Introduction
Navigating the world of autism can often feel overwhelming for parents, especially when it comes to understanding the unique behaviors exhibited by their children. One such behavior, commonly referred to as T-Rex Arms, involves a distinctive posture that many children with autism adopt, often as a means of self-soothing or expressing discomfort.
This article delves into the significance of T-Rex Arms, shedding light on the underlying sensory processing challenges that may drive this behavior. By debunking common myths and offering practical strategies, parents can gain valuable insights into their child’s needs, fostering an environment that promotes comfort and well-being.
With the right knowledge and support, caregivers can empower their children to thrive, transforming uncertainty into understanding and advocacy.
Understanding T-Rex Arms: What They Are and Their Significance in Autism
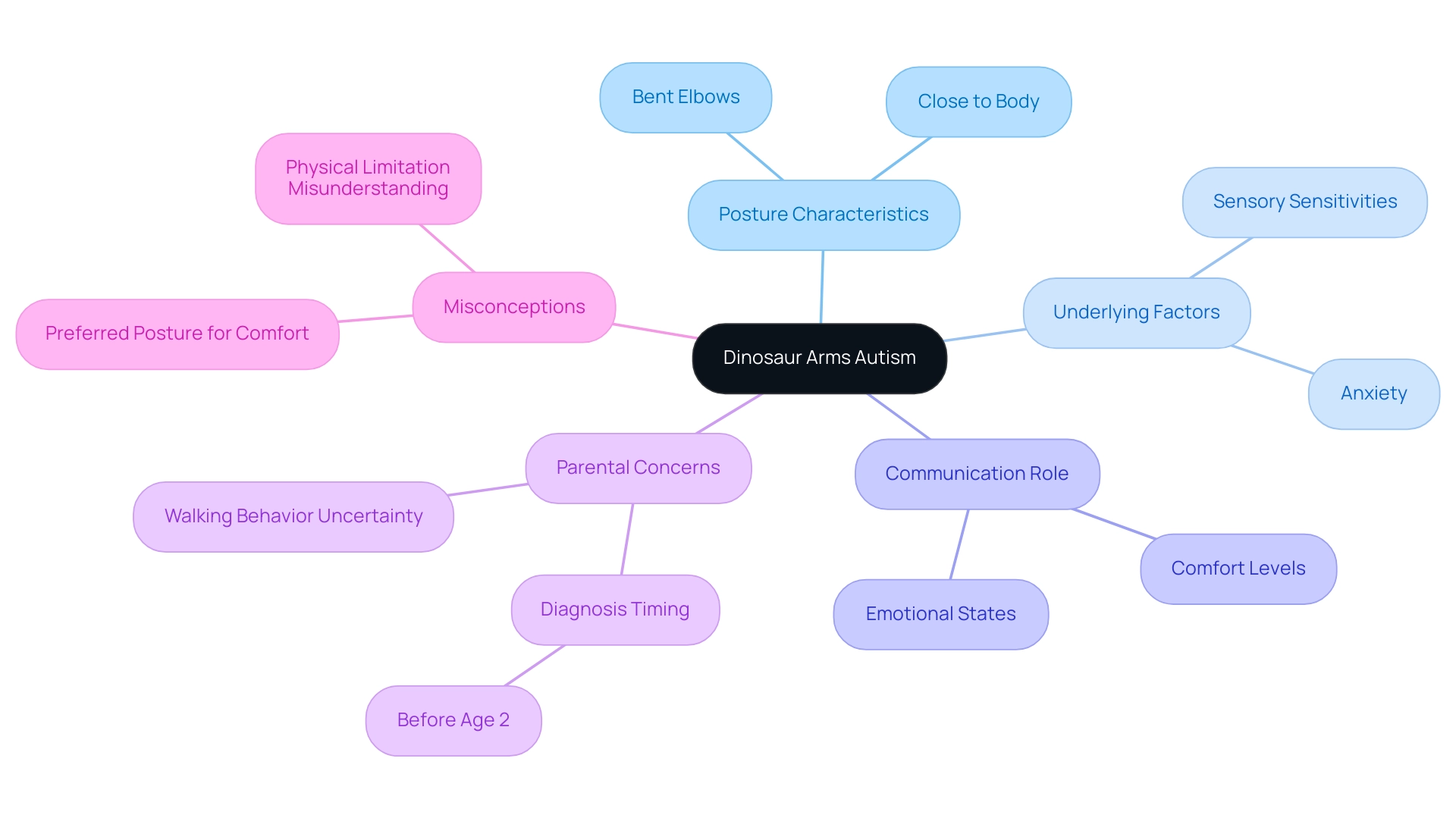
The posture known as dinosaur arms autism describes a distinctive way in which individuals hold their arms bent at the elbows and close to their bodies, reminiscent of the stance of a T-Rex dinosaur. This conduct is frequently observed in youngsters with dinosaur arms autism and can indicate a variety of underlying factors, such as sensory sensitivities or anxiety. For numerous parents, there may be uncertainty regarding their child’s walking patterns at this age, which can lead to concerns about development.
It is essential for parents and caregivers to recognize that dinosaur arms autism is not just an eccentricity; it plays a vital role in communicating comfort levels or emotional states. Sinnesaurus aptly notes,
This is why professionals are careful about diagnosing before the age of 2 at the earliest. It can sometimes be detected earlier, but sooo many autistic behaviors/stims/etc. are also just typical normal actions of babies. So it can be very tricky. I wouldn't worry about it at all!
Furthermore, the case study titled "Misconceptions about T-Rex Arms" clarifies that what some refer to as dinosaur arms autism are often misunderstood as a physical limitation, when in fact they represent a preferred posture for comfort and self-regulation, serving as a form of communication rather than a sign of weakness. By understanding these behaviors, caregivers can become more attuned to their offspring’s needs and reactions in various settings, fostering a supportive environment that promotes well-being.
The Connection Between Sensory Processing and T-Rex Arms
Processing challenges are common among youth with autism, often leading to either heightened or reduced reactions to stimuli. Significantly, 34% of youth with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are categorized as non-responding, in contrast to 19% in the modulation disorder (SMD) group and 27% in typically developing (TYPE) individuals. One observable behavior, frequently known as dinosaur arms autism, may serve as a self-soothing mechanism or a non-verbal indicator of discomfort in overwhelming environments.
For instance, a young person might adopt this posture when feeling anxious or overstimulated in crowded or noisy environments, enabling them to manage overwhelming stimuli more effectively. Comprehending this connection is essential for caregivers, as it enables them to establish settings that lessen stressors and foster comfort. As Grace Baranek, Associate Dean and Chair, emphasizes,
As clinicians pay increasing attention to pediatric traits related to perception as part of a holistic health profile, individuals at elevated likelihood of autism can be referred to critical services at earlier points.
This proactive approach enables access to interventions that can optimize sensory skills and enhance social participation, ultimately supporting the well-being of individuals with autism. Furthermore, the study confirmed previous literature differentiating individuals with ASD and SMD from typically developing individuals on behavioral and physiological measures, highlighting the distinct characteristics of each group. This understanding is essential for improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
Debunking Myths: Common Misconceptions About T-Rex Arms in Autism
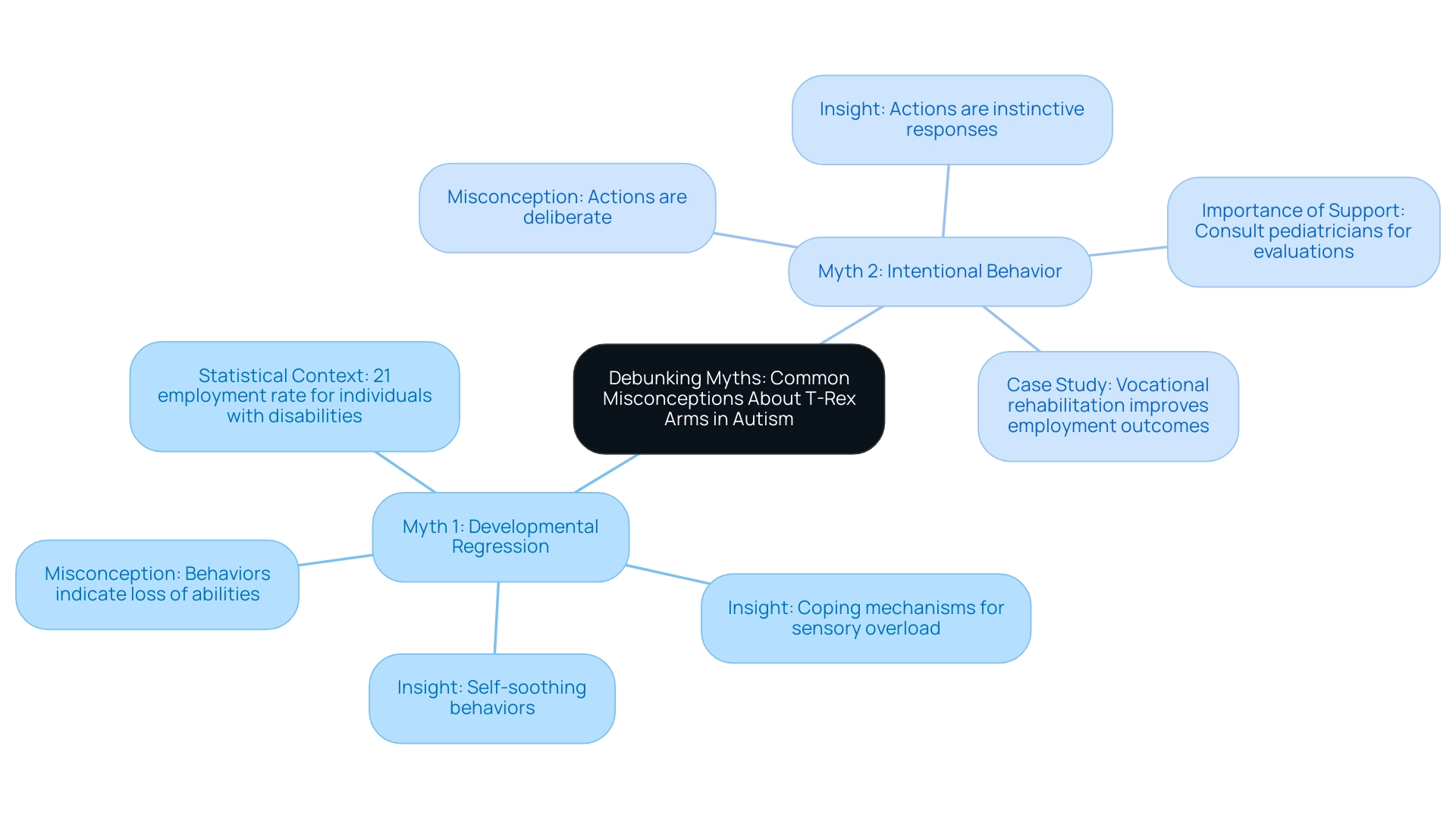
Myth 1: The arms of this dinosaur are often misconstrued as a representation of developmental regression, which has led many parents to fear that their children are experiencing dinosaur arms autism and losing abilities. However, it’s essential to recognize that certain behaviors associated with dinosaur arms autism often signify a natural coping mechanism or a source of comfort rather than a decline in development. Research indicates that these actions can be a direct response to sensory overload or emotional distress in individuals with dinosaur arms autism, showcasing the individual's need for self-soothing rather than signaling a loss of previously acquired skills.
As mentioned, only 21% of individuals with disabilities, including autism, are employed, emphasizing the significance of support systems in promoting developmental success.
Myth 2: Another common misconception is that youngsters displaying T-Rex Arms are participating in this action intentionally. On the contrary, these actions emerge as instinctive responses to their surroundings and feelings, not as deliberate acts. By debunking these myths, parents can approach their offspring's actions with understanding and compassion.
This supportive mindset is crucial for fostering an environment conducive to their offspring's growth and development.
Understanding the nuances of these behaviors empowers parents to advocate effectively for their kids, especially in contexts where the prevalence of autism is often misunderstood. As noted by researchers, including Lord, some individuals may experience a heightened expression of symptoms due to environmental factors, which further complicates the narrative around autism. Therefore, it is vital for parents to consult pediatricians for evaluations and resources if they suspect their offspring may be on the autism spectrum.
Nurturing an informed perspective allows for better support and resources tailored to each individual's unique needs.
Practical Strategies for Supporting Individuals with T-Rex Arms
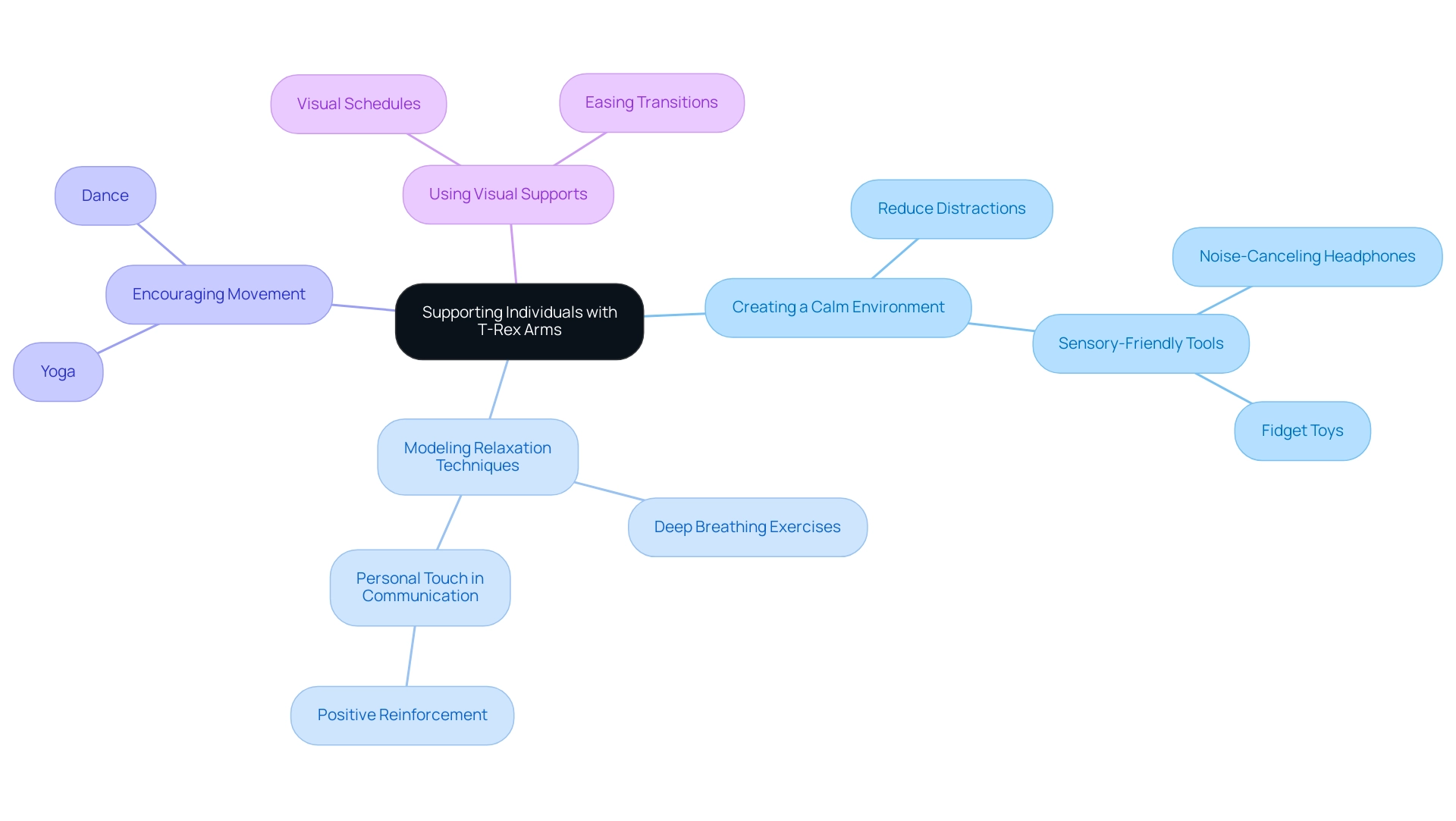
Creating a calm environment is paramount for supporting individuals with dinosaur arms autism, especially those exhibiting T-Rex Arms as a coping mechanism. Start by reducing distractions; a calm, dedicated area where your young one can retreat when feeling overwhelmed can make all the difference. Incorporating sensory-friendly tools like noise-canceling headphones and fidget toys can further help manage sensory overload, as highlighted in the case study on 'Creating Sensory-Friendly Spaces.'
According to recent insights, DCPS serves over 50,000 students, underscoring the importance of individualized strategies to address specific needs.
- Modeling relaxation techniques is another essential strategy.
- Teach your offspring deep breathing exercises or other calming techniques they can use during moments of discomfort, empowering them to manage their feelings effectively.
- A personal touch can be added by sharing experiences, such as saying, 'I love how you used a tissue!' which can resonate positively with young ones during calming exercises.
Encouraging movement is vital, too. Activities that promote flexibility, such as yoga or dance, can help reduce the tendency to adopt rigid postures, fostering a greater sense of freedom and expression.
- Visual supports play a significant role in easing transitions and changes within the environment.
- Implementing visual schedules can significantly reduce anxiety, effectively minimizing the need for behaviors associated with dinosaur arms autism.
This approach aligns with findings that emphasize the importance of understanding young people's perspectives, as only 12 studies have focused on their views. Highlighting the underrepresentation of autistic students' views can provide a critical perspective on the importance of individualized strategies. Moreover, collaboration between parents and professionals is crucial for identifying each individual's strengths and challenges, leading to better outcomes.
By creating these supportive strategies and environments, we can enhance the ability of our youth to thrive.
The Role of Occupational Therapy and Behavioral Interventions in Managing T-Rex Arms
Occupational therapy is essential in navigating the sensory processing difficulties often associated with dinosaur arms autism, particularly when addressing T-Rex Arms. Therapists work together with young individuals to develop customized strategies focused on enhancing motor skills and improving adaptive functions. Behavioral interventions, particularly Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), are pivotal in this process, focusing on reinforcing positive behaviors and equipping individuals with alternative coping mechanisms.
The effectiveness of these interventions is underscored by a remarkable 93.9% improvement in Total ABC scores after just five sessions, illustrating significant progress in addressing behavioral challenges. However, it is important to note that only 15% of insured minors referred for ABA-based behavioral health treatment received 80% or more of the recommended treatment hours, highlighting the challenges many families face in accessing effective therapy. Additionally, a case study indicates that behavioral therapy is most commonly received in public schools in nonmetropolitan areas, whereas in metropolitan areas, it is more frequently provided at home, pointing to significant variations in service delivery based on geographic context.
By engaging with skilled professionals, parents can ensure their child receives tailored support, ultimately fostering growth and development while effectively managing T-Rex Arms. As Georg Loss noted, effective communication and collaboration between therapists and families are key to successful outcomes in therapy.
Conclusion
Understanding T-Rex Arms and their significance in autism is essential for parents seeking to support their children effectively. This behavior, often misunderstood, serves as a crucial form of communication and self-soothing for many children with autism. By recognizing that T-Rex Arms are not indicative of developmental regression but rather a response to sensory overload or emotional distress, parents can approach their child’s behaviors with empathy and understanding.
Equipping caregivers with practical strategies, such as:
- Creating sensory-friendly environments
- Modeling relaxation techniques
- Encouraging movement
fosters a supportive atmosphere where children can thrive. Furthermore, the role of occupational therapy and behavioral interventions is vital in addressing sensory processing challenges and enhancing adaptive behaviors. Engaging with professionals ensures that children receive the tailored support they need, empowering both them and their families.
Ultimately, by debunking myths and embracing informed perspectives, parents can advocate effectively for their children. This advocacy not only promotes understanding and acceptance but also paves the way for children to develop their unique strengths. With knowledge and support, navigating the complexities of autism becomes a journey of empowerment, transforming challenges into opportunities for growth and connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the term "dinosaur arms autism" refer to?
Dinosaur arms autism describes a distinctive posture where individuals hold their arms bent at the elbows and close to their bodies, resembling the stance of a T-Rex dinosaur. This behavior is often observed in children with autism and can indicate sensory sensitivities or anxiety.
Why might parents be concerned about their child's walking patterns related to dinosaur arms autism?
Parents may feel uncertain about their child's walking patterns at a young age, which can lead to concerns about developmental milestones. Understanding that dinosaur arms autism is a form of communication can alleviate some of these worries.
How should caregivers interpret dinosaur arms autism?
Caregivers should recognize that dinosaur arms autism is not merely an eccentricity but a vital form of communication that reflects an individual's comfort levels or emotional states.
At what age can professionals typically diagnose autism, and why?
Professionals are usually careful about diagnosing autism before the age of 2, as many behaviors associated with autism can also be typical actions of babies. This makes early diagnosis tricky.
What is the significance of understanding dinosaur arms autism in terms of emotional regulation?
Understanding this behavior helps caregivers become more attuned to their children's needs and reactions, allowing them to create supportive environments that promote well-being.
How common are processing challenges among youth with autism?
Processing challenges are common among youth with autism, with 34% categorized as non-responding to stimuli, compared to 19% in the modulation disorder group and 27% in typically developing individuals.
In what situations might a young person display dinosaur arms autism?
A young person may adopt this posture when feeling anxious or overstimulated in crowded or noisy environments, as a self-soothing mechanism or non-verbal indicator of discomfort.
What is the importance of understanding the connection between dinosaur arms autism and sensory processing?
Comprehending this connection allows caregivers to create settings that reduce stressors and foster comfort, ultimately supporting the well-being of individuals with autism.
How does the proactive approach to autism diagnosis benefit individuals?
A proactive approach enables individuals at higher likelihood of autism to be referred to critical services earlier, optimizing sensory skills and enhancing social participation.
What does the study mentioned in the article reveal about the differences between individuals with ASD, SMD, and typically developing individuals?
The study confirms that individuals with ASD and SMD exhibit distinct behavioral and physiological characteristics compared to typically developing individuals, which is essential for improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.




