Overview
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Level 2 is crucial for parents and caregivers who are navigating this journey. Individuals at this level require significant support in social communication and daily activities, which can be challenging for families.
Tailored interventions, such as speech therapy and social skills training, play a vital role in enhancing the abilities of those with Level 2 ASD. Early intervention is key, as it can significantly impact their development.
It’s essential to foster a supportive community where families can share experiences and resources. Together, we can create an environment that nurtures growth and understanding for all individuals with ASD.
Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted developmental condition that presents unique challenges in social communication and behavior. With approximately 14.4% to 15.2% of children diagnosed with ASD, understanding its varying levels is crucial for providing the right support. This article delves into the intricacies of Level 2 Autism, highlighting specific characteristics, symptoms, and therapeutic approaches essential for fostering development and improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
As the landscape of autism awareness evolves, so too does the need for effective early interventions and personalized strategies that empower families and communities to navigate the complexities of this disorder. By exploring the significance of tailored support and the importance of building robust networks, this piece aims to shed light on how to best advocate for children with Level 2 Autism and ensure they receive the care they deserve.
An Overview of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Levels
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental disorder that presents challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. Understanding the classification of ASD into three distinct levels is crucial for determining the appropriate support individuals may need.
Individuals at level 2 of autism spectrum disorder need help but can manage daily activities with some assistance. They may find social interactions challenging and often require support to navigate these situations effectively.
Stage 2 of autism spectrum disorder level 2 indicates a need for considerable assistance. Individuals diagnosed at this level face more significant challenges in communication and social skills, frequently requiring focused support to engage with others and develop essential life skills.
Individuals categorized at level 3 require significant assistance, reflecting serious difficulties in functioning across various areas. These individuals often need comprehensive, individualized care to address their unique challenges.
Grasping these levels is essential for customizing interventions and assistance strategies effectively. Recent statistics indicate that approximately 14.4% to 15.2% of youngsters are diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder level 2, with a notable percentage identified specifically as Level 2. This underscores the importance of recognizing the specific needs of individuals with autism spectrum disorder level 2, as they often require more intensive support to thrive.
Moreover, recent data reveal that ASD prevalence is observed across all racial and ethnic groups, with increasing identification rates among Black, Asian, and Hispanic youth. Initially, White children had higher rates of ASD, but recent shifts show that these minority groups are being identified at similar or higher rates. This change may reflect improved awareness, screening, and access to services for historically underserved populations. As noted by ASD Media: "These shifts may reflect improved screening, awareness, and access to services among historically underserved groups," highlighting the need for equitable healthcare access.
Real-world examples of interventions for individuals with autism spectrum disorder level 2 include tailored social skills training programs and communication-focused therapies. These strategies aim to enhance social engagement and improve communication abilities, ultimately fostering greater independence.
As we progress through 2025, it is crucial to remain aware of the changing landscape of ASD levels and the related assistance needs. The CDC's partner toolkit for Autism Acceptance Month serves as a valuable resource for parents and caregivers, providing insights and updates on best practices in supporting individuals with ASD. By grasping the nuances of Autism Spectrum Disorder levels, parents and caregivers can more effectively advocate for their loved ones, ensuring they receive the necessary assistance to unlock their full potential.
Defining Level 2 Autism: Characteristics and Significance
Individuals with autism spectrum disorder level 2 face significant challenges in social communication, accompanied by restricted, repetitive behaviors. At this level, many individuals exhibit certain characteristics that can affect their daily interactions:
- They often communicate using simple sentences and have limited conversational skills, which can hinder their ability to engage in meaningful interactions.
- Understanding nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language, can be particularly challenging, making social situations difficult.
- Additionally, daily activities often require extra support, and changes in routine can lead to increased anxiety and frustration.
Recognizing these characteristics is essential for parents, as it allows them to implement effective support strategies tailored to their child's unique needs. Research indicates that approximately 1 in 36 youths in the United States is diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), underscoring the importance of understanding the nuances of each level of autism.
A study focusing on family dynamics revealed that parents of individuals with ASD frequently experience heightened emotional strain, especially in their relationships with spouses. As Amela Ibrahimagic, PhD, notes, parents often share feelings of being overwhelmed, stating, 'My offspring is more demanding than most other youngsters' and 'I often lack energy.' This highlights the need for family-oriented services that can provide extensive assistance to families navigating the challenges of raising a child with level 2 Autism.
Effective interventions for children with level 2 Autism include organized communication strategies and social skills training, which can significantly enhance their ability to engage with peers and adults. Therapists emphasize the importance of consistent routines and clear expectations, as these can help reduce anxiety and foster a sense of security for the child.
By understanding the characteristics and challenges associated with level 2 Autism, parents can better advocate for their children and seek out resources that promote their development and well-being.
Recognizing Symptoms and Challenges of Level 2 Autism
Common symptoms of autism spectrum disorder level 2 encompass a range of challenges that significantly impact daily life and social interactions. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for parents seeking to support their children effectively.
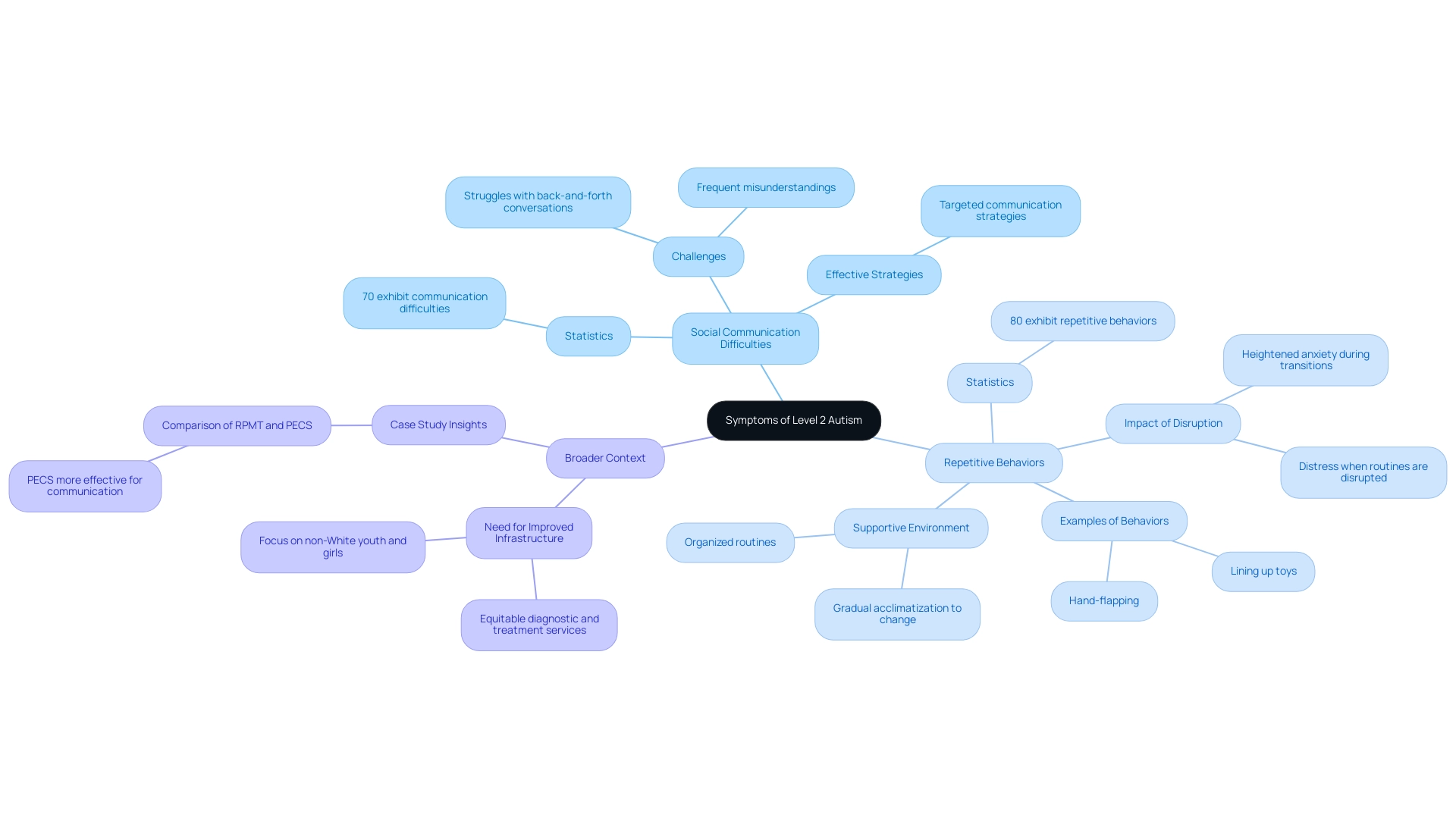
- Social Communication Difficulties: Children with Stage 2 Autism often struggle with back-and-forth conversations, leading to frequent misunderstandings. Research indicates that approximately 70% of individuals diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder level 2 exhibit notable difficulties in initiating and maintaining social interactions. This highlights the importance of targeted communication strategies that can foster connection and understanding.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Many individuals engage in repetitive movements or routines, such as hand-flapping or lining up toys. These behaviors can become distressing when disrupted, with studies indicating that nearly 80% of youngsters with autism spectrum disorder level 2 exhibit such behaviors. For parents, understanding these patterns is essential in creating a supportive environment that minimizes anxiety. Children with autism spectrum disorder level 2 often find it challenging to cope with changes in their environment or routine, which can manifest as heightened anxiety or distress, particularly during unexpected transitions. Recent studies emphasize the significance of organized routines and gradual acclimatization to change, assisting in reducing these reactions.
Identifying these symptoms is vital for parents, as it allows them to offer suitable assistance and measures customized to their offspring's specific requirements. Amanda Brignell, a noted expert in the field, underscores that understanding these symptoms is essential for effective advocacy and support. For instance, a recent case study involving 36 participants compared two intervention methods—Repetitive Practice Model Training (RPMT) and Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS)—demonstrated that PECS was more effective in enhancing non-imitative spoken communication acts.
The study utilized a cluster randomization method, ensuring that the results were robust and reliable. This emphasizes the significance of choosing effective communication strategies to tackle the specific challenges encountered by kids with autism spectrum disorder level 2.
Furthermore, it is crucial to acknowledge the wider context in which these individuals navigate their difficulties. Recent reports emphasize the need for improved infrastructure to ensure fair diagnostic, treatment, and support services for all individuals with ASD, particularly among non-White youth and girls. By understanding these symptoms and their implications, parents can better advocate for their children and seek out resources that foster effective communication and coping strategies.
As you reflect on these insights, consider sharing your experiences or questions in the comments. Together, we can create a supportive community that empowers parents and children alike.
Therapeutic Approaches for Supporting Level 2 Autism
Supporting individuals with Level 2 Autism requires a compassionate approach that encompasses a variety of therapeutic strategies tailored to their unique needs. Each method offers a pathway to growth and development, fostering a nurturing environment for these individuals.
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a cornerstone of effective therapy. This evidence-based approach is well-regarded for its ability to improve specific behaviors and skills through reinforcement strategies. Long-term, comprehensive ABA strategies have shown significant impact, with effect sizes nearing 1.5 for enhancing receptive and expressive language and communication skills. However, it's important to recognize the current research limitations, including a limited number of studies and potential biases. As Karen J. Coleman, PhD, MS, insightfully points out, "Implementing evidence-based interventions for ASD in a real-world health system comes with challenges that may not lead to the same outcomes seen in clinical trials, even with mandated insurance coverage."
Speech Therapy plays a vital role in enhancing communication skills, enabling individuals to express themselves more effectively. Statistics reveal that individuals with Level 2 Autism who engage in speech therapy often experience significant improvements in their communication abilities, which are essential for their social interactions and overall development.
Occupational Therapy focuses on improving daily living skills and sensory processing, helping individuals navigate their environments with greater ease. This approach is particularly beneficial for those diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder level 2, as it equips them with the skills necessary to manage everyday tasks and sensory challenges.
Collaboration among parents and experts is crucial in crafting a personalized support strategy that meets each individual's specific needs. By embracing these therapeutic approaches, families can nurture significant growth and development in their loved ones, ultimately enhancing their quality of life. Together, we can create a supportive community that fosters understanding and compassion.
The Importance of Early Intervention and Personalized Support
Early support is essential for children diagnosed with Level 2 Autism. It significantly enhances communication, social skills, and overall developmental progress. Research indicates that timely actions can lead to substantial improvements in developmental outcomes, making it imperative for parents to take proactive steps following a diagnosis.
Parents, consider these strategies to support your child:
- Seek Prompt Assessments and Interventions: Initiating assessments and interventions as soon as possible after diagnosis is crucial. Prompt recognition of particular difficulties enables customized assistance that meets the distinct requirements of each individual.
- Collaborate with Therapists: Working closely with therapists to develop personalized support plans is vital. These plans should address specific challenges, ensuring that interventions are relevant and effective. For instance, a case study highlighted the importance of individualized strategies focusing on enhancing communication skills, leading to improved interactions with peers and caregivers. Milani Smith, associate director of the UW Autism Center, emphasizes that "parents are taught strategies for capturing their offspring's attention and promoting communication." By using these strategies throughout the day, students are offered many opportunities to learn to interact with others.
- Engage in Ongoing Education: Parents should commit to continuous learning about autism. This knowledge enables them to better comprehend their offspring's needs and advocate effectively for essential services and assistance. Recent research emphasizes that parents equipped with effective strategies can create numerous opportunities for their children to learn and interact throughout the day.
Statistics reveal that personalized assistance is crucial for children with autism. A subgroup analysis of treatment intensity showed that high-intensity approaches, involving 191 participants across four trials, yielded more significant developmental gains compared to low-intensity approaches, which included 754 participants across twelve trials. This data reinforces the notion that tailored, intensive support can lead to better outcomes.
Furthermore, a meta-analysis focusing on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and excluding studies with high risk of bias reinforces the argument for the effectiveness of high-intensity approaches.
In 2025, the emphasis on early action remains paramount. Experts continue to advocate for prompt assistance, noting that many interventions, if not monitored for adverse effects, may lead to unintended negative consequences. The case study titled "Quality of Evidence in Autism Research" stresses the importance of monitoring these adverse events.
Consequently, parents are urged to remain knowledgeable about the latest studies and optimal methods in autism assistance, ensuring that their offspring receive the most effective care possible. ASD Media's unique value lies in its commitment to fostering collaboration and growth in the ABA therapy industry, providing a supportive community for parents and professionals alike.
Building a Support Network: Family and Community Resources
Establishing a robust assistance network is crucial for families of children with Level 2 Autism. Parents can take several proactive steps to enhance their support systems.
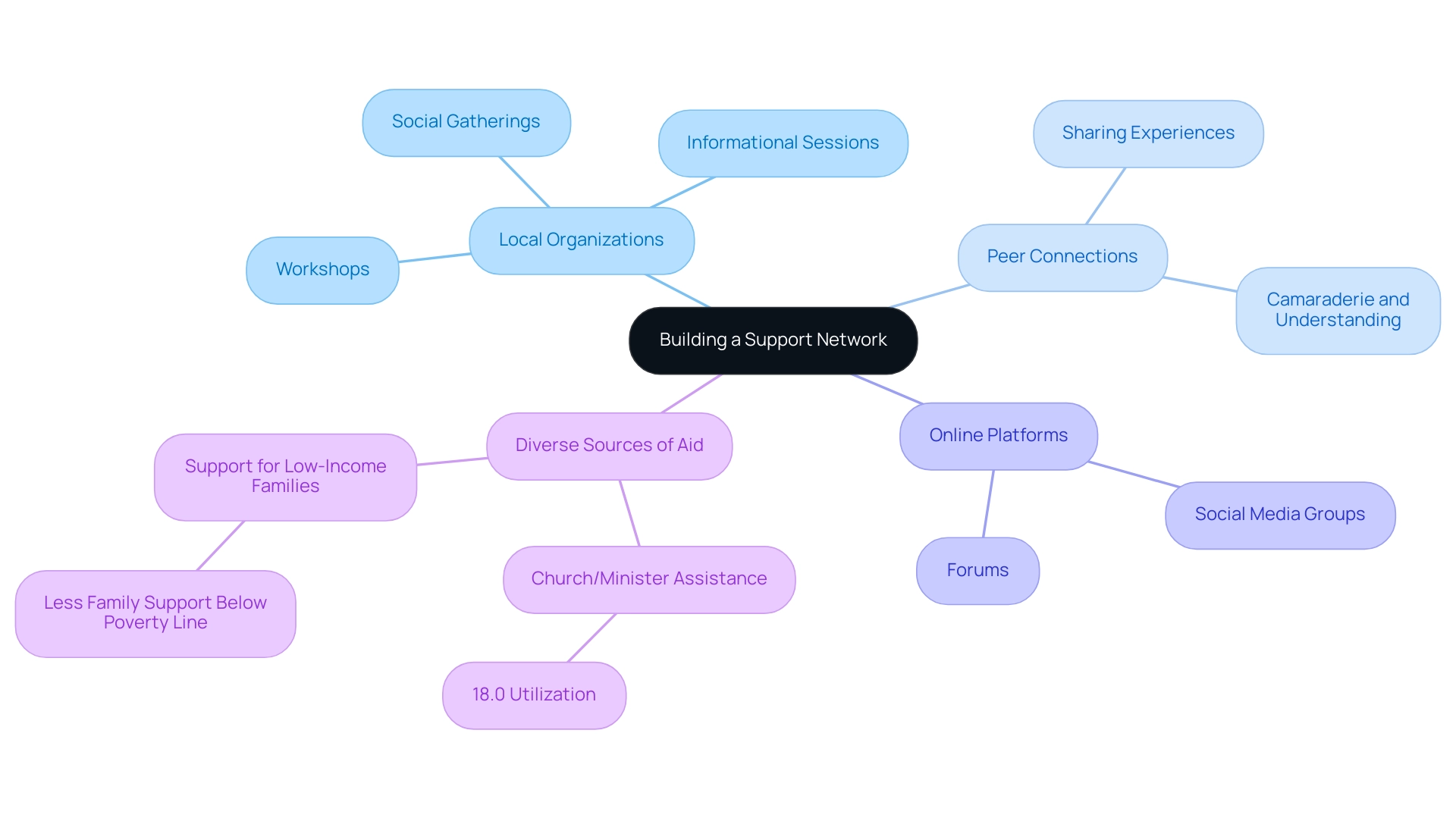
- Connect with Local Organizations: Engaging with local autism assistance groups and organizations can provide access to valuable resources and community events tailored to families. These groups often host workshops, informational sessions, and social gatherings that foster connections among families facing similar challenges.
- Engage with Other Parents: Building relationships with other parents can be incredibly beneficial. Sharing experiences and strategies for managing daily challenges not only offers practical advice but also creates a sense of camaraderie and understanding. This peer assistance can significantly alleviate feelings of isolation.
- Utilize Online Platforms: In today’s digital age, online forums and social media groups serve as vital resources for parents seeking information and guidance. These platforms enable families to engage with a wider community, exchange insights, and obtain a wealth of information about managing Level 2 Autism.
Research shows that families with robust networks experience enhanced emotional wellbeing. For instance, a study focusing on mothers of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) found that higher levels of perceived social assistance correlate with enhanced subjective wellbeing. This highlights the necessity for customized assistance strategies that resonate with the unique experiences of families.
Additionally, the study highlights that 18.0% of parents utilized church or minister assistance, indicating that diverse sources of aid can be beneficial.
Moreover, families living at or below the federal poverty line often report significantly less familial assistance compared to those above this threshold, highlighting the urgent need for increased resources and help for low-income families. As mentioned by Hogan, Linden, & Najarian, research on the usefulness of parent assistance groups is mixed, suggesting that while some may find them beneficial, others may not experience the same level of help. By actively seeking out and participating in support networks, families can navigate the complexities of autism more effectively, ensuring they have the emotional and practical resources needed to thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding Level 2 Autism is essential for providing effective support to individuals facing its unique challenges. This article has delved into the characteristics, symptoms, and therapeutic approaches necessary for nurturing development in children diagnosed with this level of Autism Spectrum Disorder. By recognizing the significant communication difficulties and the need for substantial support, parents and caregivers can tailor interventions that enhance social skills and improve overall quality of life.
The importance of early intervention cannot be overstated; timely and personalized strategies are crucial for maximizing developmental outcomes. Engaging with therapists, seeking prompt assessments, and committing to ongoing education empower parents to advocate effectively for their children. Additionally, building a robust support network through local organizations and connecting with other families can significantly alleviate feelings of isolation while providing valuable resources.
Ultimately, navigating the journey of Level 2 Autism requires a collaborative effort among families, professionals, and communities. By fostering awareness and understanding, we can create an environment where individuals with Level 2 Autism can truly thrive, unlocking their full potential and enriching the lives of those around them. Continued advocacy and support are vital to ensure that every child receives the care they deserve in their pursuit of happiness and success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental disorder characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors.
How is ASD classified into levels?
ASD is classified into three distinct levels, which help determine the appropriate support individuals may need. Level 2 indicates a need for help but allows individuals to manage daily activities with some assistance, while Level 3 requires significant assistance due to serious difficulties in functioning.
What challenges do individuals at level 2 of ASD face?
Individuals at level 2 of ASD face significant challenges in communication and social skills, often needing focused support to engage with others and develop essential life skills. They may communicate using simple sentences and struggle to understand nonverbal cues.
What percentage of youths are diagnosed with level 2 ASD?
Approximately 14.4% to 15.2% of youngsters are diagnosed with level 2 autism spectrum disorder.
How does ASD prevalence vary among different racial and ethnic groups?
ASD prevalence is observed across all racial and ethnic groups, with increasing identification rates among Black, Asian, and Hispanic youth. This reflects improved awareness, screening, and access to services for historically underserved populations.
What types of interventions are effective for individuals with level 2 ASD?
Effective interventions for individuals with level 2 ASD include tailored social skills training programs and communication-focused therapies, which aim to enhance social engagement and improve communication abilities.
What impact does having a child with level 2 ASD have on parents?
Parents of individuals with level 2 ASD often experience heightened emotional strain, particularly in their relationships, and may feel overwhelmed due to the demands of parenting a child with ASD.
What strategies can parents implement to support their child with level 2 ASD?
Parents can implement organized communication strategies, consistent routines, and clear expectations to help reduce anxiety and foster a sense of security for their child.
Where can parents find resources for supporting individuals with ASD?
Parents can refer to the CDC's partner toolkit for Autism Acceptance Month for insights and updates on best practices in supporting individuals with ASD.




