactile stimming, families can help children thrive in their sensory journeys.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is tactile stimming?
Tactile stimming encompasses self-inducing actions that engage the sense of touch, such as rubbing, scratching, or tapping surfaces, along with repetitive motions like squeezing or fidgeting with items.
Why is tactile stimming common among children with autism?
Tactile stimming is prevalent among children with autism as it serves various functions, including self-soothing and exploration of sensations.
How can parents and caregivers support tactile stimming?
Understanding tactile stimulation allows parents and caregivers to provide appropriate support and foster an environment conducive to sensory interaction.
What role does tactile stimming play in cognitive and social interactions?
Recent studies suggest that tactile stimming can enhance cognitive and social interactions, particularly when integrated into educational settings to facilitate engagement and communication among peers.
What educational implications arise from recognizing tactile stimming?
Recognizing self-stimulatory behavior as a valid form of cognitive engagement supports diverse learners and challenges traditional educational paradigms that separate mind and body.
Are tactile stimming behaviors only common among children with autism?
No, statistics indicate that tactile stimming actions are also prevalent among individuals with ADHD.
What tools can help channel tactile stimming positively?
Tools such as fidget spinners, stress balls, chewable jewelry, and tactile mats can help channel tactile stimming in a positive way.
How can tactile stimming assist children in managing anxiety?
Tactile stimming can provide a comforting and predictable source for children to calm themselves during anxious or stressful moments, helping them manage their emotions and experiences.
What therapeutic approaches can enhance the effectiveness of tactile stimming?
Approaches like cognitive behavioral therapy and understanding triggers can enhance the effectiveness of tactile stimming in managing anxiety.
Why is it important to understand the triggers of tactile stimming?
Recognizing the motivations behind tactile stimming allows parents to create supportive environments tailored to their children's sensory needs, fostering a sense of safety and stability essential for emotional well-being.




