Introduction
In a world that increasingly recognizes the diverse spectrum of neurodevelopmental conditions, understanding the intersection of autism and dyslexia becomes crucial for effective advocacy and support. As parents and educators navigate the complexities of these conditions, they encounter unique challenges that can significantly impact a child's academic and social development.
- Autism, characterized by difficulties in communication and social interactions, often overlaps with dyslexia, a learning disability that hinders reading and language processing.
- This duality not only complicates the educational landscape but also underscores the urgent need for tailored interventions and robust support systems.
By exploring the nuances of these conditions, their comorbidities, and effective strategies for intervention, this article aims to empower families and advocates with the knowledge needed to foster an inclusive environment where every child can thrive.
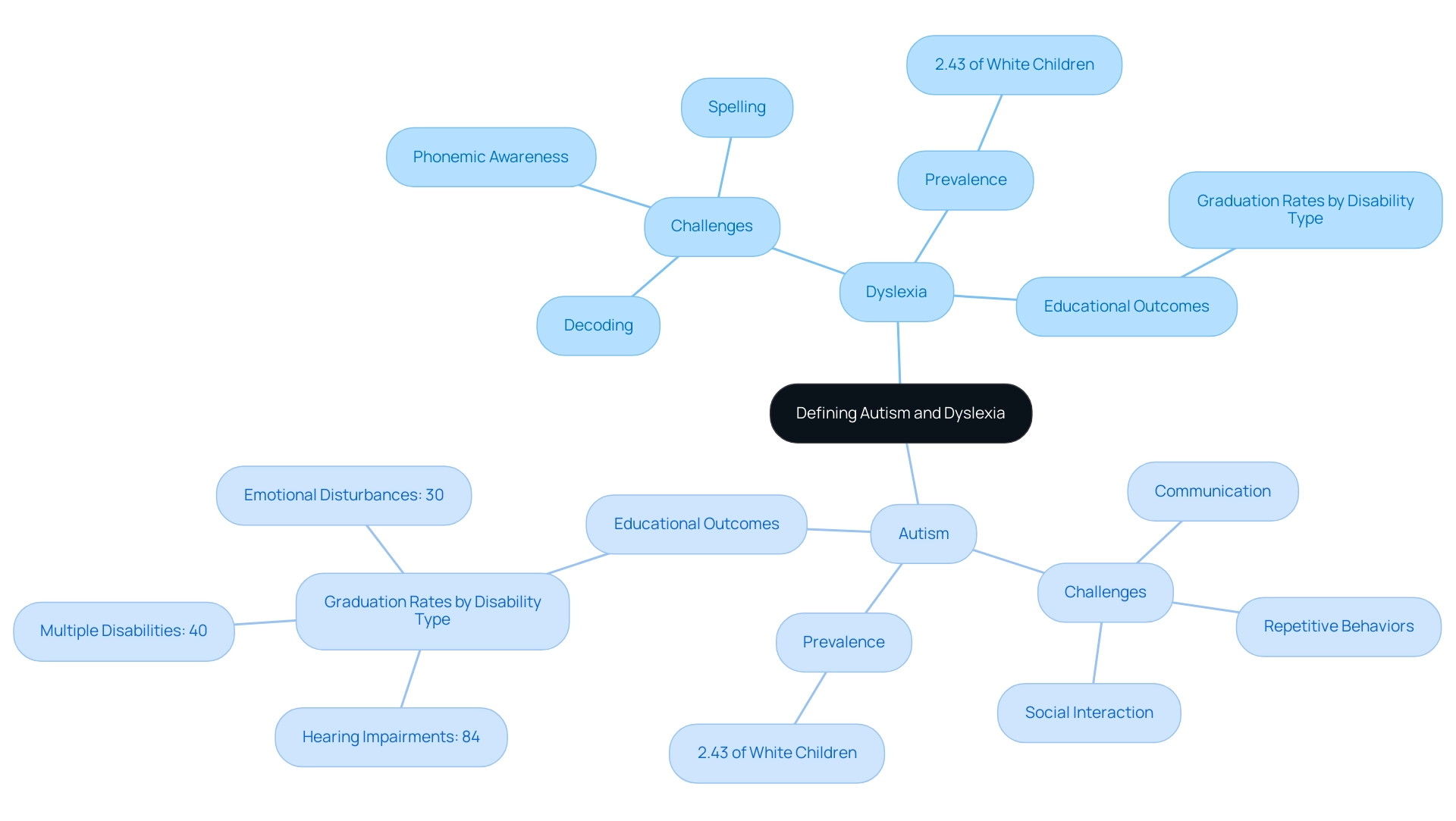
Defining Autism and Dyslexia: Key Concepts for Understanding
Dyslexia and autism are complex developmental disorders marked by unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and the presence of repetitive behaviors. Its effects vary widely among individuals, resulting in a spectrum of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Dyslexia, in contrast, is a specific learning disability that primarily affects reading and language processing skills.
Children with dyslexia typically find challenges in areas such as phonemic awareness, decoding, and spelling, which can hinder their academic progress. Understanding these definitions is vital; it enables parents and educators to recognize how each condition manifests in youth and emphasizes the need for customized support strategies. Grasping the prevalence of the condition, which affects approximately 2.43% of White children, alongside the recognition that about 15% of students in Bureau of Indian Education schools are served under IDEA, highlights the importance of informed advocacy.
The case study titled 'Impact of Disability Type on Graduation Rates' reveals that students with developmental disorders and learning difficulties face significant challenges in educational settings, with graduation rates varying considerably based on disability type. For example, while students with hearing impairments had a graduation rate of 84%, those with several disabilities, including developmental disorders, had significantly lower rates, highlighting the necessity for focused resources and assistance systems. As noted by the U.S. Department of Education, a higher percentage of male students (18%) than female students (10%) are served under IDEA in public schools.
This further emphasizes the essential requirement for advocacy and customized assistance for individuals facing both conditions.
Exploring the Connection: Autism and Dyslexia Comorbidity
Studies consistently indicate that a considerable portion of youth identified with dyslexia and autism also exhibit signs of reading difficulties, emphasizing a notable overlap between these two conditions. The challenges associated with dyslexia and autism often overlap, particularly affecting communication, social skills, and academic performance. For instance, challenges with language processing are frequent in both dyslexia and autism, which can greatly affect a young person's learning experience.
Importantly, the occurrence of developmental disorders differs across various demographic groups, with rates of:
- 29.3% among non-Hispanic Black youth
- 31.6% among Hispanic youth
- 33.4% among [[non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander youth
Baldwin](https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10971064) et al](https://autismparentingmagazine.com/autism-statistics). point out that
Twice-exceptional individuals evidence exceptional ability and disability, which results in a unique set of circumstances.
Furthermore, research indicates that perception problems are more prevalent in the dyslexia group (mean 0.40) compared to the non-dyslexia group (mean 0.22), underscoring the overlapping challenges encountered by individuals with these conditions. The case study on 'The Good Doctor' illustrates the impact of media representation on public perception of autism, providing a valuable context for understanding advocacy efforts. Recognizing these shared traits of dyslexia and autism is essential for educators and parents alike, as it enables the development of targeted interventions that address the specific needs of neurodiverse individuals.
By fostering a deeper understanding of these connections, advocates can better support children through tailored educational strategies and resources that promote their success.
Symptoms and Challenges: Navigating Life with Autism and Dyslexia
Children with autism often display a variety of symptoms, such as difficulties with social interactions, challenges in communication, and tendencies toward repetitive behaviors. When combined, dyslexia and autism can lead to symptoms that include struggles with reading fluency, comprehension, and spelling, creating a compounded effect that significantly hinders academic performance. Recent statistics indicate that 73.6% of autistic students in the U.S. manage to graduate high school, yet many face profound academic challenges as a result of these overlapping difficulties.
Reports indicate that nearly 50% of mothers of autistic individuals experience symptoms of depression, and a concerning 67.1% of mothers of autistic youth in Changsha, China, reported having both depression and anxiety symptoms, emphasizing the need for strong assistance systems. Furthermore, the prevalence of this condition is notably lower among non-Hispanic White youth (24.3) compared to non-Hispanic Black (29.3), Hispanic (31.6), and non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander (33.4) youth, underscoring disparities in diagnosis and support. Educators have voiced concerns about the unique challenges faced by neurodiverse individuals, emphasizing the necessity for tailored strategies that address dyslexia and autism.
A notable case study highlighting this issue involved parents suing prominent reading curriculum developers, which raises critical questions about the effectiveness of current educational approaches for youth with these conditions. As mentioned in Autism Parenting Magazine, fathers place significant importance on assistance with their autistic son or teen’s social development. By collaborating, parents and educators can successfully recognize these symptoms and implement suitable interventions, fostering an environment where youngsters can truly thrive.
Effective Treatments and Interventions: Supporting Neurodiverse Children
Navigating the complexities of dyslexia and autism requires a multifaceted approach to intervention. Effective strategies for young individuals facing challenges associated with dyslexia and autism often include tailored educational methods, speech and language therapy, and behavior analysis techniques. With 70-80% of students in special education diagnosed with reading disabilities having dyslexia and autism, it becomes increasingly vital for parents to prioritize early intervention.
This proactive step can greatly influence a child's academic trajectory. Structured literacy programs that emphasize phonemic awareness are especially advantageous for individuals with reading challenges, as pointed out by Ralph Moller, who remarked that 'poor phonological processing... can contribute to these reading difficulties.' Embracing the strengths of dyslexia, as discussed in the case study titled 'Conclusion on Dyslexia,' emphasizes that dyslexic thinking can lead to innovative and creative contributions, which should not be overlooked.
Additionally, Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy can be instrumental in addressing the behavioral challenges associated with disorders like dyslexia and autism. Expert insights suggest that understanding and managing these behaviors with evidence-based strategies can significantly enhance outcomes for individuals with dyslexia and autism. Collaboration among parents, educators, and therapists is crucial to create a cohesive support plan, ensuring that interventions are effective and customized to the unique needs of each individual.
Recent advancements in therapies keep progressing, offering hope and resources for neurodiverse youth to flourish. As one therapist stated, 'Personalized educational approaches can change the learning experience for young individuals with developmental challenges, enabling them to achieve their full potential.
Advocacy and Support: Building a Community for Neurodiverse Families
Advocacy is crucial in guaranteeing that individuals with dyslexia and autism obtain the customized assistance needed for their development. Parents are encouraged to connect with local advocacy groups and engage in meaningful dialogues with educators regarding their offspring's unique needs. By fostering a community of support, families can enhance access to vital resources, promote collaboration, and cultivate inclusive environments for neurodiverse individuals.
For instance, the case study titled 'Types of ABA Therapy' illustrates how different approaches within ABA can significantly impact learning outcomes, underscoring the need for personalized interventions. Sharing personal experiences and effective strategies not only empowers parents but also drives systemic changes that benefit all youth. As Kyle Coddington, CEO of Prospera Healthcare, asserts,
providing personalized, in-home ABA therapy to assist children with developmental differences across Texas build lasting skills and thrive.
This highlights the importance of tailored interventions in advocacy efforts. Furthermore, the recent discussions surrounding the authenticity of representation in 'The Good Doctor' emphasize how accurate portrayals in media can shape public perception and advocacy efforts. With the prevalence of autism among White children at 2.43%, the urgency for collective action in advocating for assistance with dyslexia and autism is evident.
By uniting as a community, we can create a powerful network that champions the rights and needs of neurodiverse families, ensuring they have the support and resources they deserve.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of autism and dyslexia is vital for parents and educators striving to support neurodiverse children effectively. The overlapping challenges of these conditions can significantly impact a child's academic and social development, necessitating informed advocacy and tailored interventions. By recognizing the unique symptoms associated with each condition and their comorbidities, families can better navigate the educational landscape and implement strategies that foster growth and success.
The importance of effective treatments and community support cannot be overstated. Early intervention, structured literacy programs, and collaboration among parents, educators, and therapists are crucial in creating a supportive environment that addresses both autism and dyslexia. The role of advocacy in connecting families with resources and promoting inclusive practices is essential for empowering parents and ensuring that every child receives the individualized attention they deserve.
As awareness of these conditions continues to grow, so does the collective responsibility to advocate for neurodiverse children. By fostering a community that prioritizes understanding, collaboration, and tailored support, families can work together to create an environment where children with autism and dyslexia can thrive. Embracing the unique strengths and challenges of each child paves the way for a brighter future, where every individual is valued and supported in their journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are dyslexia and autism?
Dyslexia is a specific learning disability that primarily affects reading and language processing skills, while autism is a complex developmental disorder characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
How do dyslexia and autism impact individuals?
The effects of dyslexia and autism vary widely among individuals, leading to a spectrum of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Children with dyslexia often struggle with phonemic awareness, decoding, and spelling, hindering their academic progress. Those with autism may face challenges in communication and social skills.
What is the prevalence of dyslexia and autism among youth?
Dyslexia affects approximately 2.43% of White children, while about 15% of students in Bureau of Indian Education schools are served under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). The occurrence of developmental disorders varies among demographic groups, with rates of 29.3% among non-Hispanic Black youth, 31.6% among Hispanic youth, and 33.4% among non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander youth.
How do graduation rates differ for students with disabilities?
Graduation rates vary significantly based on disability type. For example, students with hearing impairments have a graduation rate of 84%, while those with multiple disabilities, including developmental disorders, have considerably lower rates. This highlights the need for focused resources and assistance systems.
What is the relationship between dyslexia and autism?
Studies indicate a considerable overlap between dyslexia and autism, with many youth identified with dyslexia also showing signs of reading difficulties. Both conditions can affect communication, social skills, and academic performance, particularly through challenges with language processing.
What are twice-exceptional individuals?
Twice-exceptional individuals exhibit both exceptional abilities and disabilities, resulting in a unique set of circumstances that can affect their learning and support needs.
Why is understanding the connection between dyslexia and autism important for educators and parents?
Recognizing the shared traits of dyslexia and autism allows educators and parents to develop targeted interventions that address the specific needs of neurodiverse individuals, promoting their success through tailored educational strategies and resources.




