Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) can be a daunting journey for caregivers, but understanding its nuances is crucial for fostering the best outcomes for children. PDD encompasses a spectrum of disorders, including Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), which presents unique challenges in socialization and communication.
As prevalence rates continue to rise, awareness and early intervention become more vital than ever. By recognizing symptoms, engaging in thorough assessments, and exploring effective treatment options, caregivers can empower themselves to advocate for their children’s needs.
This article delves into the critical aspects of PDD, offering insights and resources designed to support caregivers in their efforts to navigate this intricate landscape and ensure their children receive the care they deserve.
Understanding Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD): An Overview
Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) encompasses a range of disorders, including Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and others, marked by significant delays in socialization and communication skills. Recent statistics indicate that among a study of 19,490 youths, the prevalence rates for developmental disorders reveal:
- ASD at 3.11%
- ADHD/ADD at 9.50%
- Intellectual disabilities (ID) at 1.85%
- Other developmental disorders (DD) at 5.66%
- Learning disabilities at 7.49%
Understanding PDD symptoms is essential for those providing care, as it allows them to recognize early signs and seek timely interventions, which can significantly improve outcomes.
The economic burden of ASD in the United States is substantial, with annual costs estimated between $11.5 billion and $60.9 billion, encompassing medical care, special education, and lost parental productivity. Children with ASD incur average medical expenditures significantly higher than those without ASD, highlighting the financial challenges families face. Additionally, as highlighted by Guang Yang, 'Our study reveals an increase in ASD prevalence and persistent disparities among racial-ethnic groups.'
Acknowledging these differences and the ongoing discussions, including the case-control study on MMR vaccination and the impact of PDD symptoms, is a crucial first step in effectively supporting youth with pervasive developmental disorders, ensuring they receive the necessary resources and interventions tailored to their specific needs.
Recognizing the Symptoms of PDD: Key Indicators for Caregivers
Recognizing the PDD symptoms is crucial for caregivers of individuals with Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD). Common behavioral indicators include:
- Difficulties in social interactions, such as challenges in understanding social cues, engaging in conversations, and forming relationships.
- Repetitive behaviors.
- Limited interests.
- Communication difficulties, including delayed speech or a lack of response to verbal cues.
According to Stephen J. Blumberg from the National Center for Health Statistics, 'the complexities of assessing young individuals with PTSD can lead to missed diagnoses.' The average prevalence of autistic disorder is approximately 20.6 per 10,000 individuals, underscoring the relevance of these observations. The study acknowledged limitations in diagnosing PDD symptoms, which include the potential for missed diagnoses and the complexity of evaluating young individuals with PDDs.
Therefore, guardians should stay attentive in monitoring their offspring's behavior, particularly when there are significant deviations from usual developmental milestones. This proactive approach is essential, as timely intervention can significantly influence a young person's development. If caregivers notice ongoing concerns, consulting with a pediatrician or a specialist can provide clarity and support, ensuring that young individuals receive the necessary resources for their growth and well-being.
Diagnosing PDD: Understanding the Assessment Process
Diagnosing Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) requires a thorough and collaborative evaluation by a dedicated team of professionals, including psychologists, speech therapists, and pediatricians. This comprehensive assessment typically encompasses:
- A review of developmental history
- Careful behavioral observations
- The use of standardized tests tailored to gauge the individual's unique needs
Caregivers are essential to this process, as they provide invaluable insights into their offspring's development and behaviors.
It is essential for them to come prepared with questions and to share any concerns, ensuring that every facet of their development is taken into account. By actively participating in the assessment, caregivers can help foster a holistic understanding that is critical for accurate diagnosis and effective intervention. Acknowledging that obstacles to mental health care can affect access to these crucial services highlights the significance of promoting thorough assessments that do not neglect any element of a young person's well-being.
With individuals with mental health disorders facing a 60% higher risk of obesity, understanding the broader implications of mental health is crucial. Jenna Carberg, co-founder of PostpartumDepression.org, emphasizes the importance of support, stating that it is vital for women suffering in silence and their loved ones. Furthermore, access to mental health care remains a critical issue, with 45% of those needing care not receiving it due to barriers like cost and stigma, as highlighted in a case study on access to mental health services.
This reinforces the need for comprehensive evaluations in the assessment process for PDD symptoms.
Treatment Approaches for PDD: Supporting Individuals Effectively
When exploring treatment alternatives for Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD), Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy stands out as a prominent method, showing an impressive success rate surpassing 89% in addressing PDD symptoms in youngsters with autism spectrum disorder. This therapy is designed to enhance specific behaviors and skills, making it a vital component of a comprehensive treatment strategy. Complementing ABA, speech therapy and occupational therapy play crucial roles in tackling communication hurdles and sensory processing issues.
It’s essential for caregivers to collaborate closely with therapists to tailor individualized treatment plans that align with their unique needs. Regular progress assessments are not just beneficial; they are imperative. They allow for timely adjustments to the treatment plan, ensuring that the interventions remain effective and aimed at achieving positive outcomes.
Recent research by Shokoohirad M. and Rahim Zadeh S. has evaluated the effectiveness of ABA programs on youth's emotional and social skills, further supporting its role in therapy. Additionally, Weihong Xu emphasizes the importance of ongoing assistance, stating, 'Continuous adaptation in therapy is key to achieving lasting improvements.' Furthermore, a case study titled 'Patient Outcomes and Service Discontinuation' highlights that most discontinuations of ABA services are often unrelated to treatment progress.
This finding suggests the need for ongoing exploration into the reasons behind service discontinuation and the development of additional outcome measures. Such insights reaffirm the importance of ongoing assistance and adaptation in therapy, underscoring that a steadfast commitment to effective treatment can lead to significant improvements in the lives of young individuals.
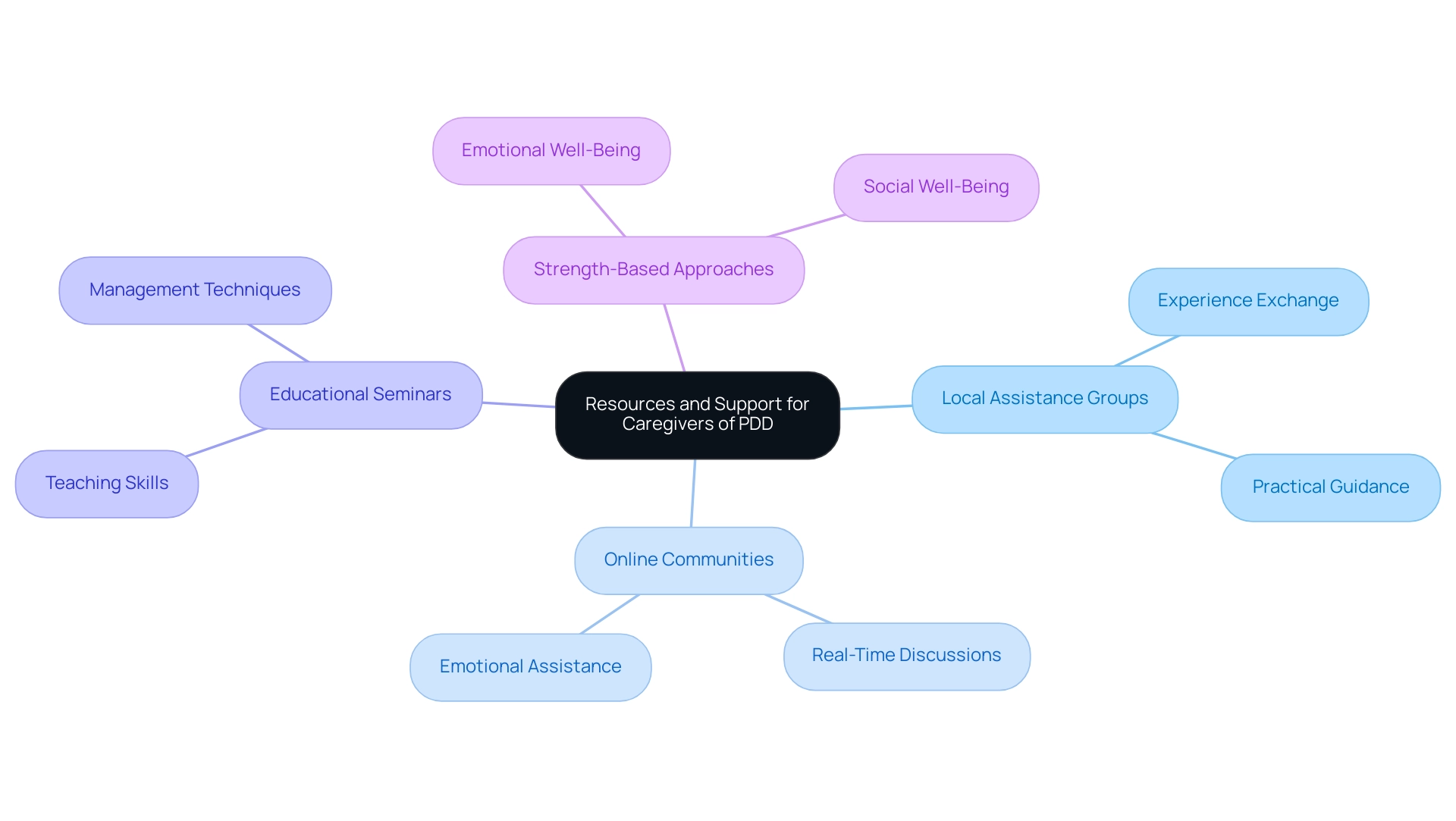
Empowering Caregivers: Resources and Support for Managing PDD
Caregivers of children experiencing PDD symptoms have access to a multitude of resources and assistance systems that can significantly enhance their ability to navigate daily challenges. Local autism assistance groups function as essential centers for connection, where individuals can exchange experiences and receive practical guidance. Online communities further expand this network, offering a platform for real-time discussions and emotional assistance.
Numerous groups provide educational seminars aimed at preparing guardians with effective management techniques suited to the specific requirements of their offspring, particularly in relation to PDD symptoms. After attending four sessions, one parent expected to learn teaching skills and strategies to manage their son's energy, illustrating the concrete benefits of these resources. Furthermore, insights from a study titled 'Conclusions on DMP Effectiveness' emphasize the importance of a strength-based approach, revealing that participants found the intervention beneficial for their emotional and social well-being.
By engaging with these platforms, caregivers can feel empowered and better prepared to advocate for their children, ensuring they receive the support needed to thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) is essential for caregivers, as it provides a framework for recognizing symptoms and seeking timely interventions that can profoundly influence a child's development. By identifying the key behavioral indicators of PDD, caregivers can take proactive steps to consult with professionals who can guide them through the assessment and diagnosis process. This collaborative approach not only fosters a comprehensive understanding of the child's needs but also empowers caregivers to be active participants in their child's care.
Effective treatment options, including Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and supportive therapies, can lead to significant improvements in communication and social skills. It is crucial for caregivers to remain engaged in their child's treatment plan, ensuring that it is tailored to their unique requirements and adjusted as necessary. Continuous support and adaptation in therapy are vital for achieving lasting outcomes, highlighting the importance of a steadfast commitment to the child's well-being.
Ultimately, the journey through PDD can be challenging, but caregivers are not alone. Numerous resources, support groups, and educational opportunities are available to help navigate these complexities. By leveraging these tools and connecting with others, caregivers can advocate effectively for their children, ensuring they receive the care and support they deserve. Embracing this journey with knowledge and community support can lead to positive outcomes, empowering both children and their families to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD)?
Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) encompasses a range of disorders, including Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), characterized by significant delays in socialization and communication skills.
What are the prevalence rates for various developmental disorders based on recent statistics?
The prevalence rates among a study of 19,490 youths are as follows: ASD at 3.11%, ADHD/ADD at 9.50%, Intellectual disabilities (ID) at 1.85%, Other developmental disorders (DD) at 5.66%, and Learning disabilities at 7.49%.
Why is understanding PDD symptoms important for caregivers?
Understanding PDD symptoms is essential for caregivers as it helps them recognize early signs and seek timely interventions, which can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with PDD.
What is the economic burden of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in the United States?
The annual costs associated with ASD in the United States are estimated between $11.5 billion and $60.9 billion, covering medical care, special education, and lost parental productivity.
What are common behavioral indicators of PDD?
Common behavioral indicators of PDD include difficulties in social interactions, repetitive behaviors, limited interests, and communication difficulties such as delayed speech or lack of response to verbal cues.
What challenges exist in diagnosing PDD symptoms?
There are complexities in assessing young individuals with PDD, which can lead to missed diagnoses. The average prevalence of autistic disorder is approximately 20.6 per 10,000 individuals, highlighting the importance of accurate assessments.
What should caregivers do if they notice concerns regarding their child's development?
Caregivers should monitor their child's behavior for significant deviations from usual developmental milestones. If ongoing concerns arise, consulting with a pediatrician or specialist can provide clarity and necessary support.




