Overview
Stimming behavior in autism is not just a characteristic; it is a natural and vital aspect of self-regulation and expression for many individuals on the spectrum. These repetitive actions play a crucial role in managing emotions and sensory experiences. Understanding these behaviors is essential, as they provide comfort and emotional stability. By fostering an accepting environment, we can help autistic individuals thrive, allowing them to navigate their unique perceptual experiences more effectively.
As parents and caregivers, recognizing the importance of stimming can be transformative. Consider how these behaviors might serve as a source of relief during overwhelming moments. When we create spaces where stimming is accepted, we empower our loved ones to express themselves freely.
Let’s work together to build a world that embraces these expressions. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and let’s support each other on this journey towards understanding and acceptance.
Introduction
In the intricate world of autism, stimming, or self-stimulatory behavior, emerges as a vital expression of individuality and emotional regulation. This behavior, often characterized by repetitive movements or sounds, serves various purposes—from soothing anxiety to enhancing sensory experiences. As research increasingly recognizes the significance of these behaviors, parents find themselves at the forefront of understanding how to support their children in navigating the complexities of their sensory needs.
By exploring the motivations behind stimming, caregivers can better appreciate its role in their child's life. Identifying its diverse forms allows for a deeper understanding of the unique ways autistic individuals communicate and cope with the world around them. Implementing effective strategies can create a nurturing environment that celebrates these differences. Together, we can foster a supportive atmosphere that not only acknowledges but also cherishes the individuality of each child.
Defining Stimming: What Every Parent Should Know
Stimming behavior in autism encompasses a variety of self-stimulatory activities, characterized by repetitive movements or sounds that many individuals on the autism spectrum engage in. Common examples include hand-flapping, rocking, spinning, and vocalizations. These actions fulfill multiple purposes, such as self-soothing, managing sensory overload, and expressing excitement.
For numerous autistic individuals, stimming is not just a behavior; it is a natural and vital part of their lives, providing comfort and assisting in emotional regulation.
Recent studies underscore the importance of understanding stimming behavior, particularly in creating a supportive environment for autistic individuals. An exploratory study titled "Reconceptualizing Autistic Stimming" advocates for a shift in research focus to better appreciate the strengths and cultural aspects of the autistic community. This research emphasizes the value of collaborating with autistic individuals to gain deeper insights into their experiences and the role stimming plays in their lives.
Statistics reveal that self-efficacy scores related to repetitive behaviors are significantly high, with a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.854 when individuals can engage in these behaviors, compared to 0.873 when they cannot. In simpler terms, when individuals can partake in self-soothing activities, they generally feel more confident and emotionally stable. Recognizing this connection can help parents understand the importance of allowing their children to express stimming behavior freely.
Understanding self-soothing actions is especially crucial for parents, as it helps them appreciate the naturalness of these practices and their role in emotional regulation. By recognizing stimming behavior as a valid form of expression, parents can foster a more accepting and supportive environment for their children. Effective strategies for managing repetitive behaviors include:
- Creating safe spaces for such actions
- Integrating sensory-friendly activities
- Using tools like sticky notes in conversations to enhance understanding of the causes and functions of these behaviors
For instance, sticky note activities in focus groups have encouraged open dialogue about stimming, allowing participants to share their thoughts and experiences.
Moreover, advances in technology, such as socially assistive robotics (SARs), show promise in enhancing the social skills of individuals with autism, particularly in areas where they face significant challenges. These technologies can offer interactive and engaging opportunities for children to practice social interactions, thereby improving their communication skills and confidence.
In summary, stimming behavior is a fundamental activity for many autistic individuals, serving as a means of self-regulation and expression. As Rebecca poignantly expressed, "Angry that they’ve been told a thousand times why I do it, the reason behind it, that it’s not affecting anyone," this sentiment reflects the frustration many autistic individuals feel when their self-soothing behaviors are misunderstood. By nurturing an understanding of stimming behavior, parents can better support their children in managing their perceptual experiences and emotional needs.
Types of Stimming Behaviors: Recognizing the Spectrum
Stimming behavior in autism can be classified into several distinct types, each serving a unique purpose in processing stimuli and self-regulation. Understanding these categories is essential for parents to recognize and support their children's needs effectively.
- Visual Stimming: This involves engaging with visual stimuli, such as watching spinning objects or lights. Children may find solace in repetitive visual patterns, which can assist them in coping with sensory overload.
- Auditory Stimming: This type includes making repetitive sounds, such as humming, tapping, or vocalizations. These auditory behaviors can provide a soothing effect, helping children express their emotions or excitement.
- Tactile Behavior: Seeking input through touch is typical of tactile behavior. Children may rub different textures, fidget with objects, or engage in activities that provide varied tactile experiences, which can be calming and grounding.
- Vestibular Sensory Activities: Movements that involve balance and motion, such as rocking, spinning, or swinging, fall under vestibular sensory activities. These actions can help youngsters manage their perceptual systems and offer a sense of stability.
Understanding these self-soothing actions, often referred to as stimming behavior in autism, enables parents to pinpoint their children's favored techniques for calming themselves and engaging with their surroundings. For instance, a young individual who frequently spins in circles may be exhibiting stimming behavior to seek vestibular input, while another who enjoys watching lights may be engaging in visual stimming.
Recent research highlights the significance of understanding these behaviors. Studies indicate that the distance between cortical representations of input, such as the thumb and lip, is notably larger in children with autism compared to typically developing peers. This suggests that perception processing in autistic individuals is fundamentally different, emphasizing the need for tailored support strategies. Additionally, a case study titled "Genetic Insights into Sensory Processing in ASD" reviews genetic factors associated with sensory processing abnormalities, indicating that genetic variations may significantly influence sensory processing in ASD.
Occupational therapists emphasize the importance of identifying these actions, observing that stimming behavior can serve as essential communication tools for children. As Ruben Kesherim states, "Recognizing this can lead to a more empathetic understanding of autism repetitive behaviors and contribute to better support strategies for those who experience them." By observing and comprehending these repetitive behaviors, parents can create supportive environments that address their child's perceptual needs, ultimately encouraging a more compassionate and effective approach to their development.
Furthermore, understanding the role of oxytocin in social bonding can provide context on how sensory processing relates to social and emotional abilities in individuals with autism.
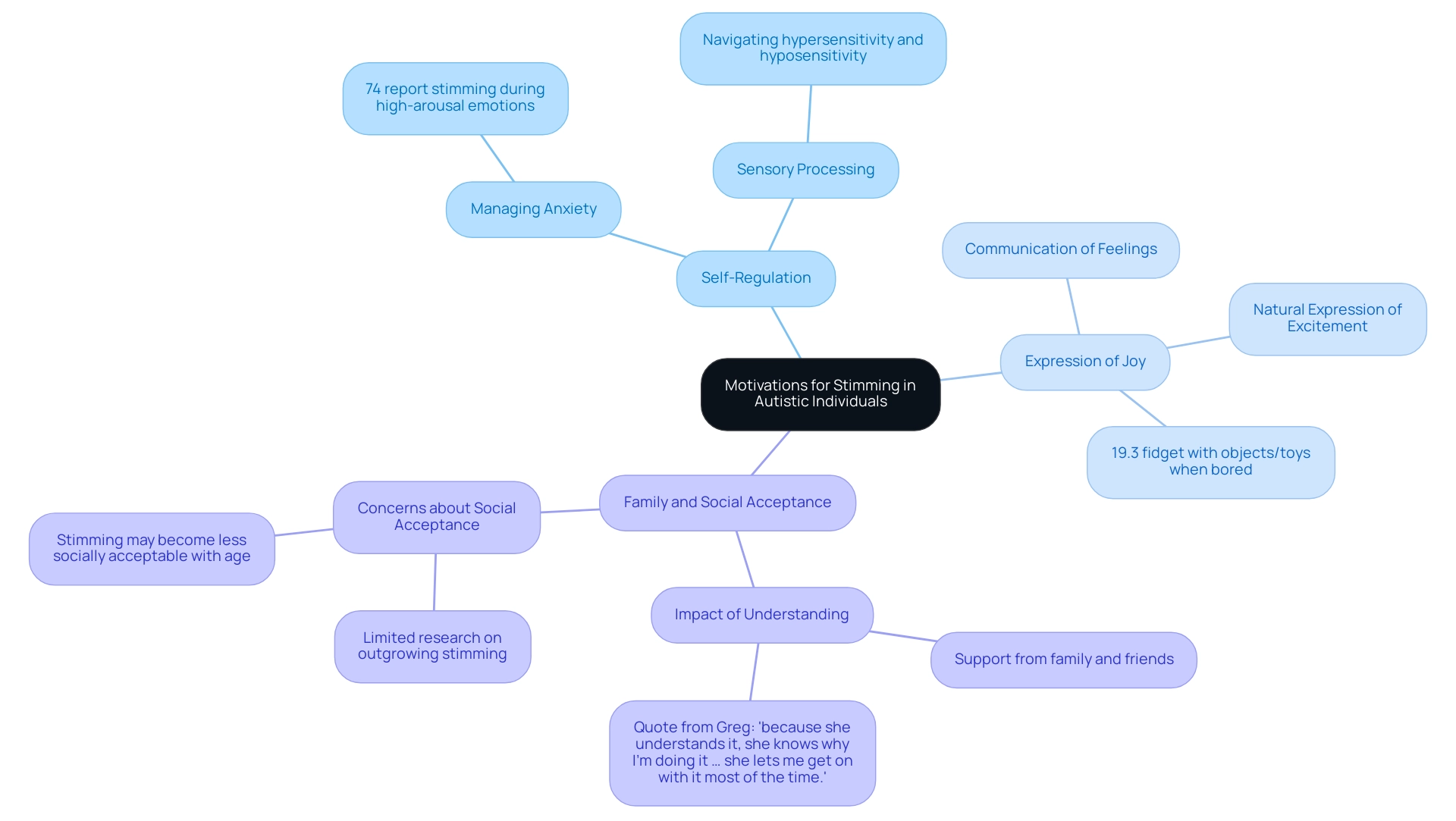
Why Do Autistic Individuals Stim? Exploring the Motivations
Autistic individuals engage in stimming for a variety of reasons, each serving a unique purpose in their daily lives.
- Self-Regulation: Stimming often acts as a vital tool for managing anxiety and overwhelming emotions. Research indicates that many individuals stim during high-arousal emotional states, such as anxiety and excitement. In a study titled "Stimming Behavior Autism and Emotional Responses," it was found that 74% of participants reported stimming behavior autism throughout most of their day, particularly when experiencing intense emotions.
Stimming behavior autism assists individuals in seeking or blocking information, enabling them to sustain a comfortable state of perception. This is crucial for those who may be hypersensitive or hyposensitive to sensory stimuli, as it enables them to navigate their environments more effectively.
- Expression of Joy: For many, repetitive movements function as a natural expression of excitement or happiness. It provides a way to communicate feelings that may be difficult to articulate verbally.
Understanding these motivations is essential for parents, as it fosters a nurturing atmosphere where self-soothing actions are acknowledged as a coping strategy rather than something to be inhibited. Statistics indicate that 19.3% of people exhibit stimming behavior autism by fidgeting with items or toys when uninterested, highlighting the widespread nature of repetitive actions among autistic individuals and underscoring the necessity for understanding and acceptance.
Moreover, perspectives from relatives and acquaintances significantly affect the acceptance of these repetitive actions. When family and friends comprehend the reasons behind these actions, they can offer the essential support, allowing individuals to engage in such activities without stigma. As one individual expressed, "because she understands it, she knows why I’m doing it … she lets me get on with it most of the time."
It is also important to recognize that there is limited research on whether individuals on the autism spectrum outgrow self-stimulatory actions. Some participants in surveys have indicated that self-stimulatory behaviors may become less socially acceptable as they age, which can raise concerns for parents.
In summary, acknowledging the complex nature of repetitive actions enables parents to better support their children, facilitating a deeper understanding of how these activities contribute to self-regulation and sensory processing.
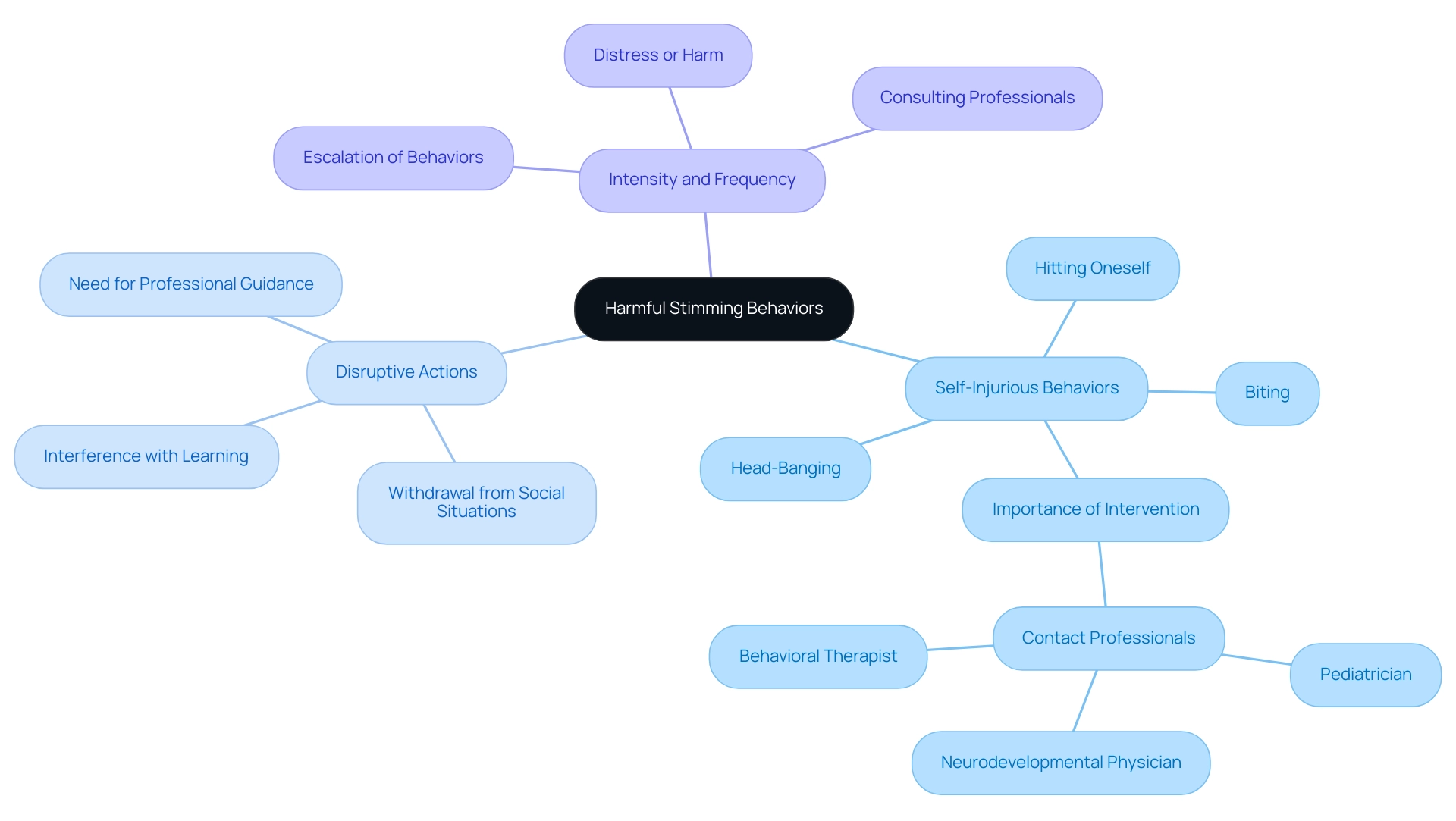
When to Be Concerned: Identifying Harmful Stimming Behaviors
While many repetitive actions serve as harmless self-regulation mechanisms, some stimming behaviors in autism can understandably raise concerns for parents. It’s important to keep an eye on certain types of stimming that may signal a need for intervention:
- Self-Injurious Behaviors: Actions like head-banging, biting, or hitting oneself can be alarming and deserve immediate attention. Research shows that approximately 70 percent of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may also face co-occurring mental health challenges, which can exacerbate these symptoms. If your child begins to display self-harming behaviors, it’s crucial to reach out to your pediatrician, neurodevelopmental physician, or behavioral therapist as soon as possible, as recommended by Eboni I. Lance M.D.
- Disruptive Actions: Stimming that disrupts daily activities or social interactions can hinder a child's ability to engage with their surroundings and peers. For example, behaviors that lead to withdrawal from social situations or interfere with learning may necessitate professional guidance.
- Intensity and Frequency: If stimming behaviors escalate in intensity or frequency to the point of causing distress or harm, seeking help becomes essential. Behavioral therapists advise parents to consult with professionals upon noticing significant changes in their child’s stimming patterns.
In these circumstances, expert advice highlights the importance of fostering a supportive environment. Parents are encouraged to maintain open communication with their children, nurturing empathy and understanding. A case study titled "Advice for Parents of Autistic Individuals Who Self-Harm" reveals that discovering your child is self-harming can be distressing. Parents are urged to seek support while learning how to effectively assist their loved ones through empathy and open dialogue.
By addressing underlying concerns and providing appropriate interventions, parents can help reduce harmful repetitive actions and enhance their children’s overall well-being. Moreover, specialists suggest that self-injury can be a learned behavior, reinforced by the reactions of others, offering parents valuable insights into the motivations behind repetitive actions. Recognizing when to be concerned about these behaviors is crucial for ensuring that young individuals receive the support they need to thrive.
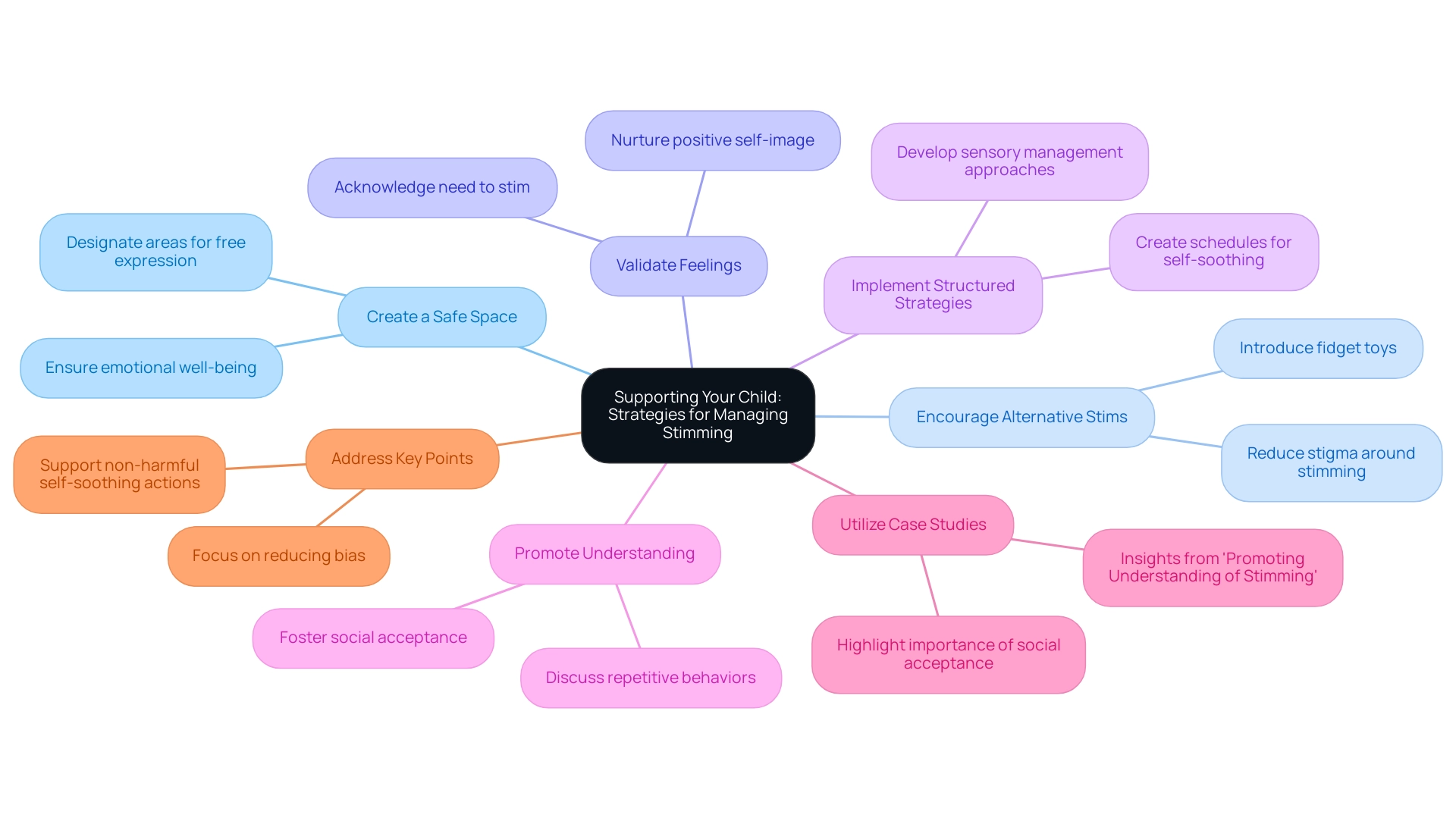
Supporting Your Child: Strategies for Managing Stimming
Supporting a child who engages in stimming behavior associated with autism requires a multifaceted approach that emphasizes understanding and acceptance. Let's explore some effective strategies together:
- Create a Safe Space: Designate areas where your child can stim freely, allowing them to express themselves without fear of judgment. This safe environment is crucial for their emotional well-being and comfort.
- Encourage Alternative Stims: Introduce fidget toys or tools that offer similar tactile input in a more socially acceptable way. Research shows that these tools can help young individuals manage their sensory needs while reducing stigma around self-stimulatory behaviors.
- Validate Feelings: Acknowledge your child's need to stim and reassure them that it's perfectly okay to express themselves. This validation nurtures a positive self-image and emotional resilience. Experts emphasize that accepting stimming behaviors can significantly enhance a child's overall well-being. As Dr. Steven K. Kapp notes, "Individuals with autism contend that stimming serves as crucial coping strategies."
- Implement Structured Strategies: Develop approaches that help manage sensory-seeking actions in a way that aligns with social norms. For instance, creating a schedule with designated times for self-soothing can empower children, helping them feel more in control and prepared for social interactions.
- Promote Understanding: Talk with your child about their repetitive behaviors, discussing how these actions assist in coping with sensory overload or emotional stress. This conversation not only empowers them but also fosters social acceptance among peers. Insights from case studies, such as those in 'Promoting Understanding of Stimming,' reveal that when autistic individuals feel accepted, they are more likely to engage in stimming openly, leading to better mental health outcomes.
- Utilize Case Studies: Consider insights from case studies that illustrate the importance of social acceptance in destigmatizing self-stimulatory behavior. For example, studies indicate that when autistic individuals feel accepted, they are more inclined to engage in self-soothing behaviors openly, resulting in improved mental health outcomes.
- Address Key Points: It's vital to focus on reducing bias and supporting non-harmful self-soothing actions. By applying these strategies, you can create an environment that not only meets your child's needs but also fosters a deeper understanding of repetitive actions within the community.
Remember, your journey in supporting your child is important, and every step you take toward understanding and acceptance makes a difference.
Creating a Safe Space: Sensory-Friendly Environments for Stimming
Creating a sensory-friendly environment is essential for supporting individuals with autism, especially in facilitating healthy stimming behavior. Consider these key strategies:
- Adjusting Lighting: Opt for soft, natural light rather than harsh fluorescent bulbs. Research shows that appropriate lighting can significantly reduce anxiety levels in autistic individuals, fostering a calmer atmosphere that is conducive to learning and interaction.
- Reducing Noise: Implement sound-absorbing materials, such as carpets and acoustic panels, to minimize auditory distractions.
Studies indicate that 73% of educators believe many autistic students encounter perceptual differences. This highlights the importance of a calm atmosphere for effective participation. Additionally, overwhelming stimuli can hinder youngsters from envisioning future job possibilities, as articulated by individuals like Cassandra and Casey.
- Organizing Space: Keep areas free of clutter to assist in minimizing overwhelming stimuli. A well-structured space can enhance concentration and ease, allowing youngsters to navigate their surroundings more simply. These modifications not only create a more pleasant atmosphere but also encourage positive self-soothing activities, which can be beneficial for processing information, particularly regarding stimming behavior. For instance, a recent study on Multi-Sensory Environments (MSE) demonstrated that interactive equipment could enhance engagement and social interaction among autistic individuals. The findings revealed that youngsters exhibited diverse actions based on their interaction with the environment, underscoring the importance of tailored perceptual experiences.
Integrating these approaches into homes and educational settings can lead to significant improvements in the well-being of autistic individuals, nurturing a space where they can thrive. As specialists in environmental psychology emphasize, the layout of a space greatly influences perceptual behaviors, making it essential to create environments that cater to the unique needs of each individual. Moreover, future studies are encouraged to assess the profiles of children with and without various pathologies and to conduct interventions in different natural settings. This could enhance their ability to manage effectively with diverse stimuli in educational contexts.
This aligns with recent calls for incorporating sensory processing considerations into the Autism and Education strategy, highlighting the timeliness and relevance of creating sensory-friendly environments.
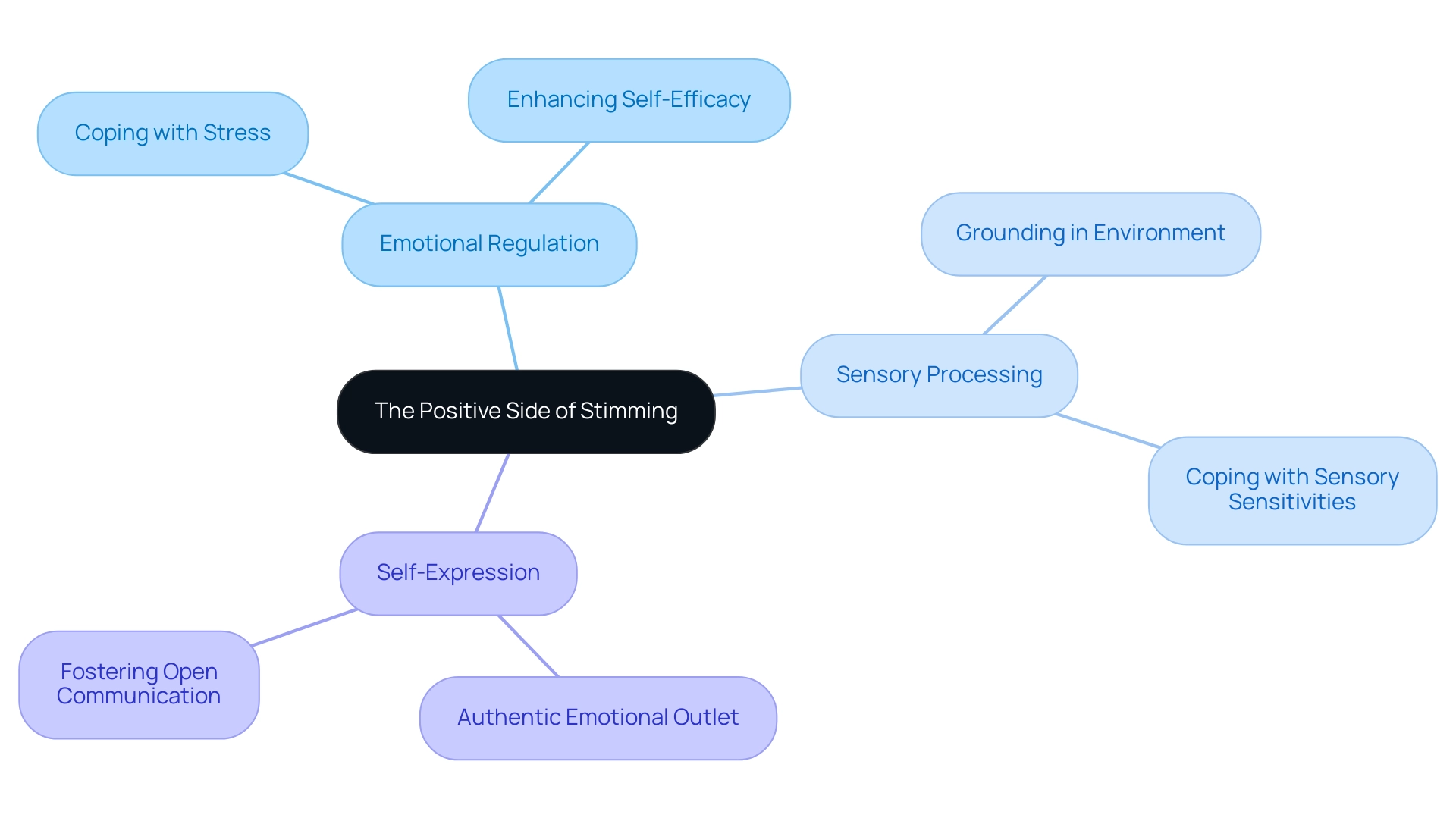
Challenging Misconceptions: The Positive Side of Stimming
Stimming, often misunderstood and viewed negatively, plays a crucial role in the lives of many autistic individuals, offering several positive aspects that deserve recognition.
Emotional regulation is one of the primary benefits of stimming. For many individuals, engaging in these repetitive behaviors serves as a vital tool for managing emotions and coping with stress. They often find that stimming helps them navigate overwhelming feelings, providing a sense of calm and stability. In fact, studies indicate that stimming behavior can significantly enhance self-efficacy, particularly among autistic individuals, allowing them to better manage everyday challenges.
Additionally, stimming aids in sensory processing. For many, self-soothing behaviors provide essential input that helps ground them in their environment. This conduct can reduce overwhelming stimuli, enabling individuals to engage with their surroundings more efficiently. Research has demonstrated that autistic individuals frequently encounter increased sensitivities, and stimming behaviors, including repetitive movements, can act as a coping strategy to alleviate these challenges. A study named "The Complex Experiences of Autistic Adults" emphasizes the commonness of sensitivities and stimming in autistic individuals, illustrating how these repetitive actions can improve self-efficacy and function as a helpful coping mechanism.
Moreover, stimming allows for self-expression. It provides individuals with a means to express their feelings in a way that feels authentic and natural. This form of self-expression is crucial for emotional well-being, as it offers an outlet for feelings that might otherwise be difficult to articulate. Embracing self-regulatory actions fosters environments where individuals can convey themselves openly, resulting in favorable experiences in autism-accepting settings. As Steven K Kapp noted, "Greater understanding of such repetitive behaviors may, therefore, help elucidate appropriate support for a variety of people."
Recognizing these advantages enables parents to accept their child's self-soothing actions, realizing that they are not merely repetitive movements but significant expressions of emotional and physical needs. As the neurodiversity movement gains traction, the emphasis on supporting non-harmful self-soothing actions continues to grow, reinforcing the idea that these practices are integral to the well-being of autistic individuals. In a recent study, only 6% of participants indicated that self-stimulatory behavior was generally negative, highlighting the predominantly positive effect it can have on emotional regulation and perception.
In summary, stimming encompasses multifaceted self-stimulatory actions that play a significant role in emotional regulation, sensory processing, and self-expression for autistic individuals. By fostering an understanding of these positive aspects, parents can better support their children in navigating the complexities of their experiences.
Resources for Parents: Finding Support and Information
For parents seeking additional support and information about stimming and autism, a wealth of valuable resources awaits you:
- National Autistic Society: This organization provides comprehensive guides and support tailored for families, helping them understand autism and its associated behaviors, including stimming.
- Autism Speaks: As a leading resource, Autism Speaks offers extensive information on autism, equipping parents with practical resources to navigate their unique challenges.
- Local Support Groups: Connecting with other parents can be incredibly beneficial. These groups not only provide emotional support but also facilitate the sharing of experiences and strategies. Research shows that involvement in support groups can significantly boost parenting confidence and lessen stress, leading to better outcomes for young ones. Indeed, studies indicate that caregiver-mediated interventions enhance parenting confidence and decrease stress, which is crucial for effective support.
- Caregiver-Mediated Interventions: Engaging in interventions that involve caregivers has shown promise in improving parenting skills and reducing stress. For instance, combining these interventions with stress-reduction techniques, such as Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) and Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR), can enhance the effectiveness of the strategies implemented at home. A case study titled "Strategies to Enhance Caregiver Implementation" highlights that chronic stress can impede the ability to learn and implement new strategies, underscoring the importance of caregiver motivation and support.
- Expert Recommendations: Professionals in the field encourage parents to actively seek out information and support tailored to their specific needs. This can include workshops, online forums, and local community resources that focus on stimming behavior, autism, and sensory processing.
- Statistics: It's important to note that ASD prevalence among non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander youth is 33.4%, underscoring the need for accessible resources and support for diverse communities. Additionally, CDC data estimates a male-to-female ratio of 4:1 in autism, but other research suggests a ratio closer to 3:1, highlighting the varying experiences of families affected by autism.
By leveraging these resources, parents can navigate their journey with greater confidence and understanding, ultimately fostering a supportive environment for their children. ASD Media is dedicated to fostering collaboration and growth in the ABA therapy industry, providing a platform for parents and professionals to share experiences and strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding stimming is crucial for parents of autistic children. These behaviors play a significant role in emotional regulation and sensory processing. Stimming includes a variety of repetitive actions, like hand-flapping, rocking, and vocalizations. Each action serves unique purposes—self-soothing, expressing excitement, or managing sensory overload. By recognizing the different types of stimming and their motivations, caregivers can create a nurturing environment that validates and supports their child's individual needs.
Fostering acceptance and understanding of stimming behaviors is essential. They are not merely repetitive actions but vital forms of self-expression for many autistic individuals. Parents can implement various strategies, such as:
- Creating safe spaces for stimming
- Encouraging alternative sensory tools
- Promoting open communication about these behaviors
This proactive approach helps children manage their sensory experiences and cultivates empathy and acceptance within their communities.
While most stimming behaviors are benign, awareness of potentially harmful actions is necessary. Parents should monitor for self-injurious or disruptive stimming and seek professional guidance when needed. By addressing these concerns and emphasizing the positive aspects of stimming—like emotional regulation and sensory processing—parents can empower their children to navigate their unique experiences confidently.
Embracing stimming as a legitimate and beneficial behavior enables parents to provide better support for their autistic children. By fostering an understanding of the complexities surrounding stimming, caregivers can help cultivate a more accepting society that values the individuality of each child. This ultimately enhances their overall well-being and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stimming behavior in autism?
Stimming behavior in autism encompasses a variety of self-stimulatory activities characterized by repetitive movements or sounds, such as hand-flapping, rocking, spinning, and vocalizations. These actions serve multiple purposes, including self-soothing, managing sensory overload, and expressing excitement.
Why is stimming behavior important for individuals with autism?
For many autistic individuals, stimming is a natural and vital part of their lives, providing comfort and assisting in emotional regulation. It helps them manage their sensory experiences and emotional needs.
What recent research has been conducted on stimming behavior?
An exploratory study titled "Reconceptualizing Autistic Stimming" emphasizes the importance of understanding stimming behavior and advocates for collaboration with autistic individuals to gain insights into their experiences and the role stimming plays in their lives.
How does stimming behavior relate to self-efficacy?
Statistics indicate that self-efficacy scores related to repetitive behaviors are significantly higher when individuals can engage in stimming activities, suggesting that participation in self-soothing behaviors contributes to greater emotional stability and confidence.
What strategies can parents use to support their children's stimming behavior?
Effective strategies for managing repetitive behaviors include creating safe spaces for stimming, integrating sensory-friendly activities, and using tools like sticky notes to enhance understanding of the causes and functions of these behaviors.
What are the different types of stimming behavior?
Stimming behavior can be classified into several types: 1. Visual Stimming: Engaging with visual stimuli, such as watching spinning objects or lights. 2. Auditory Stimming: Making repetitive sounds, like humming or tapping. 3. Tactile Behavior: Seeking input through touch, such as rubbing different textures. 4. Vestibular Sensory Activities: Movements involving balance and motion, like rocking or swinging.
How does understanding stimming behavior benefit parents and children?
Understanding stimming behavior enables parents to recognize their children's preferred self-soothing techniques and create supportive environments that address their perceptual needs, ultimately fostering a more compassionate approach to their development.
What role does technology play in supporting individuals with autism?
Advances in technology, such as socially assistive robotics, show promise in enhancing the social skills of individuals with autism by providing interactive opportunities for practicing social interactions, thereby improving communication skills and confidence.




