Overview
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) symptoms encompass a range of challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors, reflecting the diverse experiences of individuals on the spectrum. The article supports this by detailing diagnostic criteria, prevalence statistics, and the importance of early intervention strategies, emphasizing the need for tailored support to improve outcomes for those affected by ASD.
Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, presenting a unique set of challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. The term "spectrum" aptly captures the diverse experiences and abilities of those diagnosed, ranging from exceptional skills in specific areas to substantial difficulties in daily functioning.
As research continues to evolve, so does the understanding of this disorder, emphasizing the need for greater awareness and tailored support. With its rising prevalence, particularly among underrepresented groups, recognizing and addressing the symptoms of ASD is crucial not only for enhancing individual outcomes but also for fostering a more inclusive society.
This article delves into the intricacies of ASD, exploring its:
- Diagnostic criteria
- Daily manifestations in children and adults
- Vital role of early intervention and support strategies
Defining Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Overview
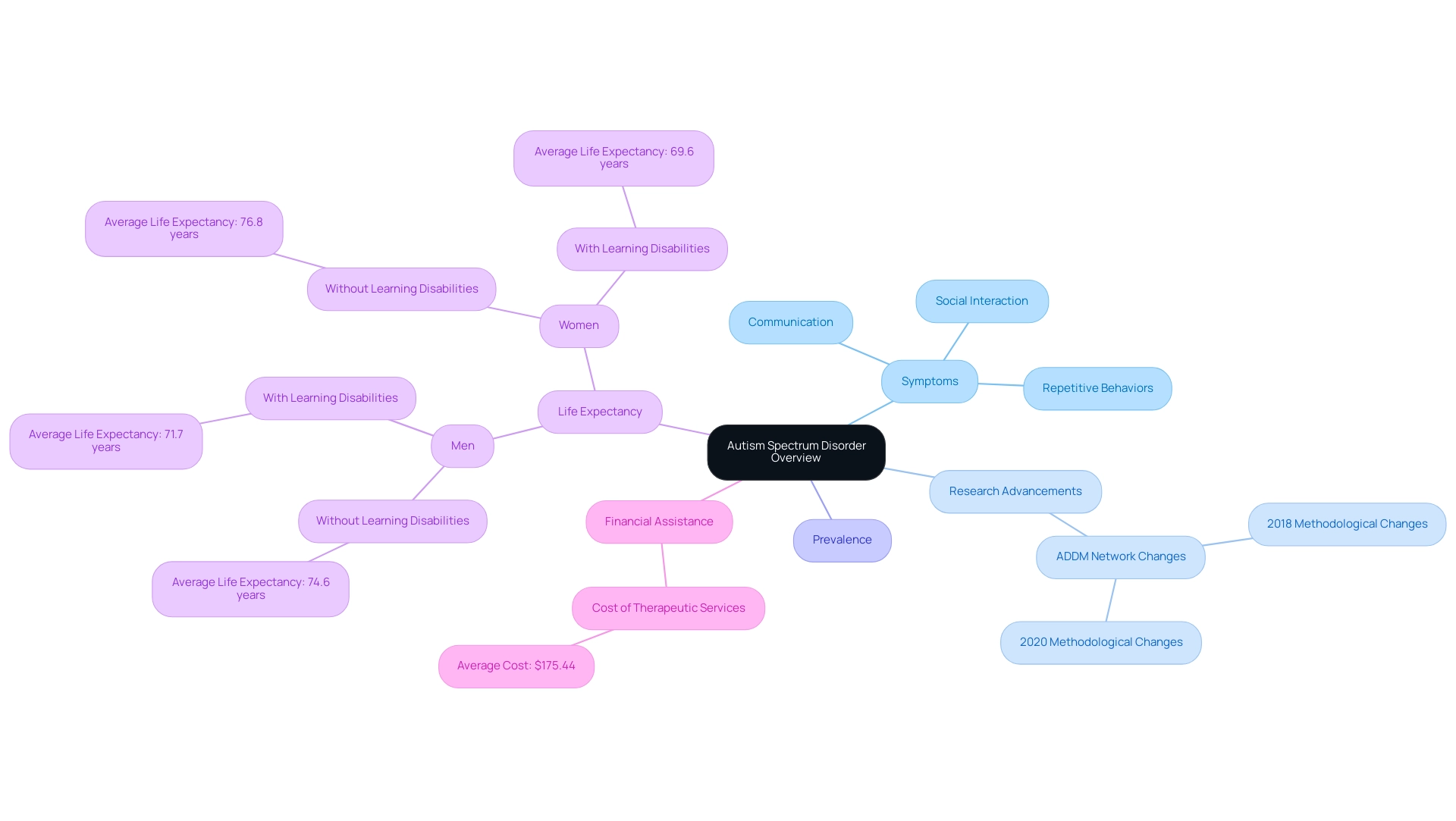
Autism Spectrum Disorder symptoms include a diverse array of challenges, particularly in social interaction, communication, and the presence of repetitive behaviors. The term 'spectrum' aptly describes the varying degrees of autism spectrum disorder symptoms and the different levels of independence among individuals. For instance, while some may excel in certain areas, such as visual skills or memory, others may face significant challenges in daily activities.
Recent advancements in research, including methodological changes by the ADDM Network in 2018 and 2020, have refined the definitions and population estimates for ASD, leading to a more nuanced understanding of this disorder. Current data indicates that the prevalence of ASD continues to rise, highlighting the significance of awareness and assistance. As noted by experts, "the co-occurrence of these two disorders stems from genetic and structural brain differences that characterize them," highlighting the complexity of individual experiences.
Recognizing these distinctions is essential to appreciate how autism spectrum disorder symptoms affect daily life and the specific assistance needs of individuals across the spectrum. For example, research into the life expectancy of autistic individuals indicates that, depending on the severity of symptoms and quality of life, many can live into their 70s. Specifically, autistic men without learning disabilities average a life expectancy of 74.6 years, while those with learning disabilities average 71.7 years.
For women, the averages are 76.8 years without learning disabilities and 69.6 years with learning disabilities. Additionally, the financial aspect of assistance is significant, with the cost of therapeutic behavioral services averaging $175.44. This emphasizes the necessity of personalized assistance and understanding to foster positive outcomes for those on the spectrum.
Diagnostic Criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) delineates clear criteria for the diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). These criteria encompass:
- Persistent deficits in social communication and interaction
- Restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities
These are characteristics of autism spectrum disorder symptoms. Autism spectrum disorder symptoms must manifest during early developmental periods, resulting in significant impairment in social, occupational, or other critical areas of functioning.
Accurate diagnosis typically requires a thorough evaluation by qualified professionals, integrating developmental history and observational assessments. Recent findings indicate a notable increase in ASD identification, particularly among non-White youth and girls, highlighting the urgent need for improved diagnostic and support services tailored to meet these populations' needs. According to a report, the prevalence of ASD among adults increased by 275%, from 0.7 per 1000 persons to 2.7 per 1000 persons among White individuals from 2011 to 2022.
As noted by Williams AR in the MMWR Surveillance Summary, 'Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years,' enhancing detection and outreach efforts can contribute to more equitable healthcare practices. The case study titled 'Racial and Ethnic Disparities in ASD Diagnosis' reveals that relative increases in ASD diagnosis rates were greater among racial and ethnic minority groups compared to White individuals, reinforcing the need for improved detection and outreach efforts to ultimately enhance outcomes for youth who may be underserved.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Autism in Daily Life
Children with autism spectrum disorder symptoms often exhibit a range of behaviors that can manifest in their daily lives. Among the most prevalent autism spectrum disorder symptoms are:
- Difficulties in understanding social cues
- Challenges in maintaining conversations
- A strong preference for routines or repetitive behaviors
For instance, at home, a young person may show noticeable resistance to changes in their daily routines or develop intense interests in specific topics, which can sometimes overshadow other activities.
Additionally, struggles with eye contact are common among individuals with autism spectrum disorder symptoms, making it harder for them to connect with others. In social situations, individuals may find that engaging with peers and navigating group dynamics is particularly challenging due to autism spectrum disorder symptoms. Recent findings highlight that 3.9% of individuals with ASD underwent evaluations that ruled out the diagnosis more recently than those confirming it, underscoring the ongoing challenges in recognizing the condition and the need for heightened awareness.
Furthermore, according to the case definition for ASD in 2020, children aged 8 years who received a written ASD diagnostic statement, a special education classification of the condition, or an ASD ICD code are included, reflecting the evolving understanding of the disorder. Judith Ursitti, co-founder and president of the Profound Autism Alliance, emphasizes the importance of this recognition, stating,
The continuing recognition of profound autism will open the doors to more inclusive research like the CDC’s. Only then can targeted advocacy increase access to critically needed supports and services for this marginalized population.
A case study from the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network revealed that 61.9% of individuals displaying autism spectrum disorder symptoms received a developmental evaluation by the age of 36 months, indicating that timely recognition can lead to essential interventions. Additionally, with 5% of all students in the U.S. not completing high school, the long-term effects of the condition on educational outcomes cannot be overlooked. Such insights into the daily expressions of this condition not only assist parents and educators in offering focused support but also promote a more inclusive atmosphere for these individuals.
Understanding Autism Symptoms in Adults: Challenges and Experiences
Adults on the spectrum often face significant challenges in social situations, manifesting as difficulties in:
- Initiating conversations
- Interpreting body language
- Managing sensory overload in bustling environments
These challenges are compounded in workplace settings, where abrupt changes in routine or communication styles that deviate from their preferences can create additional stress. Notably, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2023) reports that prevalence estimates are for 8-year-old children across 11 monitoring sites, indicating that approximately 2% of eight-year-old children today are diagnosed with the condition.
This statistic underscores the growing need to address adult experiences through tailored support and understanding. Misconceptions and stigma surrounding the condition contribute to feelings of isolation among many adults. Furthermore, findings from the case study titled "Autism-Specific Healthcare Experiences" reveal significant differences in healthcare interactions, with autistic individuals reporting lower quality interactions with healthcare professionals compared to their non-autistic counterparts.
Addressing the challenges faced by adults with autism spectrum disorder symptoms requires a nuanced understanding of their social experiences and the environment in which they thrive. By fostering awareness and creating supportive spaces, we can empower individuals with ASD to navigate these complex social landscapes more effectively while also advocating for improved healthcare access and quality.
Strategies for Managing Autism Symptoms: The Role of Early Intervention and Support
Timely support plays a crucial role in improving results for individuals with autism spectrum disorder symptoms. Among the most effective strategies is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, which emphasizes behavior modification through reinforcement techniques. Recent research, including findings from Welterlin et al. (2012), highlights the effectiveness of ABA, showcasing a mean age of participants at 30.5 years and a demographic composition of 90% males. The study provided Hedges' g values for self-injurious behavior (SIB) and other measurements, illustrating the positive impact of ABA across various developmental areas. Expert Fayge Orzel states,
Our skilled team is prepared to assist with your offspring's growth and well-being.
We are committed to offering tailored ABA therapy solutions that promote growth. Additionally, the case study titled 'Does Stimming Mean You're Neurodivergent?' explores the connection between stimming behaviors and neurodivergence, improving comprehension of these behaviors in the context of neurological differences.
Parents and professionals can implement structured routines, visual schedules, and social skills training to bolster development. Collaboration with educators and therapists is essential, ensuring that techniques applied at home and school are consistent and effective. Furthermore, access to support groups and resources empowers families to successfully navigate the challenges associated with raising a youth facing autism spectrum disorder symptoms.
As new strategies emerge for managing autism spectrum disorder symptoms in 2024, the importance of early intervention remains clear, contributing significantly to improved life outcomes for children on the spectrum.
Conclusion
The exploration of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) highlights the complexity of this neurodevelopmental condition, emphasizing the diverse experiences of individuals affected by it. From the diagnostic criteria outlined in the DSM-5 to the daily manifestations observed in both children and adults, it is evident that ASD presents unique challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. The rising prevalence of ASD, particularly among underrepresented groups, underscores the urgent need for increased awareness and tailored support services that address the specific needs of these populations.
Recognizing the symptoms of autism, whether in childhood or adulthood, is essential for fostering understanding and inclusion. The challenges faced by individuals on the spectrum—ranging from difficulties in social situations to navigating educational and workplace environments—call for a concerted effort to create supportive spaces that empower them. Moreover, early intervention strategies, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), demonstrate significant effectiveness in enhancing developmental outcomes, reiterating the importance of timely support and intervention.
Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of ASD not only benefits individuals and their families but also contributes to a more inclusive society. By prioritizing awareness, improving diagnostic practices, and providing consistent support, the collective effort can lead to better outcomes for individuals with autism and help dismantle the stigma surrounding the disorder. Embracing the spectrum of experiences within ASD fosters an environment where everyone can thrive, reinforcing the message that understanding and support are key to navigating the complexities of autism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder symptoms include challenges in social interaction, communication difficulties, and the presence of repetitive behaviors.
What does the term 'spectrum' refer to in Autism Spectrum Disorder?
The term 'spectrum' describes the varying degrees of symptoms and the different levels of independence among individuals with autism, indicating that some may excel in certain areas while others may face significant challenges.
How has recent research impacted the understanding of Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Recent advancements, particularly methodological changes by the ADDM Network in 2018 and 2020, have refined definitions and population estimates for ASD, leading to a more nuanced understanding of the disorder and highlighting the rising prevalence of ASD.
What is the life expectancy for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Life expectancy varies; autistic men without learning disabilities average 74.6 years, while those with learning disabilities average 71.7 years. For women, the averages are 76.8 years without learning disabilities and 69.6 years with learning disabilities.
What are the financial aspects associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder?
The average cost of therapeutic behavioral services for individuals with ASD is approximately $175.44, emphasizing the necessity for personalized assistance to foster positive outcomes.
What criteria are used for diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder according to the DSM-5?
The DSM-5 outlines criteria that include persistent deficits in social communication and interaction, and restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities, which must manifest during early developmental periods and cause significant impairment.
How has the identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder changed in recent years?
There has been a notable increase in ASD identification, particularly among non-White youth and girls, highlighting the need for improved diagnostic and support services tailored to these populations.
What demographic trends are observed in the prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder?
From 2011 to 2022, the prevalence of ASD among adults increased significantly among White individuals, with a reported increase of 275%, indicating a greater need for enhanced detection and outreach efforts, especially for racial and ethnic minority groups.




