Overview
Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires support primarily in communication and social interactions, as individuals often struggle with initiating conversations and interpreting social cues. The article emphasizes the importance of early recognition and intervention strategies, such as personalized education plans and behavioral therapies, which can significantly enhance the interpersonal skills and overall quality of life for those affected.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) presents unique challenges and opportunities for individuals and their families. Defined by the need for support in social communication and repetitive behaviors, children with Level 1 ASD often grapple with interpreting social cues and maintaining conversations, which can hinder their interactions with peers. Recent statistics reveal a notable prevalence of ASD, particularly among males, emphasizing the importance of tailored support and early intervention.
As awareness grows, the conversation shifts toward recognizing not only the challenges but also the remarkable strengths that these children possess, such as:
- Exceptional attention to detail
- Passionate interests
This article delves into the characteristics, symptoms, and effective strategies for supporting children with Level 1 Autism, highlighting the critical role of early intervention and the potential for meaningful growth and development.
What is Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Level 1 autism spectrum disorder is characterized by the need for support in managing communication difficulties and restricted, repetitive behaviors. Individuals with level 1 autism spectrum disorder typically encounter challenges in initiating and sustaining conversations, often finding it hard to interpret social cues effectively. They may also display repetitive behaviors, such as hand-flapping or a strong preference for routine.
Recent statistics reveal that the overall prevalence of ASD is 27.6 per 1,000 youths, with a male-to-female ratio of 11.4, indicating a significantly higher prevalence of ASD among males compared to females. Furthermore, in Arizona, the prevalence of ASD is reported at 26.8 per 1,000 children, highlighting the importance of regional data in understanding this condition. Judith Ursitti, co-founder and president of the Profound Autism Alliance, emphasizes,
The continuing recognition of profound autism will open the doors to more inclusive research like the CDC’s.
This acknowledgment is crucial for parents and caregivers as it establishes the foundation for effective assistance and intervention strategies tailored to the unique needs of individuals with level 1 autism spectrum disorder. Understanding these characteristics not only aids in providing appropriate assistance but also enhances advocacy efforts aimed at improving resources and support available for these individuals.
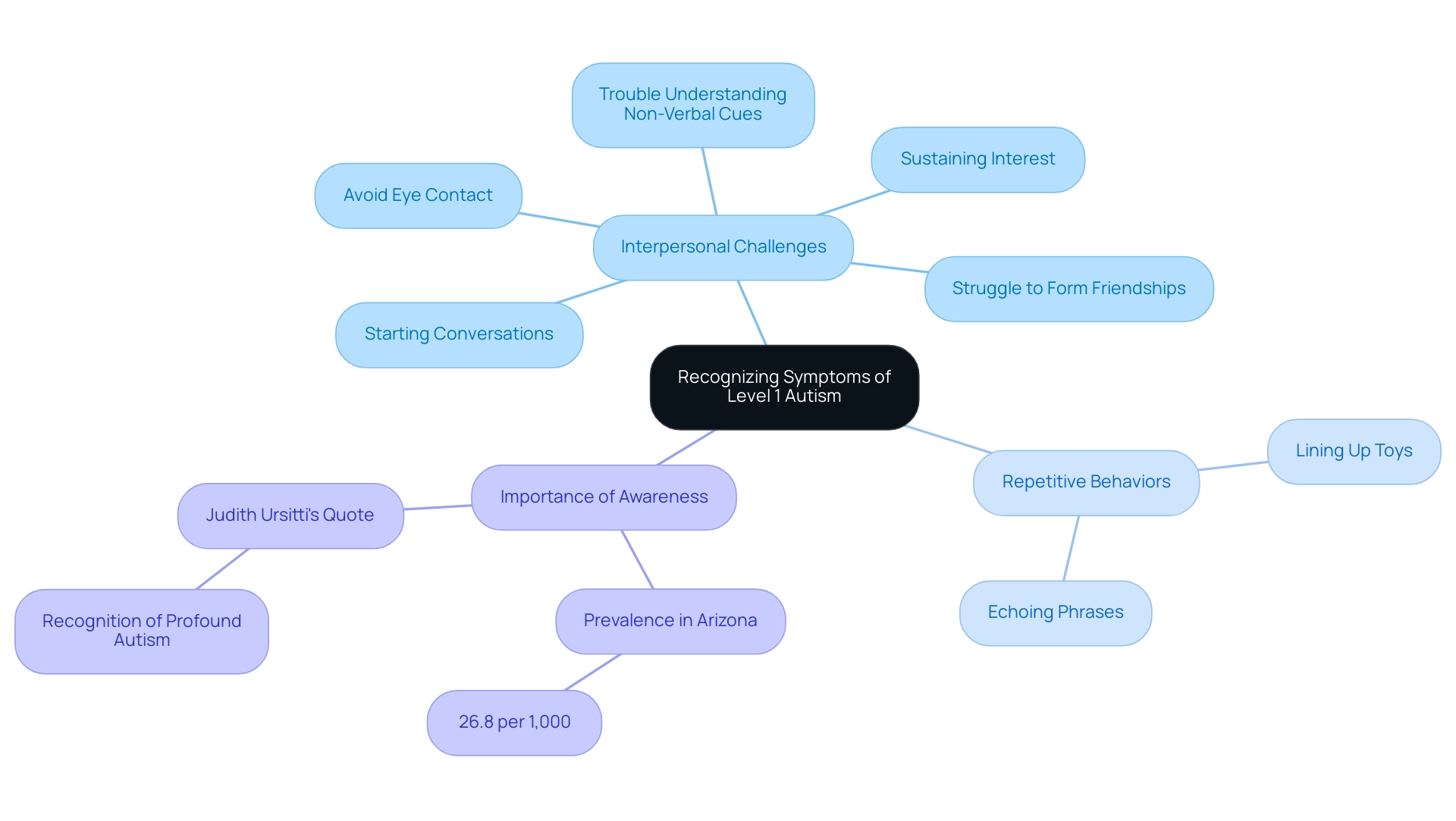
Recognizing Symptoms of Level 1 Autism
Common symptoms of level 1 autism spectrum disorder often manifest as challenges in interpersonal interactions. For instance, children may:
- Avoid eye contact
- Have trouble understanding non-verbal cues
- Struggle to form friendships
Additionally, repetitive behaviors, such as lining up toys or echoing phrases, are frequently observed.
In Arizona, the prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder is reported at 26.8 per 1,000, highlighting the importance of awareness among parents. A case study titled 'Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder: Requiring Assistance' illustrates how individuals with level 1 autism spectrum disorder may encounter interpersonal challenges that require some help, such as:
- Starting conversations
- Sustaining interest
With the appropriate assistance, individuals can enhance their interpersonal abilities and establish significant connections.
Parents are encouraged to remain vigilant for these indicators, as early recognition is crucial. Judith Ursitti, co-founder and president of the Profound Autism Alliance, emphasizes the importance of this awareness:
The continuing recognition of profound autism will open the doors to more inclusive research like the CDC’s. Only then can targeted advocacy enhance access to critically needed assistance and services for this marginalized population.
By recognizing these indicators early, parents can enable access to effective assistance and measures, ultimately improving their offspring's interpersonal abilities and chances for significant relationships. Furthermore, the CDC's autism prevalence estimates, based on 8-year-old children across 11 monitoring sites, underscore the urgency of recognizing symptoms early to ensure timely intervention.
Social Interaction Challenges in Level 1 Autism
Children diagnosed with level 1 autism spectrum disorder often face notable difficulties in interactions. This group may struggle significantly with interpreting interpersonal cues, which can lead to frequent misunderstandings with their peers. For example, a young person with level 1 autism spectrum disorder might not grasp when a classmate is joking or could misinterpret a friendly gesture as an aggressive act.
Studies show that 8% of autistic learners in the U.S. do not complete high school, in contrast to 5% of all students, highlighting the urgent need for early support in skill development. Parents play an essential part in this process; they can improve their offspring's interpersonal abilities by demonstrating suitable interactions and establishing secure environments where kids can practice these skills. Engaging in structured activities, such as music therapy, has shown promising results.
In a study where youngsters took part in 52 weekly music therapy sessions, enhancements were not only noted in their musical abilities—such as singing melodies and playing scales—but also in standardized assessment scores, indicating that such programs can significantly improve both musical and interpersonal competencies. According to Blythe Lagasse, an author in the field, "Preliminary evidence indicates the effectiveness of music therapy techniques for youth with ASD, with a 2014 Cochrane review showing that music therapy methods are successful for enhancing interaction, verbal communication, initiating behavior, and emotional reciprocity." Additionally, the average cost of therapeutic behavioral services is $175.44, a factor that parents should consider when seeking interventions.
By leveraging these strategies and resources, parents can effectively support their offspring in navigating social landscapes.
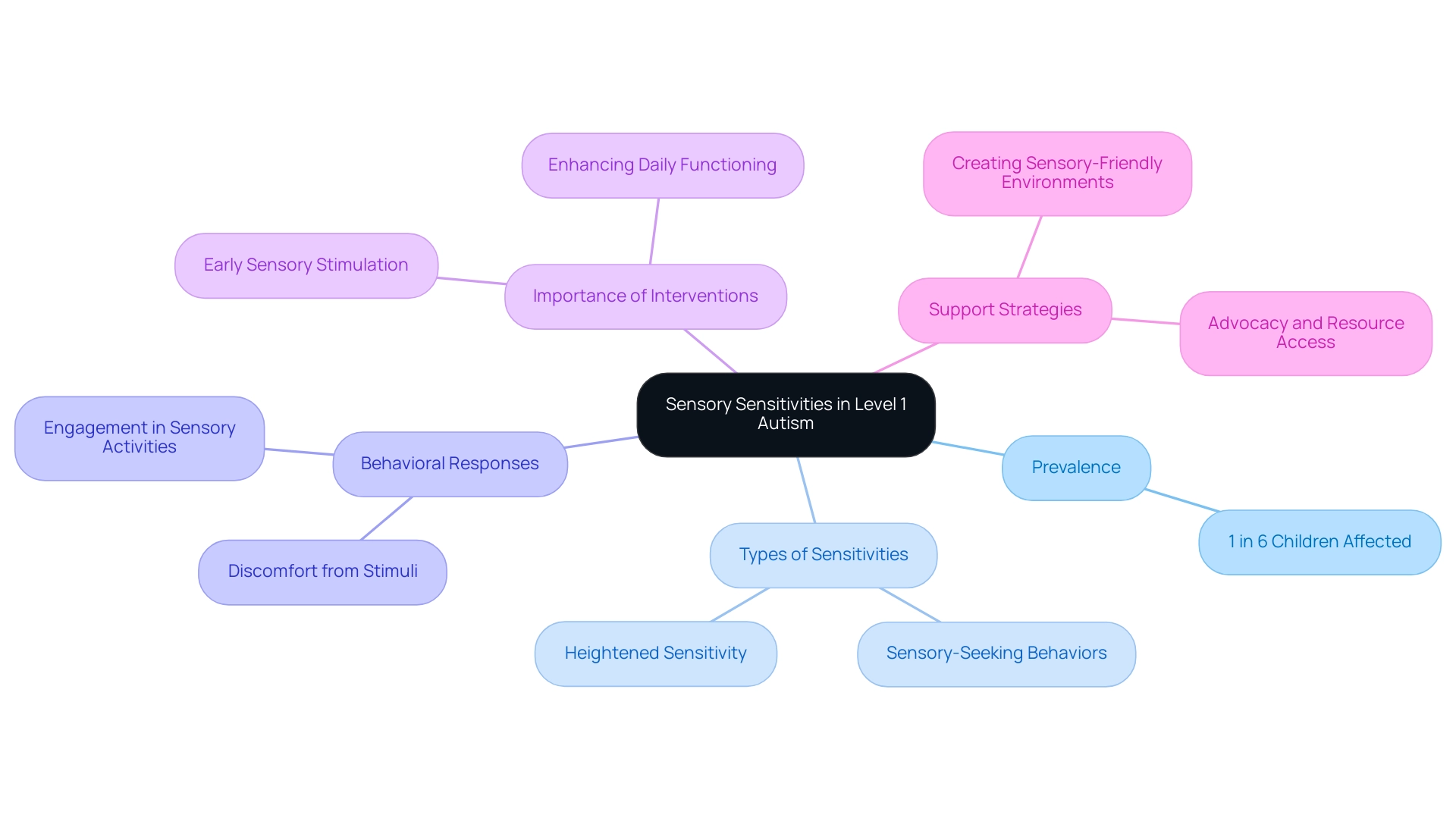
Understanding Sensory Sensitivities in Level 1 Autism
Children diagnosed with level 1 autism spectrum disorder frequently exhibit a range of sensory sensitivities that can significantly impact their daily lives. Research by Carter et al. (2009) indicates that sensory processing irregularities affect approximately 1 in every 6 youngsters, underscoring the prevalence of these challenges.
Some young individuals may demonstrate heightened sensitivity to various stimuli, including sounds, lights, textures, or smells, which can lead to noticeable discomfort or distress. In contrast, other individuals may actively seek out sensory experiences, engaging in behaviors such as spinning or jumping to fulfill their sensory needs. According to Simonetta Panerai, PsyD, early interventions that utilize sensory stimulation are crucial for enhancing the daily functioning of individuals diagnosed with level 1 autism spectrum disorder.
Furthermore, cultural biases and access to resources may contribute to disparities in autism diagnosis, highlighting the importance of advocacy and support for all families. Therefore, it is essential for parents to closely observe their offspring's reactions to different sensory inputs. By doing so, they can effectively create a sensory-friendly environment tailored to their individual's unique needs and preferences, which is vital for promoting comfort and reducing anxiety in everyday situations.
Additional insights from occupational therapists emphasize that understanding these sensory sensitivities is key to developing effective strategies for support.
Effective Treatment and Support Strategies for Level 1 Autism
Efficient treatment methods for youngsters diagnosed with level 1 autism spectrum disorder include a variety of approaches, particularly personalized education plans (IEPs), interpersonal skills training, and behavioral interventions. IEPs play a crucial role in customizing educational experiences to meet the unique needs of each child, facilitating their academic success and community integration. Recent insights from educators emphasize the myriad benefits of IEPs, including personalized support that fosters growth in key areas.
As emphasized by Afsharnejad et al., through an analysis of 18 studies, there is moderate overall efficacy (g=0.60, p<.001) in supporting socialization among autistic adolescents, highlighting the significance of structured approaches like social skills training. Among behavioral interventions, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) stands out due to its structured methodology aimed at reinforcing positive behaviors and teaching essential skills. Research indicates that ABA can significantly enhance adaptive functioning for children with level 1 autism spectrum disorder, providing them with valuable tools for daily living.
The demographic context from Welterlin et al. (2012), which involved a sample size of 20 participants, predominantly male (90%), with a mean age of 30.5 years, further reinforces the relevance of these strategies in addressing the needs of individuals with autism. In addition to these strategies, parents are encouraged to engage in support groups, which offer vital networks of resources and community support, promoting a shared understanding among peers.
A relevant case study on Social Skills Groups illustrates how these structured environments facilitate the improvement of social interactions through guided practice. As the landscape of autism treatment evolves, the focus on customizing approaches continues to be paramount, particularly for adolescents, where future studies should prioritize Individual Participant Data (IPD) meta-analysis to refine these strategies further.
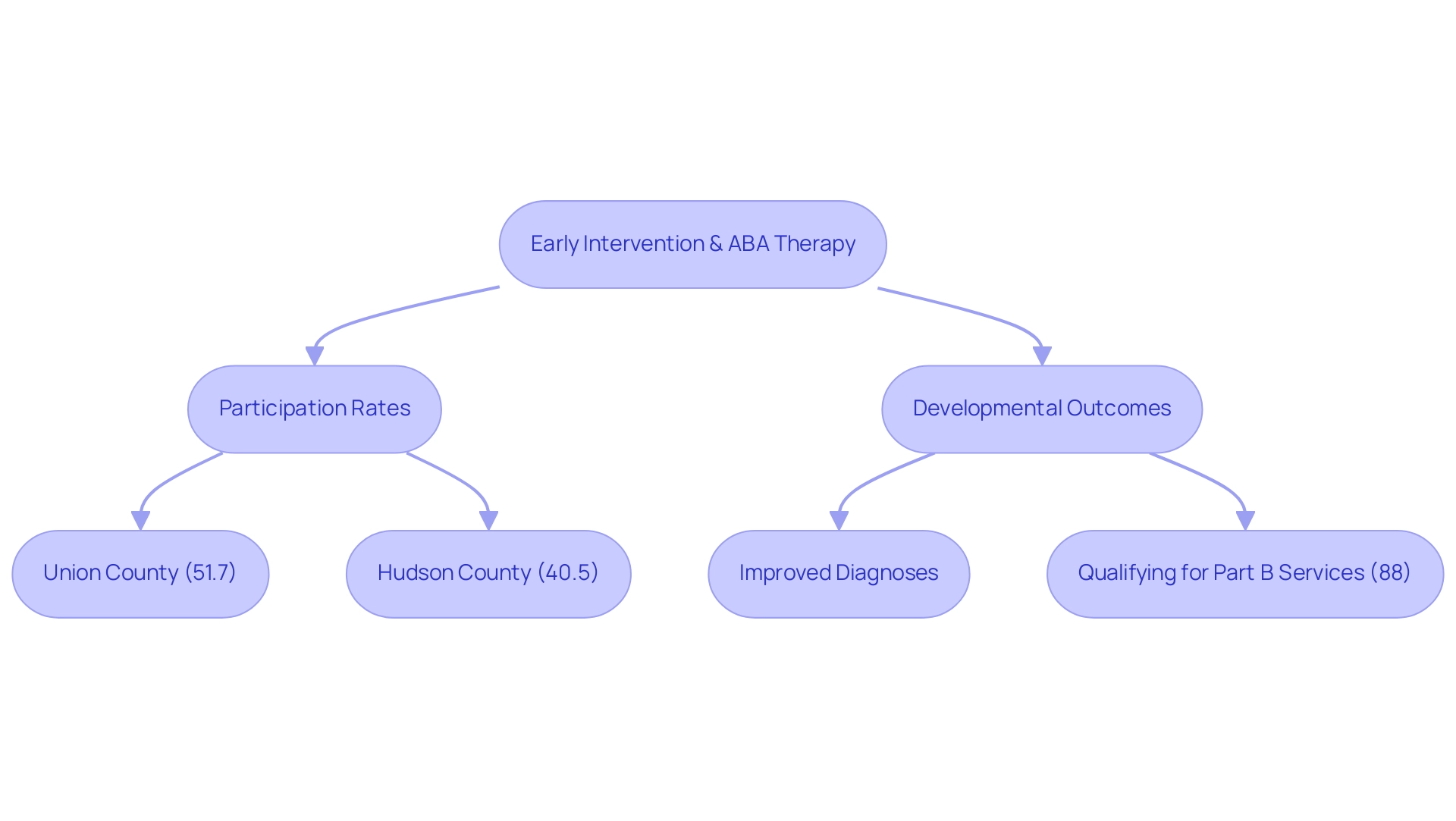
The Role of Early Intervention and ABA Therapy in Level 1 Autism
Timely support is essential for individuals diagnosed with level 1 autism spectrum disorder, with Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy rising as a notably effective method. Research indicates that initiating therapy at an early age significantly enhances developmental outcomes. For instance, in New Jersey, Union County reported that 51.7% of individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) received Early Intervention Program (EIP) services, while Hudson County had a lower rate of 40.5%.
This disparity not only emphasizes the significance of access to early support services but also indicates that areas with higher participation rates may experience improved developmental pathways for youth. A study titled 'Consequences of EIP Participation on ASD Diagnosis' found that 88% of youths who engaged in EIP also qualified for Part B services under IDEA. This discovery highlights the essential function of early assistance in enabling earlier diagnoses, which can result in enhanced educational outcomes and support systems for individuals with ASD.
Amelia Walter, a Research Associate at the University of New South Wales, emphasized this point, stating,
The present project, an initial study of a community dissemination of the ESDM early support for ASD within care settings, has the potential for significant clinical and economic benefits.
This emphasizes the importance of ABA therapy in the context of early support, as it utilizes structured strategies designed to teach young individuals essential skills, thus assisting them in overcoming challenges and developing crucial life competencies. As research continues to demonstrate the effectiveness of early ABA therapy, it becomes increasingly clear that such interventions are not just beneficial but essential for individuals with level 1 autism spectrum disorder.
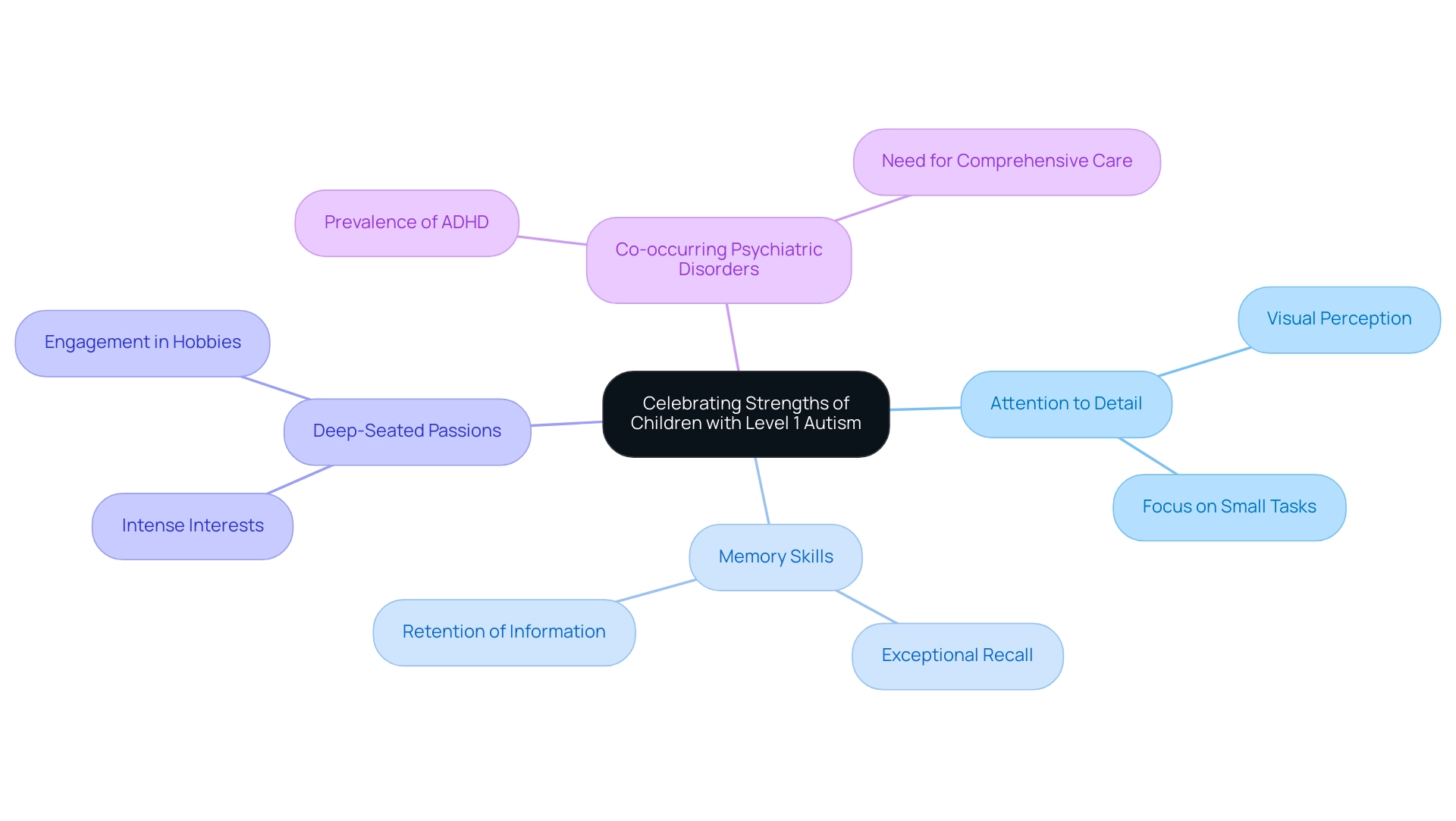
Celebrating Strengths: Unique Abilities of Children with Level 1 Autism
Children diagnosed with level 1 autism spectrum disorder often demonstrate remarkable strengths that can significantly enhance their quality of life. These strengths include:
- Heightened attention to detail
- Exceptional memory skills
- Deep-seated passions for particular interests
Research indicates that recognizing and nurturing these abilities can lead to increased self-esteem and motivation among these young individuals.
Notably, the average number of reported qualities in the ID-only group was 3.67, highlighting the diverse strengths that can be found in individuals with level 1 autism spectrum disorder. Furthermore, a substantial 91% of individuals with ASD may also have co-occurring psychiatric disorders, such as ADHD. This emphasizes the importance of a tailored approach to care that addresses both unique talents and potential challenges.
By recognizing these disorders alongside their strengths, parents and caregivers can develop more effective support strategies. To cultivate a positive self-image and foster personal growth, it is essential for parents to celebrate these traits. By providing opportunities for their offspring to engage deeply with their interests and excel in their areas of strength, parents can help build a supportive environment that not only acknowledges their abilities but also encourages a sense of belonging and confidence.
As noted by the CDC, 'This information can help us learn about factors that might put youth at risk for ASD, and can help communities direct their service and outreach efforts to those who need it most.' Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring that every child receives the support they need to thrive.
Conclusion
The journey of navigating Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is multifaceted, characterized by both challenges and remarkable strengths. Understanding the unique characteristics and symptoms associated with Level 1 ASD is essential for parents and caregivers. By recognizing the signs early, such as difficulties in social interactions and sensory sensitivities, families can seek timely interventions that foster improved social skills and daily functioning.
Effective treatment strategies, including individualized education plans and applied behavior analysis, play a crucial role in supporting children with Level 1 ASD. These approaches not only address their specific needs but also encourage a structured environment conducive to learning and growth. Importantly, the role of early intervention cannot be overstated; initiating therapy at a young age significantly enhances developmental outcomes, paving the way for a brighter future.
Moreover, while it is vital to address the challenges faced by children with Level 1 ASD, celebrating their strengths is equally important. Heightened attention to detail, exceptional memory, and passionate interests can be powerful assets when nurtured appropriately. By fostering these abilities, parents can help cultivate self-esteem and motivation, allowing their children to thrive both socially and academically.
In conclusion, supporting children with Level 1 Autism requires a holistic approach that combines early intervention, effective treatment strategies, and a celebration of their unique strengths. By embracing this multifaceted perspective, families can empower their children to navigate the complexities of ASD and unlock their full potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Level 1 autism spectrum disorder?
Level 1 autism spectrum disorder is characterized by the need for support in managing communication difficulties and restricted, repetitive behaviors. Individuals often struggle with initiating and sustaining conversations and interpreting social cues.
What are common symptoms of Level 1 autism spectrum disorder?
Common symptoms include challenges in interpersonal interactions such as avoiding eye contact, having trouble understanding non-verbal cues, struggling to form friendships, and displaying repetitive behaviors like lining up toys or echoing phrases.
What is the prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
The overall prevalence of ASD is 27.6 per 1,000 youths, with a male-to-female ratio of 11.4, indicating a higher prevalence among males. In Arizona, the prevalence is reported at 26.8 per 1,000 children.
Why is early recognition of Level 1 autism spectrum disorder important?
Early recognition is crucial as it enables access to effective assistance and intervention measures, which can improve interpersonal abilities and enhance the chances for significant relationships for individuals with Level 1 autism spectrum disorder.
How can parents support children with Level 1 autism spectrum disorder?
Parents can support their children by remaining vigilant for symptoms, recognizing indicators early, and seeking appropriate assistance to help enhance their children's interpersonal skills and establish meaningful connections.
What role does research play in understanding Level 1 autism spectrum disorder?
Continued recognition and research into profound autism are essential for improving resources and support. It helps establish effective assistance and intervention strategies tailored to the unique needs of individuals with Level 1 autism spectrum disorder.




