Introduction
Children with Level 1 Autism, often classified within the high-functioning autism spectrum, face unique challenges in social communication and interaction. Recognizing these challenges and providing appropriate support and interventions is crucial for parents and professionals. This article provides an overview of Level 1 Autism, strategies for improving social skills, interventions for forming friendships, and promoting independence. It also highlights the importance of creating a supportive and inclusive environment for individuals with high-functioning autism. By understanding the distinctive traits and requirements of Level 1 Autism, parents and professionals can offer the necessary support to enhance the social skills and overall well-being of these children.
1. Understanding Level 1 Autism: An Overview
"Children with Level 1 Autism, often classified within the high-functioning autism spectrum, demonstrate a certain level of independence, yet face distinctive challenges in social communication and interaction. They may find initiating social engagements, building friendships, or maintaining relationships difficult. Moreover, they may display repetitive behavior patterns and have specific, narrowly focused interests. Recognizing these unique traits and requirements is crucial for parents and professionals alike to provide appropriate support and interventions.
For social communication, several strategies can be employed, tailored to the specific needs of the child. These strategies may include social skills training, peer modeling, visual supports, and structured play activities. Creating a supportive and inclusive environment where the child can practice and develop their social communication skills is essential. Collaboration with professionals like speech therapists and behavioral therapists can also be beneficial in formulating an individualized plan.
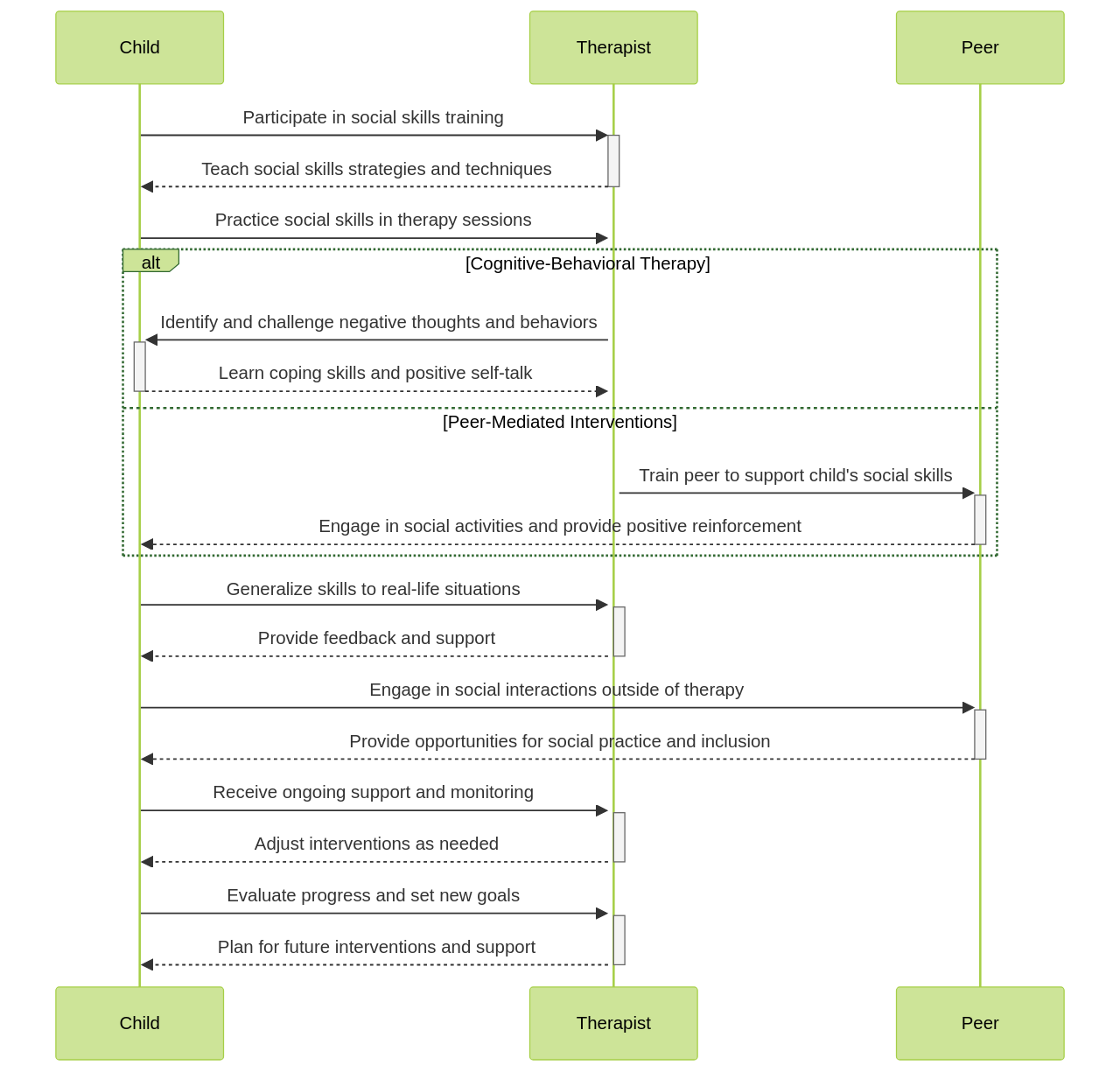
Interventions for improving social skills can include approaches such as social skills training, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and peer-mediated interventions. These methods focus on teaching specific social skills like initiating and maintaining conversations, understanding nonverbal cues, and perspective-taking. Providing opportunities for social interaction and practice in real-world settings is also vital. These interventions should be tailored to the individual's needs and strengths, and consistently implemented over time for the best outcomes.
Children with Level 1 Autism can benefit from strategies to help them form and maintain friendships. Encouraging social skills development through structured playdates, social skills groups, and peer modeling can be effective. Teaching them how to initiate and maintain conversations, share toys or interests, and take turns can also help. Providing opportunities for positive social interactions and offering support and guidance when needed is crucial. Additionally, fostering understanding and empathy among peers can create inclusive friendships.
Understanding the social interaction challenges faced by individuals with high-functioning autism can be complex. Recognizing that they may have difficulty with social cues, nonverbal communication, and social norms is essential. They may find initiating and maintaining conversations, interpreting facial expressions and body language, and understanding others' perspectives challenging, making it difficult to form and maintain relationships. Providing appropriate support and interventions to help develop and enhance their social skills is key.
To foster independence in children with Level 1 Autism, providing appropriate tools and strategies is essential. This can include implementing visual schedules, breaking tasks into smaller steps, and using social stories to help them understand and navigate different situations. Providing clear and consistent expectations, offering praise and reinforcement for independent behavior, and teaching self-help skills can also promote independence.
Promoting social inclusion for individuals with high-functioning autism involves providing effective strategies for enhancing social skills. This can be done through targeted interventions and step-by-step tutorials that focus on teaching social skills in a structured and systematic manner. By providing the necessary tools and support, they can develop and improve their social skills, enhancing their social inclusion and overall quality of life.
Addressing repetitive behaviors in children with Level 1 Autism involves effective strategies that promote social skills and overall development. Providing a supportive and structured environment for the child, incorporating visual supports and schedules, and using positive reinforcement and rewards can motivate the child and encourage desired behaviors. Collaborating with professionals, like therapists and educators, can be beneficial in developing and implementing individualized strategies for addressing repetitive behaviors.
There are resources available for parents and professionals working with individuals with high-functioning autism, providing support, information, and strategies to navigate autism support services and promote social skills. To develop social skills in children with Level 1 Autism, implementing effective strategies and interventions is essential. These strategies may include structured social skill training programs, peer modeling, and social stories. Creating opportunities for social interactions and providing support and guidance during social situations can also be beneficial. Tailoring interventions to the specific needs and abilities of each child and providing ongoing support and reinforcement to help them generalize their social skills in various settings is essential.
Creating a supportive and inclusive environment for individuals with high-functioning autism is crucial for their well-being and development. This involves implementing strategies and practices that address their unique needs and promote their social, emotional, and cognitive growth. Providing clear communication, visual supports, and sensory accommodations can help individuals with high-functioning autism feel understood and supported. Fostering an inclusive community that values diversity and promotes acceptance can contribute to a positive and inclusive environment for individuals with high-functioning autism."
Autism Speaks, a comprehensive website, provides an array of resources and information about autism. Their offerings span across articles, toolkits, podcasts, and events, all aimed at supporting individuals with autism, their families, and caregivers. By bridging the gap to information, tools, and resources, Autism Speaks aims to reduce healthcare service barriers for those with autism and advocates for meaningful employment opportunities within the autistic community. They also offer a directory of resources and a dedicated Autism Response Team (ART) that provides personalized support.
Furthermore, Autism Speaks has developed the "Roadmap to Housing and Residential Supports," an interactive tool designed to assist autistic adults in finding appropriate housing options and supports. This roadmap caters to individuals at various life stages, ranging from young adults exploring housing options for the first time to older adults nearing retirement. It provides action steps such as evaluating current living situations, understanding the available supports and services, and establishing daily living routines. The Autism Response Team (ART) is another resource that connects individuals and families affected by autism with valuable information and support. The insights gathered highlight the significance of personalized support and the necessity for continuous adaptation to meet evolving needs and circumstances of individuals.
2. The Role of Parents as Advocates in ABA Therapy
Parents are the bedrock of advocacy for children with Level 1 Autism, often being the primary observers of their child's unique behaviors and the first to initiate professional intervention. In the realm of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, parents have the power to ensure the therapy aligns with their child's unique needs and interests. To achieve this, it's critical to conduct a thorough assessment and work closely with a qualified ABA therapist to create a personalized treatment plan. Regular evaluation and adjustment of therapy techniques and strategies based on the child's progress and evolving needs are also essential. This can involve modifying the reinforcement system, adjusting the schedule or intensity of therapy sessions, or incorporating new teaching methods.
Parents are not mere observers but active participants in the therapy process. They can reinforce the skills acquired during therapy sessions in the home environment and other settings, helping solidify the benefits of the therapy. To do this effectively, parents can implement strategies and techniques at home that align with the therapy goals. This can include practicing skills taught in therapy sessions, using visual supports and schedules, providing reinforcement and rewards for desired behaviors, and collaborating with the ABA therapist to ensure consistency in interventions. By doing so, parents become extensions of the therapy, providing consistent reinforcement of learned behaviors outside of formal sessions.
In addition to therapists, parents can also benefit from the support of educational advocates and consultants. These professionals can guide parents in understanding their child's rights, defining desired outcomes, and monitoring progress. They can assist in gathering evidence and information to bolster advocacy efforts, ensuring children receive appropriate supports and services in school. To achieve this, parents can consult resources and information specifically tailored to the needs of children with autism. There are numerous organizations, websites, and support groups that provide guidance and strategies for advocating for individuals on the autism spectrum.
Another critical aspect of advocacy is nurturing self-advocacy in children. Parents play a crucial role in fostering independence and responsibility in their children, preparing them for the demands of adulthood. However, it's equally essential to understand the benefits of experiencing failure and learning from it. This involves gradually stepping back and allowing children to take ownership of their responsibilities, including schoolwork and schedules.
In conclusion, parents are the most influential advocates for their children with Level 1 Autism. Their role extends beyond merely securing services and supports but also includes fostering self-advocacy and independence, ensuring their children are equipped with the necessary skills for future success.
3. Navigating Support Services for Level 1 Autism
The spectrum of support services for children diagnosed with Level 1 Autism and their families is broad and varied. These services encompass special education programs, speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills groups, among others. Nevertheless, the journey to understanding and utilizing these services can seem overwhelming. The key to overcoming this challenge lies in accessing accurate information and resources, which empowers parents to make informed decisions about the most appropriate options for their child.
Recognizing that each child is unique is paramount. A strategy that works for one child may not necessarily work for another. Drawing from the shared experiences of the High Needs Autism Advocates (HNAA) community, the journey of a child with autism is often compared to playing a video game with random controls or navigating a foreign country with unfamiliar language and cultural norms.
In Ontario, Canada, individuals with intellectual disabilities and autism, including their families, have access to supports and services through two main funding and registration pathways. These are the Ontario Disability Support Program (ODSP) and the Developmental Services Ontario (DSO). ODSP provides employment supports such as job seeker support, while DSO provides placement services for community connection and supported independent living.
Accessing employment supports through ODSP is generally quicker and simpler than accessing supports through DSO. Moreover, individualized funding is available through the Passport program, which can be used to purchase community connection and living supports. This funding adheres to specific guidelines and can be combined with DSO placement or used as a "fee for service" arrangement, currently priced at $50 per hour, although this is subject to change.
The DSO placement process can be lengthy, sometimes taking years, with no guaranteed timeline. Despite this, organizations like LiveWorkPlay are always ready to accept referrals and have staff allocated to provide support.
Navigating the path to accessing supports and services for individuals with intellectual disabilities and autism may seem complex, but with clarity and understanding, this process can be successfully navigated. The role of organizations like LiveWorkPlay in providing assistance and support is invaluable in this journey. It is vital to remember that occupational therapy is a common intervention for children with autism, including those with Level 1 Autism. It focuses on helping individuals develop the skills they need for everyday activities, thereby improving their overall quality of life.
The use of social skills groups can also be beneficial for children with Level 1 Autism. These groups provide a structured and supportive environment for children to practice and develop their social skills. The groups often include activities and exercises that focus on communication, social interaction, and problem-solving.
To navigate these support services, it is crucial to research and gather information about the available resources and programs. Reaching out to local schools and educational institutions to see if they have any specialized programs or support services for children with autism can be helpful. Connecting with other parents who have children with Level 1 Autism can provide valuable insights and recommendations for navigating support services.
To make informed decisions about these services, understanding the specific needs and challenges of children with Level 1 Autism is crucial. Consulting with professionals such as pediatricians, psychologists, or therapists who specialize in autism can provide valuable insights and guidance.
Finding the best options for children with Level 1 Autism requires considering strategies that can enhance their social skills. Implementing effective strategies, such as those mentioned in news articles, can provide the necessary support and assistance to children with Level 1 Autism. These strategies may include promoting social skills, using key terms and glossaries, and accessing unlimited digital resources for information and guidance. It is crucial to tailor the options to the specific needs and abilities of each child, ensuring their development and well-being.
4. Effective Strategies for Managing Challenging Behaviors in Level 1 Autism
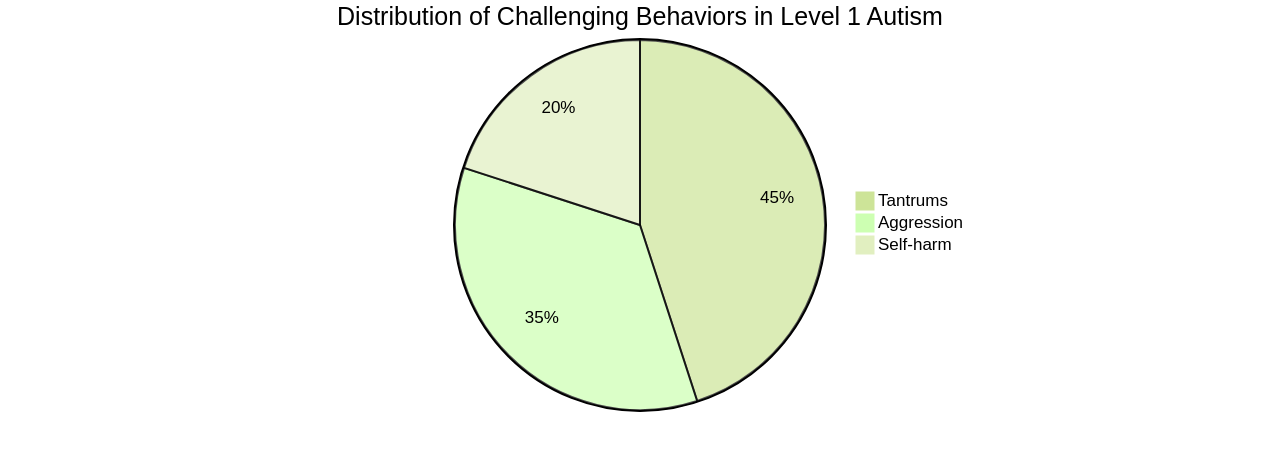
"Children diagnosed with Level 1 Autism can sometimes exhibit challenging behaviors such as aggression, tantrums, or self-harm. To manage these effectively, a comprehensive approach involving various strategies is necessary. These strategies can include behavior modification techniques, visual supports, social stories, and structured routines. It's crucial to develop an individualized plan that addresses the child's specific needs, with the close involvement of a healthcare professional or therapist who specializes in autism. Providing a supportive and understanding environment, implementing clear and consistent expectations, and using positive reinforcement can also be helpful in managing these behaviors.
Visual supports serve as an effective behavior management technique for children with Level 1 Autism. They provide visual cues and reminders that help children understand and follow routines, rules, and expectations. These visual supports can range from visual schedules and social stories to visual prompts. Positive reinforcement is another effective technique that involves providing praise, rewards, or privileges for desired behaviors to motivate and reinforce positive behavior. Structured and predictable routines can offer a sense of security and help reduce anxiety for children with Level 1 Autism. Clear and simple language should be used when communicating with the child to avoid any misunderstandings.
Positive reinforcement strategies can reduce challenging behaviors in children with Level 1 Autism. Rewards or incentives for desired behaviors, such as following instructions or engaging in appropriate social interactions, can motivate these children to exhibit these behaviors more frequently. This approach can decrease the occurrence of challenging behaviors and promote the development of more positive and adaptive behaviors.
Social stories can be an effective strategy for addressing challenging behaviors in children with Level 1 Autism. These narratives provide clear and concise information about social situations, expectations, and appropriate behaviors, helping children with Level 1 Autism learn and understand social cues and expectations. This approach can improve social skills and reduce challenging behaviors.
Implementing visual schedules can be beneficial for promoting behavior management. These schedules provide a visual representation of daily activities and routines, helping children understand expectations and transitions. The use of visual cues such as pictures, symbols, or written words can give children a clear understanding of what is expected of them throughout the day, reducing anxiety, improving focus, and enhancing communication skills.
Behavioral interventions can be effective in managing challenging behaviors. These interventions focus on teaching children appropriate behaviors and skills while reducing or eliminating challenging behaviors. Techniques such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), social skills training, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and parent training programs can be used. Each intervention should be tailored to the specific needs and abilities of each child with Level 1 Autism.
Working together with professionals to develop a behavior management plan can be beneficial in providing effective strategies for enhancing social skills. A comprehensive plan that addresses the specific needs and challenges of children with Level 1 Autism can be developed with the help of professionals who have expertise in autism. This collaborative approach can create a supportive and structured environment that promotes positive behavior and social interaction, enhancing the overall development and well-being of the children.
Tailoring behavior management strategies to meet the specific needs of children with Level 1 Autism can be highly beneficial. By understanding the unique challenges and strengths of each child, educators and caregivers can develop personalized strategies to support their social and behavioral development. This may include implementing visual supports, providing clear and consistent expectations, utilizing positive reinforcement, and incorporating sensory-based interventions.
To support parents in implementing behavior management techniques, it is important to provide them with resources and tools. This can include educational materials, workshops, and guidance from professionals who specialize in autism support services. Offering support groups or online forums where parents can connect with and learn from each other can be beneficial. Ensuring that parents have access to evidence-based strategies and interventions tailored to their child's specific needs is essential.
Participating in the Autistic community can provide a sense of belonging and access to resources. The Autastic community, specifically designed for late-identified autistic individuals who are also people of color, offers support, resources, and a sense of belonging. The community organizes peer workshops, events, and even has reserved spaces for trans members and seniors. They also run an Autastic shop selling various products like books, fidgets, and apparel. The community operates primarily on monthly donations and patronage, dedicating a portion of the revenue back to the community. The Autastic community strongly advocates for support and understanding for late-identified autistic individuals of color and encourages others to join and contribute to the community."
5. Enhancing Social Skills Development in Children with Level 1 Autism
"Children with Level 1 Autism often encounter difficulties in understanding social cues, participating in conversations, and forming friendships. As parents, your role in fostering their social skills development is pivotal. This can be achieved by creating situations for social engagement, demonstrating appropriate social behaviors, and encouraging positive social interactions.
Visual aids are an effective tool in teaching children to grasp and develop critical social skills such as taking turns, sharing, and using an appropriate tone of voice. Resources like choice wheel templates, listening posters, and voice level charts can be utilized to impart these skills. Activities and conversation starters can be structured to stimulate communication and socialization. For example, visual supports can be employed to guide children when making and receiving phone calls, including video calls. Sequence strips and routine booklets can be used to navigate children through these social interactions.
Social skills training programs, like social stories and social scripts, have proven to be beneficial in guiding children with Level 1 Autism on how to behave and respond appropriately in social situations. These programs can be incorporated into structured social skills groups, which serve as a valuable resource by providing a platform for children to practice their social skills with peers. These groups can leverage play and non-verbal communication, which are crucial in developing social skills. Activities at the center and visual boundaries can be used to facilitate social interaction. For example, a social skills group conducted over two weeks saw success where children shared objects or pictures and participated in activities that catered to their interests.
Teaching social cues to children with Level 1 Autism can be effectively done through strategies that use step-by-step tutorials to enhance social skills. This approach helps children learn how to interpret and respond to social cues in a significant manner, thereby improving their overall communication skills. It is crucial to provide a supportive and structured environment that encourages social learning and offers opportunities for practice and reinforcement.
Developing conversational skills, especially taking turns in a conversation, can be a challenging task for children with Level 1 Autism. In this regard, explicit teaching of the concept of taking turns using visual aids or social stories can be beneficial. Demonstrating turn-taking during conversations can serve as a model for children to follow. Visual cues like a visual timer or a token system can be used to signal when it's time to take turns. Creating opportunities for children to practice turn-taking in structured settings, such as during therapy sessions or social skills groups, can be beneficial. Providing children with scripts or prompts to use during conversations can help them initiate and take turns. Positive reinforcement, such as praise or rewards, when children successfully take turns in a conversation can help motivate and encourage them to continue practicing the skill.
To help children with Level 1 Autism make friends, it is essential to focus on enhancing their social skills. Encouraging social interactions, providing opportunities for playdates or group activities, and teaching basic social skills such as taking turns, sharing, and making eye contact can all be beneficial. Additionally, using visual aids, social stories, or role-playing can help children with autism understand and practice social situations.
Parents can employ effective techniques that support social skills development in children with Level 1 Autism. These techniques focus on creating a structured and supportive environment, providing clear and consistent communication, and promoting social interactions and play.
In essence, the development of social skills in children with Level 1 Autism is a multifaceted process that involves a combination of strategies. Parents can play an instrumental role in this process by actively engaging and utilizing the resources available to them. This can significantly aid their children in navigating their social world more effectively."
6. Creating a Supportive Community for Parents and Professionals
The nurturing environment within the sphere of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a critical component in providing a space for mutual learning, emotional support, and the exchange of experiences. A notable initiative in this regard is ASD Media, an organization dedicated to cultivating a supportive and inclusive community.
Being a part of this community, as a parent or professional, allows access to a wealth of resources and support specifically designed for those dealing with autism. ASD Media's newsletter, a key resource, keeps subscribers abreast of the latest developments in the field. It provides unlimited digital access to articles, glossaries, and key terms pertinent to those seeking information on autism. This ongoing connection with the community can be a valuable source of information, support, and networking opportunities, contributing to professional development and growth.
Choosing the right ABA facility for a child diagnosed with autism can be a daunting journey, fraught with anxiety, uncertainty, and misinformation. Hence, it is essential to equip oneself with a set of questions to ensure the safety of the child and the quality of therapy they receive. The red flags to watch out for include undue emphasis on reducing self-stimulatory behavior, insistence on teaching sustained eye contact, focus on 'recovering' or 'curing' autistic individuals, reliance on forced compliance, recommending an unjustifiably high number of therapy hours, using food as a primary reinforcer, and refusal to collaborate with other providers.
Cassie Hauschildt, a mother of an autistic child and an advocate for children with autism, authored an article on this subject. She shares her personal journey and offers mentorship to other parents navigating a similar path. Cassie also manages a Facebook group, "The Dino Nuggets Corner," which serves as a platform for support and information dissemination.
The responsibility lies not only with the ABA providers to update their practices and prioritize their clients' well-being but also with parents to conduct thorough research and pose the right questions. Ensuring alignment with ethical standards and catering to the unique needs of the individual is of utmost importance.
The process of building a supportive community for parents and professionals in ABA therapy is facilitated through resources and platforms for connection, sharing experiences, and accessing information. This can be achieved through online forums, support groups, and educational workshops where parents and professionals can learn from each other and exchange ideas. A network of experienced professionals who can mentor and provide guidance to parents is also an integral part of creating this supportive community.
Creating an inclusive community in the field of ABA therapy can be achieved through various strategies. One such strategy is ongoing training and education for therapists and practitioners. This includes workshops, seminars, and conferences focusing on topics such as cultural competence, diversity, and inclusion, ensuring therapists can better serve a diverse range of clients and create a more inclusive environment. Incorporating diverse perspectives and voices in decision-making processes and program development can also foster inclusivity within the ABA therapy community.
Online communities or forums dedicated to ABA therapy can be a valuable resource to share experiences and learn from others in the field. These platforms provide a space for individuals and professionals to connect, ask questions, and share their experiences and insights. Attending conferences, workshops, or seminars related to ABA therapy can offer opportunities to network with others in the field and learn from their experiences. Ongoing professional development and staying up-to-date with the latest research and best practices in ABA therapy can also contribute to the exchange of knowledge and learning from others in the field.
Emotional support plays a crucial role in the ABA therapy community. It helps individuals receiving therapy to cope with the challenges they may face during their treatment journey. Emotional support can come in various forms, such as encouragement, empathy, and understanding from therapists, caregivers, and peers. This support system helps individuals feel valued, motivated, and empowered, enhancing their overall well-being and improving their outcomes in ABA therapy.
7. Empowering Parents through Access to Resources and Continuous Learning
Empowering parents of children with Level 1 Autism is a critical aspect of providing effective support. This involves equipping parents with a wide array of resources and creating a conducive environment for continuous learning. These resources can be diverse, including educational materials, online communities, and workshops.
The "Hello" platform, an initiative by the National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC), is an excellent example of such resources. This platform encourages discussion and helps establish connections among members on topics related to early learning. Parents can leverage this platform to identify professionals in their areas of interest and engage in substantive conversations about their child's needs. However, it also underscores the challenges faced by families in accessing resources in indigenous languages, indicating a need for more inclusive educational materials.
Continuous learning allows parents to stay informed about the latest research and strategies in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy. This knowledge ensures that parents can provide the most effective support for their child. An example of such learning opportunities is the free online summit "Parenting Teens in Uncertain Times." Here, over 30 experts from diverse fields, including neuroscience, parenting, child development, and well-being, discuss a variety of topics. These range from understanding the adolescent brain to addressing mental health crises among teens, equipping parents with the knowledge and tools necessary to nurture resilient and thriving children.
Furthermore, parents can find a wealth of resources designed to support children with Level 1 Autism. These resources offer guidance and information on best supporting their child's needs. It's essential for parents to seek out these resources to ensure they have the necessary tools and knowledge to help their child thrive. Organizations, programs, and online platforms offer valuable information and support to help parents navigate the challenges and empower their children with autism.
There are also continuous learning opportunities available for parents of children with Level 1 Autism. These programs aim to empower parents and provide them with the necessary skills and knowledge to navigate autism support services. Parents can enhance their understanding of autism and develop strategies to promote social skills in their children through these programs. They often include glossaries of key terms related to promoting social skills in children with autism. Online resources such as articles and webinars also exist to further their knowledge and keep them updated on the latest research and techniques in autism support.
In essence, empowering parents involves more than merely providing resources. It encompasses creating an environment where parents can learn, grow, and connect with others on a similar journey. This ongoing support and education equip parents with the skills and knowledge they need to effectively support their child with Level 1 Autism.
Conclusion
Children with Level 1 Autism face unique challenges in social communication and interaction. Recognizing these challenges and providing appropriate support and interventions is crucial for parents and professionals. This article has provided an overview of Level 1 Autism, strategies for improving social skills, interventions for forming friendships, and promoting independence. It has highlighted the importance of creating a supportive and inclusive environment for individuals with high-functioning autism.
The main points of the article include the importance of tailored strategies for social communication, interventions for social skills development, strategies for forming friendships, promoting independence, managing challenging behaviors, and accessing support services. These strategies involve utilizing visual supports, social stories, structured routines, positive reinforcement, and collaboration with professionals.
Understanding the distinctive traits and requirements of Level 1 Autism is essential in providing the necessary support to enhance the social skills and overall well-being of these children. By implementing effective strategies and interventions, parents and professionals can create a supportive environment that fosters independence, promotes social inclusion, and enhances the overall quality of life for individuals with high-functioning autism.
The broader significance of this article's topic lies in its potential to improve the lives of children with Level 1 Autism by equipping parents and professionals with valuable strategies and resources. By understanding the unique challenges faced by these children and implementing evidence-based interventions, we can help them develop vital social skills, form meaningful friendships, promote their independence, and ensure their overall well-being.
In conclusion, it is crucial to recognize the distinctive traits of Level 1 Autism and provide appropriate support to enhance social skills. Creating a supportive environment that fosters independence and inclusivity is key. By implementing effective strategies tailored to each child's needs, we can enable children with Level 1 Autism to thrive socially and improve their overall quality of life. To learn more about supporting individuals with high-functioning autism start now.




