Overview
Understanding autism stimming behaviors is vital for parents and advocates. These actions play essential roles, such as self-soothing and sensory regulation, for individuals on the autism spectrum. The article explores various forms of stimming and their purposes, emphasizing the importance of fostering acceptance and understanding. Recognizing these behaviors can lead to more effective support strategies, ultimately enhancing emotional well-being for those affected.
As we delve deeper, consider how stimming might manifest in your child's life. Perhaps you've noticed certain repetitive movements or sounds that seem to bring them comfort. These behaviors are not merely quirks; they are meaningful expressions of their needs. By embracing and understanding stimming, we can create a nurturing environment that supports emotional health.
We invite you to reflect on your experiences and share your stories. How have you navigated the challenges of understanding stimming? Your insights could help others in similar situations. Together, we can foster a community of support and understanding, ensuring that every individual on the autism spectrum feels seen and valued.
Introduction
In a world where understanding and acceptance of neurodiversity are increasingly vital, stimming behaviors emerge as a significant aspect of the autistic experience. Short for self-stimulatory behavior, stimming encompasses a range of repetitive motions and sounds that serve crucial functions for many individuals on the autism spectrum, from self-soothing to sensory regulation. As research sheds light on the benefits of these behaviors, it becomes clear that they are not merely quirks but essential tools for emotional and sensory management.
For parents and advocates, grasping the nuances of stimming is paramount. Understanding these behaviors empowers them to support autistic individuals in navigating their unique sensory worlds. This article delves into the complexities of stimming, exploring its types and purposes, while also offering strategies that can foster a more accepting environment for those who engage in these natural behaviors. Together, we can create a more compassionate space for everyone.
Defining Stimming: What Every Parent Should Know
Stimming, short for self-stimulatory behavior, refers to a variety of repetitive movements or sounds that individuals, especially those with autism, often exhibit. Common forms of stimming include:
- Hand-flapping
- Rocking
- Spinning
- Various vocalizations
For parents, grasping the concept of autism stimming behaviors is crucial, as these actions represent a natural and integral part of many autistic individuals' lives, serving important functions like self-soothing and sensory regulation.
Research shows that autism stimming behaviors can significantly aid autistic individuals in managing their emotions. A recent study published on September 26, 2023, highlighted the prevalence of these behaviors, revealing that they are not only common but also beneficial for handling sensory sensitivities and promoting self-efficacy. The study utilized various statistical methods, including Chi-square analysis and ANOVAs, to evaluate group differences, providing a solid foundation for understanding the impact of these repetitive behaviors.
By understanding the role of autism stimming behaviors, parents can support their children more effectively, fostering an environment where these behaviors are recognized as valid and essential.
Experts emphasize the importance of acknowledging self-stimulatory actions. As one autism expert noted, recognizing these behaviors can lead to better coping strategies for autistic individuals, helping them navigate their surroundings with greater ease. Additionally, Rebecca shared her feelings, stating, "I felt ‘[a]ngry that they’ve been told a thousand times why I do it, the reason behind it, that it’s not affecting anyone,’" highlighting the need for understanding and acceptance of self-regulating behaviors within the broader community.
Moreover, case studies from focus groups exploring sensory-seeking dynamics illustrate how sharing experiences can deepen our understanding of the reasons behind these actions. Participants engaged in activities that encouraged conversation, demonstrating that self-soothing behaviors often serve as a crucial resource for emotional and sensory control.
In summary, grasping autism stimming behaviors is vital for parents and advocates. By recognizing the significance of these actions, they can better support their children in developing effective coping strategies and navigating the complexities of their sensory experiences.
Types of Stimming Behaviors: Recognizing the Spectrum
Understanding autism stimming behaviors, or self-stimulatory actions, is vital for parents and advocates. These behaviors can be categorized into several distinct types, each addressing unique sensory needs and functions. Recognizing these categories enables caregivers to respond effectively to their child's specific actions, fostering a supportive environment.
- Visual Stimming: Children may engage in watching spinning objects or flickering lights, which can provide comforting visual stimulation.
- Auditory Stimming: Making repetitive sounds or vocalizations helps children regulate their auditory input, creating a sense of control.
- Tactile Stimming: Rubbing or touching various textures allows young individuals to explore their surroundings through touch, offering valuable sensory feedback.
- Vestibular Stimming: Movements such as rocking or spinning assist with balance and sensory integration, promoting a sense of stability.
- Proprioceptive Stimming: Activities like jumping or squeezing enhance body awareness, providing calming and grounding effects for the individual.
Identifying these forms of autism stimming behaviors is crucial for parents seeking to address their child's self-harming tendencies and enhance overall wellness. Occupational therapists emphasize that understanding the purpose behind these actions can lead to more empathetic support strategies. For instance, a child engaging in visual sensory behaviors may be attempting to calm themselves in overwhelming environments, while auditory sensory activities could serve as expressions of excitement or anxiety.
As Ruben Kesherim observed, "Acknowledging this can result in a more compassionate comprehension of autism self-stimulatory actions and aid in developing improved support strategies for those who encounter them."
Research studies have classified autism stimming behaviors in autistic individuals, revealing that these actions are not merely repetitive but often serve crucial processing functions. A case study titled 'Theoretical Models of Sensory and Social Features in ASD' discusses how sensory processing abnormalities can influence social actions, suggesting that autism stimming behaviors may play a role in social interactions as well. This aligns with findings from the SFARI Gene database, which lists 264 genetic, 42 pharmacologically induced, and 4 inbred mouse models of ASD, providing a scientific context for understanding the complexities of autism.
Real-world examples illustrate the variety of autism stimming behaviors: a young person may spin in circles to achieve vestibular stimulation, while another may arrange toys for tactile exploration. Innovative approaches, such as socially assistive robotics, have shown promise in enhancing social skills among individuals with ASD, highlighting new avenues for support. By comprehending these actions, parents can create nurturing environments that address their child's needs, ultimately promoting improved emotional regulation and social skills growth.
Why Do Autistic Individuals Stim? Exploring the Purpose Behind Stimming
Autistic individuals may engage in repetitive actions for a variety of reasons, each serving a distinct purpose in their daily lives. Understanding these motivations is essential for parents and advocates, as it allows them to support their loved ones in ways that honor their unique experiences and needs.
Self-Regulation: These actions are vital in helping individuals manage overwhelming emotions or external stimuli. Research indicates that autism stimming behaviors, which encompass repetitive actions or sounds, can provide a soothing effect, enabling individuals to regain control in stressful situations.
Sensory Seeking: Many autistic individuals partake in stimming as a means of self-soothing to address specific sensory needs. This behavior can offer comfort or pleasure, serving as a way to explore and engage with their surroundings. A study published in the journal Autism, which involved interviews and focus groups with 32 autistic adults, revealed that stimming often enhances sensory experiences, highlighting its positive aspects and the necessity for interventions that recognize these benefits. For those who find verbal expression challenging, these behaviors can convey feelings or needs, bridging the gap when words are insufficient. This perspective aligns with the understanding that presuming competence is a matter of dignity and respect for individuals with disabilities, as emphasized by Philip David Zelazo from the Institute of Development at the University of Minnesota.
By fostering an environment that respects and understands autism stimming behaviors, caregivers can help autistic individuals navigate their perceptual worlds more effectively. Let’s create spaces where these behaviors are acknowledged and valued, ensuring that every individual feels seen and supported in their journey.
Stimming as a Coping Mechanism: Emotional and Sensory Regulation
Autism stimming behaviors are vital coping mechanisms for many autistic individuals, helping them to regulate emotions during challenging situations. For instance, a young person may engage in rocking motions when feeling anxious, providing a calming effect and a sense of control. This behavior is not merely a repetitive action; it is a crucial strategy for emotional management, enabling young individuals to cope with overwhelming feelings and sensory overload.
Research highlights that autism stimming behaviors, such as rocking, are significantly linked to emotional states, emphasizing their importance in managing anxiety and stress. Notably, studies have shown that intellectual age, as measured by Mullen scores, correlates strongly with in-phase rocking in both typically developing individuals and those with ASD. This underscores the connection between cognitive development and self-soothing actions.
Moreover, autism stimming behaviors offer familiar and calming sensory input, which is essential for individuals facing sensory overload. By engaging in these actions, youngsters can create a personal sanctuary amid external chaos. Parents and caregivers should recognize the significance of self-soothing and autism stimming behaviors in their child's emotional toolkit, understanding that these actions are not only natural but also vital coping strategies.
As Dr. Christopher Hanks, a clinical associate professor of internal medicine, points out, "Maybe we as a society need to change our approach rather than changing the individual," highlighting the importance of acceptance.
While many self-stimulatory actions are positive, it is crucial to be mindful of instances where they may lead to self-injury, such as head-banging or biting. In these cases, identifying the underlying causes is essential for effective intervention. For example, if self-injurious behaviors are observed, exploring potential mood or mental health issues can offer insights into alternative communication methods or safer practices.
The case study titled 'Addressing Harmful Repetitive Actions' illustrates that while such behaviors are generally positive, understanding the underlying causes of harmful actions is vital for intervention. By fostering an environment that embraces and encourages autism stimming behaviors, parents can support their children in thriving emotionally and socially, reinforcing the idea that these actions are valid expressions of individuality. Additionally, public understanding of self-stimulatory actions is evolving, with an increasing demand for greater acceptance of these practices in society.
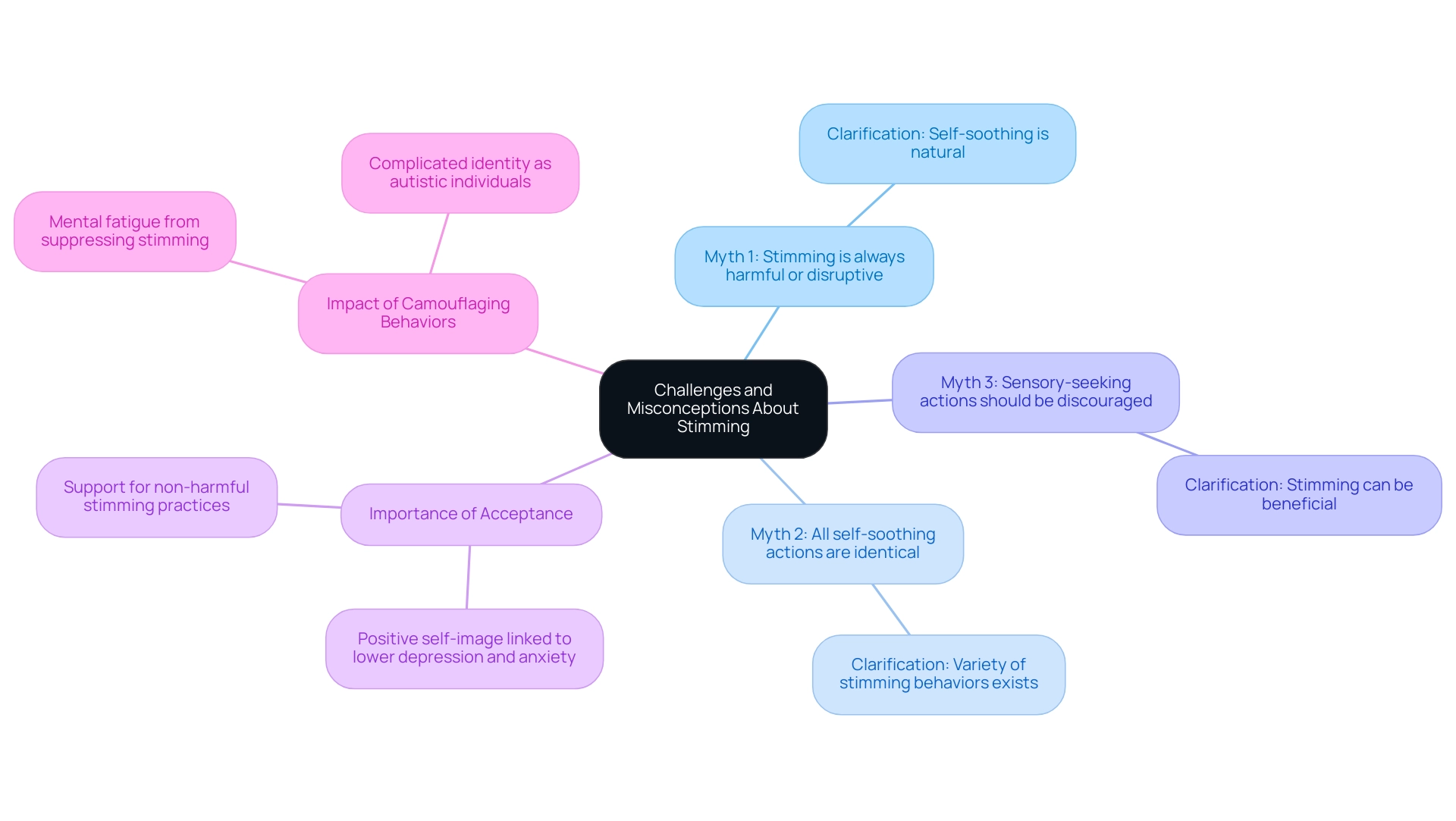
Challenges and Misconceptions: Addressing Common Myths About Stimming
Misinterpretations related to autism stimming behaviors can contribute to stigma and hinder the acceptance of autistic individuals. It's crucial to understand these behaviors, as they play a significant role in emotional well-being. Let's explore some prevalent myths together:
- Myth 1: Stimming is always harmful or disruptive. In reality, self-soothing, which includes autism stimming behaviors, is a natural activity essential for self-regulation and processing stimuli. These behaviors can help individuals manage intense sensory input and express emotions, ultimately enhancing their well-being.
- Myth 2: All self-soothing actions are identical. Autism stimming behaviors manifest in various forms, such as hand-flapping, rocking, or vocalizations, each serving different purposes for the individual. Recognizing this variety is crucial for understanding their importance.
- Myth 3: Sensory-seeking actions should be discouraged or removed. Research indicates that autism stimming behaviors can be beneficial, providing comfort and coping mechanisms for stress. Instead of trying to eliminate these actions, it is essential to endorse non-harmful self-soothing practices, as they contribute positively to emotional well-being.
Addressing these misunderstandings empowers parents to create a more inclusive atmosphere for their children. By fostering comprehension and supporting their needs, parents can help combat the stigma associated with autism stimming behaviors. As Steven Zauderer notes, these actions may seem unusual to onlookers, yet they are often vital for self-regulation and sensory stimulation.
Moreover, studies reveal that autistic individuals with a positive self-image experience lower levels of depression and anxiety, underscoring the importance of acceptance and support in their lives. Additionally, the case study on camouflaging actions illustrates how societal pressures can lead autistic individuals to suppress their natural self-soothing practices, potentially exacerbating mental fatigue and negatively impacting their mental well-being. This highlights the need for a nuanced understanding of autism stimming behaviors, advocating for support that respects non-harmful actions rather than seeking to eradicate them.
Managing Stimming Behaviors: Strategies for Parents and Advocates
Parents often seek effective strategies to manage stimming behaviors while honoring their child's unique needs. One impactful approach is to create a safe space. Designate specific areas where stimming is not only accepted but encouraged. These areas should be free from distractions and furnished with sensory-friendly materials, enabling young people to engage in self-soothing activities without fear of judgment.
Another valuable strategy is to provide alternatives. Introducing tactile toys or fidget tools can serve as constructive outlets for self-regulation. Research indicates a significant positive correlation between the use of fidget toys and sensory-seeking actions, with a correlation coefficient of r(42) = 0.274 and a p-value of .040. This suggests that these tools can effectively assist youngsters in managing their sensory needs.
Educating others is also crucial. Facilitating understanding among family members, teachers, and peers about the nature and purpose of self-stimulatory behavior fosters a supportive environment. This acceptance can help young individuals feel less isolated in their behaviors.
Monitoring triggers is another essential step. By observing and identifying situations that lead to increased stimming, parents can minimize these triggers, creating a more comfortable environment for their children.
Applying these strategies not only assists children in expressing their innate behaviors but also encourages a deeper understanding of their processing requirements, especially in relation to autism stimming behaviors. For instance, a study titled "Impact of Fidget Spinners on On-Task Conduct in Students with ADHD" revealed that while these tools increased on-task conduct for some students, they also highlighted the need for structured environments that accommodate diverse sensory needs. Furthermore, Hanft et al. noted that "a causal relationship between neuronal reactions and actions lacks empirical evidence, so actions cannot be assumed to be the result of reactions in the brain at the cellular level." This underscores the importance of customized strategies in effectively managing repetitive actions.
It's also important to consider differing opinions. One teacher expressed strong disagreement with the effectiveness of fidget spinner interventions, indicating that students did not complete their work despite appearing quieter. This emphasizes the need for personalized approaches that address each individual's unique requirements.
By sharing experiences and insights, we can create a community of support for one another. What strategies have you found helpful in your journey? Let's continue this conversation together.
Seeking Professional Help: Therapy Options for Stimming Behaviors
When autism stimming behaviors intensify to a level where they become problematic or harmful, seeking professional assistance is crucial. There are several effective therapy options available to support children in managing these behaviors:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): Recognized as one of the most effective interventions for individuals diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), ABA focuses on reinforcing positive behaviors while systematically reducing harmful stimming through structured interventions. This evidence-based approach has shown significant success in improving overall behavior and social skills. As noted by Wolf et al., one individual who received ABA therapy 'continues to wear his glasses, does not have tantrums, has no sleeping problems, is becoming increasingly verbal, and is a new source of joy to the members of his family.'
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapists play a crucial role in creating individualized programs tailored to the distinct requirements of every young person. These plans enhance healthier coping strategies, assisting children in navigating their experiences more effectively. Research indicates that occupational therapy can significantly enhance sensory functions, leading to improved emotional well-being and social interactions. Additionally, sensory toys, as explored in the case study "Exploring the Best Baby Sensory Toys for Autism," have been shown to promote cognitive development, social growth, and emotional well-being, complementing therapy options.
- Counseling: Engaging in therapy can provide essential emotional support for both the young person and their family. Counseling addresses underlying issues linked to anxiety or stress, equipping families with strategies to manage the challenges connected to repetitive actions.
It is essential to advocate for the rights and dignity of individuals diagnosed with ASD, recognizing their unique experiences and needs. Parents should thoughtfully evaluate these choices when seeking extra assistance in managing their child's autism stimming behaviors. By collaborating with professionals, families can create a comprehensive support system that fosters growth and development, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for children with autism.
Embracing Stimming: Fostering Acceptance and Understanding
Embracing autism stimming behaviors as an intrinsic aspect of an autistic individual's conduct is crucial for fostering acceptance and understanding. These behaviors—such as hand-flapping, humming, or rubbing textures—serve as vital self-regulation tools that provide comfort and joy. Research indicates that when parents celebrate their child's unique forms of self-expression, it significantly enhances their overall well-being.
For instance, a study revealed that individuals who felt acknowledged by their families were more free to express their sensory actions, leading to enhanced productivity and emotional well-being. This is further supported by the case study titled "Understanding and Acceptance of Self-Stimulatory Actions," which highlighted that supportive settings play a crucial role in the acceptance of such actions, positively contributing to individuals' overall well-being.
Statistics show that approximately 10% of adults engage in fidgeting behaviors, underscoring the natural inclination towards self-soothing actions across all ages. By encouraging a positive view of self-soothing behaviors, parents can help their children feel accepted and valued, which is essential for their self-esteem. Open discussions about self-stimulatory behavior not only reduce stigma but also cultivate a more inclusive environment for everyone involved.
Expert insights emphasize the importance of education and awareness in fostering acceptance of non-harmful self-stimulatory behaviors. Advocates stress that understanding these actions can lead to increased empathy and support from friends and relatives. As one advocate noted, "because she understands it, she knows why I’m doing it … she lets me get on with it most of the time …" This illustrates the profound impact that acceptance can have on an individual's ability to thrive.
To promote acceptance and understanding of self-regulating actions, parents can take proactive measures. These include:
- Educating themselves and others about the importance of these practices.
- Encouraging discussions that normalize such expressions.
- Creating supportive environments where young individuals feel free to express themselves.
It is also vital to recognize that the study's results may not pertain to young individuals or non-verbal autistic people, emphasizing the necessity for a nuanced comprehension of repetitive actions. By embracing autism stimming behaviors, parents not only validate their child's experiences but also contribute to a broader culture of acceptance and understanding within the community.
Conclusion
Embracing stimming as a natural and essential part of the autistic experience is crucial for fostering a more inclusive and understanding society. Stimming behaviors, which can include hand-flapping and vocalizations, play vital roles in emotional regulation, sensory processing, and communication. By recognizing the diverse forms of stimming and their purposes, parents and advocates can better support autistic individuals as they navigate their sensory worlds.
The significance of stimming goes beyond individual experiences; it serves as a call for societal acceptance. By addressing common misconceptions about stimming, we can help dismantle stigma and promote a culture of understanding. Creating safe spaces for stimming, providing sensory-friendly tools, and educating others about these behaviors are proactive steps that can lead to a more compassionate environment.
Ultimately, fostering acceptance of stimming enhances not only the well-being of autistic individuals but also enriches the community as a whole. By championing understanding and appreciation for these behaviors, we can cultivate a culture that values neurodiversity, empowering autistic individuals to thrive and express their true selves without fear of judgment. Let us take action together, creating a world where every individual is embraced for who they are.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stimming and who typically exhibits it?
Stimming, short for self-stimulatory behavior, refers to a variety of repetitive movements or sounds that individuals, especially those with autism, often exhibit. Common forms of stimming include hand-flapping, rocking, spinning, and various vocalizations.
Why is understanding stimming behaviors important for parents?
Grasping the concept of autism stimming behaviors is crucial for parents because these actions are a natural and integral part of many autistic individuals' lives, serving important functions like self-soothing and sensory regulation.
How do stimming behaviors help autistic individuals?
Research shows that autism stimming behaviors can significantly aid autistic individuals in managing their emotions, handling sensory sensitivities, and promoting self-efficacy.
What types of stimming behaviors are there?
Stimming behaviors can be categorized into several types: Visual Stimming (watching spinning objects or flickering lights), Auditory Stimming (making repetitive sounds or vocalizations), Tactile Stimming (rubbing or touching various textures), Vestibular Stimming (movements like rocking or spinning), and Proprioceptive Stimming (activities such as jumping or squeezing).
How can understanding stimming behaviors lead to better support for autistic individuals?
Understanding the purpose behind stimming behaviors allows caregivers to respond effectively and empathetically, fostering a supportive environment that addresses the child's specific sensory needs.
What role do sensory processing abnormalities play in stimming behaviors?
Research indicates that sensory processing abnormalities can influence social actions in autistic individuals, suggesting that stimming behaviors may play a role in social interactions as well.
Can stimming behaviors be beneficial in social settings?
Yes, innovative approaches, such as socially assistive robotics, have shown promise in enhancing social skills among individuals with ASD, highlighting new avenues for support.
How can parents create a nurturing environment for their autistic children?
By comprehending the significance of stimming actions, parents can create environments that address their child's needs, ultimately promoting improved emotional regulation and social skills growth.




