Overview
Medication for autism in adults is essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life, with various options such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, stimulants, and anti-anxiety medications tailored to individual needs. The article illustrates this by detailing the specific roles and effectiveness of each medication type, emphasizing the importance of personalized treatment plans and ongoing collaboration between healthcare providers and caregivers to navigate potential challenges in medication management.
Introduction
Navigating the world of medication for adults with autism can be both a challenging and empowering journey. With a variety of options available, understanding the specific roles of different medications is crucial for enhancing the quality of life for individuals on the spectrum. From antidepressants that help stabilize mood to antipsychotics that manage severe behavioral issues, each category offers unique benefits tailored to address specific symptoms.
As the landscape of autism treatment continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly important for advocates and caregivers to stay informed about the latest developments in medication management. This article delves into the various medication options, their applications, and the importance of integrating these treatments with therapy and support services, ultimately equipping parents and advocates with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions for their loved ones.
Overview of Medication Options for Adults with Autism
Adults with developmental disorders have access to a range of treatment options, such as medication for autism in adults, aimed at managing symptoms and improving overall quality of life. Each category plays a crucial role in addressing specific challenges faced by individuals on the spectrum:
- Antidepressants: These medications are frequently prescribed to combat anxiety and depression, helping to stabilize mood and alleviate distress. Research indicates that when used appropriately, medication for autism in adults can significantly enhance emotional regulation in those with developmental disorders.
- Antipsychotics: Essential for managing severe behavioral issues and mood swings, antipsychotics serve as a type of medication for autism in adults, offering a calming effect that makes daily interactions more manageable. Notably, the use of medication for autism in adults, such as risperidone and valproate, is prevalent among specific age groups, particularly those aged ≥ 15 years, as highlighted in the study titled "Utilization of Psychopharmacological Treatments for ASD in Macedonia." This demonstrates the significance of medication for autism in adults in care plans.
- Stimulants: Occasionally used as a medication for autism in adults to address attention difficulties, particularly when ADHD symptoms are present, stimulants can enhance focus and reduce impulsivity. However, expert opinions suggest that non-stimulants may be more suitable than stimulants for many autistic patients, highlighting the need for personalized medication for autism in adults based on their unique clinical profiles.
- Medication for autism in adults: These are specifically aimed at lowering anxiety levels that can hinder their daily functioning. By addressing anxiety, people can experience improved engagement in social situations and other activities, which may be enhanced with medication for autism in adults.
Comprehending the distinct purposes of each type of medication for autism in adults is vital, as the appropriate choice will depend on individual needs and circumstances. Recent studies, including a review published in JAMA, emphasize the ongoing exploration of medication for autism in adults and their effectiveness in treating autism-related symptoms. Furthermore, it's crucial to recognize that the World Health Organization estimates that 1 in every 100 children worldwide has a developmental disorder, emphasizing the importance of exploring medication for autism in adults as treatment alternatives for this population.
As the landscape of treatment options, such as medication for autism in adults, continues to evolve, Parent Advocates should remain informed about these developments to make empowered decisions for their loved ones.
Types of Medications and Their Uses in Autism Treatment
When considering medication for autism in adults, it's essential to understand the different categories available and their potential benefits.
-
Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), such as fluoxetine, have been shown to effectively manage anxiety and depression, which are frequently experienced by individuals on the spectrum.
Current research underscores the need for further studies on SSRIs in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), particularly focusing on subgroup variables and larger trial samples, as highlighted in recent Cochrane reviews. The total sample size of the meta-analysis was 899, emphasizing the importance of robust research in this area.
-
Antipsychotics: Medications like risperidone and aripiprazole are often prescribed to reduce irritability and aggression, presenting a valuable option for caregivers.
A notable case study by Sanchez et al. (1995) concentrated on adults with recognizable causes of the condition and discovered that clomipramine intervention led to an average score of 5.6 on the Clinical Global Impression Scale for Severity (CGI-S), signifying its efficacy in managing symptoms.
-
Stimulants: While primarily used to address ADHD symptoms, stimulants such as methylphenidate can also play a role in care strategies for adults with developmental disorders, particularly when attention-related challenges are present.
-
Anti-anxiety Medications: Benzodiazepines may offer short-term relief for anxiety symptoms, but it’s crucial for caregivers to exercise caution due to the potential for dependency. Recent findings also suggest that for sustained attention tasks, there was no significant effect of group, drug, or group by drug interaction on head displacement, indicating that pharmaceutical effects can vary widely.
This categorization not only aids caregivers in understanding the potential benefits of each type of medication for autism in adults but also empowers them to make informed decisions when navigating care options for the well-being of adults with developmental disorders. As Eileen M. Daly emphasizes, it is vital that these discussions are grounded in comprehensive research and tailored to individual needs.
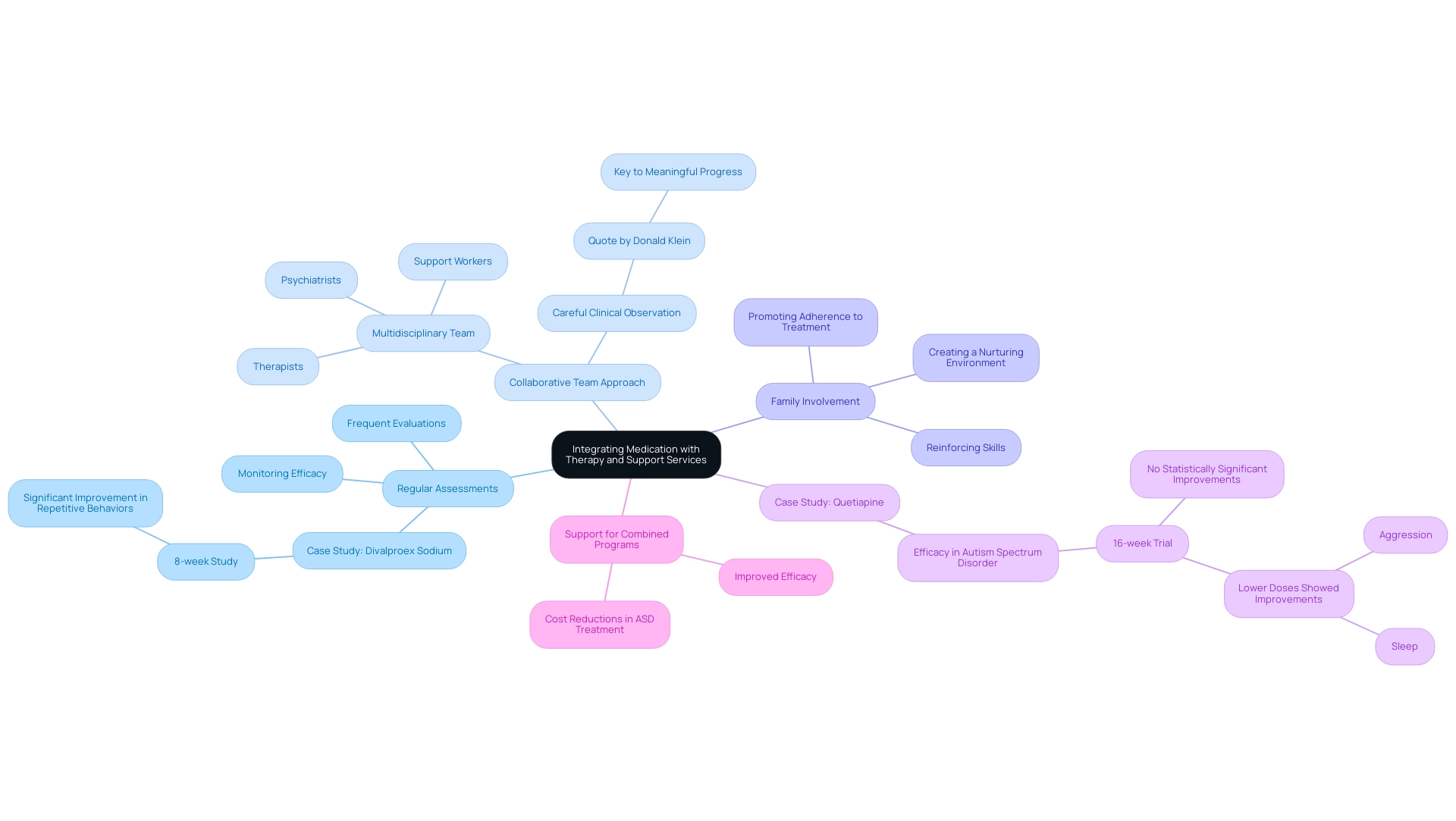
Integrating Medication with Therapy and Support Services
The use of medication for autism in adults, when combined with behavioral therapies like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), can significantly improve results. Here’s how to effectively combine both approaches:
- Regular Assessments: It is crucial to schedule frequent evaluations with healthcare providers to monitor both the efficacy of medication and the progress made in therapy. These assessments enable prompt modifications that enhance the care plan. For instance, an 8-week study of divalproex sodium demonstrated significant improvement in repetitive behaviors, highlighting the importance of treatment in conjunction with therapy.
- Collaborative Team Approach: Engage a multidisciplinary team that includes therapists, psychiatrists, and support workers to ensure a coordinated approach to treatment. This collaboration fosters comprehensive care, addressing both behavioral and biological needs. As Donald Klein, an early pioneer in psychopharmacology, noted, "the key to meaningful progress was careful clinical observation," underscoring the value of a thorough approach.
- Family Involvement: Involving family members in therapy sessions can reinforce the skills learned and promote adherence to treatment. Family support plays a vital role in creating a nurturing environment, which is essential for the individual’s progress.
Additionally, referring to the case study on quetiapine, while no statistically significant improvements were demonstrated, lower doses showed notable effects on aggression and sleep, illustrating real-world examples of treatment efficacy in autism. This integrated strategy not only fosters a supportive environment but also paves the way for more significant improvements in daily functioning and overall well-being. By taking these steps, parent advocates can help ensure that their loved ones receive the holistic care they deserve.
Challenges in Medication Management for Autistic Adults
Navigating medication for autism in adults can be complex and requires a nuanced understanding of various challenges that may arise. One significant concern is the potential for side effects, which can vary widely among individuals. Some medications may lead to unwanted side effects, emphasizing the need for ongoing communication with healthcare providers to monitor and address these issues effectively.
As Dr. Christopher McDougle, director of Massachusetts General Hospital’s Lurie Center for Autism, notes,
When symptoms of significant irritability persist and other causes have been ruled out, using an atypical antipsychotic can be very helpful.
This emphasizes the significance of customizing treatment plans, particularly regarding medication for autism in adults, to the unique reactions of each person.
Additionally, adherence to treatment regimens is often a struggle for adults with autism, necessitating the implementation of strategies that encourage consistent use. It is essential to acknowledge that people may undergo complex interactions with medication for autism in adults prescribed for co-occurring conditions, further complicating management efforts. For instance, in a case study examining bipolar disorder in high-functioning adults with ASD, it was noted that while lithium could be beneficial, anti-seizure medications are generally advised as first-line options for individuals with developmental disabilities.
This highlights the necessity for personalized care strategies.
Moreover, it is important to note that combination approaches of alpha agonists and stimulants, which are FDA-approved for ADHD in non-ASD populations, may not be the same as the medication for autism in adults, complicating the decision-making process for healthcare providers. Additionally, when considering treatments such as risperidone, dosing at or below 2 mg/day in divided doses may help mitigate weight gain and metabolic side effects, highlighting the need for careful monitoring.
By recognizing these challenges, parents can cultivate a cooperative relationship with healthcare professionals, ensuring that care plans remain adaptable and responsive to the evolving needs of autistic adults. Staying informed about the latest developments in treatment management, including potential side effects and adherence statistics, empowers parents to advocate effectively for their loved ones.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Autism Medication Management
Healthcare providers are crucial partners in the treatment management process for adults with developmental disorders, including medication for autism in adults, guiding families toward effective therapeutic strategies. An initial assessment is crucial; it involves comprehensive evaluations to identify the most suitable treatment options tailored to the individual's unique needs. This step sets the foundation for a personalized approach that acknowledges the diverse experiences of those on the autism spectrum, which may include the use of medication for autism in adults, while ongoing monitoring is equally important.
Regular evaluations of the effectiveness and side effects of medication for autism in adults enable healthcare providers to make timely adjustments, ensuring that care remains beneficial. Parents must be proactive in this dialogue, as a recent statistic revealed that 73% of parents viewed psychopharmacological approaches as only partially effective. This highlights the necessity of continuous evaluation and open communication.
Technology-based strategies can also enhance the healthcare experience for autistic individuals.
- Tools such as social stories and virtual reality can support treatment management by providing engaging and accessible ways for patients to understand their plans and the importance of adherence.
Education is another critical component when considering medication for autism in adults. Healthcare providers should equip parents and caregivers with thorough information about treatments, including medication for autism in adults, as well as expected outcomes and potential side effects. This knowledge empowers families to make informed decisions and advocate effectively for their loved ones.
Real-world examples, such as the case study on memantine in children with Pervasive Developmental Disorders (PDDs), illustrate the complexities of treatment management. While some memory improvement was noted in the study, it also highlighted that there were no significant changes in language or IQ measures, and minimal overall improvement was reported. This underscores the importance of tailored approaches and the need for ongoing assessment of the efficacy of medication for autism in adults. Finally, connecting families with additional resources and support groups fosters a community of shared experiences and strategies.
By maintaining open lines of communication with healthcare providers, parents can ensure that their loved ones receive the best possible care. As Samar Z. Hamdan aptly noted,
Proactivity, flexibility, and collaboration should guide the process of transforming the healthcare system.
This collaborative spirit is pivotal in navigating the complexities of autism medication management.
Conclusion
Navigating the landscape of medication for adults with autism presents both challenges and opportunities. With a clear understanding of the various medication options—ranging from antidepressants and antipsychotics to stimulants and anti-anxiety medications—caregivers can make informed choices that significantly enhance the quality of life for their loved ones. Each medication plays a specific role in addressing symptoms, highlighting the importance of tailoring treatment to individual needs and circumstances.
Integrating medication with behavioral therapies and support services further optimizes outcomes. By adopting a collaborative approach that includes regular assessments, multidisciplinary teams, and family involvement, caregivers can foster an environment that promotes both emotional and functional well-being. This holistic strategy not only addresses immediate concerns but also empowers individuals on the spectrum to thrive in their daily lives.
Ultimately, the journey of medication management requires ongoing communication with healthcare providers and a commitment to adapting treatment plans as needed. By staying informed about the latest developments and advocating for personalized care, parents and advocates can navigate this complex terrain effectively. Ensuring that adults with autism receive comprehensive and responsive support is essential in enhancing their overall well-being and helping them lead fulfilling lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of medication are available for adults with autism?
Adults with autism have access to several types of medications, including antidepressants, antipsychotics, stimulants, and anti-anxiety medications, each aimed at managing specific symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
How do antidepressants help adults with autism?
Antidepressants, particularly Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) like fluoxetine, are prescribed to manage anxiety and depression, which are common in individuals on the autism spectrum. They can help stabilize mood and alleviate distress.
What role do antipsychotics play in the treatment of autism in adults?
Antipsychotics, such as risperidone and aripiprazole, are used to manage severe behavioral issues and mood swings, providing a calming effect that facilitates daily interactions and reduces irritability and aggression.
When are stimulants used for adults with autism?
Stimulants, like methylphenidate, are occasionally used for adults with autism to address attention difficulties, especially when symptoms of ADHD are present. However, non-stimulants may be more appropriate for many autistic patients.
What are the effects of anti-anxiety medications on adults with autism?
Anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines, may provide short-term relief for anxiety symptoms, but caregivers should be cautious due to the potential for dependency.
Why is it important to understand the different medication categories for autism in adults?
Understanding the distinct purposes of each medication category is crucial for selecting the appropriate treatment based on individual needs and circumstances, ensuring effective management of autism-related symptoms.
What does current research indicate about the effectiveness of medication for autism in adults?
Recent studies, including a Cochrane review, emphasize the need for further research on the effectiveness of medications for autism, particularly SSRIs, to better understand their impact on different subgroups within the autism spectrum.
How prevalent are developmental disorders globally?
The World Health Organization estimates that 1 in every 100 children worldwide has a developmental disorder, highlighting the importance of exploring treatment options, including medication for autism in adults.
What should caregivers consider when choosing medication for adults with autism?
Caregivers should consider the unique clinical profiles of individuals, the potential benefits and risks of each medication type, and stay informed about ongoing research to make empowered decisions for their loved ones.




