Introduction
Understanding autism can be a complex journey, but it is one that holds the key to unlocking the potential of countless children. With autism prevalence on the rise, particularly highlighted by recent statistics from Egypt, the importance of recognizing and addressing varying severity levels has never been more critical.
This article delves into the three distinct classifications of autism severity, providing invaluable insights into the support needs of individuals at each level:
-
Minimal Assistance:
From the subtle challenges faced by those requiring minimal assistance to the profound needs of individuals who require substantial support, caregivers will find guidance on tailoring their approaches to foster growth and development. -
Moderate Assistance:
Caregivers will learn to identify the support required for individuals who fall into this category, ensuring that necessary resources are available. -
Substantial Support:
This classification focuses on the profound needs of individuals who require substantial support, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive care strategies.
Additionally, the significance of early diagnosis and intervention is explored, emphasizing how timely support can dramatically improve outcomes. As caregivers navigate this landscape, understanding the dynamic nature of autism severity and implementing practical strategies can empower them to advocate effectively for their children’s needs, ensuring a brighter future for families impacted by autism.
An Overview of Autism Severity Levels
The systematic categorization of autism severity levels includes three distinct classifications: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3. Each of the autism severity levels signifies the degree of support required, with:
- Level 1 indicating a need for minimal assistance
- Level 2 suggesting substantial support
- Level 3 reflecting an essential requirement for very substantial support
This classification framework is essential for caregivers as it allows them to tailor their strategies to meet the specific needs of those they care for effectively.
In 2024, the occurrence of developmental disorders in Egypt is noted at 89.40 per 10,000 youngsters, highlighting the significance of these classifications globally. Moreover, a study by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows that around 75% of adults identified with developmental disorders in the United States experience either underemployment or total unemployment, highlighting the long-term implications of assistance requirements. By recognizing and understanding autism severity levels, caregivers are better equipped to advocate for necessary resources in educational and therapeutic settings.
Various forms of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy address individual needs, improving learning experiences and assistance strategies for individuals with autism. Furthermore, it is essential for workers in the community to be informed about these classifications to assist parents in navigating the planning and assistance process efficiently. Practical instances, like the research on the needs of parents with autistic children, show that:
- Mothers often prioritize professional qualities and respite services
- Fathers tend to concentrate on developmental assistance
Clearly articulating these differing caregiver needs enhances the ability to provide customized assistance services for families navigating autism.
Understanding the Three Levels of Autism: Characteristics and Support Needs
Level 1 (Requiring Support)
Individuals at this level may face challenges with interpersonal interactions and organizational tasks, yet they can function independently with appropriate support. Common traits include difficulty starting conversations or interpreting interpersonal cues. To help these individuals thrive, customized interpersonal skills training and organizational strategies are invaluable.
Recent findings indicate that interventions aimed at enhancing communication and community engagement can significantly improve functioning. As McCauley et al. (2020) emphasize, fostering autonomy and daily living skills is crucial for their development.
In Wisconsin, the prevalence of autism is notably higher in females at 42.6 (95% CI: 39.4–45.9) compared to 28.1 (95% CI: 26.2–30.0) in males, highlighting the need for targeted assistance across genders.
Level 2 (Requiring Substantial Assistance)
In contrast, individuals with Level 2 autism often exhibit more significant communication and social interaction difficulties. They typically require considerable assistance to manage daily activities, which may involve behavioral interventions and structured routines. For instance, a recent study in Wisconsin highlighted that 808 children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) were reported, with a notable evaluation rate of 57.5% for children with IQ ≤70 by age 36 months.
This highlights the significance of early and substantial assistance, particularly for those encountering more pronounced challenges. The structured environment and consistent routines can profoundly impact their ability to navigate daily life. Experts suggest that implementing evidence-based interventions, such as visual schedules and social stories, can facilitate communication and understanding.
The results from the developmental evaluation case study highlight the effectiveness of early intervention strategies, especially for youth with varying IQ levels.
Level 3 (Requiring Very Substantial Assistance)
Individuals categorized under Level 3 exhibit severe difficulties in both communication and behavior, necessitating intensive assistance. These individuals often benefit from one-on-one interventions, constant supervision, and highly tailored educational programs designed to meet their unique needs. Comprehending the differences among autism severity levels is vital for caregivers, as this information enables them to tailor their methods efficiently, ensuring that every individual receives the appropriate assistance at the right moment.
As emphasized by McCauley et al. (2020), the long-term goals of autonomy, daily living skills, relationships, and employment are essential for assessing outcomes.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention in Autism
Thorough investigation highlights the significance of early detection and intervention for young individuals with developmental disorders, showing that prompt assistance can result in notably improved results. Current statistics indicate that 36.5% of caregivers utilize Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, which is known for its ability to address developmental delays, enhance communication skills, and mitigate behavioral challenges. Fayge Orzel emphasizes this point, stating,
Longitudinal studies reveal that individuals who begin therapy by age two are three times more likely to thrive in inclusive educational environments compared to those who start later.
As advocates, caregivers must remain vigilant for the early signs of autism severity levels and proactively seek evaluations when concerns arise, utilizing neuropsychological assessment methods as discussed in the Journal of International Neuropsychological Society (2017). Accessing support early not only boosts a young person's ability to succeed in home and school settings but also fosters improved communication and coping strategies within the family dynamic. ABA therapy can reshape family dynamics, enhancing communication and coping strategies, which is crucial for overall family well-being.
By understanding the diverse approaches of ABA therapy, as illustrated in the case study titled 'Types of ABA Therapy,' which details how various methods can be tailored to individual needs, parents can champion the cause of early intervention, ensuring their offspring receive the best possible start in their developmental journey.
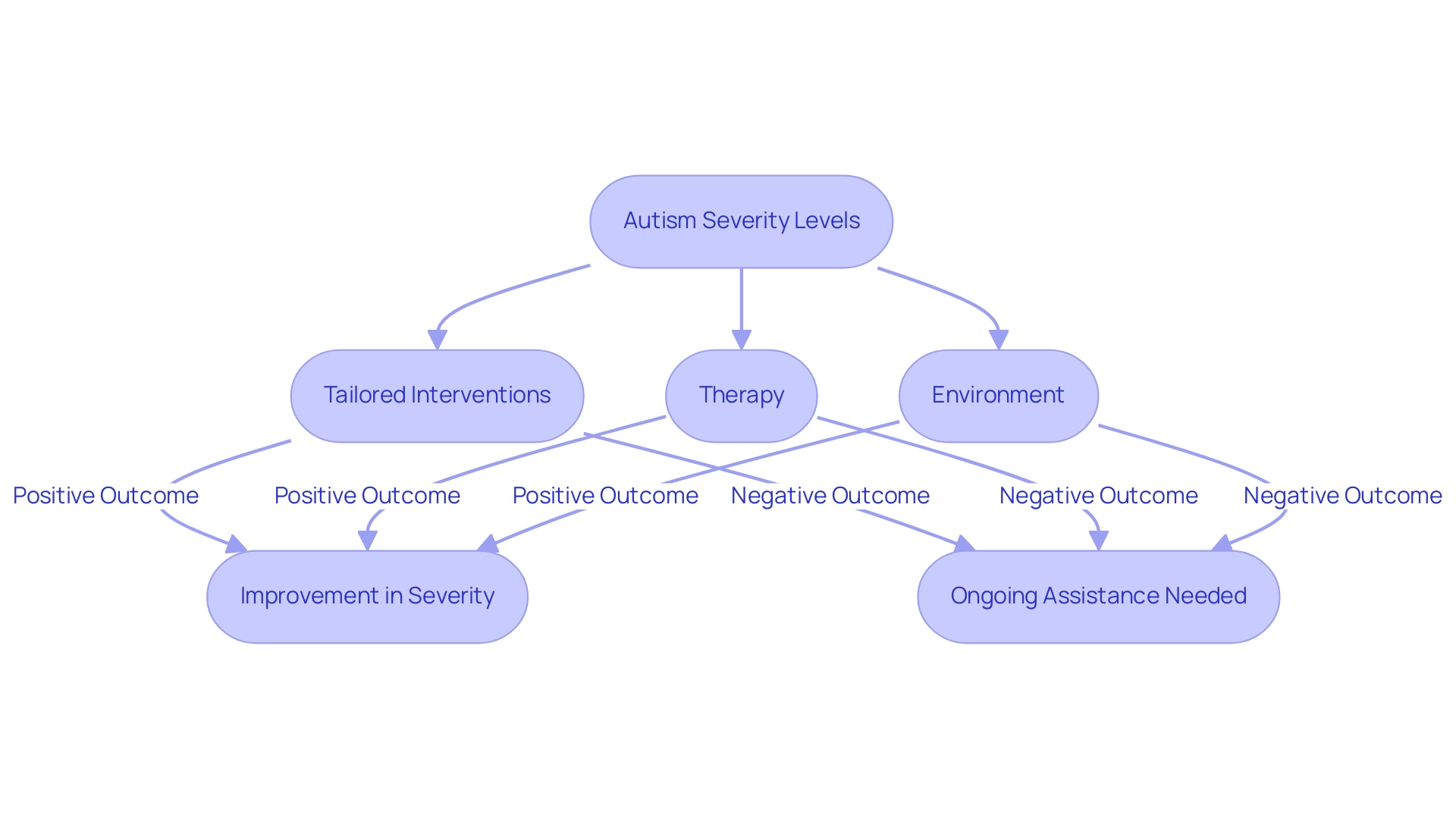
Can Autism Severity Change Over Time? Insights for Caregivers
Yes, the autism severity levels of the condition are not static; they can change over time due to a multitude of factors, including tailored interventions, therapy, and the individual's environment. Recent research has highlighted this dynamic, with Lin et al. (2022) evaluating 106 youngsters and 48 adolescents over a 7-year period, revealing that changes in severity are common throughout early life.
Furthermore, a recent study by Fountain, Winter, & Bearman examined patterns of autism symptom trajectories in a large sample of youth, finding evidence of six distinct trajectories of autism symptom severity, indicating that such changes are quite common. Caregivers should take heart, as many youngsters demonstrate significant improvements, transitioning from higher autism severity levels to lower ones with appropriate support. For instance, the University of Western Australia Longitudinal Study evaluated 27 individuals across a 9-year period, showing that while mean symptom severity remained stable, individual severity changes were common.
However, it’s essential to recognize that some young individuals, depending on their autism severity levels, may require ongoing assistance throughout their lives. Empowered parents are encouraged to remain flexible and responsive to their offspring's evolving needs, continually assessing the effectiveness of their strategies and making necessary adjustments. Such commitment not only fosters growth but also enhances the likelihood of positive developmental outcomes.
Practical Strategies for Supporting Individuals with Autism
- Create Structured Routines: Establishing predictable daily schedules is fundamental in providing stability and security for young individuals with developmental differences. Research indicates that young individuals in structured environments often demonstrate significant improvements in behavior and learning outcomes. In fact, Delaware and Kentucky have the youngest age of first intervention at just 3.7 years, underscoring the importance of early intervention in structured routines. Consistency in routines not only reduces anxiety but also cultivates a sense of safety, allowing them to thrive in their daily activities.
- Use Visual Supports: Incorporating visual schedules, charts, and social stories plays a pivotal role in enhancing understanding and communication for individuals across the autism spectrum, particularly in relation to autism severity levels. These visual aids have been shown to enhance understanding, allowing young learners to grasp complex concepts more easily. By employing visual supports, caregivers can bridge communication gaps and foster more effective interactions.
- Encourage Communication: It's essential to foster communication through diverse methods tailored to each individual's unique needs, whether it be verbal language, sign language, or communication devices. Offering various avenues for expression empowers young individuals to convey their thoughts and feelings, significantly reducing feelings of isolation and loneliness often experienced by those with different autism severity levels.
- Encourage Interpersonal Skills: Participating in activities that foster interaction—such as playdates or skills groups—can be incredibly beneficial. These interactions should be tailored to the child's comfort level, allowing them to develop essential interpersonal skills in a supportive environment. Real-world examples demonstrate that such engagements can lead to improved social understanding and relationships.
- Seek Professional Support: Collaborating with professionals, including ABA therapists, speech therapists, and occupational therapists, is crucial in developing personalized strategies to address specific challenges. According to FAIR Health Inc., the average costs associated with autism services can be explored, offering insights into the financial aspect of seeking professional assistance. This highlights the significance of investing in expert guidance, as emphasized in the case study titled "The Importance of Consistency in ABA Therapy Programs," which reinforces that consistency is a cornerstone for effective outcomes. This support is instrumental in creating effective interventions that promote growth and development.
By implementing these strategies, caregivers can cultivate nurturing environments that cater to their child's distinctive needs, ultimately fostering their growth and development.
Conclusion
Understanding the varying levels of autism severity is essential for caregivers dedicated to supporting their children. This article has explored the three classifications—Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3—each requiring different degrees of assistance. Recognizing these levels allows caregivers to tailor their approaches, ensuring that every child receives the specific support necessary for their unique challenges.
The importance of early diagnosis and intervention cannot be overstated. Timely support improves outcomes significantly, enabling children to thrive in both educational and social settings. By remaining vigilant for early signs of autism and advocating for appropriate resources, caregivers can make a profound difference in their children's lives.
Moreover, the dynamic nature of autism severity highlights the potential for change over time. With the right interventions and support, many children can transition to lower severity levels, reinforcing the idea that progress is possible. This flexibility empowers parents to adapt their strategies as their child's needs evolve, fostering an environment conducive to growth.
Implementing practical strategies such as structured routines, visual supports, and professional collaboration is vital in nurturing the development of children with autism. By embracing these approaches, caregivers can create a stable and supportive environment, ultimately paving the way for brighter futures for their families. Each step taken in understanding and addressing autism severity contributes to a more inclusive and compassionate society, where every child has the opportunity to reach their full potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three levels of autism severity?
The three levels of autism severity are Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3. Level 1 indicates a need for minimal assistance, Level 2 suggests substantial support, and Level 3 reflects an essential requirement for very substantial support.
Why is the classification of autism severity levels important for caregivers?
This classification framework helps caregivers tailor their strategies to meet the specific needs of those they care for, ensuring that individuals receive the appropriate support based on their severity level.
What is the prevalence of developmental disorders in Egypt?
In 2024, the occurrence of developmental disorders in Egypt is noted at 89.40 per 10,000 youngsters.
How do autism severity levels relate to employment outcomes for adults with developmental disorders in the United States?
Approximately 75% of adults identified with developmental disorders in the United States experience either underemployment or total unemployment, highlighting the long-term implications of assistance requirements.
What types of therapy can address the needs of individuals with autism?
Various forms of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy can be used to address individual needs, improving learning experiences and assistance strategies for individuals with autism.
What are some differences in caregiver needs between mothers and fathers of autistic children?
Mothers often prioritize professional qualities and respite services, while fathers tend to focus on developmental assistance. Recognizing these differing needs enhances the ability to provide customized assistance services for families.
What challenges do individuals at Level 1 of autism face?
Individuals at Level 1 may struggle with interpersonal interactions and organizational tasks but can function independently with appropriate support. They often have difficulty starting conversations or interpreting social cues.
What type of support do individuals at Level 2 require?
Individuals with Level 2 autism typically need substantial assistance to manage daily activities, which may include behavioral interventions and structured routines.
What are the characteristics of individuals categorized under Level 3 autism?
Individuals in Level 3 exhibit severe communication and behavioral difficulties, requiring intensive assistance, one-on-one interventions, constant supervision, and highly tailored educational programs.
How can understanding autism severity levels benefit caregivers in the long term?
Understanding these levels allows caregivers to tailor their methods effectively, ensuring that every individual receives appropriate assistance at the right moment, which is crucial for achieving long-term goals related to autonomy, daily living skills, relationships, and employment.




