Introduction
In recent years, the landscape of autism diagnosis has undergone a profound transformation, with prevalence rates soaring and awareness growing. As of 2023, approximately 1 in 44 children in the United States are diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), a statistic that not only highlights the increasing recognition of this condition but also underscores the pressing need for informed advocacy and support.
With demographic disparities revealing significant gaps in diagnosis and intervention, it becomes essential for parents and educators to understand these trends and their implications. By remaining vigilant and proactive, advocates can ensure that every child, regardless of background, receives the tailored resources and support necessary for success.
This article delves into the current state of autism prevalence, the impact on educational systems, and the critical importance of early diagnosis and intervention, providing a comprehensive overview for those committed to making a difference in the lives of children with autism.
Current Autism Prevalence Rates: A Statistical Overview
Recent research reveals a notable increase in the prevalence rates of developmental disorders, which have risen dramatically over the past few decades. In 2000, the prevalence was 6.7 per 1,000 youths, or 1 in 150, highlighting the significant rise in autism percentage to approximately 1 in 44 individuals diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in the United States as of 2023, according to the CDC. This statistic represents a substantial increase driven by improved awareness and diagnostic practices.
Such growth in diagnosis highlights the essential requirement for parents and educators to stay informed about these trends. Comprehending the current autism percentage is essential not only for acknowledging the challenges that families encounter but also for promoting customized support and resources that can effectively address the needs of individuals with ASD. The research highlights what many parents instinctively understand: that progress is attainable, even as young individuals continue to meet the criteria for ASD.
In fact, 79.2% of caregivers reported that Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) reduced their child's meltdowns, while 89.9% noted improvements in communication, reinforcing the importance of targeted interventions.
Demographic Disparities in Autism Diagnoses
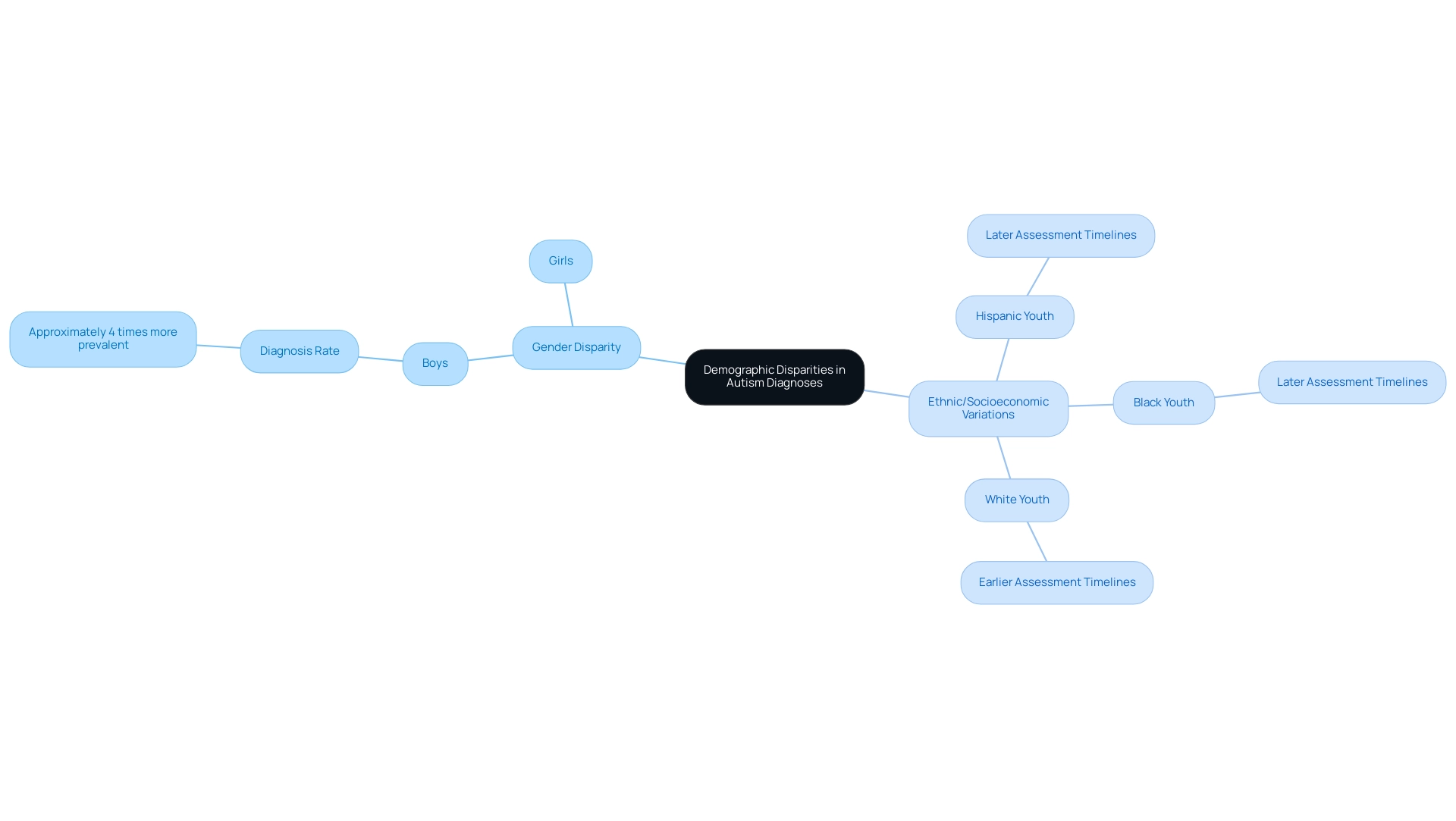
Research consistently demonstrates that autism identifications are approximately four times more prevalent in boys than in girls, highlighting a significant gender disparity in identification rates. Furthermore, significant variations exist in assessment timelines across different ethnic and socioeconomic groups. For example, research shows that Hispanic and Black youth often receive later assessments compared to their white counterparts.
This discrepancy can lead to missed opportunities for early intervention, which is crucial for effective support. Understanding these demographic disparities is vital for parents and educators who are advocating for equitable resources and timely interventions for all children. As emphasized in recent findings, H.L.B. states,
Future research exploring the screening of ASC should actively recruit and record a racially and ethnically diverse population to measure cultural invariance.
Furthermore, Stewart and Austin (2009) reported an SRMR of 0.071 in their model evaluating conditions related to autistic spectrum assessments, emphasizing the requirement for further investigation of diagnostic standards across varied populations. Modabbernia et al. (2017) also examined environmental risk factors related to developmental disorders, suggesting that these factors may contribute to the observed disparities in diagnosis rates. Such insights emphasize the importance of inclusivity in research concerning developmental disorders, ensuring that all communities receive the assistance they require. By remaining informed and proactive, advocates can help bridge these gaps and promote better outcomes for children from all backgrounds.
Impact of Rising Autism Rates on Education and Support Systems
As the autism percentage continues to rise, educational institutions are encountering significant challenges in adapting their curricula and support systems to meet the needs of all students. Many schools are now prioritizing inclusive education strategies, which involve specialized training for educators to better understand and support students with autism. This transition highlights the significance of promoting open communication and cooperation between parents and schools, acknowledging that both play crucial roles in ensuring students receive the customized support essential for success.
According to the U.S. Department of Education, approximately 464,000 students aged 14 to 21 served under IDEA exited school, with 74 percent graduating with a regular diploma; however, the autism percentage related to dropout rates and educational outcomes for autistic students necessitate further research and action. Furthermore, social workers must be educated to assist parents in planning for their offspring's future, breaking this planning into manageable steps that include educational and employment pathways. Additionally, the evolving representation of the condition is reflected in advocacy symbols; for instance, while the puzzle piece has been widely recognized, many activists now promote alternative symbols like the rainbow infinity sign to foster inclusion and a more positive representation of the autistic experience.
By adopting a proactive strategy and adjusting to the increasing rates of developmental disorders, schools can foster an environment where every student has the chance to succeed.
Exploring the Causes Behind Increasing Autism Rates
The increasing frequency of developmental disorder diagnoses can be attributed to a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Current research indicates that at least 60% of children diagnosed with this condition also face two comorbid disorders, highlighting the multifaceted nature of this developmental disorder. Experts are increasingly recognizing that environmental influences—such as exposure to toxins and various prenatal factors—may significantly impact the autism percentage.
Although the precise causes remain elusive, ongoing studies are pivotal in unraveling these connections. A notable initiative set to launch on July 13, 2024, will explore the efficacy of ABA behavior modification techniques, highlighting the importance of informed approaches to treatment and support. As the study further suggests, social workers need to be educated to help parents plan and to separate planning into manageable bits while supporting parents through each stage of the planning process.
As awareness increases, especially concerning the underdiagnosis of the condition in females and marginalized communities, illustrated by the difficulties emphasized in the case study 'Challenges in Diagnosis', it becomes crucial for parents and educators to remain informed and involved. This ongoing conversation among researchers and advocates highlights the importance of ongoing research and education, empowering parents to navigate the complexities of conditions and advocate effectively for their offspring.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention in Autism
Prompt identification and assistance serve as essential components in aiding individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders, directly affecting their developmental paths. Research indicates that individuals who initiate therapy by age two are three times more likely to thrive in inclusive educational settings compared to those who begin later, as highlighted by author Fayge Orzel. In fact, the autism percentage shows that 36.5% of caregivers for individuals with developmental disorders utilize ABA therapy for their offspring, underscoring the widespread recognition of early intervention's benefits.
Parents and educators must remain vigilant in recognizing early signs, such as delays in speech and social skills, to seek timely support. The use of diagnostic tools like the following enhances the accuracy of early detection, ultimately guiding appropriate interventions:
- Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R)
- Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS)
- Gilliam Autism Rating Scale-2 (GARS-2)
- Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS-G)
Recent findings from a systematic review and meta-analysis highlight the global burden of suicide mortality among individuals on the spectrum, stressing the crucial requirement for early support and intervention.
Moreover, evidence underscores that early interventions can significantly boost communication abilities, social skills, and overall functioning. By actively engaging in their child's development and advocating for early support, parents can pave the way for more promising outcomes, ensuring their children receive the best possible care from the very beginning. Additionally, the evolution of symbols in autism advocacy, such as the transition from the puzzle piece to the rainbow infinity sign, reflects a growing understanding of the importance of representation and inclusion, further reinforcing the need for early diagnosis and intervention.
Conclusion
The significant rise in autism prevalence, now affecting approximately 1 in 44 children in the U.S., underscores the urgent need for informed advocacy from parents and educators. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial, as children who receive support by age two are more likely to thrive in inclusive settings. Recognizing early signs and implementing effective interventions, like Applied Behavior Analysis, can lead to meaningful improvements in communication and social skills.
It is also vital to address demographic disparities in autism diagnoses. Children from diverse backgrounds often experience delays in receiving necessary support, hindering their development. Advocating for equitable resources and timely interventions ensures that all children receive the tailored support they need.
As educational systems adjust to the rising prevalence of autism, collaboration between parents and schools is essential. Inclusive education strategies and specialized training for educators can create an environment where every child can succeed. Open communication and advocacy within schools are critical for enhancing educational outcomes.
In conclusion, the evolving landscape of autism diagnosis and intervention highlights the importance of proactive advocacy. By focusing on early support, addressing disparities, and actively engaging in educational processes, parents and advocates can help ensure that every child with autism has the opportunity to thrive. With commitment and awareness, positive change is not only possible but achievable, paving the way for brighter futures for children on the spectrum.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current prevalence rate of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in the United States?
As of 2023, the prevalence rate of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in the United States is approximately 1 in 44 individuals, which represents a significant increase from 6.7 per 1,000 youths (or 1 in 150) in the year 2000.
What factors have contributed to the increase in autism diagnoses?
The substantial rise in autism diagnoses is primarily driven by improved awareness and diagnostic practices.
Why is it important for parents and educators to stay informed about autism prevalence rates?
Understanding the current autism percentage is essential for recognizing the challenges families face and for promoting customized support and resources that effectively address the needs of individuals with ASD.
What percentage of caregivers reported improvements for their children with ASD after receiving Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)?
According to recent reports, 79.2% of caregivers indicated that ABA reduced their child's meltdowns, and 89.9% noted improvements in communication.
Is there a gender disparity in autism diagnoses?
Yes, research indicates that autism identifications are approximately four times more prevalent in boys than in girls.
Are there disparities in assessment timelines for autism across different ethnic and socioeconomic groups?
Yes, studies show that Hispanic and Black youth often receive later assessments compared to their white counterparts, which can lead to missed opportunities for early intervention.
What is the significance of understanding demographic disparities in autism diagnosis?
Recognizing these disparities is vital for advocating for equitable resources and timely interventions for all children, ensuring that every community receives the necessary support.
What do recent findings suggest about future research in autism screening?
Future research should actively recruit and record a racially and ethnically diverse population to measure cultural invariance in autism screening processes.




