Overview
Understanding pervasive developmental disorder (PDD) is crucial for parents and caregivers because it encompasses a range of conditions, including Autism Spectrum Disorder, that significantly impact socialization and communication skills. The article emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and intervention, as well as the need for accurate information to dispel misconceptions, ultimately highlighting how tailored support can improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) can be a daunting journey for families, yet it is one that is increasingly important to understand. This spectrum of conditions, which includes Autism Spectrum Disorder and Asperger's Syndrome, affects a significant number of children, highlighting the urgent need for effective interventions and support systems.
As awareness grows, so does the recognition of early diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies as critical components in improving outcomes for affected individuals. From identifying symptoms to exploring treatment options like Applied Behavior Analysis, this article delves into the multifaceted approaches necessary for fostering communication, social skills, and overall well-being in children with PDD.
By building supportive networks and dispelling common misconceptions, parents and caregivers can empower themselves and their children to thrive in a world that often misunderstands the challenges of developmental disorders.
What is Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD)?
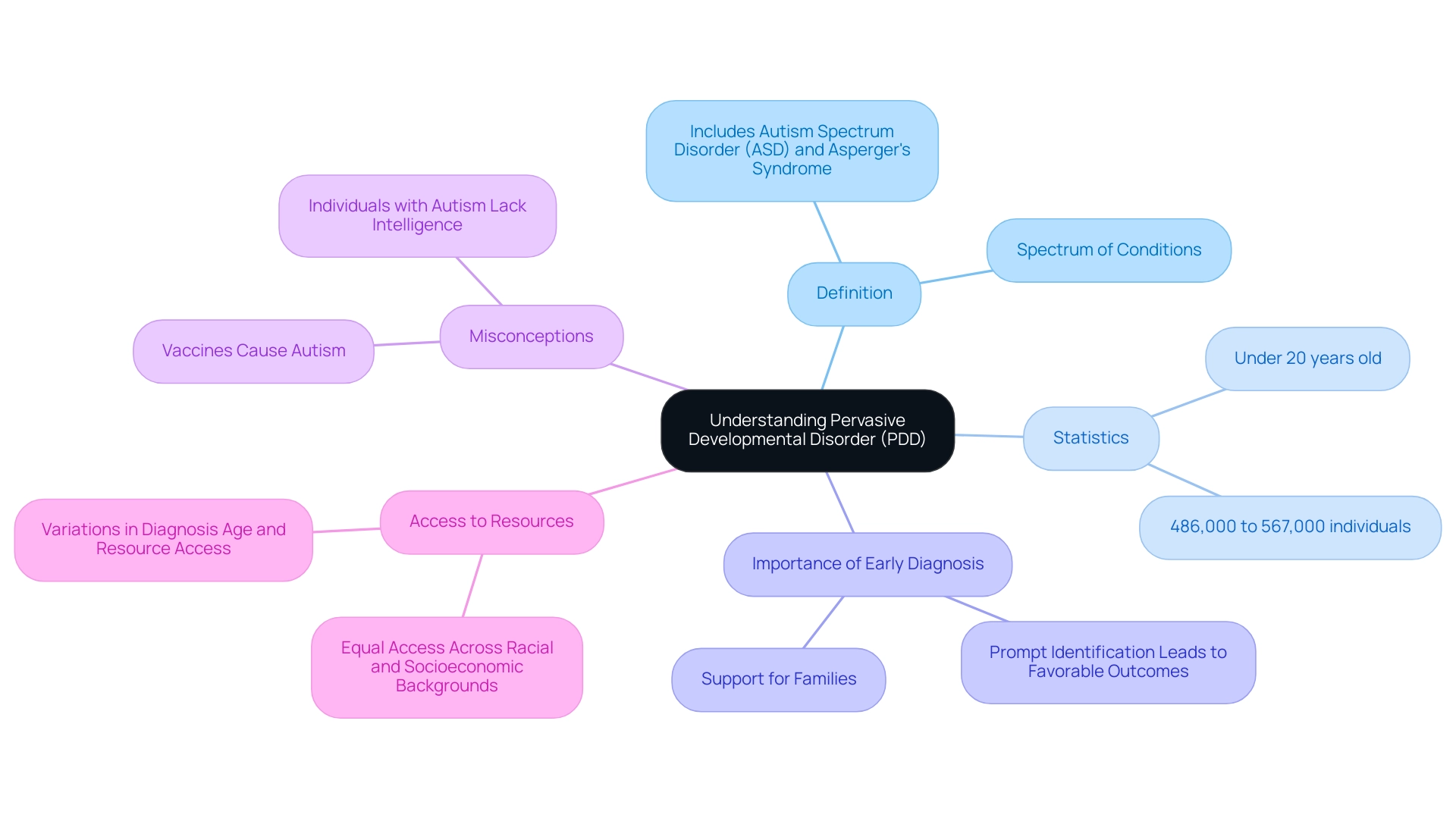
Pervasive developmental disorder (PDD) refers to a spectrum of conditions characterized by significant delays in socialization and communication skills. This classification includes Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Asperger's Syndrome, among others. Current estimates suggest that between 486,000 and 567,000 individuals under 20 years old in the U.S. have a pervasive developmental disorder, highlighting the urgent need for effective services and support tailored for this population.
Understanding pervasive developmental disorder is vital for parents and caregivers, as it profoundly affects how young ones interact with their surroundings and develop essential social skills. Early diagnosis and intervention are especially vital; research emphasizes that prompt identification can lead to more favorable outcomes for individuals on the spectrum. As Laura NG, a Clinical Operations Manager, aptly states,
It is important to dispel these misconceptions and promote accurate information and understanding about autism.
This approach ensures that families receive the necessary support and resources, enabling them to navigate the complexities of pervasive developmental disorder effectively. Moreover, autism does not discriminate; it affects individuals across all racial and socioeconomic backgrounds, with similar prevalence rates but variations in diagnosis age and access to resources. Ensuring equal access to these resources is fundamental to enhancing the overall well-being of those affected by pervasive developmental disorder.
Additionally, common misconceptions about autism, such as the belief that individuals with autism lack intelligence or that vaccines cause autism, have been debunked by scientific research and must be addressed to foster a more accurate understanding of PDD.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Pervasive Developmental Disorder
Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) encompasses a range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual's ability to communicate, interact socially, and engage in typical behaviors. Common indicators may include:
- Challenges in verbal and non-verbal communication
- Difficulties in understanding and responding to social cues
- A tendency for repetitive behaviors
For instance, a child might avoid eye contact, exhibit intense focus on specific subjects, or struggle to initiate conversations.
According to Benjamin Zablotsky, during 2019–2021, the prevalence of any developmental disability was higher in boys (10.76%) than girls (5.31%). This statistic highlights the necessity for vigilance among parents, especially considering the public health challenge of late diagnoses in the United States, which can hinder early assistance efforts. Identifying these symptoms early is essential, as it can lead to timely assessments and strategies that promote growth and improve quality of life.
Pediatricians stress the importance of documenting concerning behaviors and seeking professional guidance when patterns arise. Such prompt assistance is crucial, with research showing that effective support can greatly enhance results for youngsters with a pervasive developmental disorder. Moreover, differences in prevalence among demographic groups, such as Hispanic, Black, Asian, and White youth, highlight the varying impacts of developmental disabilities, further emphasizing the urgency for early recognition and customized support.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Pervasive Developmental Disorder
Treatment for pervasive developmental disorder typically requires a multifaceted approach, as each child presents unique needs and strengths. Common therapies include:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- Speech therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Social skills training
ABA, in particular, has demonstrated potential in promoting communication, social interactions, and self-care skills through organized approaches.
A meta-analysis focused on ABA-based interventions noted potential effectiveness in areas such as socialization and expressive language, although overall effectiveness for general symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) remains inconclusive, with no significant heterogeneity across studies for receptive language (I = 0%, p = 0.52) and no significant effectiveness in the overall synthesis (p = 0.84). This highlights the necessity for parents to work closely with healthcare professionals in developing a comprehensive treatment plan. By incorporating various therapies, caregivers can ensure a holistic approach that maximizes assistance for their children while addressing specific challenges.
Experts emphasize that evidence-based practice in ABA is crucial, as it integrates the best available evidence with clinical expertise and client values, leading to more ethical and effective treatment decisions. As one expert, Weiyi Liang, noted,
This study was supported by the Joint Construction Project of Henan Medical Science and Technology Research Plan (No.2018020223),
underscoring the significance of structured support systems in treatment outcomes. Additionally, the findings from the study on the effectiveness of ABA-based approaches suggest that while these methods showed promise in specific areas, overall effectiveness for general symptoms of ASD was not supported.
The call for further research into optimal interventions for high-functioning individuals with ASD reinforces the ongoing need for adaptive and responsive therapeutic strategies.
Building a Support Network for Parents and Caregivers
Establishing a robust assistance network is crucial for alleviating the stress that often accompanies raising a child with a pervasive developmental disorder. Parents are encouraged to explore local assistance groups as well as online communities dedicated to autism and developmental disorders. These interactions can lead to valuable insights, emotional encouragement, and shared strategies for navigating daily challenges.
Notably, research indicates that perceived stress among parents in urban settings, such as a community-based study conducted in Delhi in 2020, highlights the importance of these networks in mitigating family stress. Furthermore, a Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of 0.874 for the Index of Wellbeing and Index of General Affect highlights the effectiveness of these assistance systems in enhancing parental well-being. Working together with teachers and healthcare specialists can further improve the assistance framework, ensuring that the young person's needs are effectively represented in both educational and therapeutic settings.
By fostering these connections, parents not only find solace in shared experiences but also empower themselves to advocate for their offspring more effectively. As one parent noted, the ability to discuss challenges with others facing similar struggles is an invaluable resource in their journey. Additionally, 94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good, reinforcing the credibility of the information regarding parental stress and support networks.
Utilizing current resources and engaging with established networks can significantly bolster the well-being of both parents and youngsters navigating the complexities of pervasive developmental disorder.
The Role of Applied Behavior Analysis in Managing Pervasive Developmental Disorder
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a structured method focused on understanding and improving specific behaviors through targeted strategies. This methodology involves deconstructing complex skills into smaller, more manageable tasks and reinforcing positive behaviors to promote learning. For individuals with a pervasive developmental disorder, ABA can significantly assist in developing essential communication, social skills, and daily living abilities.
As one parent expressed, "Well, gosh. If I had the answer to this question, I could solve all my son’s problems," highlighting the emotional challenges faced by families. Research indicates that roughly one-quarter of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) may experience regression in language or social skills, typically between 18 and 24 months, underscoring the need for effective interventions.
Additionally, psychiatric conditions are identified in 70% to 90% of young individuals with ASD, further illustrating the necessity for comprehensive support. By collaborating with certified ABA therapists, parents can create tailored programs that cater to their individual needs, fostering an environment conducive to learning and growth. A case study titled "The Importance of Clear Communication Between Therapists and Families" emphasizes the necessity of clear communication, detailing strategies to facilitate open dialogue and understanding.
The overarching aim is to empower young individuals to achieve their fullest potential while enhancing their overall quality of life. With the right support, children diagnosed with a pervasive developmental disorder can experience marked improvements in their interactions and daily functioning, reflecting the positive impact of ABA techniques.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) is crucial for improving the lives of affected children and their families. This spectrum of conditions, including Autism Spectrum Disorder and Asperger's Syndrome, presents unique challenges that require early diagnosis and tailored interventions. Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to timely assessments, which are vital in implementing effective treatment strategies.
Effective treatments, such as:
- Applied Behavior Analysis
- Speech therapy
- Occupational therapy
offer promising avenues for fostering communication and social skills. However, it is essential for parents to collaborate with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive and adaptable treatment plan that meets their child's specific needs.
Equally important is the establishment of strong support networks for parents and caregivers. Engaging with local and online communities can provide invaluable emotional support and practical strategies for navigating daily challenges. By fostering these connections and advocating for their children's needs, families can empower themselves and enhance their overall well-being.
In conclusion, the journey through PDD can be daunting, but with early recognition, effective treatment strategies, and robust support systems, families can navigate this complex landscape. By building awareness and understanding, society can create a more inclusive environment where children with PDD can thrive and reach their fullest potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is pervasive developmental disorder (PDD)?
Pervasive developmental disorder (PDD) refers to a spectrum of conditions characterized by significant delays in socialization and communication skills, including Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Asperger's Syndrome.
How many individuals in the U.S. are estimated to have a PDD?
Current estimates suggest that between 486,000 and 567,000 individuals under 20 years old in the U.S. have a pervasive developmental disorder.
Why is understanding PDD important for parents and caregivers?
Understanding PDD is vital for parents and caregivers because it profoundly affects how young individuals interact with their surroundings and develop essential social skills.
What role does early diagnosis and intervention play in PDD?
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial as research indicates that prompt identification can lead to more favorable outcomes for individuals on the spectrum.
What misconceptions about autism need to be addressed?
Common misconceptions include the belief that individuals with autism lack intelligence or that vaccines cause autism. These have been debunked by scientific research.
How does PDD affect individuals across different demographics?
Autism does not discriminate and affects individuals across all racial and socioeconomic backgrounds, although there are variations in diagnosis age and access to resources.
What are some common symptoms of PDD?
Common symptoms of PDD may include challenges in verbal and non-verbal communication, difficulties in understanding and responding to social cues, and a tendency for repetitive behaviors.
What statistics highlight the prevalence of developmental disabilities in boys versus girls?
During 2019–2021, the prevalence of any developmental disability was higher in boys (10.76%) than in girls (5.31%).
Why is it important for parents to document concerning behaviors in their children?
Documenting concerning behaviors is essential as it allows parents to seek professional guidance and facilitate timely assessments and strategies that promote growth and improve quality of life.
How do differences in prevalence among demographic groups affect the urgency for early recognition of PDD?
Differences in prevalence among demographic groups, such as Hispanic, Black, Asian, and White youth, highlight the varying impacts of developmental disabilities, emphasizing the need for early recognition and customized support.




